Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (7): 1124-1129.doi: 10.12307/2023.780
Previous Articles Next Articles
Role and mechanism of noncoding RNA in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Liu Tao, He Zhijun, Li Jinpeng, Song Yuan, Yao Xingzhang, Chen Wen, Li Yan, Bai Bihui
- Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-08Accepted:2023-01-04Online:2024-03-08Published:2023-07-17 -
Contact:Li Jinpeng, Master, Associate chief physician, Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Liu Tao, Attending physician, Gansu Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730050, Gansu Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 81660802 (to HZJ) and 81860863 (to SY); Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Program (Key Research and Development Program), No. 21YF5FA (to HZJ); Gansu Provincial Science and Technology Program (Youth Science and Technology Program), No. 21JR11RA211 (to LT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Tao, He Zhijun, Li Jinpeng, Song Yuan, Yao Xingzhang, Chen Wen, Li Yan, Bai Bihui. Role and mechanism of noncoding RNA in diabetic peripheral neuropathy[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1124-1129.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

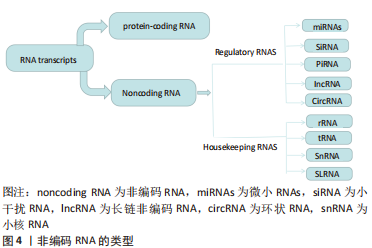
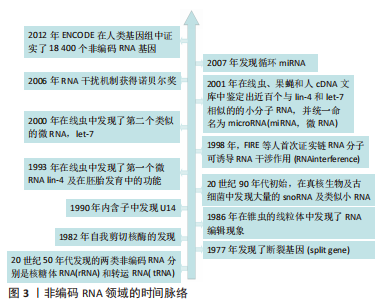
2.1 ncRNA概述 ncRNAs是不编码蛋白质的RNA分子,通过各种调节过程有助于维持细胞和组织的稳态。在过去的几十年里,ncRNA在哺乳动物细胞中的作用和调控受到了广泛关注[7-9]。ncRNA分子可以直接或间接调节基因表达,处理其他RNA分子,或充当其他RNA物种的调节器。通过其各种功能,ncRNA分子在身体几乎每个组织的发育和内环境稳定中发挥着重要作用[10-12]。 ncRNA的类别:ncRNAs在调节糖尿病神经病变的病理生理过程中起着核心作用。在研究最广泛的调节性ncRNA物种中,有lncRNAs、环状RNAs(circular RNAs,circRNAs)和miRNAs。在20世纪70年代首次在病毒中观察到CircRNA,而在20世纪90年代初,非哺乳动物和哺乳动物细胞中发现了miRNAs和lncRNAs[13-15]。从那时起,这个领域一直在扩大。ncRNA领域的时间脉络见图3,ncRNA 的类型见图4。"

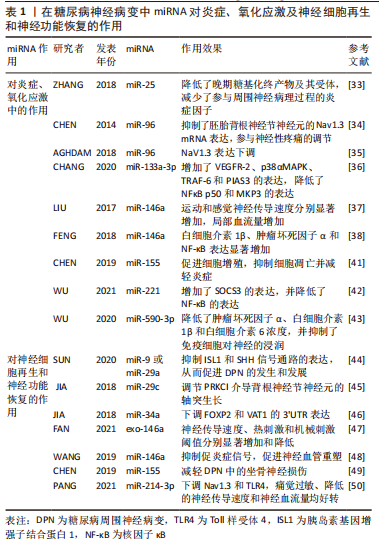
2.1.1 miRNA miRNA是来自核基因组编码和非编码部分的20-22个核苷酸(nt)单链RNA分子,它们直接或间接调节细胞质中的基因表达,在某些情况下还调节线粒体中的基因表达。miRNA通过降解特定靶mRNA分子或直接抑制蛋白质翻译来沉默蛋白质表达[16-17]。在某些情况下,它们也可能稳定mRNA分子。每个miRNA都有可能通过相互作用靶向多个mRNA转录本,基于Watson-Crick对位于其5′端的6-8 nt序列的识别,即“种子”序列[18]。 2.1.2 lncRNAs lncRNAs是一类异质性更强的单链或双链RNA分子,可任意定义为长度大于200 nt,长度小于10 000 nt,聚-a尾的存在与否决定lncRNA的稳定性。超过17 000个lncRNA分子可能由人类基因组(134)编码,包括线粒体基因组(43103)。lncRNAs具有多种功能,可以作为信号、传感器、稳定和诱饵分子,供其他ncRNAs调节细胞中的基因表达[19-20]。这类ncRNAs还通过为调节蛋白提供支架、驱动变构修饰和促进组蛋白甲基化来直接调节蛋白表达和活性[21-22]。 2.2 糖尿病神经病变中ncRNA的表达谱 目前,基因测序有两种类型,包括微阵列测序和高通量测序[23]。与微阵列测序相比,高通量测序具有灵敏度高、特异性强、能够发现重要的新lncRNA的优势。随着高通量测序技术的发展,已发现多种ncRNA在糖尿病及其并发症中发挥重要作用[24]。GONG等[25]研究了链脲佐菌素诱导的DPN小鼠和对照组的腰脊髓背角中差异表达的miRNA,miRNA微阵列的结果显示,有42个miRNA发生显著改变;定量实时聚合酶链反应(qRT-PCR)验证表明,DPN组织中两个显著差异表达的候选miRNA(miR-184-5p和miR-190a-5p)显示出与微阵列分析相同的变化。DU等[26]通过微阵列分析在DPN小鼠中鉴定出1 481个差异表达的lncRNAs和1 096个差异表达的mRNA;功能分析表明,转化生长因子β受体结合是最重要的分子功能,内源性大麻素逆行信号是最重要的mRNA途径;钙离子转运是lncRNAs第二重要的生物学过程,发现了289个相邻和57个重叠的lncRNA-mRNA对,包括ENSMUST0000150952 Mbp和AK081017-Usp15,它们可能参与了DPN的发病机制。GUO等[27]进行了一项微阵列研究,有983个lncRNAs和1 357个mRNA异常表达;利用生物信息学分析,发现了558个GO和94个KEGG;此外,信号网络分析表明,整合素受体,包括Itgb3、Itgb1、Itgb8和Itga6,可能是网络调节的重要参与者。ZHANG等[28]对大鼠坐骨神经损伤后进行功能富集分析,结果表明776个表达差异的lncRNA是第4天特有的,其功能主要集中在创伤愈合、磷酸酶结合和MAPK信号通路;317个表达差异lncRNA是第7天特有的,它们的功能主要集中在离子跨膜转运通道活性上;这两天共有579个表达差异lncRNA,它们的功能主要集中在轴突、PI3K-Akt信号通路和细胞周期。