Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (28): 4578-4585.doi: 10.12307/2024.424
Previous Articles Next Articles
The role and mechanism of TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis
Chen Ying1, Xia Tianqin1, Hua Jianlin1, Yin Jinzhu2, Song Lijuan1, 2, Wang Qing1, Yu Jiezhong3, Huang Jianjun1, 2, Ma Cungen1
- 1The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine/Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Sinopharm Coal Group, Datong 037003, Shanxi Province, China; 3Institute of Brain Science, Shanxi Datong University, Datong 037009, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2023-04-06Accepted:2023-07-26Online:2024-10-08Published:2023-11-27 -
Contact:Ma Cungen, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine/Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China Huang Jianjun, Professor, Master’s supervisor, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine/Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Sinopharm Coal Group, Datong 037003, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Chen Ying, Master candidate, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine/Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China Xia Tianqing, Master candidate, The Key Research Laboratory of Benefiting Qi for Acting Blood Circulation Method to Treat Multiple Sclerosis of State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine/Research Center of Neurobiology, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81473577 (to MCG); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81903596 (to WQ); 2022 Shanxi Provincial Science and Technology Innovation Young Talent Team, No. 202204051001028 (to SLJ); Shanxi Provincial Applied Basic Research Program Project, No. 201901D211538 (to SLJ); Medical Science and Technology Leadership Team of Shanxi Provincial Healthcare Commission, No. 2020TD05 (to MCG); Funding for Discipline Construction of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2023XKJS-02 (to MCG); Science and Technology Innovation Team of Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine in 2022, Nos. 2022TD2006 (to WQ) and 2022TD2010 (to SLJ); Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine Young Scientist Cultivation Project, No. 2021-PY-QN-09 (to SLJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Ying, Xia Tianqin, Hua Jianlin, Yin Jinzhu, Song Lijuan, Wang Qing, Yu Jiezhong, Huang Jianjun, Ma Cungen. The role and mechanism of TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in multiple sclerosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4578-4585.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
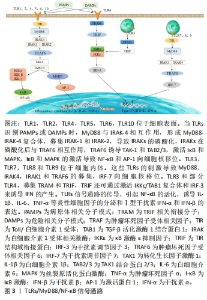
2.1 TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB信号系统的结构与功能 TLRs是一类Ⅰ型跨膜受体,在先天性免疫反应中起着关键作用;MyD88是主要TLRs的衔接子,可以通过活化NF-κB和其他导致促炎分子合成的转录因子,促进炎症因子的产生,从而启动炎症反应。 2.1.1 TLRs的结构与功能 TLRs具有与其他Ⅰ型跨膜糖蛋白受体相似的结构,由细胞外结构域、胞膜结构及胞内区域3部分组成[4],细胞外结构域是一个富含亮氨酸的重复N端结构域,具有检测广泛的病原体相关分子模式(pathogen-associated molecular patterns,PAMPs)和内源性危险相关分子模式(damage associated molecular patterns,DAMPs)的能力,从而激活炎症反应;胞膜结构是富含半胱氨酸的跨膜区;胞内区又叫Toll/白细胞介素1受体(Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor,TIR)结构域,细胞质TIR总是存在于C-末端结构域,是一个保守的白细胞介素1受体(interleukin-1 receptor,IL-1R)家族,与下游衔接分子结合[2]。 TLRs是一类在先天性免疫反应中发挥重要作用的Ⅰ型跨膜受体家族,它们可以识别各种各样的细菌、真菌、原生动物和病毒成分,并能激活免疫反应,是固有免疫与适应性免疫之间的桥梁。TLRs家族成员不仅可以促进病原体的清除,而且能参与自身免疫病等疾病的发生发展。它们在与免疫应答相关的几种细胞类型上大量表达,如巨噬细胞、树突状细胞、T 细胞、B细胞和上皮细胞[5]。目前,已经在人类中发现了10个TLRs(TLR1-10)。TLRs根据其位置分为2组,TLR 1,2,4,5,6和10定位于细胞表面;TLR 3,7,8和9定位于细胞内区[6]。这些TLRs家族分子识别相应配体,激活下游信号转导通路,触发免疫反应,诱导细胞因子、趋化因子产生,在免疫反应中发挥重要的作用[7]。 2.1.2 MyD88的结构与功能 MyD88是TLRs的下游衔接蛋白,在TLRs信号通路的信号转导中有非常重要的作用。TLRs信号通路主要包括MyD88依赖性和MyD88非依赖性2条通路。除TLR3外,所有TLRs都通过MyD88介导下游信号通路。MyD88蛋白包含3个结构域:Toll/白细胞介素1受体(TIR)结构域、中间域和死亡结构域(death domain,DD)。白细胞介素1受体结构域包含130个氨基酸,它的作用主要是通过与蛋白质的结合来向下游传递信号,而死亡结构域包含90个氨基酸,死亡结构域和中间域共同被表达后可与白细胞介素1受体相关激酶(interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase,IRAK)结合并引发其自磷酸化,继而迅速激活下游NF-κB信号通路,促使炎性细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α等的合成、分泌和释放,产生炎症反应,从而对人体的免疫反应产生影响[8-10]。 