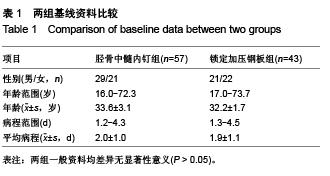
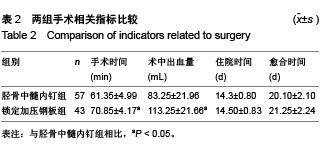
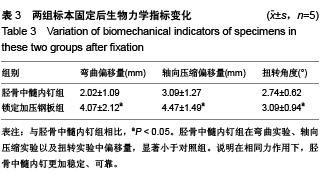
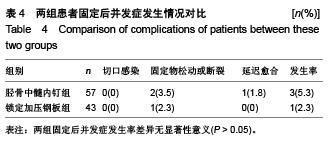
| [1] 李建明,付新民,韩丽.有限切开复位锁定加压钢板治疗胫骨骨折67例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(4):938.[2] YF Y, ZH X, GM Z, et al. Modified classification and single-stage microsurgical repair of posttraumatic infected massive bone defects in lower extremities. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2013;29(9):593-600.[3] 彭朝华,杨彬,邹秋富,等.微创锁定加压钢板固定术中失误及固定后早期并发症分析[J].四川医学,2012,33(6):965-967.[4] Ostermann PA, Seligson D, Henry SL. Local antibiotic therapy for severe open fractures. A review of 1085 consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1995;77(1):93-97.[5] 葛宝丰,胥少汀,徐印坎.实用骨科学[M].2版.北京:人民军医出版社. 2004.[6] Haidukewych GJ, Ricci W. Locked plating in orthopaelic reauma: a clinical update. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2008;16(6):347-355.[7] 查国春,陈泽林,齐小波.经皮微创锁定加压钢板内固定治疗胫骨骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(12):1448-1450.[8] 曾晓峰,赵建宁,陆维举,等.三种固定方法治疗胫骨干骨折的疗效比较[J].医学研究生学报,2004,17(3):236-239.[9] 梁银澎,肖胜捷,王洪.交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨骨折不愈合[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(2):189-190.[10] 陈雪辉.交锁髓内钉内固定和AO外固定支架治疗胫腓骨开放骨折的疗效对比[J].中国全科医学,2012,13(13):1910-1912.[11] 邢益仿.钢板及交锁髓内钉内固定治疗胫骨干骨折的疗效观察[J].医学综述,2012,18(19):3299-3300.[12] 金浩,丁星刚,把其兵,等.两种手术方式治疗胫骨骨折73例回顾性分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(11):1047-1049.[13] 马敏,蔡俊丰,尹峰,等.两种术式治疗胫骨中段闭合性骨折的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(18):1661-1664.[14] 张辉,陶巍栋,曹一民,等.胫骨干骨折2种微创手术的比较与分析[J].临床急诊杂志,2010,11(2):102-103.[15] 楚宇鹏,孔建中,牟暇平,等.交锁髓内钉与LCP内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折的放射学及临床疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2010, 25(12):1080-1082.[16] 黄加张,陈文均,汤超亮,等.交锁髓内钉和微创解剖钢板治疗胫骨远端骨折的对比研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(7):656-657.[17] 邹勇,王朝亮,黄素芳.交锁髓内钉和钢板内固定在胫骨骨折中的应用体会[J].宁夏医学杂志,2007,29(3):247-248.[18] 吴超,谭伦,罗晓中,等.闭合复位经皮锁定钢板与交锁髓内钉治疗胫骨干中下段骨折的疗效比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 18(8): 633-637.[19] 张磊,董启榕,顾军,等.锁定加压钢板、交锁髓内钉内固定治疗胫骨骨折疗效比较[J].山东医药,2012,52(38):82-83.[20] 金浩,丁星刚,把其兵,等.两种手术方式治疗胫骨骨折73例回顾性分析[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(11):1047-1049.[21] 邢益仿.钢板及交锁髓内钉内固定治疗胫骨干骨折的疗效观察[J].医学综述,2012,18(19):3299-3300.[22] 田文,王富明,黄俭,等.髓内钉、锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗胫骨下段骨折疗效比较[J].