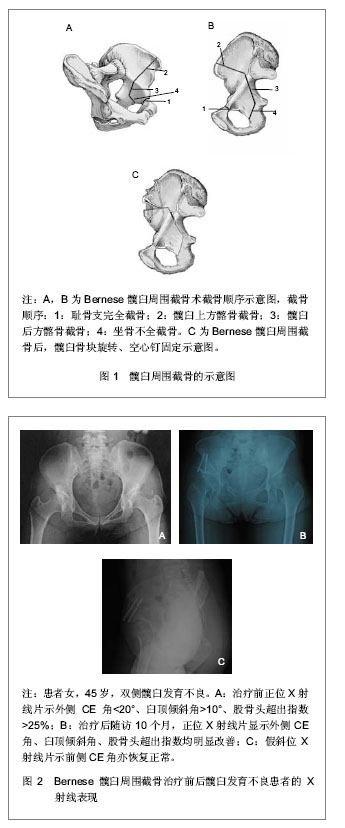
| [1] Okano K, Enomoto H, Osaki M, et al. Outcome of rotational acetabular osteotomy for early hip osteoarthritis secondary to dysplasia related to femoral head shape: 49 hips followed for 10-17 years. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(1):12-17.[2] Leunig M, Ganz R. Mini-symposium: children-osteotomies around the hip:(iii)Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Current Orthopaedics. 2007;21(2):100-108.[3] Siebenrock KA, Schöll E, Lottenbach M, et al. Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999; (363): 9-20.[4] Kralj M, Mavcic B, Antolic V, et al. The Bernese periacetabular osteotomy: clinical, radiographic and mechanical 7-15-year follow-up of 26 hips. Acta Orthop. 2005;76(6):833-840.[5] Pogliacomi F, Stark A, Wallensten R. Periacetabular osteotomy. Good pain relief in symptomatic hip dysplasia, 32 patients followed for 4 years. Acta Orthop. 2005;76(1): 67-74.[6] Clohisy JC, Barrett SE, Gordon JE, et al. Periacetabular osteotomy for the treatment of severe acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(2):254-259.[7] Peters CL, Erickson JA, Hines JL. Early results of the Bernese periacetabular osteotomy: the learning curve at an academic medical center. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(9): 1920-1926.[8] Steppacher SD, Tannast M, Ganz R, et al. Mean 20-year followup of Bernese periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7):1633-1644.[9] Hussell JG, Mast JW, Mayo KA, et al. A comparison of different surgical approaches for the periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(363):64-72.[10] Kiyama T, Naito M, Shiramizu K, et al. Ischemia of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve during periacetabular osteotomy using Smith-Petersen approach. J Orthop Traumatol. 2009; 10(3):123-126.[11] Pogliacomi F, Stark A, Vaienti E, et al. Periacetabular osteotomy of the hip: the ilioinguinal approach. Acta Biomed. 2003;74(1):38-46.[12] Matta JM, Stover MD, Siebenrock K. Periacetabular osteotomy through the Smith-Petersen approach. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(363):21-32.[13] Ganz R, Leunig M. Twenty years of experience with the Bernese periacetabular osteotomy for residual acetabular dysplasia. Treatment of osteoarthritic change in the hip. 2007: 147-161. [14] Lequesne M, Bellaïche L. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement: an update. Joint Bone Spine. 2012;79(3): 249-255.[15] Jamali AA, Mladenov K, Meyer DC, et al. Anteroposterior pelvic radiographs to assess acetabular retroversion: high validity of the "cross-over-sign". J Orthop Res. 2007;25(6): 758-765.[16] Kalberer F, Sierra RJ, Madan SS, et al. Ischial spine projection into the pelvis: a new sign for acetabular retroversion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(3):677-683.[17] Beck M, Kalhor M, Leunig M, et al. Hip morphology influences the pattern of damage to the acetabular cartilage: femoroacetabular impingement as a cause of early osteoarthritis of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005;87(7): 1012-1018.[18] Philippon MJ, Wolff AB, Briggs KK, et al. Acetabular rim reduction for the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement correlates with preoperative and postoperative center-edge angle. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(6):757-761.[19] Siebenrock KA, Schoeniger R, Ganz R. Anterior femoro-acetabular impingement due to acetabular retroversion. Treatment with periacetabular osteotomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(2):278-286.[20] Leunig M, Rothenfuh D, Beck M, et al. Surgical dislocation and periacetabular osteotomy through a posterolateral approach: a cadaveric feasibility study and initial clinical experience. Oper Tech Orthop. 2004;14(2):49-57.[21] Beck M, Leunig M, Ellis T, et al. The acetabular blood supply: implications for periacetabular osteotomies. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003;25(5-6):361-367.