2.1.3 NF-κB的结构与功能 NF-κB是Rel蛋白家族的异源或同源二聚体,NF-κB家族由5个相关的转录因子组成,包括RelA (p65)、RelB、c-Rel、NF-κB1(p50)和NF-κB2(p52),这些转录因子有以下共同之处:N-末端300个氨基酸Rel同源结构域,负责序列特异性DNA结合,二聚化和抑制性蛋白质结合。这些蛋白质还包含负责NF-κB核易位的核定位序列(nuclear localization sequence,NLS)蛋白。RelA、c-Rel和RelB含有C端转录激活结构域,转录激活结构域负责NF-κB激活后的转录活性,因此能激活靶基因的表达[11]。 NF-κB蛋白能与B细胞κ-轻链增强子特异性结合,上调多种基因的表达。NF-κB是一种几乎广泛存在于各种动物细胞内的信号转导通路,响应外界刺激诸如细胞因子、辐射、重金属和病毒。NF-κB信号通路是调控炎症细胞因子、趋化因子、细胞黏附分子和诱导型一氧化氮合酶产生的重要通路,在炎症反应、免疫调节、神经元死亡和脱髓鞘等过程中起着重要的调控作用[12]。NF-κB信号通路的异常调控可导致多种免疫疾病、慢性炎症和癌症的发生。此外,NF-κB还与突触可塑性和记忆有关。NF-κB一般通过p50与p65结合的异源二聚体起作用[13]。当一些炎症因子、生长因子和趋化因子(如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α)等存在的时候,可以激活NF-κB,NF-κB激活IκB激酶(IKK,Inhibitor of Kappa B Kinase)磷酸化,并通过泛素蛋白酶途径降解,在IκB激酶和NF-κB复合物解聚之后,通过暴露出其核定位序列,它们会被转运至细胞核内与其相关的DNA序列结合,从而启动基因转录并释放细胞因子[14]。NF-κB转导途径包括经典通路和非经典通路[15],经典的NF-κB通路主要是对微生物和促炎细胞因子如肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1信号的响应,可诱导RelA或cRel包含复合物的活化,并调控促炎基因及细胞生存相关基因的表达。肿瘤坏死因子α不能激活非经典的NF-κB途径,但是肿瘤坏死因子家族细胞因子淋巴毒素B、CD40配体(CD40L和TNFSF3)、B细胞激活因子(BAFF和TNFSF13B)和NF-κB受体激活剂(RANKL和TNFSF11)等可以激活,进而导致RelB/p52复合体的激活[16]。 2.2 TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路在多发性硬化/实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎发病中的作用 2.2.1 TLRs的作用 TLRs是参与病原体识别和宿主防御的受体家族。它们定位于几种免疫相关细胞类型的表面或细胞内,如巨噬细胞、树突状细胞、T细胞、B细胞、少突胶质细胞(oligodendrocyte,OL)、上皮细胞和内皮细胞等。在多发性硬化患者和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的中枢神经系统中,多种TLRs的表达升高。如在多发性硬化患者的脑和脊髓中发现了10个功能性TLRs,即TLR1-TLR10,在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠中发现了12个活跃的TLRs,即TLR1-9和TLR11-13[8]。文章主要聚焦TLR2和TLR4进行讨论。 TLR2:是一种细胞表面TLRs,由多种细胞类型表达,如树突状细胞、T细胞、B细胞、肥大细胞和上皮细胞。作为一种模式识别受体,TLR2可以结合多种外源性配体和内源性配体(主要以内源性危险相关分子模式的形式),在多发性硬化和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发病机制中起促进作用;反之,通过使用DAMPs抗体抑制DAMP信号,则可以减弱实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎。当组织损伤或炎症存在时,DAMPs的表达会间歇性增强,提供了内源性TLR2配体来介导疾病的促进作用[17]。已有证据表明,TLR2信号参与了多发性硬化和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发病机制,多发性硬化患者的外周血、脑脊液单个核细胞中和脱髓鞘病灶中的TLR2水平上调,并在患者的大脑和脑脊液中发现了几种TLR2配体,包括高迁移率族蛋白B1(high mobility group protein 1,HMGB1),它们可以激活神经元和小胶质细胞中的TLR2信号,从而增加白细胞介素1α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12、肿瘤坏死因子α和干扰素γ(Interferon-γ,IFN-γ)等炎性因子的水平[1]。研究发现,TLR2可能通过上调Th1/Th17细胞的相关反应,诱导γδ T细胞,抑制少突胶质细胞成熟,参与多发性硬化及实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎发病过程[6]。另有研究表明,TLR2信号系统对髓鞘的再生发挥抑制作用,如少突胶质前体细胞体外成熟为少突胶质细胞受到TLR2的抑制,并且内源性TLR2配体透明质酸可能是这种髓鞘再生抑制的相关介质。相反,在溶血卵磷脂诱导脱髓鞘后,TLR2基因缺失的小鼠(TLR2?/?小鼠)可表现出增强的髓鞘再生能力[17]。通过这些研究发现在多发性硬化和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发病过程中,TLR2的大量表达,促进炎症因子的释放,抑制髓鞘再生,在今后的研究工作中,研究者们可以将抑制TLR2的表达作为治疗多发性硬化的研究方向。 用髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白35-55免疫的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠脑内,TLR2表达水平呈时间相关性增高。在大脑中表达TLR2的区域,I-κBα、单核细胞趋化蛋白1(monocyte chemotactic protein-1,MCP-1)和肿瘤坏死因子α的表达也增加[18]。几种TLR2配体可以下调调节性T细胞(regulatory T cells,Tregs)的免疫抑制作用,诱导调节性T细胞向Th17分化,TLR2激活可促进Th17细胞增殖及分泌Th17细胞因子[19]。除了激活自身免疫性T细胞,TLR2的激活也可以介导促炎因子的分泌,正五聚蛋白3(pentraxin-3,PTX3)是一种在炎症过程中释放的蛋白质,在组织损伤中发挥着不同的作用,在TLR2激动剂刺激的人类小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞中已经报道了正五聚蛋白3的分泌增加[20]。研究表明,TLR2缺乏可通过耐受外来抗原保护小鼠免受实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎。当患有实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的野生(wilde type,WT)小鼠感染呼吸道病原体肺炎链球菌时,小鼠的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎症状恶化;然而,在TLR2基因缺陷的小鼠中,肺炎链球菌的促炎作用消失[21]。 来源于牙龈卟啉单胞菌的磷酸化二氢神经酰胺通过抗原递呈细胞(antigen presenting cells,APC)和降低调节性T细胞而显著改善实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状;然而,它们未能在TLR2缺陷小鼠中发挥这一作用。同样,TLR2表达的降低会使疾病朝着良好的预后发展。雷公藤红素是一种从雷公藤根中提取的五环三萜类化合物,可降低实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的临床评分,可能是通过减少TLR2在脑中的表达[22]。文章发现髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白35-55免疫的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠中TLR2表达升高,促炎因子的分泌增多,而TLR2缺乏和TLR2表达的降低可以改善实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状,使疾病朝着良好的预后发展。 TLR4:与TLR2类似,TLR4也是一种表面TLRs,已被证明参与了多发性硬化的发病机制。