FENG等[29]在DPN和2型糖尿病大鼠的坐骨神经中进行LncRNA微阵列分析,确定了与miR-146a-5p结合的差异表达lncRNAs;此外,通过qRT-PCR验证了与miR-146a-5p潜在结合的lncRNA,通过生物信息学预测和实验技术鉴定miR-146a-5p靶向的基因,TRAF6、IRAK1和SMAD4被鉴定为miR-146a-5p靶向基因,主要在炎症信号通路中富集;LncRNAs可能通过作为miR-146a-5p的ceRNAs来调节炎症,从而参与DPN的发病机制。ASHJARI等[30]发现糖尿病患者的lncRNA NEAT-1表达水平显著升高,而miR-183-5p表达水平显著降低;此外,糖尿病患者中miR-433-3p的表达水平显著降低,ITGA4、SESN1和SESN3的mRNA表达显著升高。NEAT-1可能靶向miR-183-5p和miR-433-3p,因此ITGA4、SESN1和SESN3的表达受到影响。NEAT-1及相关miRNA和基因的表达失调可能参与了糖尿病的发病机制。上述结果表明,lncRNA和miRNA表达谱集中在炎性相关信号通路、氧化应激、自噬和促炎细胞因子,由此达到调控炎症损伤的作用,保护神经元细胞,从而有效控制DPN的进展和恶化。 2.3 miRNA及其与糖尿病神经病变的联系 糖尿病引起的持续高血糖状态被认为是多种病理途径的主要原因,包括氧化应激、细胞凋亡、炎症和神经退行性变。由于活性氧的形成和浓度增加,氧化应激与炎症和神经退行性变有关。此外,氧化应激增强内源性活性氧和抗氧化防御系统之间的不平衡,引发慢性炎症和组织损伤[31]。miRNA调节许多生物过程,并与复杂疾病的不同方面相关。在神经退行性疾病患者和糖尿病患者中观察到miRNA的差异表达,因为它们在调节糖尿病诱导的炎症和神经退行性反应中起着重要作用[32]。 2.3.1 在糖尿病神经病变中miRNA对炎症、氧化应激的作用 ZHANG等[33]观察到db/db小鼠的活性氧和Nox4表达增加,同时miR-25减少;MiR-25抑制剂治疗增加了施万细胞中烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸的活性,而MiR-25前体的过度表达导致了相反的结果;MiR-25前体在mRNA和蛋白质水平上降低了蛋白激酶C的激活,降低了Nox4的表达。晚期糖基化终产物(AGEs)和晚期糖基化终产物受体(RAGE)在从糖尿病小鼠获得的血清和周围神经中增加,并且在从wt小鼠获得的施万细胞中进行miR-25抑制剂治疗导致了相同的效果;然而,miR-25前体转染降低了晚期糖基化终产物及其受体,并进一步减少了参与周围神经病理过程的炎症因子。miR-25降低蛋白激酶C-α的磷酸化,在糖尿病周围神经中产生较少的活性氧,因此它在氧化/硝化应激的调节以及随后的神经功能障碍中发挥重要作用。 CHEN等[34]采用慢性收缩性坐骨神经损伤(CCI)大鼠模型发现同侧背根神经节内miR-96水平降低,但Nav1.3水平升高;鞘内注射miR-96 抑制CCI诱导的Nav1.3表达;miR-96在体外抑制了胚胎背根神经节神经元的Nav1.3 mRNA表达;miR-96通过抑制CCI大鼠背根神经节中Nav1.3的表达参与神经性疼痛的调节。AGHDAM等[35]也发现糖尿病降低了miR-96的表达水平,但显著上调了坐骨神经中NaV的表达;在运动训练中,miR-96表达被逆转,同时NaV1.3表达下调。 CHANG等[36]通过向正常大鼠坐骨神经内(神经外膜)注射AAV-miR-133a-3p和向糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经内注射miR-133a-3p拮抗剂,分析miR-133a-3p与DPN之间的关联,转染RSC96施万细胞的miR-133a-3p模拟物增加了VEGFR-2、p38αMAPK、TRAF-6和PIAS3的表达,降低了NFκB p50和MKP3的表达;在糖尿病大鼠中,给予miR-133a-3p拮抗剂可减轻DPN并下调p-p38磷酸化,坐骨神经中miR-133a-3p的过度表达导致了这种疼痛。 LIU等[37]发现将miR-146a类似物给药于糖尿病小鼠后,血浆和坐骨神经组织中的miR-146a水平升高,运动和感觉神经传导速度分别显著增加,坐骨神经组织中的局部血流量增加;miR-146a模拟物治疗也显著降低了db/db小鼠对热刺激阈值的反应,增加了异硫氰酸荧光素-葡聚糖灌注血管的密度,增加了表皮内神经纤维的数量、髓鞘厚度和坐骨神经的轴突直径;此外,miR-146a治疗分别减少和增加了经典和交替激活的巨噬细胞表型标记物。对miRNA靶阵列的分析显示,miR-146a模拟物极大地抑制了许多促炎症基因和下游相关细胞因子的表达。FENG等[38]也发现DPN的神经传导速度和miR-146a表达水平显著降低;DPN组中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和活化B细胞的核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa-B,NF-κB)的表达显著增加;miR-146a的表达水平与白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子α和NF-κB的水平呈负相关,miR-146a参与了DPN的发病机制,其表达水平与加重坐骨神经损伤的炎症反应密切相关。Nano-miR-146a-5p改善了DPN大鼠的神经传导速度,减轻了坐骨神经的形态学损伤和脱髓鞘;Nano-miR-146a-5p可抑制坐骨神经中炎性细胞因子、半胱天冬酶3和裂解半胱天冬酶3的表达;此外,nano-miR-146a-5p增加了髓鞘碱性蛋白的表达,这些结果都表明,nano-miR-146a-5p对DPN大鼠模型的周围神经具有保护作用,可能通过调节炎症反应和细胞凋亡来实现[39]。糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经中miR-146a和NF-κB的表达增加,TRAF6的表达减少;此外,糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经中的NF-κB活性和肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素1β浓度均高于对照组,结果表明NF-κB-miR-146a负反馈回路的缺陷可能参与了糖尿病神经病变的发病机制[40]。 CHEN等[41]发现miR-155的沉默或Nrf2的恢复促进细胞增殖,抑制细胞凋亡并减轻炎症;miR-155拮抗剂诱导的抑制增加了DPN大鼠的运动神经传导速度和感觉神经传导速度,增强了血管生成,减轻了炎症;此外,当在体外和体内恢复Nrf2时,miR-155产生的效应被逆转,表明miR-155靶向并抑制DPN中的Nrf2。miR-155沉默被发现可以减轻DPN中的坐骨神经损伤,突出了其作为DPN治疗靶点的潜力。 WU等[42]诱导lenti-miR-221抑制剂可显著降低DPN大鼠中miR-221的表达。