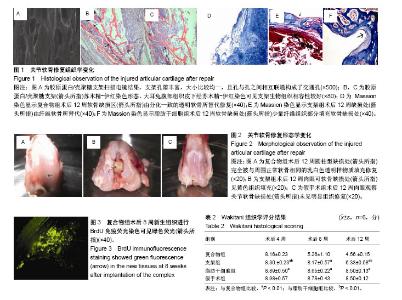
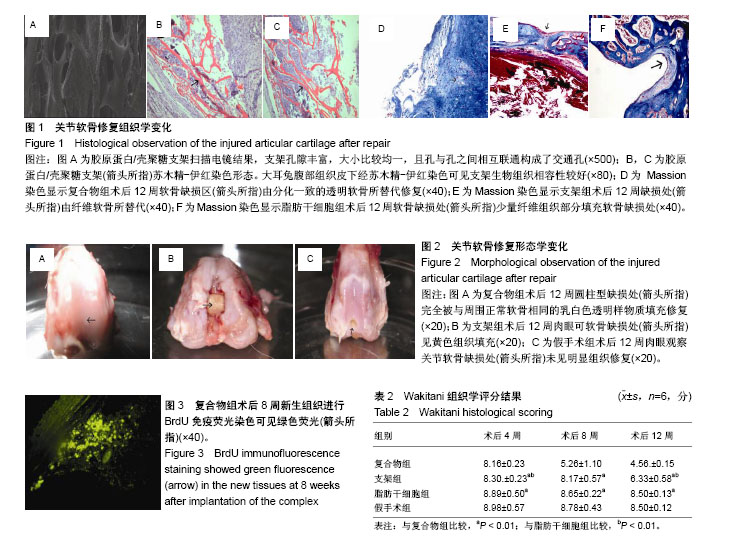
| [1] 王腾飞,宋兴华,龙志成,等.脂肪干细胞在羟基磷灰石/β-磷酸三钙复合体在兔椎体缺损修复中的应用效果[J].山东医药, 2018, 58(3):38-41.[2] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [3] Ahmadia Kia N, Bahram AR, Ebrahimi M, et al. Comprative analysis of chemokine receptor’s expression in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. J Mol Neurosci. 2011;44(3):178-185. [4] Feng G, Wan YQ. Adenovirus-mediated expresson of growth and differentiation factor-5 promotes chondrogenesis of adipose stem cells. Growth Factors. 2008;26(3):132-142.[5] Masuda K. Biological repair of the degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(4): 441-451. [6] 金长礼,李德华,李洪禹,等.GDF-5诱导hASSCs分化为软骨样细胞[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(1):3-5.[7] 王征,马云胜,穆长征,等.胶原蛋白复合壳聚糖支架的制备及生物学性状:壳聚糖及胶原比例筛选[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(29):5367-5370.[8] 戚亦萍,吴明媛,王明海,等.兔膝关节炎骨关节组织切片的制备方法[J].上海交通大学学报(农业科学版),2009,27(3):314-317.[9] Wakitani S, Goto T, Young RG, et al. Repair of large full-thickness ariticular cartilage defects with allograft articular chondrocytes embedded inacollagengel. Tissue Eng. 1998; 4(4):429.[10] 鲁谊,张海龙,李屹龙,等.关节镜下微骨折或自体软骨移植术治疗肘关节剥脱性骨软骨炎早期临床疗效[J].中华骨科杂志, 2018, 38(1):1-7.[11] 王庆,黄华杨,张涛,等.基质诱导自体软骨细胞治疗移植修复膝关节软骨损伤的早期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(1):28-34.[12] Fini A, Orienti I. The role of chitosan in drug delivery. Am J Drug Deliv. 2003;143-159. [13] Takeuchi H, Yamamoto H, Kawashima Y. Mucoadhesive nano particulate systems for peptide drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):39-54. [14] 王斯琪,卢海源,呈腊梅.3种不同组织来源的间充质干细胞促内皮祖细胞血管形成作用的比较[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2018, 43(2):184-191.[15] 段炼,黄柳明,刘刚,等.成人脂肪干细胞的体外多向分化能力观察[J].山东医药,2017,57(40):38-41.[16] 汪兆艳,郭建巍,杨印祥,等.自体与异体脂肪间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性心肌梗死的比较研究[J].解放军医学杂志, 2017, 42(9):788-792.[17] 林涛,陈竹,袁德超,等.壳聚糖水凝胶复合脂肪间充质干细胞修复兔关节软骨缺损[J].中华创伤杂志,2016,32(4):357-362.[18] 舒雄,郑蕊,杰永生,等.脂肪干细胞复合真皮脱细胞基质修复兔关节软骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国医药生物技术, 2017,12(2): 143-148.[19] Wang Z, Ma YS, Mu CZ, et al. Preparation and biological characteristics of collagen-chitosan composite scaffold: Proportion of chitosan and collagen. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(29): 5367-5370. [20] 王宇,王琪,杜明昌,等.ADSCs和β-TCP复合支架及其对猪膝关节软骨缺损组织Collagenll, Sox-9表达的影响[J].山东医药, 2016,56:(32):1-4.[21] Takeuchi H, Yamamoto H, Kawashima Y. Mucoadhesive nanoparticulate systems for peptide drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001;47(1):39-54.[22] 李春波,王红,陈增淦,等.兔脂肪干细胞与聚羟基乙酸/壳聚糖支架材料生物相容性[J].复旦学报(医学版),2014,41(5):610-616.[23] 聂德康,施炜,郭俊,等.覆盖人脐带血间充质干细胞颗粒状壳聚糖支架制备的组织工程学研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2016,33(6): 1593-1596.[24] Kelly D, Prendergast PJA. Mechanobiological analysis of osteochondral defect repair. Transactions of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2004;29(2): 666-669.[25] Duda GN, Maldonado ZM, Klein P, et al. On the influence of mechanical conditions in osteochondral defect healing.J Biomech. 2005;38(4):843-851. [26] 吴佳奇,扬天府,刘洋,等.多孔PA66/n-HA复合BMSCs修复兔膝关节软骨缺损的初步研究[J].生物医学工程, 2008,25(6): 1349-1353. [27] Athanasiou KA, Korvick D, Schenck R. Biodegradable implants for the treatment of osteochondral defects in a goat model. Tissue Eng. 1997;3(4):363-373. [28] 金常礼,李德华,李洪秀,等.GDF-5诱导hADSCs分化为软骨样细胞[J].中国实用医药,2012,7(1):3-5.[29] 李战梅,刘康,冯刚,等.生长分化因子5促进脂肪干细胞成软骨分化的实验研究[J].西部医学,2010,8(22):1380-1384.[30] 胡志斌,严志焜.更多脂肪干细胞更强抑制移植排斥反应作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017,34(12):2278.[31] 姜晓蕾,杨朝忠,韩宝芹,等.壳聚糖及其衍生物作为组织工程角膜支架的研究进展[J].眼科新进展,2017,37(4):392-395. |