当病原刺激TLR4受体后会活化胞内IκB激酶复合体,NF-κB转移至核内使小胶质细胞向促炎表型转化,分泌促炎因子[23]。TLR4可以识别不同种类的外源性PAMPs和内源性配体,如脂多糖和坏死细胞。脂多糖起到佐剂的作用,促进实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的严重程度。在体外,内毒素通过作用于Th17细胞来增加白细胞介素17的分泌。脂多糖刺激后,Th1、Th17细胞中NF-κB的磷酸化水平升高;脂多糖能刺激抗原提呈细胞分泌多种细胞因子,如白细胞介素6、白细胞介素23、干扰素γ和转化生长因子β。此外,脂多糖、结核分枝杆菌和正五聚蛋白3,通常用于诱导实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎,已被证明通过TLR4途径发挥作用[2]。 正五聚蛋白3上调中枢神经系统中TLR4信号中的P-选择素,导致淋巴细胞聚集。正五聚蛋白3用于实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的诱导,可以增加血脑屏障的通透性,防止自身反应性T细胞耐受。正五聚蛋白3未能诱导TLR4缺陷小鼠与实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的淋巴细胞滚动和黏附,这也表明TLR4在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的诱导中是必需的[24]。除了正五聚蛋白3,另一种名为Env-ms的蛋白质被报道通过TLR4破坏血脑屏障并促进多发性硬化的发展。Env-ms是多发性硬化相关反转录病毒的包膜蛋白,可在大多数多发性硬化患者中发现,该包膜蛋白可促进脑内皮细胞黏附分子1(intercellular adhesion molecule-1,ICAM-1)的表达。细胞黏附分子1的增加可促进致病淋巴细胞与血管内皮细胞的黏附,帮助其跨越血脑屏障。Env-ms的致病作用依赖于TLR4,用小干扰RNA(siRNA)敲除TLR4可消除Env-ms的作用[25]。一些内源性配体、外源性配体和蛋白质表明TLR4在多发性硬化的发病机制中必不可少,TLR4不仅促进了多发性硬化的发展,而且敲除TLR4基因无法成功建立实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠模型,在今后可以通过敲除TLR4基因或抑制TLR4信号通路的传导,缓解多发性硬化的发病进程。 多发性硬化患者单个核细胞的TLR4表达显著增加,脑脊液中单核细胞TLR4及高迁移率族蛋白B1亦显著增加[26]。表达白细胞介素17和白细胞介素1的获得性免疫T辅助细胞由于具有跨越血脑屏障的能力,被认为在多发性硬化早期存在着一种潜在的致病作用。有研究显示,获得性免疫T辅助性细胞Th17和Th1在进入脑组织后,能够通过TLR4识别髓鞘蛋白而被活化,进而产生促炎细胞因子白细胞介素6和白细胞介素23,小胶质细胞受到激活的Th17和Th1细胞分泌的细胞因子的刺激,这导致它们参与神经炎症反应,损害和杀死神经元,从而参与多发性硬化的发病[27]。其他研究显示,TLRs配体在脑组织中通过信号传导途径活化TLRs,主要包含了TLR3和TLR4,引起炎症因子干扰素γ和白细胞介素17水平增高,就会直接导致多发性硬化的发生[28]。这些结果表明,TLR4在多发性硬化中表达升高,被特异性识别后产生促炎细胞因子,导致神经炎症反应的发生,促进多发性硬化的发病进程,但其具体作用仍需要进一步研究。 TLR4基因敲除的小鼠很难建立实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎,并且在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的病变区域,炎症因子和趋化因子CCL25的分泌会减少,Th17细胞中CCR9的表达也会降低,趋化和迁移能力也会降低,所以有人认为TLR4可能是通过CCL25/CCR9信号传导来介导Th17的浸润,从而参与实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发生[29]。TLR4基因敲除后促使星形胶质细胞分泌炎症因子的功能减弱,且TLR4?/?小鼠的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的临床症状较野生小鼠轻[2]。在髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白35-55免疫后,TLR4?/?小鼠较野生组体质量减轻变少,发病时间延长,神经功能改善,炎症细胞浸润减少,髓鞘脱落减少,髓鞘碱性蛋白表达升高,提示TLR4基因敲除可显著缓解实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎带来的影响[30]。 然而,其他研究显示了不同的结果,如在髓磷脂少突胶质细胞糖蛋白35-55诱导的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型中,TLR4?/?小鼠的症状较野生型小鼠更加严重,而且树突状细胞和辅助性T细胞高表达白细胞介素6和白细胞介素23[31],TLR4?/?小鼠的Th17细胞数量增加、血清白细胞介素17水平升高,且脾脏单个核细胞中白细胞介素6和白细胞介素23的表达也增加[32]。因此,大多数的研究结果均表明TLR4基因在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎动物模型发病中至关重要,TLR4基因敲除后可显著缓解实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎带来的各种影响,TLR4基因敲除后在多发性硬化和实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎是否具有有害作用,还需在未来的研究中进行进一步验证。 2.2.2 MyD88的作用 MyD88是TLRs和白细胞介素1受体家族的下游衔接子。MyD88将TLRs家族成员与白细胞介素1R相关激酶家族联系起来。MyD88的激活导致NF-κB、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和激活蛋白1(activator protein-1,AP-1)的激活,这些信号分子的激活促进促炎细胞因子如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和干扰素α的产生[2]。在神经元中,白细胞介素1β的激活依赖于两条信号通路,一条是MyD88依赖性,可导致炎症;另一条是MyD88非依赖性,具有神经保护作用。当TLRs识别病原体相关分子模式或危险相关分子模式时,MyD88的死亡结构域与白细胞介素1受体相关激酶4(Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 4,IRAK-4)的死亡结构域相互作用,形成 MyD88-IRAK-4复合物,募集白细胞介素1受体相关激酶1(interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1,IRAK-1)和白细胞介素1受体相关激酶2(interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 2,IRAK-2),导致白细胞介素1受体相关激酶的磷酸化。白细胞介素1受体相关激酶在磷酸化后离开MyD88并与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(tumor necrosis factor receptor correlated-factor 6,TRAF6)相互作用。然后,肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6可诱导人转化生长因子激酶1和转化生长因子激酶1结合蛋白(TAB)2和3的激活,因此通过磷酸化I-κB(IκB)激活了NF-κB 信号传导途径。Iκ-B的磷酸化导致其本身的泛素化和降解,以及随后的NF-κB向细胞核的释放和易位[33-34]。此外,转化生长因子激酶1还可以激活c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun N-terminal protein kainse,JNK)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)和磷脂酰肌醇3激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase,PI3K),这些下游激酶和通路的激活导致一连串的炎症反应[2]。 MyD88非依赖信号通路则是通过调节蛋白Toll受体相关的干扰素激活蛋白直接与TLR3结合,激活NF-κB和干扰素调节因子3(interferon regulatory factor-3,IRF-3),诱导干扰素β(interferon β,IFN-β)产生[15],TLR4依赖于Toll受体相关的分子活化的Toll受体相关的干扰素激活蛋白,Toll受体相关的干扰素激活蛋白可与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3和肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6相互作用。肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6与受体互作蛋白激酶1(receptor-interacting protein kinase 1,RIPI)的活化可诱导NF-κB的核易位,肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子3与TBK1/IKKi的相互作用使干扰素调节因子3磷酸化,导致其转位到细胞核并启动干扰素γ的产生,具体的信号通路见图3 [35]。"

