Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4572-4577.doi: 10.12307/2024.457
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of m6A methylation regulating bone metabolism for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis
Chen Xiangshan1, Liu Hua1, Sun Weikang2, Li Huanan3
- 1Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Clinical Medicine, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330100, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-07-04Accepted:2023-08-24Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Li Huanan, MD, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China -
About author:Chen Xiangshan, Master candidate, Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82360937 (to CXS [project participant]); Second Jiangxi Provincial Session of the National Medical Master Deng Yunming Famous Doctor’s Studio, No. [2021]201 (to LHN); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2023GXNSFAA026075 (to CXS [project participant]); Key Research Laboratory of Arthralgia Syndrome, No. (2022)8 (to LHN); Jiangxi Provincial Innovation Special Funds for Postgraduates in 2022, No. YC2022-s864 (to SWK); Guangxi Innovation Program for Postgraduate Education in 2023, No. YCSW2023405 (to LH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xiangshan, Liu Hua, Sun Weikang, Li Huanan. Mechanism of m6A methylation regulating bone metabolism for prevention and treatment of osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4572-4577.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
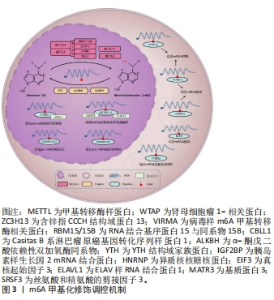
2.1 m6A甲基化概述 m6A甲基化是指发生在RNA腺苷第6位氮原子上的甲基化修饰,于1974年首次在大鼠的mRNA中发现,普遍存在于病毒、植物和哺乳动物中,在人体的生理与病理过程中发挥着重要作用[7-8]。 在生理方面,m6A甲基化修饰可以修饰调控胚胎干细胞的分化[9],还可以影响细胞分裂、免疫稳态、脂肪生成等生物过程[10]。在病理方面,m6A甲基化修饰可以诱导肝细胞癌、前列腺癌、宫颈癌等多种恶性肿瘤的发生[11],还可以影响阿尔茨海默症[12]、动脉粥样硬化[13]、炎症性肠病等多种系统疾病的发展[14]。m6A甲基化主要发生在信使RNA (messenger RNA,mRNA)中,除mRNA外,在核糖体RNA(rRNA)、小核RNA(snRNA)、微小RNA(miRNA)、长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)以及环状RNA(circRNA)中均存在m6A修饰位点[15],占所有RNA修饰的60%以上[16]。 mRNA中的m6A甲基化主要存在于终止密码子和3’非翻译区(3’-UTR)附近,在编码序列和5’非翻译区(5’-UTR)中也少量存在,通常嵌入常见序列为保守序列5’-RRACH-3’(R=G/A,H=A/C/U),其中A被甲基化[17]。 m6A甲基化是一个动态可逆的过程,主要由3个部分相互调节:由m6A甲基转移酶(编码器,writers)催化mRNA甲基化,m6A去甲基化酶(消码器,erasers)则可以对已经甲基化的mRNA去甲基化,进行可逆调节,最后由m6A甲基识别蛋白(解码器,readers)读取[18-19],具体见图3所示。"
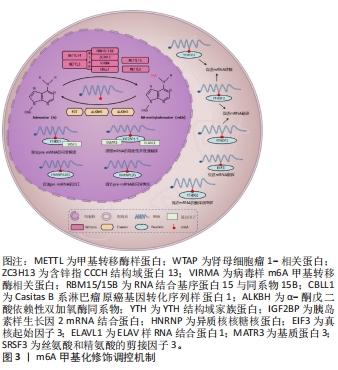
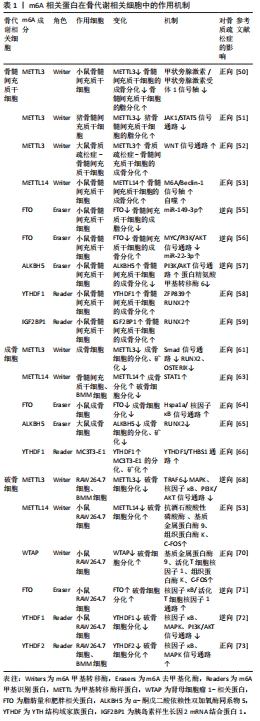
2.1.1 m6A甲基转移酶 m6A甲基转移酶是m6A甲基化的编码器,也被称为“Writers”,是由多种成分组成的甲基转移酶复合物,可以将供体上的甲基转移到受体腺苷第6位氮原子上。甲基转移酶复合物主要由甲基转移酶样蛋白3(methyltransferase like-3,METTL3)、METTL14、肾母细胞瘤1相关蛋白(Wilms’ tumor 1 associated protein,WTAP)3种蛋白质构成[20]。METTL3和METTL14同属于一个大的甲基转移酶家族,可催化甲基转移至腺苷[21],但二者具体作用不同,METTL3是一种在真核生物中高度保守的S-腺苷基甲硫氨酸结合亚基,也是甲基转移酶复合物中唯一具有催化活性的亚基,METTL3可以将甲基从S-腺苷基甲硫氨酸或S-腺苷同型半胱氨酸转移到受体腺苷上,其表达强弱将会直接影响m6A的总甲基化水平[22]。而METTL14的催化中心退化,因此不具备催化活性,但METTL14具有METTL3催化活性所必需的基序,缺乏METTL14,METTL3也将失去催化活性[23]。WTAP是甲基转移酶活性的调节亚基,可将METTL14-METTL3募集到mRNA标靶上,而它缺少的情况下,METTL3的RNA结合能力会显著降低[24]。研究表明,使用小干扰RNA(small interfering RNA,siRNA)敲低HeLa和293FT细胞中METTL3、METTL14和WTAP后,多聚腺苷酸化RNA中的m6A水平分别降低了约30%,40%和50%[25]。 甲基转移酶复合物还包括含锌指CCCH结构域蛋白13,它可以将甲基转移酶复合物锚定在细胞核中以促进m6A甲基化,敲低含锌指CCCH结构域蛋白13后,大部分WTAP将错位至细胞质[26];病毒样m6A甲基转移酶相关蛋白,它是甲基转移酶复合物中已知最大的蛋白,可以募集催化其他甲基转移酶到指定区域选择性甲基化[27];RNA 结合基序蛋白15及其同系物RNA 结合基序蛋白15B可以通过WTAP与METTL3-METTL14形成的异二聚体结合,将甲基转移酶复合物招募到RNA中的特定位点进行甲基化,敲低RNA 结合基序蛋白15/15B表达将导致m6A甲基化总体水平降低[28];Casitas B系淋巴瘤原癌基因转化序列样蛋白1是一种潜在的环指型E3泛素连接酶,它影响分布在5’-UTR和起始密码子周围的m6A修饰[29]。