DPN大鼠的机械缩足阈值和热缩足潜伏期值均显著降低,当miR-221被抑制时,机械缩足阈值和热缩足潜伏期值均显著增加。在链脲佐菌素处理的DPN大鼠和高糖诱导的SH-SY5Y细胞中,miR-221的敲除显著增加了SOCS3的表达,并降低了NF-κB的表达,说明通过靶向DPN中的SOCS3,抑制miR-221可以减轻疼痛,减少炎症因子的表达。 WU等[43]发现miR-590-3p-agomir减轻了db/db小鼠的疼痛相关行为,降低了肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6浓度,并抑制了免疫细胞对神经的浸润;miR-590-3p通过靶向RAP1A和抑制T细胞浸润来改善糖尿病周围神经痛,提示外源性miR-590-3p可能是糖尿病周围神经痛临床治疗的潜在候选者。 2.3.2 在糖尿病神经病变中miRNA对神经细胞再生和神经功能恢复的作用 SUN等[44]发现慢病毒介导的胰岛素基因增强子结合蛋白1(insulin gene enhancer binding protein,1ISL1)的强制表达激活了sonic hedgehog(SHH)信号通路,增加了运动神经传导速度和痛觉阈值,并调节了糖尿病大鼠坐骨神经中神经营养因子的表达,提示ISL1可以延缓糖尿病进展,促进坐骨神经损伤后的神经再生和修复。然而,慢病毒介导的miR-9或miR-29a的强制表达加重了糖尿病,并拮抗了ISL1对DPN的有益作用。miR-9和miR-29a通过与ISL1结合,通过SHH信号通路促进DPN发展的潜在作用。JIA等 [45]发现糖尿病db/db小鼠在背根神经节神经元、坐骨神经和足垫组织中表现出miR-29c的显著上调。糖尿病小鼠坐骨神经组织和背根神经节神经元中的PRKCI蛋白水平显著降低。在PRKCI基因3’UTR处含有miR-29c结合位点的质粒和miR-29c模拟物的共同转染有效地降低了发光活性,当PRKCI基因3’UTR处的miR-29c种子序列发生突变时,发光活性被消除。在体外,高糖显著上调和降低了背根神经节神经元中的miR-29c和PRKCI蛋白水平,这与轴突生长的显著减少有关。在高糖条件下,siRNA击倒背根神经节神经元内源性miR-29c克服了PRKCI蛋白和轴突生长的降低。此外,在正常葡萄糖条件下,siRNA敲除背根神经节神经元中的PRKCI可显著抑制轴突生长。总之,这些发现表明,miR-29c通过在高血糖状态下靶向PRKCI,是背根神经节神经元轴突生长的负调节因子。 JIA等[46]发现在db/db小鼠的背根神经节、坐骨神经和脚垫组织中,miR-34a过度表达;生物信息学分析表明,miR-34a可能以FOXP2和VAT1为靶点。在高糖条件下,在糖尿病组织和培养的背根神经节神经元中,这些靶点降低;双荧光素酶分析显示,miR-34a通过靶向FOXP2和VAT1的3’UTR下调其表达;FOXP2和VAT1的敲除降低了轴突生长,表明miR-34a及其FOXP2和VAT1的靶基因参与了高血糖条件下的背根神经节神经元损伤。 间充质基质细胞衍生的外泌体(exo na?ve)可以缓解神经血管功能障碍,促进功能恢复。FAN等[47]研究了含有miR-146a的工程化间充质基质细胞外显体(exo-146a),并比较了exo-146a和exo-na?ve对糖尿病(db/db)DPN小鼠的治疗效果,Exo-146a具有高负载能力,全身给药后在周围神经组织中积累了强大能力,与Exo-na?ve相比,在神经恢复方面的治疗效果显著增强;用exo-146a治疗糖尿病小鼠2周后,神经传导速度、热刺激和机械刺激阈值分别显著增加和降低,而exo-naive治疗需要4周时间才能实现这些改善;与exo-na?ve相比,exo-146a通过抑制Toll样受体(Toll-like receptors,TLR)-4/NF-κB信号通路,显著抑制外周血炎性单核细胞和内皮细胞的激活。WANG等[48]采用Tβ4治疗显著增加了表皮内神经纤维密度,增加了坐骨神经组织中局部血流量和异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)-右旋糖酐灌注血管的密度;在体外,用Tβ4处理背根神经节神经元和小鼠真皮内皮细胞(mde)可显著增加轴突生长和毛细血管样管形成,而阻断miR-146a则减弱Tβ4诱导的轴突生长和毛细血管形成。 miR-146a可能通过介导Tβ4诱导的糖尿病小鼠抑制促炎症信号,促进神经血管重塑。 CHEN等[49]发现db/db小鼠坐骨神经miR-155表达明显抑制,miR-155类似物升高坐骨神经和血浆中miR-155水平;它还增强了坐骨神经的血流量和感觉神经和运动神经的传导速度,灌流血管密度显著改善,表皮内神经纤维升高,髓鞘厚度和坐骨神经轴突直径增加。 PANG等[50]发现DPN大鼠的运动和感觉神经传导速度以及神经血流量降低,服用miR-214-3p后,链脲佐菌素诱导的痛觉过敏、降低的神经传导速度和神经血流量均显著逆转,可显著改善背根神经节中糖尿病神经病变大鼠的病理改变;此外,Nav1.3和TLR4被确定为miR-214-3p的靶点,MiR-214-3p可能通过下调Nav1.3和TLR4发挥作用。 目前,miRNA在糖尿病及其并发症中的作用不断被深入研究,不仅因为它们参与了发病机制,而且其可作为潜在的疾病生物标志物。选择性miRNA模拟物或抑制剂的使用可能是一种潜在的治疗工具,其目的是恢复或抵消神经系统中miRNA水平的减少或增加。此外,由于其在血清中的稳定性和易于检测,miRNA也可能成为包括DPN在内的多种疾病的新诊断工具。见表1。"

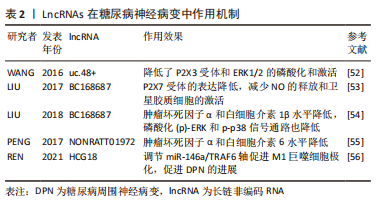
DPN是神经病理性疼痛的主要原因。5’-三磷酸腺苷(ATP)在正常情况下会引发疼痛并增加炎症介导的疼痛。ATP激活P2X阳离子可渗透离子通道受体和P2Y G蛋白偶联受体。P2X3受体在外周感觉神经元的疼痛传递中起着至关重要的作用。P2X3受体介导糖尿病神经病大鼠的机械异常性疼痛。uc.48+是一种lncRNA,WANG等[52]发现,uc.48+ 小干扰RNA(small interfering RNA,siRNA)治疗降低了糖尿病背根神经节中P2X3受体和ERK1/2的磷酸化和激活,随后糖尿病大鼠的热痛觉过敏和机械性痛觉过敏降低。因此,uc.48+ siRNA 治疗可能通过抑制背根神经节初级感觉神经元中P2X3受体介导的兴奋性传递来缓解DPN。 BC168687是另一个最近被证明在糖尿病神经性疼痛中调节P2X嘌呤受体的lncRNA。LIU等[53]通过鞘内注射BC168687 siRNA后,DPN大鼠背根神经节中P2X7受体的表达降低;此外,BC168687 siRNA可能会减少NO的释放和卫星胶质细胞的激活,从而抑制背根神经节神经元的兴奋,缓解DPN大鼠的疼痛行为。这些发现表明,背根神经节中卫星胶质细胞上的P2X7受体在介导DPN中发挥了重要作用,并强调了lncRNA BC168687作为DPN新治疗靶点的潜力。