由于MyD88?/?小鼠的先天免疫系统严重不足,对TLRs的特异性配体如脂多糖、肽多聚糖、脂蛋白、抗病毒化合物、CpGDNA和鞭毛蛋白等无反应[36]。MyD88?/?小鼠的巨噬细胞也不能响应脂多糖产生炎性细胞因子,因此,MyD88?/?小鼠已被广泛用作细菌病原体易感模型[37]。至于实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型,研究发现MyD88?/?小鼠完全抗实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎[36],说明MyD88在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发病机制中是必不可少的。在MyD88缺失的PLP TCR转基因小鼠中,MyD88非依赖的先天性免疫信号对髓鞘反应性T细胞的启动和自发产生实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎至关重要[38]。MyD88?/?小鼠无法识别TLRs的特异性配体产生先天免疫反应,也无法产生炎性细胞因子,因此MyD88的免疫信号在实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎发病中是至关重要的。 2.2.3 NF-κB的作用 NF-κB是一种多向调控的核转录因子,在TLR4介导炎症反应中发挥着非常重要的作用。TLR4可通过MyD88依赖和MyD88非依赖途径活化NF-κB,调节白细胞介素2、白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α等一系列炎症因子的表达,使小胶质细胞向促炎表型极化,产生大量炎症因子,包括促炎细胞因子、趋化因子、活性氧和活性氮[11],它们会加剧炎症并导致中枢神经系统脱髓鞘和神经变性。在多发性硬化患者中,TLR4主要表达在小胶质细胞上,在损伤后明显上调,上调的TLR4与配体结合后形成二聚体发生活化,并通过MyD88依赖性和非依赖性的途径活化NF-κB。由TLR4与NF-κB组成的TLR4/NF-κB信号轴可以激活肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6、Cox2的转录,从而促进炎性因子分泌及诱导Th17极化,被活化的Th17细胞会分泌大量炎症因子如白细胞介素17。而白细胞介素17可以招募单核细胞和中性粒细胞,抵达炎症部位,使白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌增加,协同白细胞介素17进一步加剧神经炎性反应[39]。NF-κB使促炎型小胶质细胞进一步介导细胞因子风暴和氧化应激,也可以形成TLR4/NF-κB信号轴激活炎性分子的转录,分泌大量炎症因子,神经炎症恶化,促进了疾病的进程。 2.3 靶向TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB治疗多发性硬化 由于大量的研究已经证实了TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路在多发性硬化发病机制中的重要作用,因而特异性地靶向TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB进行免疫干预可能在未来成为多发性硬化治疗的靶点。通过阅读文献发现了TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB的拮抗剂或抑制剂,可以通过不同的信号通路和途径,来缓解动物模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状,文章总结了TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB的拮抗剂和抑制剂药物名称及其作用机制[40-49],具体内容汇总见表1。"


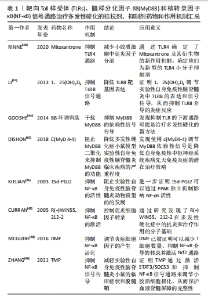
TLR4拮抗剂Mitoxantrone及其衍生物pixantrone和mitoxantrone (2-hydroxyethyl) piperazine可抑制 NF-κB 活化,并减少原代小胶质细胞中的促炎因子如肿瘤坏死因子α的产生[40]。LI等[41]发现在小鼠模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎诱导前后应用1,25(OH)2D3可有效减少脊髓炎症细胞因子表达,TLR8的抑制剂1,25(OH)2D3不仅通过抑制TLR8基因转录活性降低了TLR8基因的转录水平,而且通过抑制TLR8信号通路的不同阶段,显著降低TLR8靶基因肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的表达。TLRs拮抗剂与TLRs激动剂具有相似的结构,其中一些是从化合物文库中挑选出来的抗TLRs的单抗或小分子拮抗剂,它们结合特定的TLRs结构域,与TLRs激动剂竞争,抑制TLRs激动剂与其受体的结合,并阻断信号转导[42]。此外,它们还促进轴突的保护和少突胶质前体细胞的渗透,以修复受损的髓鞘[43]。由于MyD88对大多数TLRs(除了TLR3和部分TLR4)是必需的,因此抑制MyD88对多发性硬化有治疗效果。例如,MyD88的短形式(sMyD88)可以通过阻止白细胞介素受体相关激酶 1磷酸化来抑制TLR/MyD88信号传导。BB环诱饵肽通过干扰MyD88 TIR结构域或全长MyD88抑制TLR/MyD88信号通路[44]。DISHON等[45]研究发现MyD88的抑制剂c(MyD 4-4)以特定的方式阻断MyD88,并通过阻止MyD88二聚化来抑制MyD88功能,用c(MyD 4-4)治疗小鼠可降低小鼠实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型临床疾病的严重程度,研究也发现c(MyD4-4)抑制自身免疫性Th1/Th17细胞的分化并改善实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状,为 MyD88的抑制作用在该疾病中的治疗潜力建立了证据。 已经有研究证明PPAR激动剂(包括15d-PGJ2)抑制了NF-κB 的活性,15d-PGJ2通过抑制响应炎症刺激的IKK激活,阻止I-κB 降解,从而防止NF-κB的核转位和15d-PGJ2以PPAR-γ非依赖性方式直接抑制NF-κB与NF-κB DNA反应元件的结合两种途径抑制了NF-κB的活性[46]。抑制剂R(+)WIN 55,212-2通过抑制NF-κB的激活阻断白细胞介素1的信号通路[47]。DMF(Dimethyl fumarate)抑制NF-κB和ERK1/2活化,导致促炎细胞因子的减少[48]。TMP(tetramethylpyrazine)通过抑制NF-κB 信号传导途径来调节小胶质细胞从M1表型到 M2表型的极化,减少促炎细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β)的分泌并增加来自干扰素γ刺激的BV-2小胶质细胞的抗炎细胞因子(白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10)的分泌,来减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床症状和脱髓鞘[49]。文章发现TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB的拮抗剂或抑制剂都可以通过抑制相应信号通路的传导,减少促炎细胞因子的表达,减轻神经炎症反应,延缓疾病的进程,在今后可以通过特异性靶向TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB来缓解多发性硬化的临床症状,见表1。 此外,几种针对TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的拮抗剂已被证明对系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿性关节炎、牛皮癣和结肠炎的临床前模型有治疗作用[2]。