[1] HUNTER DJ, BIERMA-ZEINSTRA S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759.
[2] SHI Y, HU X, CHENG J, et al. A small molecule promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and inhibits osteoarthritis development. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1914.
[3] QUICKE JG, CONAGHAN PG, CORP N, et al. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021; 30(2):196-206.
[4] DIELEMAN JL, CAO J, CHAPIN A, et al. US Health Care Spending by Payer and Health Condition, 1996-2016. JAMA. 2020;323(9):863-884.
[5] YOUNG DA, BARTER MJ, SOUL J. Osteoarthritis year in review: genetics, genomics, epigenetics. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(2):216-225.
[6] 李西海,刘献祥.骨关节炎的核心病机——本痿标痹[J].中医杂志, 2014,55(14):1248-1249,1252.
[7] BERNARD NJ. Controlling chondrocyte senescence. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(6):319.
[8] NAIR L, CHUNG H, BASU U. Regulation of long non-coding RNAs and genome dynamics by the RNA surveillance machinery. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(3):123-136.
[9] SLACK FJ, CHINNAIYAN AM. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell. 2019;179(5):1033-1055.
[10] WEI LH, GUO JU. Coding functions of “noncoding” RNAs. Science. 2020; 367(6482):1074-1075.
[11] SUN H, PENG G, NING X, et al. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA in chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(1):16-30.
[12] ABBASIFARD M, KAMIAB Z, BAGHERI-HOSSEINABADI Z, et al. The role and function of long non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020;114:104407.
[13] MISHRA S, VERMA SS, RAI V, et al. Long non-coding RNAs are emerging targets of phytochemicals for cancer and other chronic diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(10):1947-1966.
[14] SONG J, AHN C, CHUN CH, et al. A long non-coding RNA, GAS5, plays a critical role in the regulation of miR-21 during osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(12):1628-1635.
[15] ZHANG Z, ZHU Z, WATABE K, et al. Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21. Cell Death Differ. 2013;20(11):1558-1568.
[16] 郑伟,董洁,李少华,等. LncRNA-GAS5抑制miR-21介导的非完全匹配靶mRNA降解[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展,2017,44(7):580-590.
[17] LIU X, SHE Y, WU H, et al. Long non-coding RNA Gas5 regulates proliferation and apoptosis in HCS-2/8 cells and growth plate chondrocytes by controlling FGF1 expression via miR-21 regulation. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):18.
[18] LIU K, LIU C, ZHANG Z. lncRNA GAS5 acts as a ceRNA for miR-21 in suppressing PDGF-bb-induced proliferation and migration in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(9):15233-15240.
[19] WANG XB, ZHAO FC, YI LH, et al. MicroRNA-21-5p as a novel therapeutic target for osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2019:kez102.
[20] ZHU H, YAN X, ZHANG M, et al. miR-21-5p protects IL-1beta-induced human chondrocytes from degradation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019; 14(1):118.
[21] 陈可冀.清宫配方集成[M].北京:北京大学医学出版社,2013.
[22] 林洁,范展彪,刘献祥.基于数据挖掘技术探讨陈可冀《清宫配方集成》中治疗骨关节炎组方的用药规律[J].中医正骨,2017,29(11): 15-19,25.
[23] 刘献祥.基于陈可冀学术思想之骨性关节炎研究[J].康复学报,2016, 26(1):2-5.
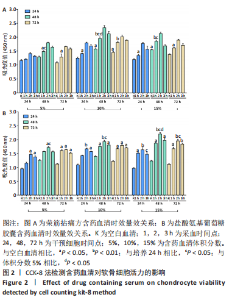
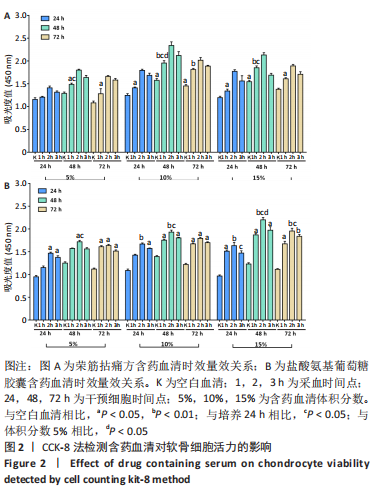
[24] 吴广文,黄艳峰,刘献祥.荣筋拈痛方治疗膝骨性关节炎的药理学基础[J].福建中医药,2018,49(3):83-85.