后续研究发现,METTL16、METTL5也具有甲基转移酶的功能,但其作用可独立于甲基转移酶复合物外[30]。综上,m6A甲基转移酶由多种蛋白质组成,共同维持m6A甲基转移酶的稳定性、保证其精准定位于RNA、高效完成m6A甲基化。但m6A甲基转移酶各蛋白之间如何相互协调,如何反馈调控m6A甲基化水平的相关研究较少,其调节机制仍需进一步完善。 2.1.2 m6A去甲基化酶 m6A去甲基化酶是m6A甲基化的消码器,也被称为“Erasers”,可以逆转m6A甲基转移酶的催化,它的发现揭示m6A甲基化是一个动态可逆的过程。脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白和α-酮戊二酸依赖性双加氧酶同系物5(alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase homolog 5,ALKBH5)是目前已被鉴定且报道的2种m6A去甲基化酶[31]。脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白可以将m6A氧化为不稳定的N6-羟甲基腺苷,再将N6-羟甲基腺苷氧化为N6-甲酰基腺苷,最后将N6-甲酰基腺苷氧化成正常腺苷[32]。研究表明,使用siRNA敲低脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白后,mRNA中m6A水平显著升高,而脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白过表达则会引起细胞中m6A水平降低[33]。ALKBH5与脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白均属于ALKB家族,并且它们都需要二价铁离子和α-酮戊二酸的去甲基化活性,但与脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白不同,ALKBH5不需要氧化步骤,它可以直接从m6A甲基化腺嘌呤中去除甲基,其活性可以显著影响mRNA的核输出和代谢[34]。 随着研究的深入,另一种RNA去甲基化酶ALKBH3被证明可以介导m6A去甲基化,但这仅存在于tRNA中,在rRNA和mRNA中并没有发现[35]。m6A去甲基化酶的作用保证了m6A甲基化的可逆调控,但目前已发现的具有m6A去甲基化活性的蛋白质种类少,其功能和机制也尚处于探索阶段,有待进一步研究。 2.1.3 m6A甲基识别蛋白 m6A甲基识别蛋白是m6A甲基化的解码器,也被称为“Readers”,可以特异性地识别m6A并与之结合,调控RNA的转录、翻译、代谢等过程,它主要由YTH(YT521-B homology family)结构域蛋白、胰岛素样生长因2 mRNA结合蛋白(Insulin-like growth factor-2 mRNA-binding protein,IGF2BP)、异质核核糖核蛋白(Heterogeneous-nuclear ribonucleoprotein,HNRNP)3个家族蛋白构成[36]。YTH家族蛋白可细分为3类:DC1家族(YTH domain-containing 1,YTHDC1)、DC2家族(YTH domaincontaining 2,YTHDC2)和DF家族(YTH m6A-binding protein 1-3,YTHDF1-3),5种蛋白质在结构上都拥有一段高度保守的YTH结构域,但是其作用各不相同[37]。DF家族位于细胞质中,YTHDF1可以通过促进m6A修饰的mRNA的核糖体组装从而加速mRNA的翻译。YTHDF2的主要功能是调节m6A修饰的mRNA的稳定性,促进mRNA的降解。而YTHDF3不仅可以与YTHDF1合作共同促进m6A修饰的mRNA的翻译,还可以协同YTHDF2降解m6A修饰的mRNA。YTHDC1位于细胞核中,可以与m6A修饰的前体mRNA(pre-mRNA)结合,募集富含丝氨酸和精氨酸的剪接因子3,从而调节pre-mRNA的可变剪接。YTHDC2是YTH家族蛋白中唯一含有解旋酶结构域的蛋白,其解旋酶结构域有助于调节m6A修饰的mRNA的翻译和降解[38-39]。 IGF2BP家族蛋白主要有IGF2BP1-3,它们可以通过募集辅因子ELAV样RNA结合蛋白1、基质蛋白3来显著增强mRNA的稳定性,此外,IGF2BP1-3还可以促进mRNA的翻译[40-41]。HNRNP家族主要包括HNRNPA2B1、HNRNPC和HNRNPG三种蛋白。HNRNPA2B1可以与miRNA微处理器复合蛋白DGCR8和Drosha核糖核酸酶Ⅲ相互作用,促进初级miRNA (pri-miRNA)的加工[42]。HNRNPC不直接识别m6A,而是选择性结合m6A修饰的转录物,诱导m6A改变RNA结合基序的局部结构,从而促进HNRNPC与mRNA的结合,加速pre-mRNA的加工。这种m6A诱导改变mRNA的识别基序局部结构,影响蛋白质与RNA相互作用的机制称为“m6A开关”(m6A-switch)[43]。HNRNPG与HNRNPC作用相似,可以调节pre-mRNA的可变剪切,也可以介导mRNA产生m6A-switch[44]。 除上述3种家族蛋白外,真核起始因子3也可以作为“Reader”,它能够与5’-UTR中含有m6A修饰的mRNA直接结合,在不依赖帽子结构的情况下独立进行翻译[45]。与m6A甲基转移酶和m6A去甲基化酶相比,m6A甲基识别蛋白数量较多,因此,m6A甲基识别蛋白还具有广阔的研究空间,在后续的研究中可以作为m6A甲基化研究主体。 2.2 m6A甲基化调控骨代谢在骨质疏松症中的作用 在人体骨骼系统中,骨代谢处于动态平衡状态,由吸收骨基质的破骨细胞和合成骨基质的成骨细胞共同维持[46]。一旦这种平衡被打破,则会导致破骨细胞主导的骨吸收增强或成骨细胞主导的骨生成减弱,骨代谢稳态失衡,骨密度降低,引发骨质疏松症[47]。而m6A甲基化可以调节骨髓间充质干细胞、成骨细胞、破骨细胞的生长、分化和代谢等过程,在骨代谢中发挥重要作用[48-50]。 2.2.1 m6A甲基化对骨髓间充质干细胞的调控 骨髓间充质干细胞可以分化形成骨、脂肪、软骨细胞,是一种具有多种分化潜能的细胞亚群,在骨形成中发挥重要作用[48]。研究发现,METTL3在小鼠的骨细胞和骨髓中普遍表达,在敲除小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中的METTL3后,骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力减弱,从机制上来说,m6A甲基化可以维持甲状旁腺激素的水平,而甲状旁腺激素可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[49],METTL3敲除后,甲状旁腺激素受体1 mRNA翻译效率降低,蛋白合成受到抑制,证明m6A可以通过调节甲状旁腺激素/甲状旁腺激素受体1信号轴影响骨髓间充质干细胞的分化平衡[50]。此外,YAO等[51]发现METTL3的沉默显著促进了猪骨髓间充质干细胞的脂肪生成过程,这是由于m6A可以通过METTL3介导JAK1/STAT5通路抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化。WU等[52]对从骨质疏松症大鼠模型中分离出的骨质疏松症-骨髓间充质干细胞进行培养,发现其甲基化水平和成骨能力均明显下降,但使用METTL3过表达慢病毒处理后,WNT信号通路被激活,逆转了骨质疏松症-骨髓间充质干细胞受损的成骨能力。除METTL3外,METTL14的敲低将会导致小鼠体内骨形成减少和自噬受损,而METTL14过表达不仅可以增加成骨相关基因的表达水平,还可以靶向促进自噬相关蛋白Beclin-1 mRNA的翻译并激活自噬[53]。 脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白在骨质疏松症患者的骨骼中上调,在骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化过程中也上调,而在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中却下调,表明脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白有利于骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化并影响骨质疏松症的发生[54]。在小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中,调节因子miR-149-3p的过表达可以与脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白基因的3’-UTR结合来抑制脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白基因的表达,起到抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的作用[55]。此外,调节因子miR-22-3p可以通过负向调节脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白,导致MYC/PI3K/AKT信号通路失活,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[56]。LI等[57]研究发现ALKBH5的过表达会负向调节骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,这是由于ALKBH5可以增强蛋白精氨酸甲基转移酶6的降解速率,通过激活PI3K/AKT通路,降低了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。m6A甲基识别蛋白在骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化中也是必不可少的。研究表明,YTHDF1基因敲除小鼠的骨小梁数量、厚度和骨密度均低于正常小鼠,且YTHDF1的过表达可以增强小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨潜力。从机制上来说,YTHDF1可以调控其下游锌指蛋白ZNF839/ZFP839的表达,而ZFP839可以与骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化所必需的关键转录因子RUNX2相互作用,增强其转录活性,从而促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨[58]。IGF2BPs作为可以稳定mRNA的结合蛋白,可以通过识别RUNX2 mRNA上的m6A位点并与之结合,显著上调骨髓间充质干细胞中RUNX2 mRNA的稳定性,增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力[59]。不仅如此,IGF2BPs还可以通过识别METTL14介导的m6A修饰位点,促进Beclin-1 mRNA稳定性并进一步促进其翻译,配合METTL14增强自噬水平达到提高骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力的目的[53]。 上述研究表明,m6A可以从多种途径调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化及成脂分化,在骨髓间充质干细胞中,组成m6A甲基转移酶复合物的多种蛋白质功能相同,可以作用于多种靶点增强骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力。m6A甲基识别蛋白可以增强下游成骨相关基因的稳定性和蛋白表达水平,还能与甲基转移酶相互配合调控自噬,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。而m6A去甲基化酶作用与m6A甲基转移酶相反,可以通过多种通路降低骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。总之,在骨髓间充质干细胞中,m6A甲基化水平对骨形成是正向的,提高m6A甲基化水平可以减少骨质疏松症的发生。 2.2.2 m6A甲基化对成骨细胞的调控 成骨细胞由骨髓间充质干细胞分化而来,具有进一步分化为骨细胞的潜能,对骨形成至关重要,且可以通过分泌细胞因子或通过直接的细胞接触对破骨细胞的分化和活性进行反馈调节,在骨代谢中发挥重要作用[60]。在成骨细胞分化过程中,METTL3的mRNA和蛋白水平均升高,在敲低成骨细胞中的METTL3后,成骨密切相关的经典Smad依赖性信号通路受到抑制,导致成骨转录因子RUNX2和OSTERIX的蛋白质水平降低,成骨细胞分化和矿化下降[61]。SUN等[62]研究发现METTL14水平与卵巢切除小鼠的骨标本中的骨形成呈正相关,在体外实验中,METTL14的过表达可以促进成骨细胞增殖、分化和基质矿化。其机制是METTL14可以通过提高成骨正向调节因子STAT1 mRNA的m6A水平,从而促进成骨细胞分化并抑制破骨细胞分化[63]。 ZHANG等[64]研究发现小鼠成骨细胞中脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白的缺失导致小鼠骨小梁数量及厚度减少,骨形成受到抑制。在体外实验中,敲低脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白会影响小鼠成骨细胞的早期分化,且更易受到基因毒性损伤,从而导致成骨细胞凋亡率增加。这是由于脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白的缺乏导致其下游靶基因Hspa1a的表达降低,而Hspa1a可以抑制核因子κB通路的激活,表明脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白可以通过Hspa1a/核因子κB通路调节成骨细胞凋亡。ALKBH5 mRNA和蛋白表达水平在大鼠颅骨成骨细胞分化过程中上调,ALKBH5敲低后,成骨细胞中RUNX2 mRNA的稳定性下降,导致RUNX2蛋白质水平降低,成骨细胞的分化、矿化受到抑制[65]。研究发现YTHDF1可以促进前成骨细胞MC3T3-E1的分化及矿化,进一步实验表明,YTHDF1是通过调控其下游因子THBS1的mRNA和蛋白表达水平从而增强MC3T3-E1细胞的成骨作用。不仅如此,缺氧可以诱导甲基化的THBS1 mRNA从细胞核转移到细胞质,被YTHDF1翻译修饰,提高THBS1的表达水平,改善由缺氧导致的成骨抑制[66],表明MC3T3-E1细胞可通过YTHDF1/THBS1通路促进成骨并防止缺氧引起的成骨抑制。 综上,m6A甲基化在成骨细胞的活性、分化和矿化中均发挥着积极作用。m6A甲基转移酶与m6A甲基识别蛋白在成骨细胞中的功能和它们在骨髓间充质干细胞中的功能类似,都有利于骨形成。但m6A去甲基化酶有利于成骨细胞的分化及矿化,在骨形成中发挥正向调节作用,这与它在骨髓间充质干细胞中的作用相反。作者认为这可能是由于在不同的细胞中,脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白和ALKBH5的作用也不同,它们在成骨细胞中的作用并不仅是去甲基化,且还扮演其他的角色并发挥着多重作用,其具体功能及作用机制仍需进一步研究。 2.2.3 m6A甲基化对破骨细胞的调控 破骨细胞是由骨髓中的造血干细胞分化而成的大型多核细胞,是人体唯一的骨吸收细胞。