如T2.5是一种针对TLR2的中和抗体,已被证明可以预防TLR2配体引起的败血症[50]。TLR7和TLR9的抑制剂IMO-3100可以减少系统性红斑狼疮、类风湿性关节炎、牛皮癣和高脂血症等小鼠模型中疾病的表现[42,51]。综上所述,尽管大多数抑制剂、拮抗剂仍处于临床前研究阶段,但它们在自身免疫性和炎性疾病中的应用前景非常广泛,成为临床治疗的候选药物。 2.4 影响TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路治疗多发性硬化的药物 除上述TLRs、MyD88、NF-κB的拮抗剂或抑制剂可以缓解实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的髓鞘脱失外,许多实验也表明影响TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的药物也可以治疗实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎,研究类型主要包括细胞实验和动物实验,细胞实验以星形胶质细胞、小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞作为实验模型,动物实验主要以髓鞘少突胶质细胞糖蛋白35-55多肽和双环己酮草酰二腙诱导的实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型为实验模型[52-61],具体的药物实验模型相关研究进展见表2。"

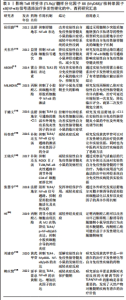
2.4.1 Rho激酶抑制剂 目前,临床使用的大多数药物只能缓解多发性硬化的症状,不能阻止疾病进程。因此,了解多发性硬化的炎症反应的细胞和分子机制,从而寻找真实有效的干预靶点,提高疾病的预防和治疗效果是迫切需要解决的现实问题。张慧宇等[52]发现Rho激酶(Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases,ROCK)抑制剂法舒地尔(Fasudil)能通过阻断TLR4/NF-κB信号通路,抑制脂多糖诱导的星形胶质细胞活化和炎性反应,抑制促炎因子一氧化氮、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6的分泌,增加抑炎因子白细胞介素10和 白细胞介素4的分泌,发挥神经保护作用。侯绍蔚等[53]发现法舒地尔腹腔内给药能使实验性自身反应性脑脊髓炎模型小鼠的临床症状得到显著改善,NF-κB表达水平降低,炎症浸润及髓鞘脱落减少。FSD-C11是法舒地尔的衍生物,作为一种新型的Rho激酶抑制剂药物,可通过抑制Toll样受体的表达干预治疗实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎,抑制外周免疫系统产生炎症因子,提高保护性细胞因子,降低中枢神经系统中M1型巨噬细胞的诱导型一氧化氮合酶水平,提高M2型巨噬细胞精氨酸酶1(Arginase 1,Arg-1)的表达水平,促使M1型巨噬细胞向M2型转变,控制中枢神经系统中炎症细胞的侵润,进而缓解实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的临床症状[54]。这些研究表明,Rho激酶抑制剂法舒地尔及其衍生物也可以通过影响TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路发挥作用,两个信号通路之间可能通过交互作用共同参与疾病的进程,为今后的研究提供了新思路。 2.4.2 丙酮酸乙酯 HE等[55]发现丙酮酸乙酯(Ethyl pyruvate,EP)诱导小胶质细胞出现M2表型,表现为诱导型一氧化氮合酶/肿瘤坏死因子α降低,精氨酸酶1/白细胞介素10升高,同时可以显著地抑制小胶质细胞在髓鞘中聚集,降低TLR4/p-NF-κB/P65和白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达,从而抑制小胶质细胞介导的神经炎症。MILJKOVIC等[56]发现丙酮酸乙酯抑制了小胶质细胞和星形胶质细胞中转录因子NF-κB的激活。这些研究表明丙酮酸乙酯可能通过影响TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路抑制神经胶质细胞的功能改善炎症微环境,并以此缓解髓鞘脱失,但是缺少直接的证据,还需要通过实验进行验证。 2.4.3 中药的活性成分 韩庆贤等[57]发现淫羊藿总黄酮可以抑制机体和体外的炎症反应,并可以显著降低TLR4、NF-κB的表达,同时还可以增加抗炎因子白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β的表达,从而减轻炎症反应,起到保护髓鞘的作用。刘建春等[58]发现黄芪甲苷通过抑制TLR4、MyD88、NF-κB/p65的表达,通过调控Th17和调节性细胞的平衡,减轻发病程度,可以有效缓解动物模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的病情,并对炎性细胞进行抑制,有望作为多发性硬化等自身免疫疾病的治疗药物。ABDIN等[22]发现雷公藤红素能降低实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的临床评分和大脑中蛋白TLR2的表达。由此可见多种中药活性成分减轻炎症反应的机制都与TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路相关,可以为中药药效物质的研究提供思路。 2.4.4 中药方剂 杨春彦[59]发现补阳还五汤能抑制TLR4/NF-κB炎性信号通路的激活及炎性因子的分泌。王晓庆等[60]研究发现补阳还五汤能通过抑制ROCKⅡ/TLR4/NF-κB炎性通路和调节外周CD4+T细胞亚群比例,从而发挥其抗炎和调节免疫作用,减轻动物模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的发病程度。中药复方益肾达络饮通过抑制NF-κB细胞信号通路的传导,改善实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型小鼠神经功能损伤,有效降低实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎模型小鼠的复发率[61]。因此,中药方剂补阳还五汤和益肾达络饮均可以通过影响TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路的传导,减少炎性因子分泌,发挥抗炎作用,减轻临床症状,为中医验方名方临床治疗多发性硬化提供了理论依据。 在多发性硬化的发生发展过程中,许多中药及西药对TLRs/MyD88/NF-κB通路都有一定的影响,他们通过抑制信号通路的传导或降低TLR4、MyD88及NF-κB的表达,抑制炎症反应,发挥神经保护作用,减轻实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的发病程度,具体的药物作用机制见表3,为今后多发性硬化的临床治疗提供理论基础和实验依据,通过综述关于中药的活性成分和中药复方影响信号通路的药物,为今后的研究提供了方向,同时也为中医药开发治疗疾病提供了新的思路方法。"

| [1] KUMAR V. Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of neuroinflammation. J Neuroimmunol. 2019;332:16-30. [2] ZHENG C, CHEN J, CHU F, et al. Inflammatory role of TLR-MyD88 signaling in multiple sclerosis. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020;12:314. [3] 赵佳莹,申艳佳,杨冉,等.多发性硬化药物研发中动物模型研究进展及应用[J].中国药理学通报,2022,38(6):801-806. [4] 邹永杰,董哲. Toll样受体4在神经系统疾病中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2016,22(13):2516-2519. [5] FERNANDEZ-PAREDES L, DE DIEGO RP, DE ANDRES C, et al. Close encounters of the first kind: innate sensors and multiple sclerosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2017; 54(1):101-114. [6] 姜炅,董蕾,秦斌,等.Toll样受体7在人胃癌细胞株中的表达及其激动剂诱导SGC-7901细胞发生凋亡的实验研究[J].