[25] 朱定钰,林木南,万宁,等. 荣筋拈痛方治疗膝骨关节炎临床疗效观察[C].呼和浩特: 第二十四届中国中西医结合骨伤科学术年会, 2017.
[26] 林洁,赵忠胜,黄艳峰,等.荣筋拈痛方对骨关节炎作用靶点的分析及验证[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(8):3743-3746.
[27] 郑春松,范展彪,叶蕻芝,等.计算机模拟研究荣筋拈痛方治疗骨关节炎的药效物质基础、作用靶点及作用特点[J].中医正骨,2017, 29(10):20-24.
[28] 郑春松,范展彪,叶蕻芝,等.从化学空间探讨荣筋拈痛方补肝肾强筋骨和祛风湿止痹痛的作用[J].风湿病与关节炎,2018,7(2):33-36.
[29] 付长龙,谢新宇,何俊君,等.基于PERK通路探讨荣筋拈痛方对软骨细胞内质网应激反应抑制作用[J].福建中医药,2022,53(4):22-24,28.
[30] 潘丹虹,李路,王文义,等.荣筋拈痛方对白细胞介素-1β诱导的体外大鼠软骨细胞自噬相关基因表达的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2022,11(2):1-5,15.
[31] 黄艳峰,陈俊,林洁,等.荣筋拈痛方对白细胞介素-1β诱导大鼠退变软骨细胞增殖的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(4):2077-2082.
[32] 朱定钰,黄艳峰,徐欣,等.基于p38 MAPK炎症相关通路探讨荣筋拈痛方对大鼠体外退变软骨细胞的机制影响[J].中医临床研究, 2021,13(16):1-5.
[33] 陈俊,郑若曦,张婷,等.荣筋拈痛方含药血清对骨关节炎大鼠SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路的影响[J].福建中医药,2021,52(7):26-29.
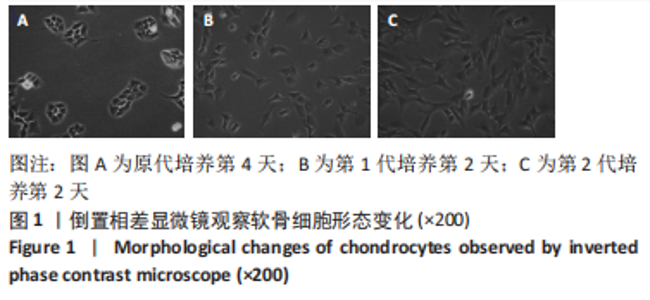
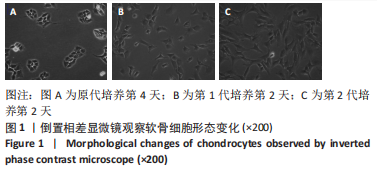
[34] 杨帆,刘保一,刘家河,等.体外培养SD大鼠关节软骨细胞原代至第3代的形态学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2161-2165.
[35] 魏伟,吴希美,李元健.药理实验方法学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:71-72.
[36] 刘建勋,韩笑,孙宇扬.含药血清药理作用强度与体内给药的量效、时效关系研究[J].中国中药杂志,2006(10):829-831.
[37] 王洪武,倪青,林兰.中药含药血清的研究进展及其在中医学中的应用[J].北京中医药,2008,27(9):698-701.
[38] 张君涛,王平,刘爱峰,等.中药含药血清制备方法的研究概述[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(11):4006-4009.
[39] 张灵娜,林兵,宋洪涛.中药血清药理学、血清药物化学的研究概况及展望[J].中草药,2015,46(17):2662-2666.
[40] 吕苏梅,张瑞丽.中老年膝骨关节炎的流行病学研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(16):4133-4135.
[41] 张红敏,谢春光,陈世伟.含药血清体外药理试验的评价[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2004(8):741-745.
[42] LI D, YANG C, YIN C, et al. LncRNA, Important Player in Bone Development and Disease. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020;20(1):50-66.
[43] HULL R, POPE FM. Osteoarthritis and cartilage collagen genes. Lancet. 1989;1(8650):1337-1338.
[44] XING D, LIANG JQ, LI Y, et al. Identification of long noncoding RNA associated with osteoarthritis in humans. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(4):288-293.
[45] XIANG S, LI Z, BIAN Y, et al. Identification of changed expression of mRNAs and lncRNAs in osteoarthritic synovium by RNA-sequencing. Gene. 2019;685:55-61.
[46] CHEN L, ZHANG Y, RAO Z, et al. Integrated analysis of key mRNAs and lncRNAs in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):1841-1849.
|