在骨吸收的同时可以通过多种途径负反馈促进成骨,维持骨代谢平衡[67]。研究表明,m6A水平和METTL3表达水平在破骨细胞分化过程中均增加,METTL3敲低将导致破骨细胞分化受到抑制且骨吸收活性下降。从机制上来说,这是由于METTL3缺失致使破骨细胞重要分化相关蛋白TRAF6的表达水平显著下降,进一步导致RANKL诱导的MAPK、核因子κB和PI3K/AKT信号通路受到抑制,破骨细胞分化和骨吸收受到抑制[68]。此外,METTL3的敲低还可以降低由炎症导致小鼠颅骨骨质溶解并抑制破骨细胞的生成[69],表明METTL3在破骨细胞分化中起到正向调节作用。但METTL14和WTAP作用却与METTL3相反,METTL14的敲低将导致RAW264.7细胞中破骨细胞分化相关基因抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、基质金属蛋白酶9、组织蛋白酶K和C-FOS的表达水平上调,WTAP的敲低也会引起基质金属蛋白酶9、活化T细胞核因子1、组织蛋白酶K和C-FOS表达水平增加,证明METTL14和WTAP可以负向调节破骨细胞分化并进一步抑制骨吸收[53,70]。 ZHUANG等[71]研究了脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白对RAW264.7细胞和骨髓单核细胞衍生的破骨细胞的影响,发现脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白过表达有助于RANKL诱导的核因子κB与活化T细胞核因子1启动子的结合,促进破骨细胞生成。进一步的动物实验与细胞实验一致,发现脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白在来自卵巢切除小鼠的骨髓单核细胞中上调,敲低脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白后,卵巢切除小鼠骨小梁和骨矿物质密度增加,破骨细胞生成及骨吸收受到抑制。表明脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白可以通过调节核因子κB/活化T细胞核因子1通路促进破骨细胞形成。在脂多糖刺激的炎症性破骨细胞分化过程中,YTHDF1表达上调,敲低YTHDF1可抑制破骨细胞相关基因Tnfrsf11a、Traf6、基质金属蛋白酶9和Acp5的表达,同时,YTHDF1的沉默还抑制了核因子κB、MAPK和PI3K/AKT信号通路中关键蛋白的磷酸化水平,导致破骨细胞形成和骨吸收水平降低,表明YTHDF1可以通过核因子κB、MAPK和PI3K/AKT信号通路调节炎症性破骨细胞分化[72]。与YTHDF1的作用相反,在RAW264.7细胞和骨髓巨噬细胞中,YTHDF2敲低上调了破骨细胞相关基因的表达和促炎细胞因子分泌,导致破骨细胞形成和骨吸收水平升高,而核因子κB和MAPK信号通路抑制剂可以有效降低由YTHDF2敲低导致的活化T细胞核因子1、C-FOS、白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α表达增强的能力,表明YTHDF2可以通过核因子κB和MAPK信号通路在破骨细胞分化和炎症反应中发挥负调节作用[73]。 与骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞相比,m6A甲基化相关蛋白在破骨细胞中的作用是杂乱的,在成骨细胞中,脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白的缺乏会导致核因子κB信号通路激活,但在破骨细胞中,脂肪量和肥胖相关蛋白的过表达也会激活核因子κB信号通路。而且同为m6A甲基转移酶的METTL3与METTL14、WTAP在破骨细胞中的作用相反,METTL3的敲低将会导致破骨细胞分化受到抑制,而METTL14、WTAP的敲低则会导致破骨细胞分化增加。此外,m6A甲基识别蛋白YTHDF1与YTHDF2在破骨细胞中的作用也相反,YTHDF1的沉默可以降低炎症性破骨细胞分化,而YTHDF2的敲低将会导致破骨细胞分化增加并加强促炎细胞因子的分泌。这再次证明了在不同细胞中,m6A甲基化相关蛋白所扮演的角色不同,发挥的功能也不同,不能等量齐观。 m6A相关蛋白在骨代谢相关细胞中的作用机制见表1。"
| [1] ENSRUD KE, CRANDALL CJ. Osteoporosis. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(3):ITC17-ITC32. [2] BROWN C. Osteoporosis: Staying strong. Nature. 2017;550(7674):S15-S17. [3] RACHNER TD, KHOSLA S, HOFBAUER LC. Osteoporosis: now and the future. Lancet. 2011;377(9773):1276-1287. [4] TYSOE O. Liver-bone crosstalk implicated in osteoporosis progression. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(8):440. [5] YANG C, DONG Z, LING Z, et al. The crucial mechanism and therapeutic implication of RNA methylation in bone pathophysiology. Ageing Res Rev. 2022;79:101641. [6] DAI X, REN T, ZHANG Y, et al. Methylation multiplicity and its clinical values in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2021;23:e2. [7] JONKHOUT N, TRAN J, SMITH MA, et al. The RNA modification landscape in human disease. RNA. 2017;23(12):1754-1769. [8] DESROSIERS R, FRIDERICI K, ROTTMAN F. Identification of Methylated Nucleosides in Messenger RNA from Novikoff Hepatoma Cells. Proc National Acad Sci. 1974;71(10): 3971-3975. [9] BATISTA PJ, MOLINIE B, WANG J, et al. m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;15(6):707-719. [10] YANG Y, HSU PJ, CHEN YS, et al. Dynamic transcriptomic m(6)A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018;28(6):616-624. [11] SUN T, WU R, MING L. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108613. [12] HAN M, LIU Z, XU Y, et al. Abnormality of m6A mRNA Methylation Is Involved in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 2020;14:98. [13] FU J, CUI X, ZHANG X, et al. The Role of m6A Ribonucleic Acid Modification in the Occurrence of Atherosclerosis. Front Genet. 