Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (23): 3682-3692.doi: 10.12307/2023.570
Previous Articles Next Articles
Wenyang Tongluo capsule intervenes with inflammation and angiogenesis in rat osteoarthritic chondrocytes
Li Gang1, Song Yun2, Liang Guoguang3
- 1Guangdong Vocational College of Food and Drug, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of General Practice, School Hospital of South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Nanhai Third People’s Hospital, Foshan 528000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-07-26Accepted:2022-10-18Online:2023-08-18Published:2023-01-14 -
About author:Li Gang, MD, Lecturer, Associate chief physician, Guangdong Vocational College of Food and Drug, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Scientific Research Project of Guangdong Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 20181183 (to LG); the Scientific Research Project of Shandong Provincial Education Department, No. 2021KTSCX235 (to LG)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Gang, Song Yun, Liang Guoguang. Wenyang Tongluo capsule intervenes with inflammation and angiogenesis in rat osteoarthritic chondrocytes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(23): 3682-3692.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
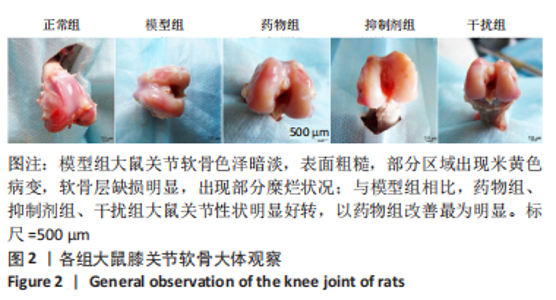
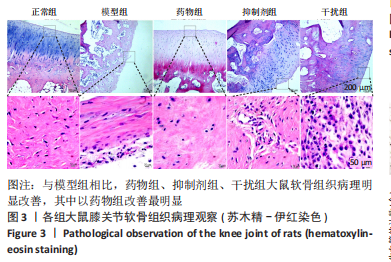
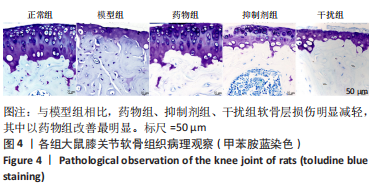
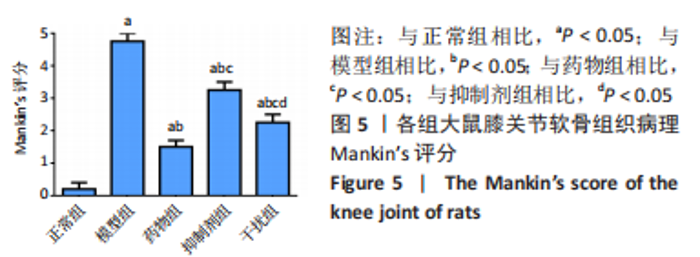
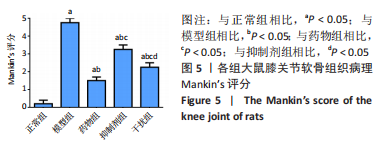
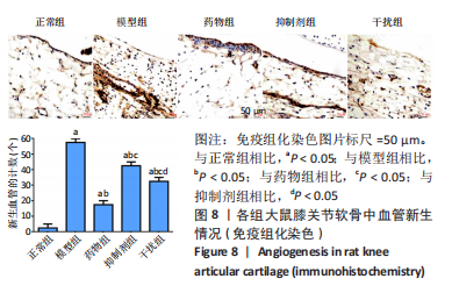
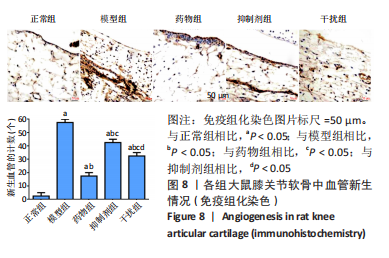
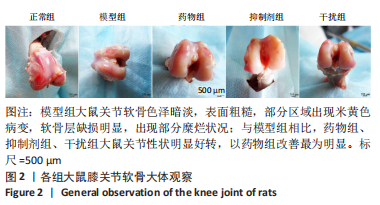
2.1.3 各组大鼠膝关节软骨大体观察 正常组大鼠行动机警,肢体协调性良好,大鼠未见明显的行为异常;模型组大鼠的肢体灵活性明显下降,出现跛行的状况,活动量明显减少,大鼠的病灶膝关节部位严重肿胀,大鼠舐足次数明显增多;与模型组相比,药物组大鼠的临床症状明显改善,跛行状况明显缓解,舐足次数明显减少;与药物组相比,抑制剂组大鼠病灶部位明显肿胀,大鼠舐足次数明显增多;与抑制剂组相比,干扰组大鼠的膝关节的肿胀以及舐足行为有所改善。 将大鼠处死后,大体观察膝关节软骨,结果显示:正常组大鼠膝关节表面光滑,色泽透明,干燥,无增生;模型组大鼠关节软骨色泽暗淡,表面粗糙,部分区域出现米黄色病变,软骨层缺损明显,出现部分糜烂状况;与模型组相比,药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组大鼠关节性状明显好转,以温阳通络胶囊组改善最为明显;与抑制剂组相比,干扰组大鼠膝关节状况有了较为明显改善,见图2。"

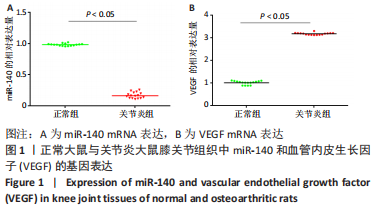