[22] Ganz R, Horowitz K, Leunig M. Algorithm for femoral and periacetabular osteotomies in complex hip deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(12):3168-3180.[23] De La Rocha A, Sucato DJ, Tulchin K, et al. Treatment of adolescents with a periacetabular osteotomy after previous pelvic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(9): 2583-2590.[24] Garbuz DS, Awwad MA, Duncan CP. Periacetabular osteotomy and total hip arthroplasty in patients older than 40 years. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(7):960-963.[25] Teratani T, Naito M, Kiyama T, et al. Periacetabular osteotomy in patients fifty years of age or older. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(1):31-41.[26] Yasunaga Y, Takahashi K, Ochi M, et al. Rotational acetabular osteotomy in patients forty-six years of age or older: comparison with younger patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A(2):266-272.[27] Millis MB, Kain M, Sierra R, et al. Periacetabular osteotomy for acetabular dysplasia in patients older than 40 years: a preliminary study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(9): 2228-2234.[28] Li PL, Ganz R. Morphologic features of congenital acetabular dysplasia: one in six is retroverted. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;(416):245-253.[29] Dora C, Mascard E, Mladenov K, et al. Retroversion of the acetabular dome after Salter and triple pelvic osteotomy for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2002; 11(1):34-40.[30] Dora C, Bühler M, Stover MD, et al. Morphologic characteristics of acetabular dysplasia in proximal femoral focal deficiency. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2004;13(2):81-87.[31] Dora C, Zurbach J, Hersche O, et al. Pathomorphologic characteristics of posttraumatic acetabular dysplasia. J Orthop Trauma. 2000;14(7):483-489.[32] Myers SR, Eijer H, Ganz R. Anterior femoroacetabular impingement after periacetabular osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;(363):93-99.[33] Clohisy JC, St John LC, Nunley RM, et al. Combined periacetabular and femoral osteotomies for severe hip deformities. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(9):2221-2227.[34] Thawrani D, Sucato DJ, Podeszwa DA, et al. Complications associated with the Bernese periacetabular osteotomy for hip dysplasia in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(8): 1707-1714.[35] Ziebarth K, Balakumar J, Domayer S, et al. Bernese periacetabular osteotomy in males: is there an increased risk of femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) after Bernese periacetabular osteotomy? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(2):447-453.[36] Dorrell JH, Catterall A. The torn acetabular labrum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1986;68(3):400-403.[37] Leunig M, Werlen S, Ungersböck A, et al. Evaluation of the acetabular labrum by MR arthrography. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997;79(2):230-234.[38] Klaue K, Durnin CW, Ganz R. The acetabular rim syndrome. A clinical presentation of dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;73(3):423-429.[39] Leunig M, Podeszwa D, Beck M, et al. Magnetic resonance arthrography of labral disorders in hips with dysplasia and impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(418):74-80.[40] Hempfing A, Leunig M, Nötzli HP, et al. Acetabular blood flow during Bernese periacetabular osteotomy: an intraoperative study using laser Doppler flowmetry. J Orthop Res. 2003; 21(6): 1145-1150.[41] Langlotz F, Stucki M, Bächler R, et al. The first twelve cases of computer assisted periacetabular osteotomy. Comput Aided Surg. 1997;2(6):317-326.[42] Suh DH, Lee DH, Jeong WK, et al. Virtual Bernese osteotomy using three-dimensional computed tomography in hip dysplasia. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(4):447-454. [43] Troelsen A, Søballe K. Advances in PAO surgery: the minimally invasive approach. Femoroacetabular Impingement. 2012:189-199. |