LIU等[54]用lncRNA BC168687 siRNA治疗链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠,发现糖尿病大鼠的机械缩足反射阈值和热缩足反射潜伏期显著增加;背根神经节中TRPV1受体的表达显著降低;lncRNA BC168687 siRNA治疗大鼠血清中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β的相对水平降低;背根神经节中的磷酸化(p)-ERK和p-p38信号通路也降低。因此,lncRNA BC168687 siRNA可能缓解TRPV1介导的糖尿病神经性疼痛。 LncRNA ONRATT021972是一种具有良好临床潜力的生物标志物,血清LncRNA NONRATT01972水平升高与2型糖尿病患者的神经性疼痛分级呈正相关,LncRNA NONR021972通过肿瘤坏死因子α相关途径加剧神经病理性疼痛[57]。抑制LncRNA NON021972可减轻神经性疼痛。NONRATT021972 siRNA治疗可降低2型糖尿病大鼠背根神经节中P2X7 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平,并抑制卫星胶质细胞的激活。此外,NONRATT021972 siRNA治疗减少了炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α)的释放,从而抑制了背根神经节神经元的兴奋性,减少了2型糖尿病大鼠的机械性和热痛觉过敏[58]。PENG等[55]也发现2型糖尿病大鼠中肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6水平升高,并且在lncRNA NONTRATT021972 siRNA的帮助下,糖尿病合并神经炎性疾病减少。 REN等[56]发现LncRNA HCG18在DPN模型和汞诱导的巨噬细胞中高表达。在DPN模型中,炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6)水平升高,M1标记物(CD11c和iNOS)的表达明显上调,并与HCG18的表达呈正相关;LncRNA HCG18促进M1巨噬细胞极化;此外,miR-146a被确定为lncRNA HCG18的靶点,miR-146a的过度表达逆转了HCG18对M1巨噬细胞极化的促进作用。同时,TRAF6是 miR-146a的靶基因,TRAF6的表达受到HCG18的正调控,而受到miR-146a的负调控,TRAF6的下调逆转了HCG18对M1巨噬细胞极化的促进作用。LncRNA HCG18通过调节miR-146a/TRAF6轴促进M1巨噬细胞极化,促进DPN的进展,该研究为DPN提供了一种可能的治疗策略。 以上研究表明lncRNAs是基因表达的重要调节因子。一些研究表明,lncRNA(如KCNA2-as、XIST、CCAT1、MRAK009713或其下游靶点)的特异性调节可能参与了神经性疼痛的发生[59]。因此,推测这些失调的lncRNA参与了DPN的发生、发展过程,继续探索将发现更多的lncRNA参与DPN的发病机制。"

| [1] REFARDT J, WINZELER B, CHRIST-CRAIN M. Diabetes Insipidus: An Update. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2020;49(3):517-531. [2] SELVARAJAH D, KAR D, KHUNTI K, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7(12):938-948. [3] SLOAN G, SELVARAJAH D, TESFAYE S. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical management of diabetic sensorimotor peripheral neuropathy. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021;17(7):400-420. [4] LIU S, HE CZ, CAI YT, et al. Evaluation of negative-pressure wound therapy for patients with diabetic foot ulcers: systematic review and meta-analysis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2017;13:533-544. [5] JAVED S, HAYAT T, MENON L, et al. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy in people with type 2 diabetes: too little too late. Diabet Med. 2020;37(4):573-579. [6] STINO AM, SMITH AG. Peripheral neuropathy in prediabetes and the metabolic syndrome. J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8(5):646-655. [7] HE X, KUANG G, WU Y, et al. Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(6):e468. [8] 潘钟杰,秦志鸿,郑铁军,等.股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1441-1447. [9] 万淑君,孔祥,吕坤.非编码RNA与糖尿病血管病变的关系[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2021,41(5):665-670. [10] REGAZZI R. MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets for the treatment of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018;22(2):153-160. [11] GAO C, FAN F, LIU X, et al. Exosomal miRNA Analysis of Aqueous Humour of Diabetes and Cataract Patients. Curr Eye Res. 2021;46(3): 324-332. [12] HE X, KUANG G, WU Y, et al. Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(6):e468. [13] SCHERM MG, DANIEL C. miRNA Regulation of T Cells in Islet Autoimmunity and Type 1 Diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2020;20(9):41. [14] KAUR P, KOTRU S, SINGH S, et al. Role of miRNAs in diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms and possible interventions. Mol Neurobiol. 2022;59(3):1836-1849. [15] DISTEFANO JK, TAILA M, ALVAREZ ML. Emerging roles for miRNAs in the development, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Curr Diab Rep. 2013;13(4):582-591. [16] LIU ZN, JIANG Y, LIU XQ, et al. MiRNAs in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021:4632745. [17] JIN ZQ. MicroRNA targets and biomarker validation for diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis. Pharmacol Res. 2021;174:105941. [18] LI Y, XU Y, HOU Y, et al. Construction and Bioinformatics Analysis of the miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Diabetic Nephropathy. J Healthc Eng. 2021;2021: 8161701. [19] CHEN Y, HE Y, ZHOU H. The potential role of lncRNAs in diabetes and diabetic microvascular complications. Endocr J. 2020;67(7):659-668. [20] LEUNG A, AMARAM V, NATARAJAN R. Linking diabetic vascular complications with LncRNAs. Vascul Pharmacol. 2019;114:139-144. [21] BISWAS S, COYLE A, CHEN S, et al. Expressions of Serum lncRNAs in Diabetic Retinopathy - A Potential Diagnostic Tool. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13: 851967. [22] LONG J, DANESH FR. Values and Limitations of Targeting lncRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy. Diabetes. 2018;67(4):552-553. [23] COELLAR JD, LONG J, DANESH FR. Long Noncoding RNAs and Their Therapeutic Promise in Diabetic Nephropathy. Nephron. 2021;145(4): 404-414. [24] LI J, WEI M, LIU X, et al. The progress, prospects, and challenges of the use of non-coding RNA for diabetic wounds. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;24:554-578. [25] GONG Q, LU Z, HUANG Q, et al. Altered microRNAs expression profiling in mice with diabetic neuropathic pain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;456(2): 615-620. [26] DU H, LIU Z, TAN X, et al. Identification of the Genome-wide Expression Patterns of Long Non-coding RNAs and mRNAs in Mice with Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Neuropathic Pain. Neuroscience. 2019;402:90-103. [27] GUO G, REN S, KANG Y, et al. Microarray analyses of lncRNAs and mRNAs expression profiling associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):15347-15359. [28] ZHANG Y, ZHU Z, LIU X, et al. Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNAs and mRNA expression profiles reveals the potential role of lncRNAs in early stage of post-peripheral nerve injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Aging (Albany NY). 2021; 13(10):13909-13925. [29] FENG Y, GE Y, WU M, et al. Long Non Coding RNAs Regulate Inflammation in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Acting as ceRNAs Targeting miR-146a-5p. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:413-422. [30] ASHJARI D, KARAMALI N, RAJABINEJAD M, et al. The axis of long non-coding RNA MALAT1/miR-1-3p/CXCR4 is dysregulated in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Heliyon. 