2.1.8 各组大鼠膝关节软骨组织中miR-140、VEGF、Bcl-2、Bax的表达 qRT-PCR检测:与正常组相比,模型组、药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显升高,miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05);与药物组相比,抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与抑制剂组相比,干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),见表2。 "
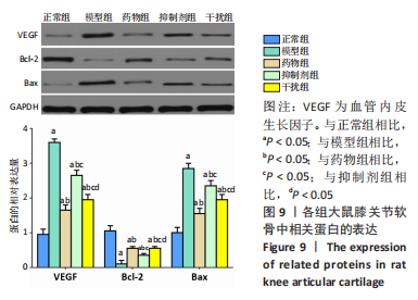
Western blot检测:与正常组相比,模型组、药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05);与药物组相比,抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与抑制剂组相比,干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),见图9。"
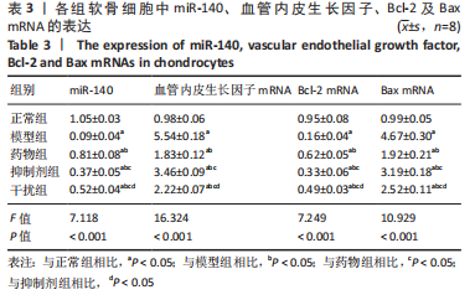
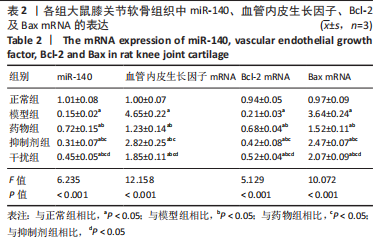
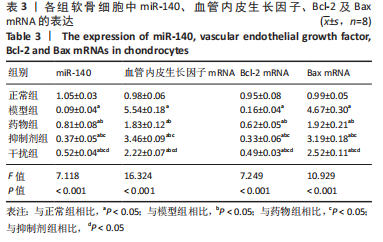
2.2.7 各组软骨细胞中miR-140、VEGF、Bcl-2、Bax的表达 qRT-PCR检测:与正常组相比,模型组、药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05);与药物组相比,抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与抑制剂组相比,干扰组VEGF、Bax的mRNA表达明显降低(P < 0.05),miR-140、Bcl-2的mRNA表达明显升高(P < 0.05),见表3。"
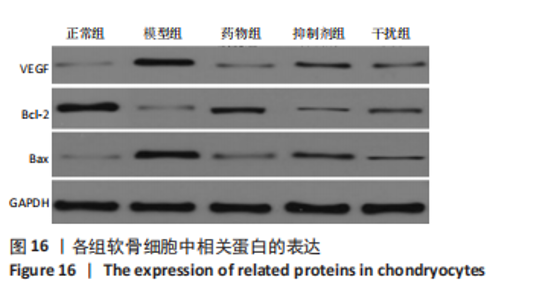
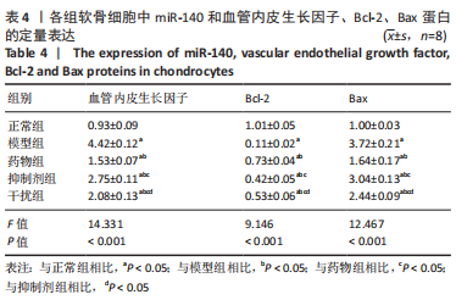
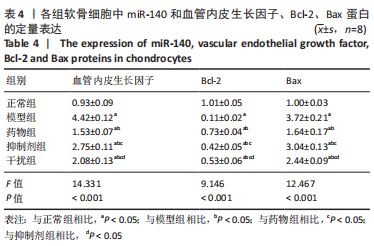
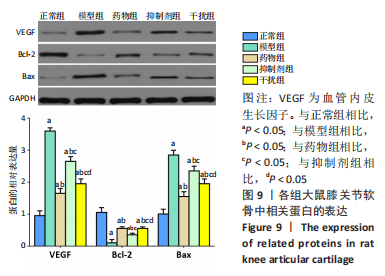
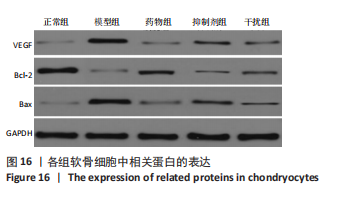
Western blot检测:与正常组相比,模型组、药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,药物组、抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05);与药物组相比,抑制剂组、干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05);与抑制剂组相比,干扰组VEGF、Bax的蛋白表达明显降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2的蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),见图16,表4。"

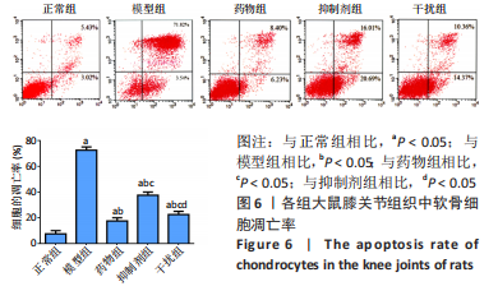
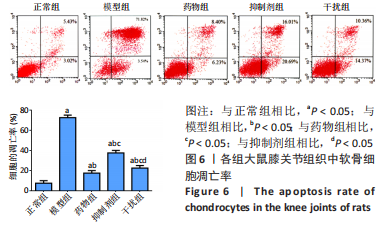
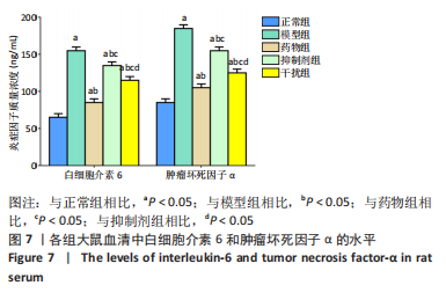
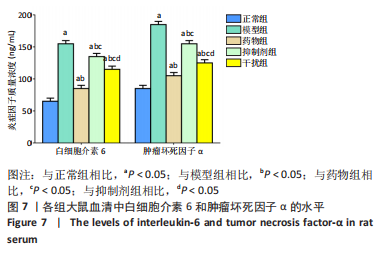
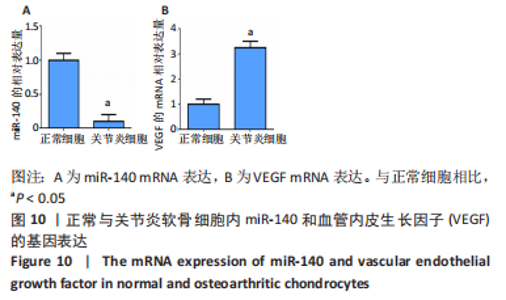
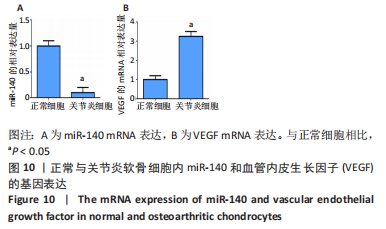
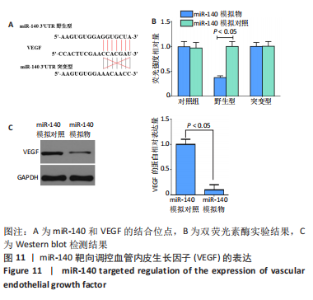
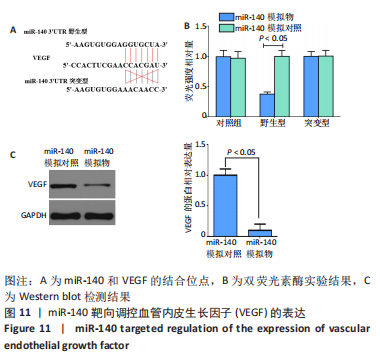
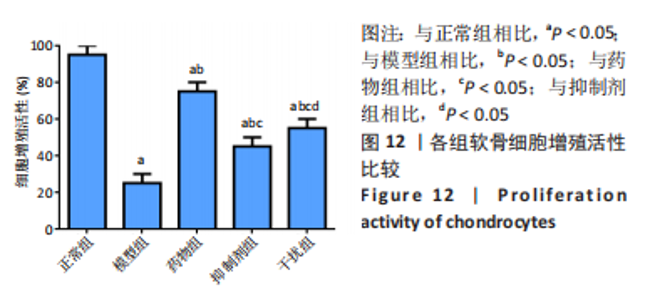
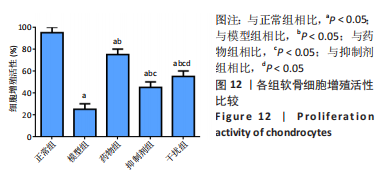
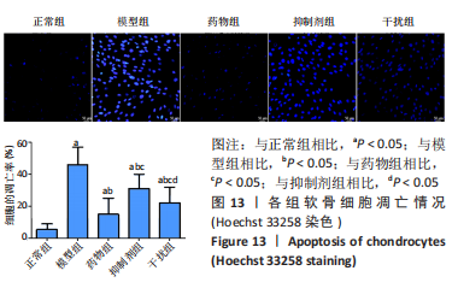
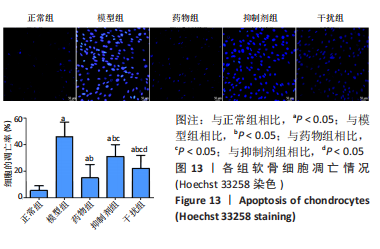
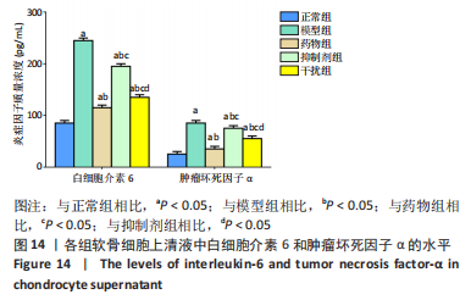
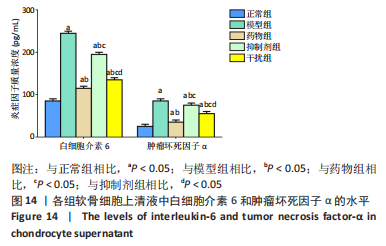
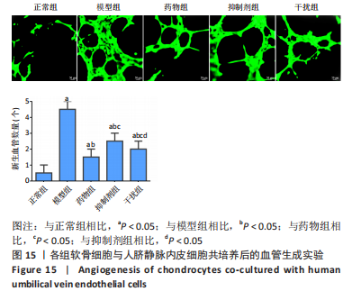
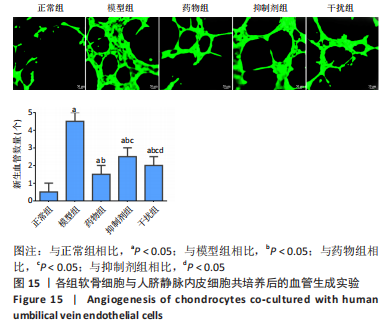