山东医药,2013,31:53-56.[23] 张锦锋,刘国东,叶登花,等.带锁髓内钉与锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨干骨折的临床对比研究[J].河北医学,2012,5:574-577.[24] 何少斌.微创经皮锁定加压钢板内固定治疗胫骨远端骨折30例临床疗效观察[J].实用临床医药杂志,2013,19:64-65+77.[25] 徐毅.锁定加压钢板(LCP)结合MIPPO技术治疗胫骨远端骨折的临床疗效分析[D].山东中医药大学,2012.[26] 张富军,杨昊,李靖,等.微创经皮钢板固定技术前置锁定加压钢板治疗肱骨中下段骨折[J].中国临床研究,2011,24(10):879-881.[27] Vives MJ, Abidi NA, Ishikawa SN, et al. Soft tissue injuries with the use of safe corridors for transfixion wire placement during external fixation of distal tibia fractures:an anaiomic study. J Orthop Trauma. 2001;15(8):555-559.[28] Jarmo AK, Toivanen, Olli V, et al. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of fractures of the tibial shaft. J Bone Joint Surg (Am). 2002;84(4):580-585.[29] 方国华,曾青东,孙新,等.带锁髓内钉与加压钢板治疗开放性胫腓骨骨折的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2003,11(2):143- 144.[30] 戈涛,张光明,侯之启,等.微创经皮钢板内固定术下运用锁定加压板治疗胫骨远端骨折[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(5):680-682.[31] Krettek C, Schandedmaier P, Miclau T, et al. Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) using the DCS in proximal and distal femoral fractures. Injury. 1997;28:20.[32] 付传玺,张彬彬.胫骨内侧钢板治疗胫腓骨骨折体会[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2010,5(8):716.[33] 马树强,李丽,王坤正,等.扩髓与非扩髓带锁髓内钉治疗开放性胫骨骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2009,15(3):183-185.[34] 熊军,余斌,欧阳汉斌,等.扩髓与非扩髓髓内钉固定治疗胫骨闭合性骨折的系统评价[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(24):2025-2029.[35] Hasenboehler E, Rikli D, Babst R. Locking compression plate with minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in diaphyseal and distal tibial fracture: a retrospective study of 32 patients. Injury. 2007;38(3):365-370.[36] 曾文卿,杨维东.胫骨干骨折中膨胀髓内钉与可吸收螺钉的疗效比较[J].咸宁学院学报(医学版),2009,23(5):408-410.[37] 王坤,刘德昌.微创经皮和有限切开复位锁定加压钢板治疗胫骨骨折的疗效比较[J].中国临床医学,2012,19(3):270-271.[38] Arora R, Lutz M, Hennerbichler A, et al. Complications following in-ternal fixation of unstable distal radius fracture with a palmar locking plate. J Orthop Trauma. 2007;21(5): 316-322.[39] Kregor PJ, Stanard JA, Zlowodzki M, et al. Treatment of distal femur fractures using the less invasie stabilization system: surgical experience and early clinical results in 103 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2004;18(8):509-520.[40] 彭朝华,杨彬,邹秋富,等.微创锁定加压钢板固定术中失误及固定后早期并发症分析[J].四川医学,2012,33(6):965-967. |
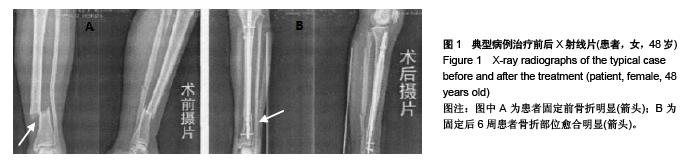
.jpg)