2021;12:733871. [14] NIE K, YIJ, YANG Y, et al. A Broad m6A Modification Landscape in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:782636. [15] HUANG H, WENG H, CHEN J. The Biogenesis and Precise Control of RNA m6A Methylation. Trends Genet. 2020;36(1):44-52. [16] ZHANG Y, GENG X, LI Q, et al. m6A modification in RNA: biogenesis, functions and roles in gliomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):192. [17] AN Y, DUAN H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol Cancer. 2022;21(1):14. [18] SHI H, WEI J, HE C. Where, When, and How: Context-Dependent Functions of RNA Methylation Writers, Readers, and Erasers. Mol Cell. 2019;74(4):640-650. [19] OERUM S, MEYNIER V, CATALA M, et al. A comprehensive review of m6A/m6Am RNA methyltransferase structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(13):7239-7255. [20] YANG B, WANG JQ, TAN Y, et al. RNA methylation and cancer treatment. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105937. [21] SCHOLLER E, WEICHMANN F, TREIBER T, et al. Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the m(6)A generating METTL3-METTL14-WTAP complex. RNA. 2018; 24(4):499-512. [22] CHEN J, FANG Y, XU Y, et al. Role of m6A modification in female infertility and reproductive system diseases. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(9):3592-3604. [23] BUJNICKI JM, FEDER M, RADLINSKA M, et al. Structure prediction and phylogenetic analysis of a functionally diverse family of proteins homologous to the MT-A70 subunit of the human mRNA:m(6)A methyltransferase. J Mol Evol. 2002;55(4):431-444. [24] PING XL, SUN BF, WANG L, et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014;24(2):177-189. [25] LIU J, YUE Y, HAN D, et al. A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol. 2014;10(2):93-95. [26] WEN J, LV R, MA H, et al. Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m(6)A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Mol Cell. 2018;69(6):1028-1038. [27] ZHANG X, LI MJ, XIA L, et al. The biological function of m6A methyltransferase KIAA1429 and its role in human disease. Peer J. 2022;10:e14334. [28] PATIL DP, CHEN CK, PICKERING BF, et al. m(6)A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 2016;537(7620):369-373. [29] WANG Y, ZHANG L, REN H, et al. Role of Hakai in m(6)A modification pathway in Drosophila. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):2159. [30] FANG Z, MEI W, QU C, et al. Role of m6A writers, erasers and readers in cancer. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11(1):45. [31] GAO R, YE M, LIU B, et al. m6A Modification: A Double-Edged Sword in Tumor Development. Front Oncol. 2021;11:679367. [32] FU Y, JIA G, PANG X, et al. FTO-mediated formation of N6-hydroxymethyladenosine and N6-formyladenosine in mammalian RNA. Nat Commun. 2013;4:1798. [33] JIA G, FU Y, ZHAO X, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7(12):885-887. [34] ZHENG G, DAHL JA, NIU Y, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49(1):18-29. [35] UEDA Y, OOSHIO I, FUSAMAE Y, et al. AlkB homolog 3-mediated tRNA demethylation promotes protein synthesis in cancer cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42271. [36] LIU C, GU L, DENG W, et al. N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:887838. [37] LIAO S, SUN H, XU C. YTH Domain: A Family of N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) Readers. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018;16(2):99-107. [38] ZACCARA S, JAFFREY SR. A Unified Model for the Function of YTHDF Proteins in Regulating m(6)A-Modified mRNA. Cell. 2020;181(7):1582-1595. [39] XU Y, ZHANG W, SHEN F, et al. YTH Domain Proteins: A Family of m(6)A Readers in Cancer Progression. Front Oncol. 2021;11:629560. [40] DEGRAUWE N, SUVA ML, JANISZEWSKA M, et al. IMPs: an RNA-binding protein family that provides a link between stem cell maintenance in normal development and cancer. Genes Dev. 2016;30(22):2459-2474. [41] HUANG H, WENG H, SUN W, et al. Recognition of RNA N(6)-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Bio. 2018;20(3):285-295. [42] ALARCON CR, GOODARZI H, LEE H, et al. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m(6)A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell. 2015;162(6):1299-1308. [43] LIU N, DAI Q, ZHENG G, et al. N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature. 2015;518(7540):560-564. [44] LIU N, ZHOU KI, PARISIEN M, et al. N6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(10):6051-6063. [45] MEYER KD, PATIL DP, ZHOU J, et al. 5’ UTR m(6)A Promotes Cap-Independent Translation. Cell. 2015;163(4):999-1010. [46] ZHANG L, ZHENG YL, WANG R, et al. Exercise for osteoporosis: A literature review of pathology and mechanism. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1005665. [47] HOCKING LJ, WHITEHOUSE C, HELFRICH MH. Autophagy: a new player in skeletal maintenance? J Bone Miner Res. 2012;27(7):1439-1447. [48] NOMBELA-ARRIETA C, RITZ J, SILBERSTEIN LE. The elusive nature and function of mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(2):126-131. [49] RICKARD DJ, WANG FL, RODRIGUEZ-ROJAS AM, et al. Intermittent treatment with parathyroid hormone (PTH) as well as a non-peptide small molecule agonist of the PTH1 receptor inhibits adipocyte differentiation in human bone marrow stromal cells. Bone. 2006;39(6):1361-1372. [50] WU Y, XIE L, WANG M, et al. Mettl3-mediated m(6)A RNA methylation regulates the fate of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4772. [51] YAO Y, BI Z, WU R, et al. METTL3 inhibits BMSC adipogenic differentiation by targeting the JAK1/STAT5/C/EBPbeta pathway via an m(6)A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. FASEB J. 2019;33(6):7529-7544. [52] WU T, TANG H, YANG J, et al. METTL3-m(6) A methylase regulates the osteogenic potential of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in osteoporotic rats via the Wnt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(5):e13234. [53] HE M, LEI H, HE X, et al. METTL14 Regulates Osteogenesis of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Inducing Autophagy Through m6A/IGF2BPs/Beclin-1 Signal Axis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022;11(9):987-1001. [54] SHEN GS, ZHOU HB, ZHANG H, et al. The GDF11-FTO-PPARgamma axis controls the shift of osteoporotic MSC fate to adipocyte and inhibits bone formation during osteoporosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018;1864(12):3644-3654. [55] LI Y, YANG F, GAO M, et al. miR-149-3p Regulates the Switch between Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of BMSCs by Targeting FTO. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;17:590-600. [56] ZHANG X, WANG Y, ZHAO H, et al. Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated miR-22-3p from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell promotes osteogenic differentiation via FTO inhibition. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):227. [57] LI Z, WANG P, LI J, et al. The N(6)-methyladenosine demethylase ALKBH5 negatively regulates the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through PRMT6. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(6):578. [58] LIU T, ZHENG X, WANG C, et al. The m(6)A “reader” YTHDF1 promotes osteogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through translational control of ZNF839. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(11):1078. [59] ZHOU S, ZHANG G, WANG K, et al. METTL3 potentiates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via IGF2BP1/m6A/RUNX2. Oral Dis. 2023. doi: 10.1111/odi.14526. [60] KIM JM, LIN C, STAVRE Z, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Communication and Bone Homeostasis. Cells. 2020;9(9):2073. [61] ZHANG Y, GU X, LI D, et al. METTL3 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation and Inflammatory Response via Smad Signaling and MAPK Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 21(1):199. [62] SUN Z, WANG H, WANG Y, et al. MiR-103-3p targets the m(6) A methyltransferase METTL14 to inhibit osteoblastic bone formation. Aging Cell. 2021;20(2):e13298. [63] WANG C, CHEN R, ZHU X, et al. METTL14 alleviates the development of osteoporosis in ovariectomized mice by upregulating m(6)A level of SIRT1 mRNA. Bone. 2023;168: 116652. [64] ZHANG Q, RIDDLE RC, YANG Q, et al. The RNA demethylase FTO is required for maintenance of bone mass and functions to protect osteoblasts from genotoxic damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(36):17980-17989. [65] FENG L, FAN Y, ZHOU J, et al. The RNA demethylase ALKBH5 promotes osteoblast differentiation by modulating Runx2 mRNA stability. FEBS Lett. 2021;595(15):2007-2014. [66] SHI D, LIU X, LI X, et al. Yth m(6)A RNA-Binding Protein 1 Regulates Osteogenesis of MC3T3-E1 Cells under Hypoxia via Translational Control of Thrombospondin-1. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1741. [67] SUN Y, LI J, XIE X, et al. Recent Advances in Osteoclast Biological Behavior. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:788680. [68] LI D, CAI L, MENG R, et al. METTL3 Modulates Osteoclast Differentiation and Function by Controlling RNA Stability and Nuclear Export. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(5):1660. [69] LI D, HE J, FANG C, et al. METTL3 Regulates Osteoclast Biological Behaviors via iNOS/NO-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Inflammatory Conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(2):1403. [70] LIU J, YOU Y, SUN Z, et al. WTAP-Mediated m6A RNA Methylation Regulates the Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells via the miR-29b-3p/HDAC4 Axis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023;12(5):307-321. [71] ZHUANG J, NING H, WANG M, et al. Downregulated fat mass and obesity-associated protein inhibits bone resorption and osteoclastogenesis by nuclear factor-kappa B inactivation. Cell Signal. 2021;87:110137. [72] HE M, LI D, FANG C, et al. YTHDF1 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress, NF-kappaB, MAPK and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways in inflammatory osteoclastogenesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022;732:109464. [73] FANG C, HE M, LI D, et al. YTHDF2 mediates LPS-induced osteoclastogenesis and inflammatory response via the NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 2021;85:110060. |