2.2.8 温阳通络胶囊通过miR-140/VEGF轴对大鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞的影响机制 在体内,当关节软骨组织处于关节炎病理状态中时,软骨组织中的miR-140的表达明显下降,VEGF的含量明显升高,白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的分泌升高,抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2与促凋亡蛋白Bax的表达失衡,大鼠软骨组织的解剖学损伤、病理损伤明显加重,软骨组织的细胞凋亡随之升高,软骨中的新生血管数量明显增多,促进关节炎的病程进展;当以温阳通络胶囊进行干预时,可明显逆转这些参数,达到改善骨关节炎的治疗效果。 在体外,软骨细胞ATDC5受白细胞介素1β炎性递质刺激,细胞中miR-140与VEGF的表达失衡,miR-140的表达明显下降,VEGF的含量明显升高,细胞的增殖活性明显下降,凋亡率明显升高,细胞上清液中白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的含量升高,人脐静脉内皮细胞成管性能明显升高,而当以温阳通络胶囊进行干预时可明显逆转这些参数,明显改善软骨细胞ATDC5的增殖活性、抑制其凋亡和促血管生成的能力,达到干预关节炎的目的。"

| [1] SUN J, SONG FH, WU JY, et al. Sestrin2 overexpression attenuates osteoarthritis pain via induction of AMPK/PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and suppression of neuroinflammation. Brain Behav Immun. 2022;102(5):53-70. [2] SOK D, RAVAL S, MCKINNEY J, et al. NSAIDs Reduce Therapeutic Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy in a Rodent Model of Posttraumatic Osteoarthritis. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(5):1389-1398. [3] 王宝娟,郑曙光,张琪,等.苗药熏蒸治疗膝骨关节炎模型兔可延缓细胞外基质的破坏[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(8):1236-1242. [4] 殷世云,吴晶金.温阳通络方抗胶原诱导性关节炎小鼠滑膜新生血管形成的机制研究[J].云南中医学院学报,2020,43(2):7-11. [5] 李慧,刘文刚,许学猛.温阳通络胶囊治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨关节炎30例临床观察[J].风湿病与关节炎,2019,8(6):24-26,37. [6] ENDISHA H, DATTA P, SHARMA A, et al. MicroRNA-34a-5p Promotes Joint Destruction During Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73(3):426-439. [7] WANG Y, SHEN S, LI Z, et al. MIR-140-5p affects chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation by targeting HMGB1 in osteoarthritis. Inflamm Res. 2020;69(1):63-73. [8] SI HB, YANG TM, LI L, et al. miR-140 Attenuates the Progression of Early-Stage Osteoarthritis by Retarding Chondrocyte Senescence. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19(3):15-30. [9] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. [10] SCOTT KM, COHEN DJ, BOYAN BD, et al. miR-122 and the WNT/β-catenin pathway inhibit effects of both interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α in articular chondrocytes in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(6):1053-1063. [11] LI D, WANG X, YI T, et al. LncRNA MINCR attenuates osteoarthritis progression via sponging miR-146a-5p to promote BMPR2 expression. Cell Cycle. 