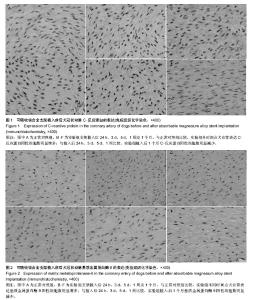
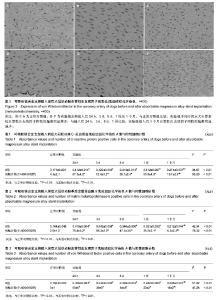
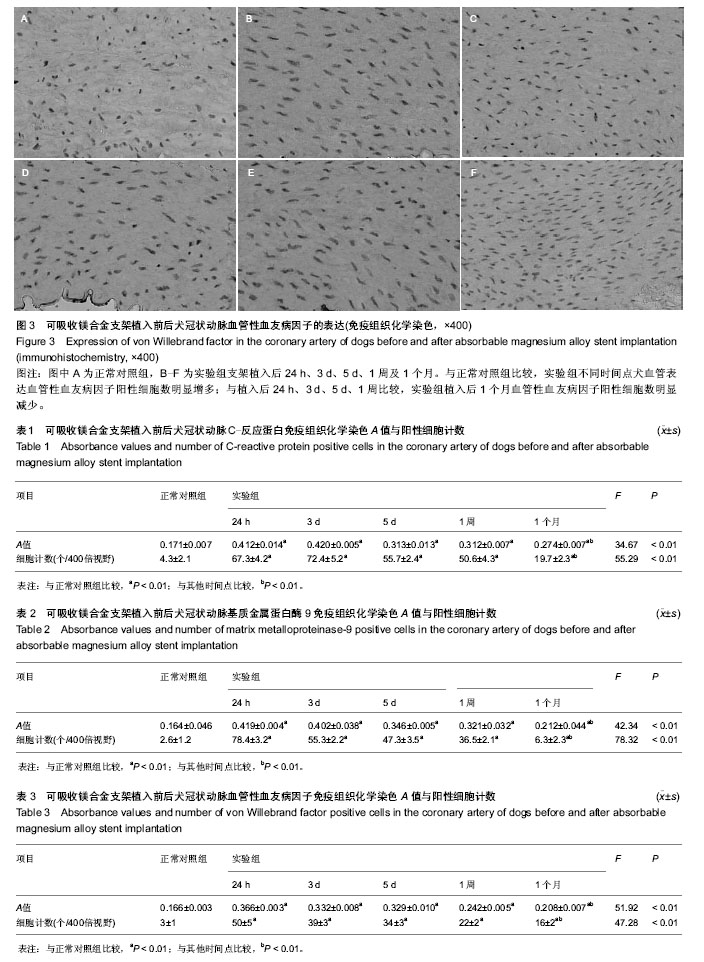
| [1] Erne P,Schier M,Resink TJ.The road to bioabsorbable stents: reachingclinical reality?Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2006; 29(1):11-16.
[2] 杨水祥,雷力成,王丽丽,等.新型血管内可吸收镁合金支架的实验研究[J].中华老年心血管病杂志,2012,14(7):743-747.
[3] 王萍,雷力成,王丽丽,等.冠状动脉内可吸收支的镁合金支架[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(43):8071-8077.
[4] Onuma Y,Ormiston J,Serruys PW.Bioresorbable scaffold technologies.Circ J.2011;75(3):509-520.
[5] Wenaweser P,Daemen J,Zwahlen M,et al.Incidence and correlates of drug-eluting stent thrombosis in routine clinical practice:4-year results from a large 2-institutional cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol.2008;52:1134-1140.
[6] Corsetti JP,Rainwater DL,Moss AJ,et al.High lipoprotein- associated phospholipase A2 Is a risk factor for recurrent coronary events in postinfarction patients.Clin Chem.2006; 52(7):1331-1338.
[7] Raposeiras-Roubín S,Barreiro Pardal C,Rodiño Janeiro B,et al.High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is a predictor of in-hospital cardiac events in acute myocardial infarctionindependently of GRACE risk score. Angiology. 2012;63(1):30-34.
[8] 黄琼,张新风.高敏CRP与冠脉狭窄程度及支架术后再狭窄相关性[J].中国医药导报,2014,16(8):1197-1199.
[9] 胡榜利,陈斌冠,杨光业,等.CRP水平与冠脉药物支架植入术后再狭窄关系的Meta分析[J].微创医学,2012,7(1):6-9.
[10] Ridker PM,Hennekens CH,Buring JE,et al. C-reactive protein and other markers of inflammation in the prediction of cardiovascular disease in women.N Engl J Med.2000; 342(12): 836-843.