南方医科大学学报, 2014,34(11):1606-1610. [7] 白自然,林倩,余雨迪,等.Toll样受体对T细胞功能及代谢的影响[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2022,49(7):1218-1225. [8] 郭鹏,张含,李长菲,等. Toll样受体通路调节Tregs功能的研究进展[J].生物工程学报,2020,36(9):1701-1712. [9] 李依峣,鲁元,王旭,等. Toll样受体家族在神经炎症性疾病中的作用机制研究进展[J].中国新药杂志,2022,31(16):1602-1607. [10] 李红梅,王显.TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路与动脉粥样硬化性心血管疾病的相关性研究进展[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2017,9(9):1132-1134. [11] YUE Y, STONE S, LIN W. Role of nuclear factor κB in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(9):1507-1515. [12] DING ZB, SONG LJ, WANG Q, et al. Astrocytes: a double-edged sword in neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1702-1710. [13] 张振武,黄绍农,凌地洋,等.延胡索甲素调节NMDAR/NF-κB介导的信号通路对利血平诱导纤维肌痛大鼠的作用及机制研究[J].解放军医药杂志,2020,32(6):14-18. [14] 杨宏鹏,张首国,曹莹,等.Toll样受体相关疾病研究进展[J].科学技术与工程,2022,22(35):15427-15435. [15] 贾国泉,沈桂权,张权,等.Toll受体介导的MyD88/TRAF6/NF-κB研究[J].新发传染病电子杂志,2017,2(2):104-107, 111. [16] LAWRENCE T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1(6):a001651. [17] WASKO NJ, NICHOLS F, CLARK RB. Multiple sclerosis, the microbiome, TLR2, and the hygiene hypothesis. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(1):102430. [18] ZEKKI H, FEINSTEIN DL, RIVEST S. The clinical course of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is associated with a profound and sustained transcriptional activation of the genes encoding toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 in the mouse CNS. Brain Pathol. 2002;12(3):308-319. [19] REYNOLDS JM, PAPPU BP, PENG J, et al. Toll-like receptor 2 signaling in CD4(+) T lymphocytes promotes T helper 17 responses and regulates the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease. Immunity. 2010;32(5):692-702. [20] UMMENTHUN K, PEFEROEN LA, FINARDI A, et al. Pentraxin-3 is upregulated in the central nervous system during MS and EAE, but does not modulate experimental neurological disease. Eur J Immunol. 2016;46(3):701-711. [21] HERRMANN I, KELLERT M, SCHMIDTH, et al. Streptococcus pneumoniae infection aggravates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via toll-like receptor 2. Infect Immun. 2006;74(8):4841-4848. [22] ABDIN AA, HASBY EA. Modulatory effect of celastrol on Th1/Th2 cytokines profile, TLR2 and CD3+ T-lymphocyte expression in a relapsing-remitting model of multiple sclerosis in rats . Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;742:102-112. [23] 丁智斌,宋丽娟,王青,等.从动物模型的视角研究多发性硬化髓鞘保护和再生的小胶质细胞靶点[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(6):753-757. [25] DUPERRAY A, BARBE D, RAGUENEZ G, et al. Inflammatory response of endothelial cells to a human endogenous retrovirus associated with multiple sclerosis is mediated by TLR4. Int Immunol. 2015, 27(11):545-553. [26] 马成东,胡全忠. Toll样受体4与神经系统疾病[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2016,16(57):59-60,63. [27] LEITNER GR, WENZEL TJ, MARSHALL N, et al. Targeting toll-like receptor 4 to modulate neuroinflammation in central nervous system disorders. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2019;23(10):865-882. [28] MCCARTHY GM, BRIDGES CR, BLEDNOW YA, et al. CNS cell-type localization and LPS response of TLR signaling pathways. F1000Res. 2017;6:1144. [29] 刘欣,邵卫,陈国华.中医药靶向TLRs治疗中枢神经系统疾病研究进展[J].中医药学报,2022,50(3):108-113. [30] 韩晶晶,张英,姚瑞芹,等.敲除toll样受体4基因对小鼠实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2022,38(3):287-292. [31] MARTA M, ANDERSSON A, ISAKSSON M, et al. Unexpected regulatory roles of TLR4 and TLR9 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 2008;38(2):565-575. [32] MARTA M, MEIER UC, LOBELL A. Regulation of autoimmune encephalomyelitis by toll-like receptors. Autoimmun Rev. 2009;8(6):506-509. [33] 张娟,尚德静.Toll 样受体 4(TLR4)信号通路及其靶向药物的研究进展[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2021,37(7):657-662. [34] 李易水,储心乔,彪雅宁,等.