2022;18(1):1-16. [12] 李长喜,吴莉峰,袁湘中,等.通络胶囊对大鼠脑缺血损伤的保护作用研究[J].中南药学,2018,16(9):1233-1236. [13] TOWNSEND K, IMBERT I, EATON V, et al. Voluntary exercise blocks ongoing pain and diminishes bone remodeling while sparing protective mechanical pain in a rat model of advanced osteoarthritis pain. Pain. 2022;163(3):476-487. [14] CHENG C, TIAN J, ZHANG F, et al. WISP1 Protects Against Chondrocyte Senescence and Apoptosis by Regulating αvβ3 and PI3K/Akt Pathway in Osteoarthritis. DNA Cell Biol. 2021;40(4):629-637. [15] SUN X, MI L, DU G, et al. Platelet-rich plasma treatment alleviates osteoarthritis-related pain, inflammation, and apoptosis by upregulating the expression levels of microRNA-375 and microRNA-337. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(1):87-98. [16] WU G, XUE P, JIN H, et al. Upregulation of P2Y12 inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in lumbar osteoarthritis through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol Biol Rep. 2022;49(7):6459-6466. [17] LEE JS, GUO P, KLETT K, et al. VEGF-attenuated platelet-rich plasma improves therapeutic effect on cartilage repair. Biomater Sci. 2022; 10(9):2172-2181. [18] ZHANG H, SHAO Y, YAO Z, et al. Mechanical overloading promotes chondrocyte senescence and osteoarthritis development through downregulating FBXW7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022; 81(5):676-686. [19] LIU J, TANG G, LIU W, et al. MiR-20a-5p facilitates cartilage repair in osteoarthritis via suppressing mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 2. Bioengineered. 2022;13(5):13801-13814. [20] CHEN WG, ZHANG SS, Pan S, et al. α-Mangostin Treats Early-Stage Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis of Rat by Regulating the CAP-SIRT1 Pathway in Macrophages. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022;16(2):509-520. [21] YANG J, LI Q, WANG T, et al. Circular RNA triple functional domain promotes osteoarthritis’ development by modulating the microRNA-136-5p/Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6070-6079. [22] SUN T, WANG F, HU G, et al. Salvianolic acid B activates chondrocytes autophagy and reduces chondrocyte apoptosis in obese mice via the KCNQ1OT1/miR-128-3p/SIRT1 signaling pathways. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2022;19(1):53-70. [23] XU Y, DUAN L, LIU S, et al. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation in osteoarthritis by serving as a sponge for microRNA-199-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):11137-11145. [24] AO L, GAO H, JIA L, et al. Matrine inhibits synovial angiogenesis in collagen-induced arthritis rats by regulating HIF-VEGF-Ang and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol Immunol. 2022;141(1): 13-20. [25] WU S, YI Z, LING M, et al. DR4-Associated Death Receptor Signal Promotes Cartilage Damage in Patients With Kashin-Beck Disease. Cartilage. 2021;3(1):789S-796S. [26] SCOTT KM, COHEN DJ, BOYAN BD, et al. miR-122 and the WNT/β-catenin pathway inhibit effects of both interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α in articular chondrocytes in vitro. J Cell Biochem. 2022;123(6):1053-1063. [27] BU Y, WU H, DENG R, et al. The anti-angiogenesis mechanism of Geniposide on rheumatoid arthritis is related to the regulation of PTEN. Inflammopharmacology. 2022;30(3):1047-1062. [28] SCHWETLIK SN, BALDOCK KL, HILL CL, et al. Chronic Stress and Arthritis: A Scoping Review. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2022;74(6):982-996. [29] DE OLIVEIRA RCG, GARDEV E, et al. Dysbiotic relationship between arthritis and the oral-gut microbiome. A critical review. J Periodontal Res. 2022;57(4):711-723. [30] SOLOMON DH, BUCALA R, KAPLAN MJ, et al. Arthritis & Rheumatology: “Mid-Term” Report. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022;74(7):1099-1101. [31] KELLER SF, MANDELL BF. Management and Cure of Gouty Arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2022;48(2):479-492. [32] DONG W, WANG B, ZHANG R, et al. Therapeutic effects of acupuncture in rheumatoid arthritis are associated with centromere protein F expression. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2022;50(3):47-54. [33] HUANG CY, WU MY, HUANG MC, et al. The Association Between Acupuncture Therapies and Reduced Fracture Risk in Patients with Osteoarthritis: A Nationwide Retrospective Matched Cohort Study. J Integr Complement Med. 2022;28(5):418-426. [34] 洪坤豪,刘文刚,陈伟健,等.