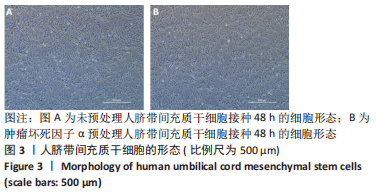
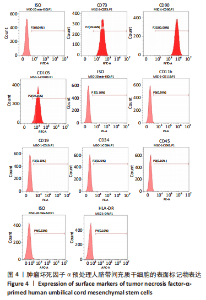
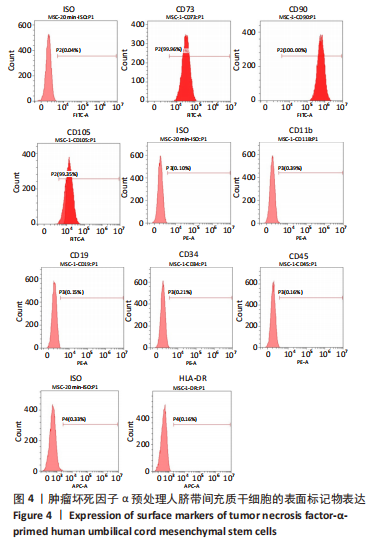
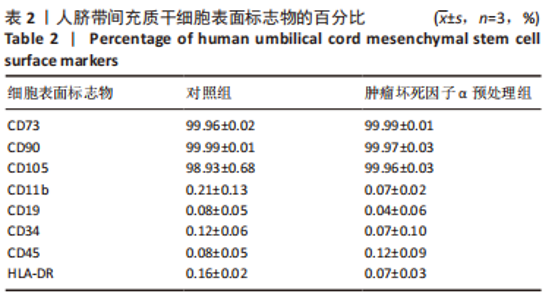
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3780-3787.doi: 10.12307/2023.673
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological characteristics of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells
Chen Zili1, Cao Ning2, Xu Meng2, Jiang Yan2, Ji Meichao2, Zheng Yangyang2, Yang Lili1
- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tianjin Fifth Central Hospital (Peking University Binhai Hospital), Tianjin 300450, China; 2Tingo Regenerative Medicine (Tianjin) Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300450, China
-
Received:2022-08-02Accepted:2022-10-12Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-18 -
Contact:Yang Lili, Attending physician, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tianjin Fifth Central Hospital (Peking University Binhai Hospital), Tianjin 300450, China -
About author:Chen Zili, Chief physician, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Tianjin Fifth Central Hospital (Peking University Binhai Hospital), Tianjin 300450, China Cao Ning, Master, Senior engineer, Tingo Regenerative Medicine (Tianjin) Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300450, China -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Project of Tianjin Binhai New Area Health and Family Planning Commission, No. 2015BWKZ003 (to CZL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Zili, Cao Ning, Xu Meng, Jiang Yan, Ji Meichao, Zheng Yangyang, Yang Lili. Biological characteristics of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-primed human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3780-3787.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

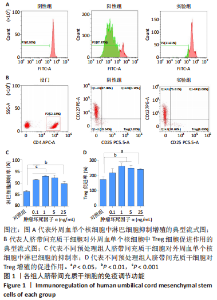
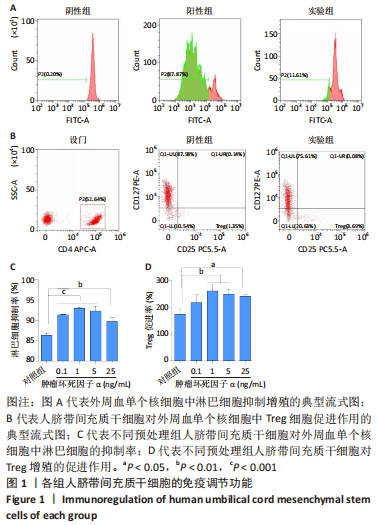
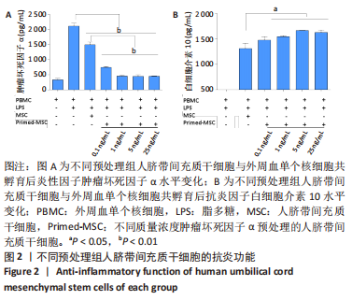
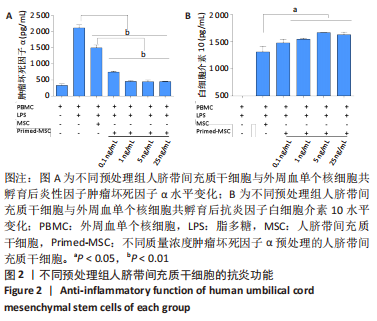
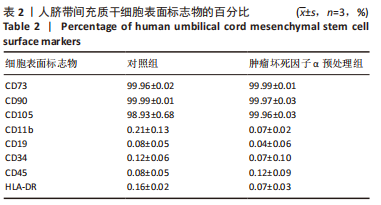
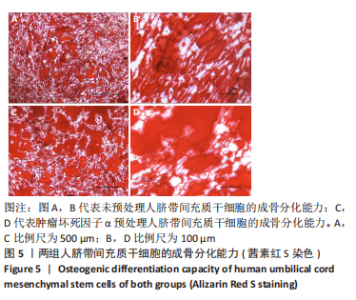
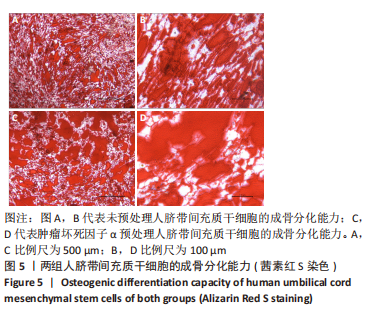
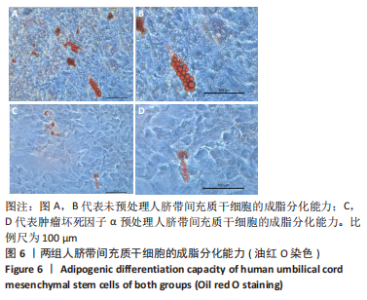
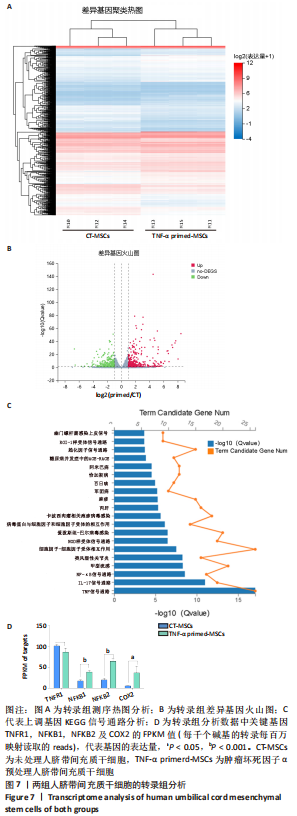
2.5 炎性因子预处理人脐带间充质干细胞的转录水平 对照组及肿瘤坏死因子α预处理组人脐带间充质干细胞的转录组测序分析发现:对照组3根脐带来源间充质干细胞的转录组数据差异相对较小,肿瘤坏死因子α预处理组3根脐带来源间充质干细胞的转录组数据组内差异一致;而对照组与肿瘤坏死因子α预处理组之间表现出的基因表达模式差异较大,表达倍数改变在2倍以上的差异基因达1 877个,其中上调基因及下调基因分别为1 045个和832个。对两组差异基因进行KEGG信号分析,其中上调的基因KEGG信号通路分析发现:肿瘤坏死因子α预处理人脐带间充质干细胞上调基因多为肿瘤坏死因子α信号通路、白细胞介素17信号通路和核因子κB信号通路且差异显著。该研究结果为肿瘤坏死因子α预处理后人脐带间充质干细胞的应激反应,迅速激活核因子κB信号通路;考虑到核因子κB信号通路在免疫调节及抗炎过程中的功能,该研究进一步对核因子κB信号通路的具体基因进行分析,包括TNFR1,NFKB1,NFKB2及COX2的表达,确定肿瘤坏死因子α预处理人脐带间充质干细胞后TNFR1基因没有显著变化,而NFKB1,NFKB2及COX2基因显著上调,见图7。该结果表明肿瘤坏死因子α预处理人脐带间充质干细胞可能通过NFKB1和NFKB2亚基转录水平的提高,影响后续COX2表达的升高,在人脐带间充质干细胞与外周血单个核细胞共孵育时,细胞处于核因子κB信号通路活化的状态,可迅速发挥免疫调节及抗炎功能;此外,下调的基因KEGG信号通路的转录变化相对较小,其中Axon guidance信号通路为主要下调信号通路,与干细胞的神经信号传递功能相关(该部分结果未展示)。"