2022;8(3):e09178. [31] WANG B, YAO J, YAO X, et al. Swertiamarin alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy in rats by suppressing NOXS/ ROS/NLRP3 signal pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021;41(6):937-941. [32] JUCHNICKA I, KUZMICKI M. Influence of MiRNAs in gestational diabetes mellitus development. Ginekol Pol. 2021;92(8):579-582. [33] ZHANG Y, SONG C, LIU J, et al. Inhibition of miR-25 aggravates diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Neuroreport. 2018;29(11):945-953. [34] CHEN HP, ZHOU W, KANG LM, et al. Intrathecal miR-96 inhibits Nav1.3 expression and alleviates neuropathic pain in rat following chronic construction injury. Neurochem Res. 2014;39(1):76-83. [35] AGHDAM AM, SHAHABI P, KARIMI-SALES E,et al. Swimming Exercise Induced Reversed Expression of miR-96 and Its Target Gene NaV1.3 in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Rats. Chin J Physiol. 2018;61(2):124-129. [36] CHANG LL, WANG HC, TSENG KY, et al. Upregulation of miR-133a-3p in the Sciatic Nerve Contributes to Neuropathic Pain Development. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(9):3931-3942. [37] LIU XS, FAN B, SZALAD A, et al. MicroRNA-146a Mimics Reduce the Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes. 2017;66(12): 3111-3121. [38] FENG Y, CHEN L, LUO Q, et al. Involvement of microRNA-146a in diabetic peripheral neuropathy through the regulation of inflammation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:171-177. [39] LUO Q, FENG Y, XIE Y, et al. Nanoparticle-microRNA-146a-5p polyplexes ameliorate diabetic peripheral neuropathy by modulating inflammation and apoptosis. Nanomedicine. 2019;17:188-197. [40] YOUSEFZADEH N, ALIPOUR MR, SOUFI FG. Deregulation of NF-кB-miR-146a negative feedback loop may be involved in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71(1):51-58. [41] CHEN J, LI C, LIU W, et al. miRNA-155 silencing reduces sciatic nerve injury in diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Mol Endocrinol. 2019;63(3):227-238. [42] WU X, WANG X, YIN Y, et al. Investigation of the role of miR-221 in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and related molecular mechanisms. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021;30(6):623-632. [43] WU Y, GU Y, SHI B. miR-590-3p Alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain by targeting RAP1A and suppressing infiltration by the T cells. Acta Biochim Pol. 2020;67(4):587-593. [44] SUN Q, ZENG J, LIU Y, et al. microRNA-9 and -29a regulate the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy via ISL1-mediated sonic hedgehog signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12):11446-11465. [45] JIA L, WANG L, CHOPP M, et al. MiR-29c/PRKCI Regulates Axonal Growth of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Under Hyperglycemia. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(1):851-858. [46] JIA L, CHOPP M, WANG L, et al. MiR-34a Regulates Axonal Growth of Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons by Targeting FOXP2 and VAT1 in Postnatal and Adult Mouse. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(12):9089-9099. [47] FAN B, CHOPP M, ZHANG ZG, et al. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy with engineered mesenchymal stromal cell-derived exosomes enriched with microRNA-146a provide amplified therapeutic efficacy. Exp Neurol. 2021;341: 113694. [48] WANG L, CHOPP M, LU X, et al. miR-146a mediates thymosin β4 induced neurovascular remodeling of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type-II diabetic mice. Brain Res. 2019;1707:198-207. [49] CHEN J, LIU W, YI H, et al. MicroRNA-155 mimics ameliorates nerve conduction velocities and suppresses hyperglycemia-induced pro-inflammatory genes in diabetic peripheral neuropathic mice. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(6):3905-3918. [50] PANG B, QIAO L, WANG S, et al. MiR-214-3p plays a protective role in diabetic neuropathic rats by regulating Nav1.3 and TLR4. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(11): 2294-2303. [51] LI Z, LI X, CHEN X, et al. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in neuropathic pain. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(1):e12528. [52] WANG S, XU H, ZOU L, et al. LncRNA uc.48+ is involved in diabetic neuropathic pain mediated by the P2X3 receptor in the dorsal root ganglia. Purinergic Signal. 2016;12(1):139-48. [53] LIU C, TAO J, WU H, et al. Effects of LncRNA BC168687 siRNA on Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by P2X7 Receptor on SGCs in DRG of Rats. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:7831251. [54] LIU C, LI C, DENG Z, et al. Long Non-coding RNA BC168687 is Involved in TRPV1-mediated Diabetic Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Neuroscience. 2018;374:214-222. [55] PENG H, ZOU L, XIE J, et al. lncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA Decreases Diabetic Neuropathic Pain Mediated by the P2X3 Receptor in Dorsal Root Ganglia. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54:511-523. [56] REN W, XI G, LI X, et al. Long non-coding RNA HCG18 promotes M1 macrophage polarization through regulating the miR-146a/TRAF6 axis, facilitating the progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(1): 471-482. [57] YU W, ZHAO GQ, CAO RJ, et al. LncRNA NONRATT021972 Was Associated with Neuropathic Pain Scoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Behav Neurol. 2017; 2017:2941297. [58] LIU S, ZOU L, XIE J, et al. LncRNA NONRATT021972 siRNA regulates neuropathic pain behaviors in type 2 diabetic rats through the P2X7 receptor in dorsal root ganglia. Mol Brain. 2016;9:44. [59] LU J, HUANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Noncoding RNAs involved in DNA methylation and histone methylation, and acetylation in diabetic vascular complications. Pharmacol Res. 2021;170:105520. [60] FILARDI T, CATANZARO G, MARDENTE S, et al. Non-Coding RNA: Role in Gestational Diabetes Pathophysiology and Complications. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(11):4020. [61] MEYDAN C, ÜÇEYLER N, SOREQ H. Non-coding RNA regulators of diabetic polyneuropathy. Neurosci Lett. 2020;731:135058. |