回旋正骨手法联合温阳通络胶囊治疗阳虚寒凝型膝骨关节炎的临床观察[J].天津中医药,2022,39(6): 715-719. [35] 朱咏梅,张田宁,方朝晖,等.温阳通络法联合理疗因子对糖尿病周围神经病变患者IL-6、TNF-α水平的影响[J].江西中医药大学学报,2020,32(5):30-33. [36] ZHAO J, LI T, LUO W. Silencing of circ-PRKCH protects against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-evoked chondrocyte damage and extracellular matrix loss by the miR-140-3p/ADAM10 axis. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2021;40(2):89-101. [37] LI H, LIU Z, GUO X, et al. Circ_0128846/miR-140-3p/JAK2 Network in Osteoarthritis Development. Immunol Invest. 2021;21(9):1-19. [38] KINGERY MT, ANIL U, BERLINBEERG EJ, et al. Changes in the Synovial Fluid Cytokine Profile of the Knee Between an Acute Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury and Surgical Reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 2022; 50(2):451-460. [39] BAGGIO C, BOSCARO C, OLIVIERO F, et al. Gender differences and pharmacological regulation of angiogenesis induced by synovial fluids in inflammatory arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;152(8):113181-113192. [40] CHILBULE SK, RAJAGOPAL K, WALTER N, et al. Role of WNT Agonists, BMP and VEGF Antagonists in Rescuing Osteoarthritic Knee Cartilage in a Rat Model. Indian J Orthop. 2021;56(1):24-33. [41] MENG Y, YIN D, QIU S, et al. Abrine promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of interleukin-1β-stimulated chondrocytes via PIM2/VEGF signalling in osteoarthritis. Phytomedicine. 2022;96(2):153906-153917. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Li Long, Li Guangdi, Shi Hao, Deng Keqi. Circular RNA as a competing endogenous RNA is involved in the regulation of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 751-757. |
| [5] | Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Li Zhe, Rong Weiming, Liao Shuning, Chen Lewei, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Screening and verification of key genes of necroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | Wan Guoli, Shi Chenhui, Wang Weishan, Li Ang, Shi Xunda, Cai Yi. Retrospective analysis of the influencing factors of chronic pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 558-564. |