| [1] DING DC, SHYU WC, LIN SZ. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011; 20(1):5-14. [2] SAMSONRAJ RM, RAGHUNATH M, NURCOMBE V, et al. Concise Review: Multifaceted Characterization of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Use in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(12):2173-2185. [3] NAGAMURA-INOUE T, HE H. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility. World J Stem Cells. 2014;6(2):195-202. [4] RAZA SS, SETH P, KHAN MA. ‘Primed’ Mesenchymal Stem Cells: a Potential Novel Therapeutic for COVID19 Patients. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021;17(1):153-162. [5] NORONHA NC, MIZUKAMI A, CALIÁRI-OLIVEIRA C, et al. Priming approaches to improve the efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cell-based therapies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):131. [6] LEVY O, KUAI R, SIREN EMJ, et al. Shattering barriers toward clinically meaningful MSC therapies. Sci Adv. 2020;6(30):eaba6884. [7] DE WITTE SF, FRANQUESA M, BAAN CC, et al. Toward Development of iMesenchymal Stem Cells for Immunomodulatory Therapy. Front Immunol. 2016;6:648. [8] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, LUKOMSKA B, JANOWSKI M. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells: From Roots to Boost. Stem Cells. 2019;37(7):855-864. [9] GALIPEAU J, KRAMPERA M, BARRETT J, et al. International Society for Cellular Therapy perspective on immune functional assays for mesenchymal stromal cells as potency release criterion for advanced phase clinical trials. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(2):151-159. [10] ČAMERNIK K, MIHELIČ A, MIHALIČ R, et al. Comprehensive analysis of skeletal muscle- and bone-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in patients with osteoarthritis and femoral neck fracture. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):146. [11] VINARDELL T, SHEEHY EJ, BUCKLEY CT, et al. A comparison of the functionality and in vivo phenotypic stability of cartilaginous tissues engineered from different stem cell sources. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(11-12):1161-1170. [12] LOTFY A, SALAMA M, ZAHRAN F, et al. Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat bone marrow and adipose tissue: a comparative study. Int J Stem Cells. 2014;7(2):135-142. [13] LA ROCCA G, LO IACONO M, CORSELLO T, et al. Human Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells maintain the expression of key immunomodulatory molecules when subjected to osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic differentiation in vitro: new perspectives for cellular therapy. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(1):100-113. [14] ZHA K, LI X, YANG Z, et al. Heterogeneity of mesenchymal stem cells in cartilage regeneration: from characterization to application. NPJ Regen Med. 2021;6(1):14. [15] DU W, LI X, CHI Y, et al. VCAM-1+ placenta chorionic villi-derived mesenchymal stem cells display potent pro-angiogenic activity. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:49. [16] MIZUKAMI A, SWIECH K. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: From Discovery to Manufacturing and Commercialization. Stem Cells Int. 2018;2018:4083921. [17] NAJAR M, RAICEVIC G, FAYYAD-KAZAN H, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells and immunomodulation: A gathering of regulatory immune cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(2):160-171. [18] NAVA MM, RAIMONDI MT, PIETRABISSA R. Controlling self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells via mechanical cues. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:797410. [19] LEROUX L, DESCAMPS B, TOJAIS NF, et al. Hypoxia preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improve vascular and skeletal muscle fiber regeneration after ischemia through a Wnt4-dependent pathway. Mol Ther. 2010;18(8):1545-1452. [20] 侯婧瑛,于萌蕾,郭天柱,等.缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究, 2021,25(7): 985-990. [21] BALDARI S, DI ROCCO G, PICCOLI M, et al. Challenges and Strategies for Improving the Regenerative Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(10):2087. [22] LINARES GR, CHIU CT, SCHEUING L, et al. Preconditioning mesenchymal stem cells with the mood stabilizers lithium and valproic acid enhances therapeutic efficacy in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2016;281:81-92. [23] MEAD B, CHAMLING X, ZACK DJ, et al. TNFα-Mediated Priming of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Enhances Their Neuroprotective Effect on Retinal Ganglion Cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61(2):6. [24] SZABÓ E, FAJKA-BOJA R, KRISTON-PÁL É, et al. Licensing by Inflammatory Cytokines Abolishes Heterogeneity of Immunosuppressive Function of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Population. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(18):2171-2180. [25] JIANG W, XU J. Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(1):e12712. [26] SHU J, HE X, ZHANG L, et al. Human amnion mesenchymal cells inhibit lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-α and IL-1β production in THP-1 cells. Biol Res. 2015;48:69. [27] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89. [28] RYAN JM, BARRY FP, MURPHY JM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells avoid allogeneic rejection. J Inflamm (Lond). 2005;2:8. [29] DORRONSORO A, FERRIN I, SALCEDO JM, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells modulate T-cell responses through TNF-α-mediated activation of NF-κB. Eur J Immunol. 2014;44(2):480-488. |
| [1] | Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Lu Dahong, Xu Junrong, Liu Xiaocui, Wang Bingyun. Clinical-grade human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells affect the improvement of neurological function in rats with traumatic brain injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 835-839. |