| [1] | Liu Jianhong, Liao Shijie, Li Boxiang, Tang Shengping, Wei Zhendi, Ding Xiaofei. Extracellular vesicles carrying non-coding RNA regulate the activation of osteoclasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1076-1082. |
| [2] | Zhou Shuliang, Xu Liang, Qian Xuefeng, Zeng Jincai, Zhu Lifan. Correlation between the expression of miRNA-142-3p, mixed lineage kinase 3 and interleukin-1beta in nucleus pulposus and the degree of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 165-171. |
| [3] | Guo Xiangying, Peng Zifu, He Yimin, Fang Hongbo, Jiang Ning. MiRNA-122 contributes to the effect of exercise on non-alcoholic fatty liver [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 272-279. |
| [4] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [5] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [6] | Song Hehua, Wei Zairong. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: research and therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1278-1285. |
| [7] | Qin Yuxing, Ren Qiangui, Li Zilong, Quan Jiaxing, Shen Peifeng, Sun Tao, Wang Haoyu. Action mechanism and prospect of bone microvascular endothelial cells for treating femoral head necrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 955-961. |
| [8] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Li Qingru. Meta-analysis of the value of exosomal miRNA for the diagnosis of chronic kidney disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 970-976. |
| [9] | Xu Luchun, Yang Yongdong, Zhao He, Zhong Wenqing, Ma Yukun, Yu Xing. Effect and mechanism of non-coding RNA in regulating neuronal apoptosis after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(33): 5404-5412. |
| [10] | Jiang Shengyuan, Zhang Yaqi, Bi Jingxin, Zhang Chengfei, Zhang Qiue, Mu Xiaohong, Bai Huizhong, Zuo Xinwei, Liu Tonghua, Qin Lingling. Tangbikang reduces sciatic nerve oxidative stress injury in a rat model of diabetic peripheral neuropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5162-5167. |
| [11] | Han Jie, Lin Zhiyu, Xu Zhiwei, Zhang Xiaoyun, Shang Yuzhi, Liu Hao. Interventional effect of microRNA on osteonecrosis of the femoral head through bone metabolism mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5238-5248. |
| [12] | Yang Huixia, Bai Zhigang, Chi Hongyang, Ma Tianlong, Ma Shengchao, Jiang Yideng. Effects of long non-coding RNA H19 on apoptosis of osteoblasts induced by dexamethasone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4513-4518. |
| [13] | Zhao Zhongsheng, Chen Zhenyuan, Huang Yunmei, Zhang Ling, Wu Guangwen, Chen Jun. Role and mechanism of Rongjin Niantong Fang for extracellular matrix metabolism of chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(28): 4448-4455. |
| [14] | Chen Zili, Cao Ning, Xu Meng, Jiang Yan, Ji Meichao, Zheng Yangyang, Yang Lili. Biological characteristics of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3780-3787. |
| [15] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3143-3150. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||