当归芍药散对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠TLR4/MyD88/JNK信号通路的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(17):24-31. [35] LIU Y, YIN H, ZHAO M, et al. TLR2 and TLR4 in autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2014;47(2):136-147. [36] PEINZ M, GARBE F, SCHMIDT H, et al. Innate immunity mediated by TLR9 modulates pathogenicity in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(2):456-464. [37] KAWAI T, AKIRA S. TLR signaling. semin immunol. 2007;19(1):24-32. [38] WEXLER AG, FRIELLE C, BERRY G, et al. The innate immune adaptor MyD88 is dispensable for spontaneous autoimmune demyelination in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2013;255(1-2):60-69. [39] ZHOU Y, CUI C, MA X, et al. Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB)-mediated inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:391. [40] RINNE M, MATLIK K, AHONEN T, et al. Mitoxantrone, pixantrone and mitoxantrone (2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine are toll-like receptor 4 antagonists, inhibit NF-κB activation, and decrease TNF-alpha secretion in primary microglia. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020;154:105493. [41] LI B, BAYLINK DJ, DEB C, et al. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses TLR8 expression and TLR8-mediated inflammatory responses in monocytes in vitro and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58808. [42] GAMBUZZA M, LICATA N, PALELLA E, et al. Targeting toll-like receptors: emerging therapeutics for multiple sclerosis management. J Neuroimmunol. 2011;239(1-2):1-12. [43] CHURCH JS, MILICH LM, LERCH JK, et al. E6020, a synthetic TLR4 agonist, accelerates myelin debris clearance, schwann cell infiltration, and remyelination in the rat spinal cord. Glia. 2017;65(6):883-899. [44] GOOSHE M, ALEYASIN AR, ABDOLGHAFFARI AH, et al. Toll like receptors: a new hope on the horizon to treat multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2014;10(10):1277-1279. [45] DISHON S, SCHUMACHER A, FANOUS J, et al. Development of a novel backbone cyclic peptide inhibitor of the innate immune TLR/IL1R signaling protein MyD88. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):9476. [46] KIELIAN T, Dew PD. Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonists on central nervous system inflammation. J Neurosci Res. 2003;71(3):315-325. [47] CURRAN NM, GRIFFIN BD, O’TOOLE D, et al. The synthetic cannabinoid R(+)WIN 55, 212-2 inhibits the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in human astrocytes in a cannabinoid receptor-independent manner. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(43):35797-35806. [48] MCGUIRE VA, RUIZ-ZORRILLA DIEZ T, EMMERICH CH, et al. Dimethyl fumarate blocks pro-inflammatory cytokine production via inhibition of TLR induced M1 and K63 ubiquitin chain formation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:31159. [49] ZHANG L, LU X, GONG L, et al. Tetramethylpyrazine protects blood-spinal cord barrier integrity by modulating microglia polarization through activation of STAT3/SOCS3 and inhibition of NF-кB signaling pathways in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2021;41(4):717-731. [50] MENG G, RUTZ M, SCHIEMANN M, et al. Antagonistic antibody prevents toll-like receptor 2-driven lethal shock-like syndromes. J Clin Invest. 2004; 113(10):1473-1481. [51] SUAREZ-FARINAS M, ARBIET R, JIANG W, et al. Suppression of molecular inflammatory pathways by Toll-like receptor 7, 8, and 9 antagonists in a model of IL-23-induced skin inflammation. PLoS One. 2013;8(12):e84634. [52] 张慧宇,郭敏芳,于婧文,等.法舒地尔(Fasudil)抑制脂多糖诱导的小鼠星形胶质细胞活化和炎性反应及其机制[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2018,34(6):505-510. [53] 侯绍蔚,刘岳婷,郭敏芳,等.盐酸法舒地尔治疗实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的潜能与抗炎作用[J].中国临床神经科学,2012,20(2):126-134. [54] 于婧文,李艳花,张海飞,等.新型Rho激酶抑制剂FSD-C11对EAE的免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志,2016,32(8):651-655. [55] HE Y, AN J, YIN JJ, et al. Ethyl pyruvate enhances spontaneous remyelination by targeting microglia phagocytosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;77: 105929. [56] MILJKOVIC D, BLAZEVSKI J, PETKOVIC F, et al. A comparative analysis of multiple sclerosis-relevant anti-inflammatory properties of ethyl pyruvate and dimethyl fumarate. J Immunol. 