| [1] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [2] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [3] | Huang Haoran, Fan Yinuo, Wei-Yang Wenxiang, Jiang Mengyu, Fang Hanjun, Wang Haibin, Chen Zhenqiu, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi. Urolithin A mediates p38/MAPK pathway to inhibit osteoclast activity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1149-1154. |
| [4] | Zhang Xiaoyun, Liu Hua, Chai Yuan, Chen Feng, Zeng Hao, Gao Zhengang, Huang Yourong. Effect of Yishen Gushu Formula on bone metabolic markers and clinical efficacyn in patients with osteoporosis of kidney deficiency and blood stasis type [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1155-1160. |
| [5] | Dai Yuexing, Zheng Liqin, Wu Minhui, Li Zhihong, Li Shaobin, Zheng Desheng, Lin Ziling. Effect of vessel number on computational fluid dynamics in vascular networks [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1206-1210. |
| [6] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [7] | Wang Wen, Zheng Pengpeng, Meng Haohao, Liu Hao, Yuan Changyong. Overexpression of Sema3A promotes osteogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells and MC3T3-E1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 993-999. |
| [8] | Zhang Min, Peng Jing, Zhang Qiang, Chen Dewang. Mechanical properties of L3/4 laminar decompression and intervertebral fusion in elderly osteoporosis patients analyzed by finite element method [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 847-851. |
| [9] | Xue Xiaofeng, Wei Yongkang, Qiao Xiaohong, Du Yuyong, Niu Jianjun, Ren Lixin, Yang Huifeng, Zhang Zhimin, Guo Yuan, Chen Weiyi. Finite element analysis of osteoporosis in proximal femur after cannulated screw fixation for femoral neck fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [10] | Kaiyisaier•Abudukelimu, Maimaitimin•Abulimiti, Li Lei, Yang Xiaokai, Zhang Yukun, Liu Shuai. Effect of lumbar CT values in the diagnosis of osteoporosis in women patients with lumbar degenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 945-949. |
| [11] | Wang Liping, Lian Tianxing, Hu Yongrong, Yang Hongsheng, Zeng Zhimou, Liu Hao, Qu Bo. HU value of chest CT vertebral body in the opportunistic screening of type 2 diabetes mellitus osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 950-954. |
| [12] | Yu Zhaoyu, Tan Lixin, Sun Kai, Lu Yao, Li Yong. Meta-analysis of cement-augmented pedicle screw for thoracolumbar degenerative diseases with osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 813-820. |
| [13] | Wei Yuanxun, Chen Feng, Lin Zonghan, Zhang Chi, Pan Chengzhen, Wei Zongbo. The mechanism of Notch signaling pathway in osteoporosis and its prevention and treatment with traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 587-593. |
| [14] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [15] | Abuduwupuer·Haibier, Alimujiang·Yusufu, Maihemuti·Yakufu, Maimaitimin·Abulimiti, Tuerhongjiang·Abudurexiti. Meta-analysis of efficacy and safety of terlipatide and bisphosphate in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 639-645. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||