| [7] | Gu Mingxi, Wang Bo, Tian Fengde, An Ning, Hao Ruihu, Wang Changcheng, Guo Lin. Comparison of early efficacy and safety of simultaneous and staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [8] | Yu He, Zheng Jiafa, Song Xiufeng, Guan Shengyi. Tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis with blood supplied fibular flap combined with hollow screw in the treatment of end-stage ankle osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 588-593. |
| [9] | Guo Yingqi, Gong Xianxu, Zhang Yan, Xiao Han, Wang Ye, Gu Wenguang. Meniscus extrusion and patellofemoral joint cartilage injury and bone marrow lesions: MRI semi-quantitative score [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [10] | Yu Jiaan, Liu Xinwei, Lian Hongyu, Liu Kexin, Li Zitao. Medial open-wedge tibial osteotomy versus lateral closed-wedge tibial osteotomy for unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 632-639. |
| [11] | Zhang Hui, Wang Jiayang, Wang Qian, Gan Hongquan, Wang Zhiqiang. Effects of hyaluronic acid combined with domestic porous tantalum on chondrocyte function under the dynamic environment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 339-345. |
| [12] | Chen Changmei, Zeng Xianchun, Wang Rongpin, Wu Jiahong. Sex and age differences in the anatomical parameters of normal knee joints evaluated by X-ray [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4647-4651. |
| [13] | Li Shaocong, He Qi, Pan Zhaofeng, Yang Junzheng, Chen Bohao, Wang Haibin, Zhou Chi. Effect of iron overload on cartilaginous tissue in a mouse model of knee osteoarthritis evaluated by micro-CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4658-4663. |
| [14] | Ma Wei, Pang Jian, Zhang Jiefan, Xu Kun, Wang Yongyu, Zhang Min, Chen Bo, Shi Ying, Zhan Hongsheng. Analysis of influencing factors of fear of falling in patients with knee osteoarthritis and construction of nomogram model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4690-4695. |
| [15] | Chen Cai, Zeng Ping, Liu Jinfu. Long non-coding RNAs regulate osteoarthritis by mediating chondrocyte-related mechanisms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4729-4735. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||