2015;194(6):2493-2503. [57] 韩庆贤,丁智斌,李晓慧,等.基于抑制小胶质细胞介导的炎症反应探讨淫羊藿总黄酮保护髓鞘的机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(3):1357-1361. [58] 刘建春,张红珍,郭文娟,等.黄芪甲苷对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎小鼠的防治作用[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(6):3119-3122. [59] 杨春彦.补阳还五汤对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的神经保护和免疫调节作用研究[D].太原:山西中医学院,2016. [60] 王晓庆,田倩倩,李艳花,等.补阳还五汤对EAE小鼠免疫调节的作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2017,33(1):52-57. [61] 关东升,高颖,娄丽霞,等. 益肾达络饮对实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎NF-κB信号传导通路的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2012,18(7):732-735. |
| [1] | Weng Rui, Lin Dongxin, Guo Haiwei, Zhang Wensheng, Song Yuke, Lin Hongheng, Li Wenchao, Ye Linqiang. Abnormal types of intervertebral disc structure and related mechanical loading with biomechanical factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1436-1442. |
| [2] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [3] | Chen Zhiling, Huang Xuecheng, Pan Min, Huang Ying, Wu Yuntian. Evaluation of the relationship between neck and shoulder pain and scalene muscles based on shear wave elastography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1265-1270. |
| [4] | Zeng Fanzhuo, Li Yuxin, Sun Jiachen, Gu Xinyang, Wen Shan, Tian He, Mei Xifan. Efficient strategies for microglia replacement in spinal cord injury models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [5] | Liu Tao, Zhang Wenkai, Ma Ziqian, Zhang Yan, Chen Xueming. Riluzole interferes with the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia of rats with spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [6] | Mu Bingtao, Yu Jingwen, Liu Chunyun, Guo Minfang, Meng Tao, Yang Pengwei, Wei Wenyue, Song Lijuan, Yu Jiezhong, Ma Cungen. Immunomodulatory effect of astragaloside IV on T cells of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1057-1062. |
| [7] | Yang Yifeng, Huang Jian, Ye Nan, Wang Lin. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 955-960. |
| [8] | Liu Anhong, Cai Mengmeng, Han Xiao, Wang Zhanhui. Research status on element selection of medical magnesium alloy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 777-782. |
| [9] | Yang Yuqing, Chen Zhiyu. Role and application of early transient presence of M1 macrophages in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [10] | Liu Luxing, Di Mingyuan, Yang Qiang. Signaling pathways in the mechanism underlying active ingredients of Chinese medicine in the treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 609-614. |
| [11] | Yan Binghan, Li Zhichao, Su Hui, Xue Haipeng, Xu Zhanwang, Tan Guoqing. Mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine monomers in the treatment of osteoarthritis by targeting autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [12] | Tian Yong, Zhou Ying, Gu Yongxiang, Yang Guohui. Metformin pretreatment induces cardiac autophagy to reduce myocardial injury in septic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4469-4476. |
| [13] | Peng Yi, Li Xiaolong. Effect of molar distalization with clear aligners on occlusal vertical dimension in different vertical craniofacial patterns [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(28): 4559-4564. |
| [14] | Zhao Guangjian, Liu Danan, Zhou Bo, Wang Yao. Action mechanism by which fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 inhibits macrophage pyroptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4005-4012. |
| [15] | Wang Shaona, Gao Chen, Fan Feiyan, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Action mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine and mesenchymal stem cells regulating immune response in treatment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(25): 4087-4093. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||