[11] Horne BD,Muhlestein JB,Strobel GG,et al.Greater pathogen burden but not elevated C-reactive protein increases the risk of clinical restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention. Am Hean J.2002;144(3):491-500.
[12] 王欣,李玉光,王伟,等.冠状动脉雷帕霉素洗脱支架术后C-反应蛋白水平的变化[J].中国综合临床,2007,23(6):540-542.
[13] 王茜,李兴朝,闵新文,等.血清hs-CRP水平对急性心肌梗死PCI术后亚急性支架内血栓形成的预测价值[J].海南医学院学报, 2013,19(8):1042-1044,1047.
[14] 赵然尊,石蓓,许官学.冠状动脉支架置入术后患者基质金属蛋白酶变化对再狭窄的影响[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2009, 11(9):701-704.
[15] 殷忠,李兰荪,栾荣华,等.急性冠脉综合征患者PCI术后外周血MMP-9水平的连续观察及其临床意义[J].心脏杂志,2008, 20(1): 58-60.
[16] Lee CS,Kwon YW,Yang HM,et al. New mechanism of rosiglitazone to reduce neointimal hyperplasia:activation of glycogen synthase kinase-30 followed by inhibition of MMP-9.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2009;29(4):472-479.
[17] Hughes D,Fu AA,Puggioni A,et al.Adventitial transplantation of blood outgrowth endothelial cells in porcine haemodialysis grafts alleviates hypoxia and decreases neointimal proliferation through a matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated pathway--a pilot study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(1): 85-96.
[18] Reininger AJ,Heijnen HF,Schumann H.Mechanism of platelet adhesion to von Willebrand factor and microparticle formation under high shear stress. Blood.2006;107(9):3537-3545.
[19] Vargova K,Totll Zsamboki E,Beres BJ,et al.Circulating endothelial cell count,plasma vWF and soluble ICAM-1 levels following primary or elective percutancous coronary intervention.Atherosclerosis.2008;198(2):366-372.
[20] Gorog DA,Douglas H,Ahrned N,et al.Coronary angioplasty enhances platelet reactivity through von Willebrand factor release.Heart.2003;89(3):329-330.
[21] Llau JV,Ferrandis R,Sierra P,et al.Prevention of the renarrowing of coronary arteries using drug-eluting stents in the perioperative period: an update.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2010;6:855-867.
[22] Savonitto S,D'Urbano M,Caracciolo M,et al.Urgent surgery in patients with a recently implanted coronary drug-eluting stent: a phase II study of 'bridging' antiplatelet therapy with tirofiban during temporary withdrawal of clopidogrel.Br J Anaesth.2010; 104(3):285-291.
[23] Korte W,Cattaneo M,Chassot PG,et al.Peri-operative management of antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: joint position paper by members of the working group on Perioperative Haemostasis of the Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis Research (GTH), the working group on Perioperative Coagulation of the Austrian Society for Anesthesiology, Resuscitation and Intensive Care (ÖGARI) and the Working Group Thrombosis of the European Society for Cardiology (ESC).Thromb Haemost.2011;105(5): 743-749.
[24] Metzler H,Kozek-Langenecker S,Huber K.Antiplatelet therapy and coronary stents in perioperative medicine--the two sides of the coin.Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol.2008;22(1): 81-94.
[25] Wiviott SD,Braunwald E,McCabe CH,et al.Intensive oral antiplatelet therapy for reduction of ischaemic events including stent thrombosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes treated with percutaneous coronary intervention and stenting in the TRITON-TIMI 38 trial: a subanalysis of a randomised trial.Lancet. 2008;371(9621):1353-1363.
[26] Finkel JB,Marhefka GD,Weitz HH.Dual antiplatelet therapy with aspirin and clopidogrel: what is the risk in noncardiac surgery? A narrative review.Hosp Pract (1995).2013;41(1): 79-88.
[27] Byrne RA, Schulz S, Mehilli J, et al.Rationale and design of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 6 versus 12 months clopidogrel therapy after implantation of a drug-eluting stent: The Intracoronary Stenting and Antithrombotic Regimen: Safety And EFficacy of 6 Months Dual Antiplatelet Therapy After Drug-Eluting Stenting (ISAR-SAFE) study.Am Heart J. 2009;157(4):620-4.e2.
[28] 李永存.ACS患者血浆vWF、ADAMTS13水平与冠脉病变程度的相关性研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2013.
[29] 王临光,冯小平.不同支架对冠心病患者介入术后炎症因子的影响[J].心脏杂志,2008,20(1):55-57. |