| [2] | Zhang Qijian, Xu Ximing. Acquisition and application of ectodermal mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 928-934. |
| [3] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [4] | Liu Haichao, Wang Hao, Wang Shizhong, Lin Jianping, Jin Jing, Chen Shaoqing. Effects of point-pressing of the spleen meridian on inflammatory factors and calcium homeostasis in the skeletal muscle of acute blunt contusion rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3123-3128. |
| [5] | Wang Chenyu, Yao Jiawei, Xu Xiongfeng, Qiu Bo. Screening and analysis of differentially expressed genes in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3224-3229. |
| [6] | Zhang Yuwei, Liu Chuanchuan, Mao Jiaqi, Zhang Qingqing, Liu Hong, Chen Ying, Ma Lan. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes treated with hypoxic preconditioning inhibits proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(19): 2986-2992. |
| [7] | Zhang Houjun, Jiang Shengyuan, Deng Bowen, Liu Gang, Bai Huizhong, Tao Jingwei, Fan Xiao, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Mechanism by which tetramethylpyrazine improves inflammatory microenvironment after spinal cord injury in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(11): 1701-1707. |
| [8] | Yang Xu, Wang Feiqing, Zhao Jianing, Zhang Chike, Liang Huiling, Qi Shasha, Wu Dan, Liu Yanqing, Tang Dongxin, Liu Yang, Li Yanju. Effects of multiple myeloma cell conditioned medium on proliferation and differentiation of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1514-1520. |
| [9] | Wang Xinxin, Wang Jingxin. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in treatment of secondary lymphedema [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1603-1609. |
| [10] | Zhang Yuqing, Wu Jun. Opportunities and challenges of COVID-19 therapy using mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(10): 1618-1625. |
| [11] | Liu Siqi, Wu Mingrui, Qiao Lingran, Xie Liying, Chen Siyu, Han Zhibo, Zuo Lin. Effects of hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on diabetic wound repair in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(1): 21-27. |
| [12] | Tang Wenjing, Wu Siyuan, Yang Chen, Tao Xi. Inflammatory responses in post-stroke depression [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1278-1285. |
| [13] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [14] | Liu Yiyi, Qiu Junqiang, Yi Longyan, Zhou Cailiang. Effect of resistance training on interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in middle-age and elderly people: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 804-812. |
| [15] | Liu Jin, Li Zhen, Hao Huiqin, Wang Ze, Zhao Caihong, Lu Wenjing. Ermiao san aqueous extract regulates proliferation, migration, and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synovial cells in collagen-induced arthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 688-693. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||