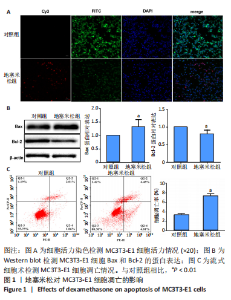
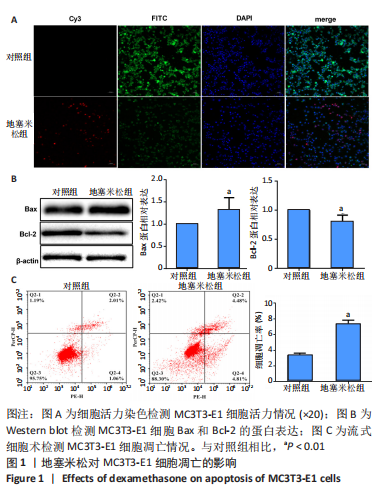
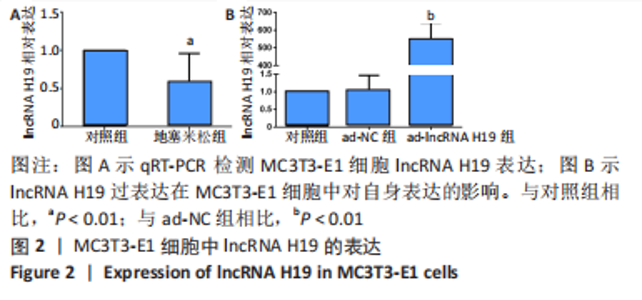
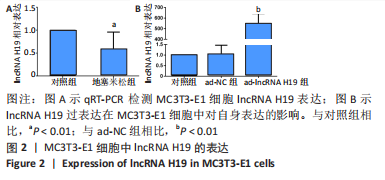
[1] Yang F, Zhang X Song T, et al. Huogu injection alleviates SONFH by regulating adipogenic differentiation of BMSCs via targeting the miR-34c-5p/MDM4 pathway. Gene. 2022;838:146705.
[2] Liang XZ, Luo D, Chen YR, et al. Identification of potential autophagy-related genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):86.
[3] 魏治文, 宋红梅. 中西医治疗激素性股骨头坏死的研究进展[J]. 按摩与康复医学,2021,12(11):51-53+58.
[4] Fan ZQ, Bai SC, Xu Q, et al. Oxidative Stress Induced Osteocyte Apoptosis in Steroid‐Induced Femoral Head Necrosis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(7):2145-2152.
[5] Wang B, Gong S, Shao W, et al. Comprehensive analysis of pivotal biomarkers, immune cell infiltration and therapeutic drugs for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Bioengineered. 2021; 12(1):5971-5984.
[6] WEINSTEIN RS, NICHOLAS RW, MANOLAGAS SC. Apoptosis of osteocytes in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the hip. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85(8):2907-2912.
[7] Wang G, Zhang L, Yan C, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-576-5p protects from steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by suppressing ANXA2. Cell Cycle. 2021;21(1):49-62.
[8] Zheng Yl, Song G, Guo Jb, et al. Interactions Among lncRNA/circRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseases. 2021;9:753931.
[9] Peng S, Cao L, He S, et al. An Overview of Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in Bone Regeneration from Mesenchymal Stem Cells. 2018; 2018:8273648.
[10] Silva Am, Moura Sr, Teixeira Jh, et al. Long noncoding RNAs: a missing link in osteoporosis. 2019;7:10.
[11] Li X, Li Q, Jin X, et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 knockdown inhibits the cell viability and promotes apoptosis of thyroid cancer cells through regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway. 2019;18(3):1863-1869.
[12] 孔劲松, 陈滔, 郑鑫, 等 丹参素对地塞米松诱导MC3T3-E1成骨细胞损伤的保护作用 [J]. 江苏医药,2022,48(5):436-440.
[13] Ronchetti S, Ayroldi E, Ricci E, et al. A Glance at the Use of Glucocorticoids in Rare Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases: Still an Indispensable Pharmacological Tool? Front Immunol. 2021;11: 613435.
[14] Buttgereit F, Palmowski A. How to taper glucocorticoids in inflammatory rheumatic diseases? A narrative review of novel evidence in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and giant cell arteritis. Joint Bone Spine. 2022;89(1):105285.
[15] 胡兆林, 常峰. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2022,28(3):466-470.
[16] Peng CH, Lin WY, Yeh KT, et al. The molecular etiology and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Tzu Chi Medical J. 2021;33(3): 212-223.
[17] Kar R, Riquelme MA, Hua R, et al. Glucocorticoid-Induced Autophagy Protects Osteocytes Against Oxidative Stress Through Activation of MAPK/ERK Signaling. JBMR Plus. 2018;3(4):e10077.
[18] Yu Y, Wang S, Zhou Z. Cartilage Homeostasis Affects Femoral Head Necrosis Induced by Methylprednisolone in Broilers. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):4841.
[19] Li J, Xu X, Wei C, et al. Long noncoding RNA NORAD regulates lung cancer cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and invasion by the miR-30a-5p/ADAM19 axis. 2020;13(1):1-13.
[20] Zhu X, Bu F, Tan T, et al. Long noncoding RNA RP11-757G1.5 sponges miR-139-5p and upregulates YAP1 thereby promoting the proliferation and liver, spleen metastasis of colorectal cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39(1):207.
[21] Li L, Wang H, Li H, et al. Long noncoding RNA BACE1-antisense transcript plays a critical role in Parkinson’s disease via microRNA-214-3p/Cell death-inducing p53-target protein 1 axis. Bioengineered. 2022; 13(4):10889-10901.
[22] Fico A, Fiorenzano A, Pascale E, et al. Long non-coding RNA in stem cell pluripotency and lineage commitment: functions and evolutionary conservation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(8):1459-1471.
[23] Chen J, Ao L, Yang J. Long non-coding RNAs in diseases related to inflammation and immunity. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(18):494.
[24] Li T, Jiang H, Li Y, et al. Estrogen promotes lncRNA H19 expression to regulate osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs and reduce osteoporosis via miR-532-3p/SIRT1 axis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2021;527:111171.
[25] Chen S, Liu D, Zhou Z, et al. Role of long non-coding RNA H19 in the development of osteoporosis. Mol Med. 2021;27(1):122.
[26] Li T, Xu Y, Wang Y, et al. Differential expression profiles of long noncoding RNAs and mRNAs in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after exposure to a high dosage of dexamethasone. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):9.
[27] Wang H, Wei P, Zhang Y, et al. LncRNA TCONS_00023297 Regulates the Balance of Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation in Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Coupling Process of Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:697858.
[28] Huang G, Zhao G, Xia J, et al. FGF2 and FAM201A affect the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture. Gene. 2018;652:39-47.
[29] Chen X, Li J, Liang D, et al. LncRNA AWPPH participates in the development of non‑traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head by upregulating Runx2. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(1):153-159.
[30] 杨剑云, 周宇. 长链非编码RNA HOXD-AS1在疾病中作用机制研究进展[J]. 新医学,2021,52(1):1-4.
[31] 张向阳. LncRNA EPIC1保护成骨细胞免受地塞米松损伤[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学,2019.
[32] KIM B, LEE KY, PARK B. Icariin abrogates osteoclast formation through the regulation of the RANKL-mediated TRAF6/NF-κB/ERK signaling pathway in Raw264.7 cells. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:181-190.
[33] Klomp Je, Klomp Ja, Der Cj. The ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling network: the final frontier in RAS signal transduction. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021;49(1):253-267. |