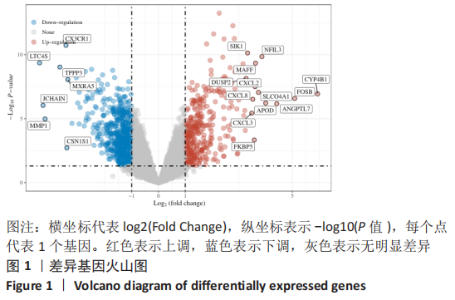
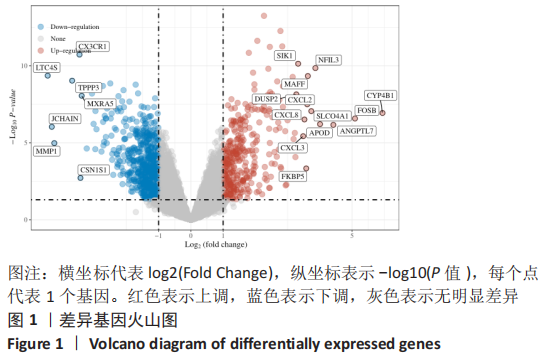
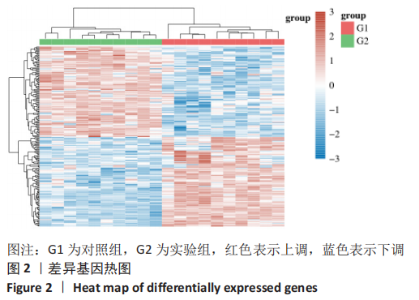
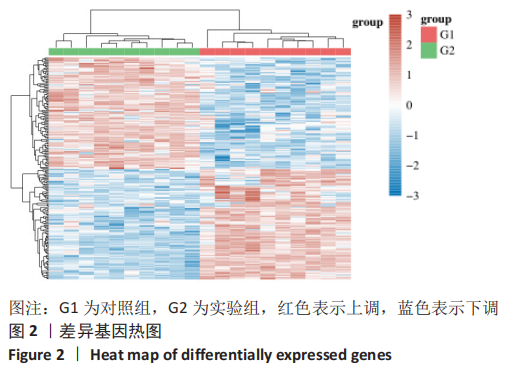
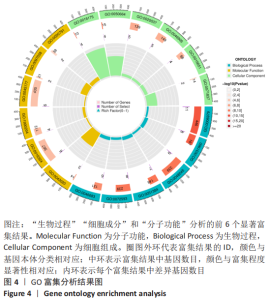
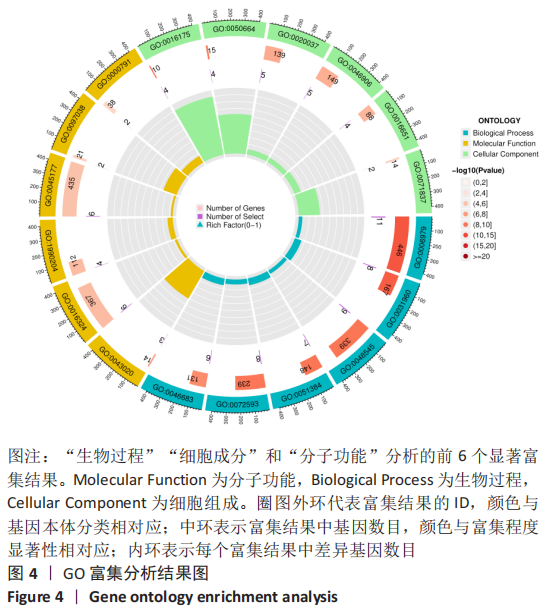
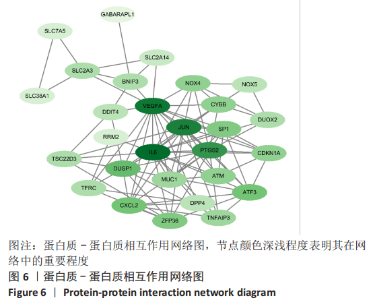
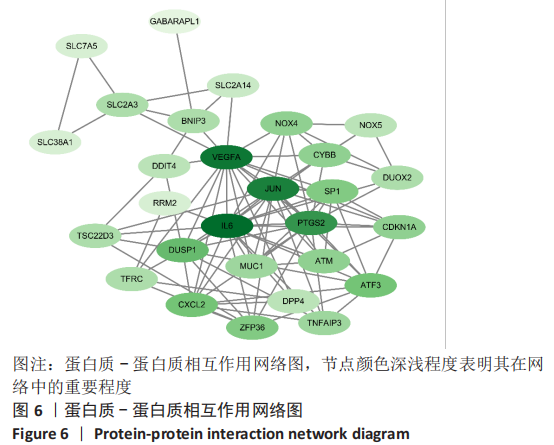
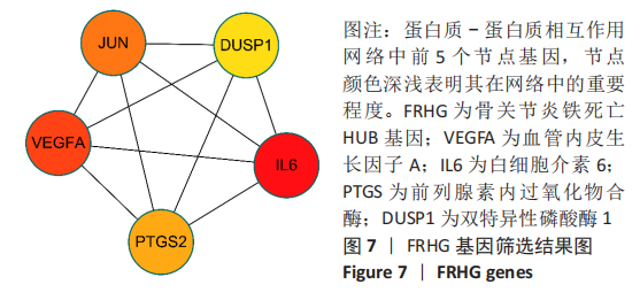
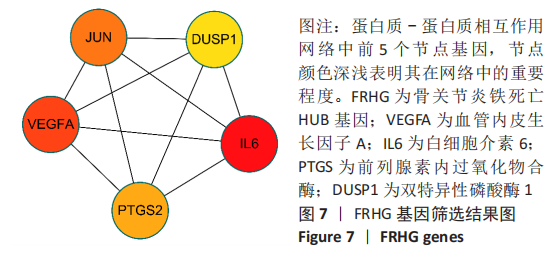
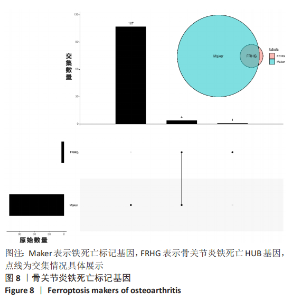
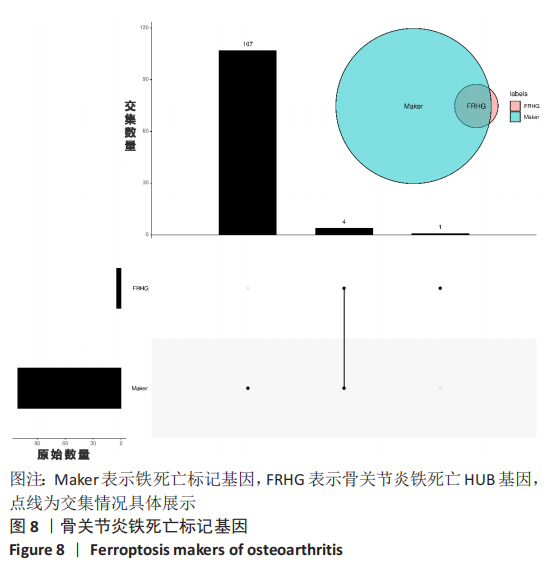
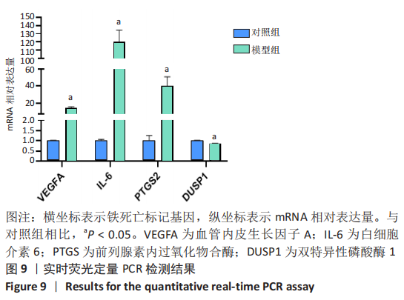
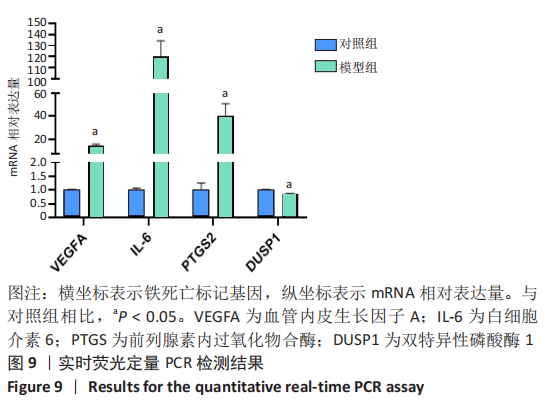
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (17): 2637-2643.doi: 10.12307/2023.437
Bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis
Li Zhe1, Yuan Changshen2, Guan Yanbing1, Xu Wenfei2, Liao Shuning1, Rong Weiming1, Mei Qijie2, Duan Kan2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2022-05-31Accepted:2022-07-05Online:2023-06-18Published:2022-10-20 -
Contact:Yuan Changshen, Master, Associate chief physician, Orthopedic Department of the Limbs, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Li Zhe, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Nos. 82060875 (to YCS) and 82160912 (to DK); Natural Science Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019QN022 (to YCS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhe, Yuan Changshen, Guan Yanbing, Xu Wenfei, Liao Shuning, Rong Weiming, Mei Qijie, Duan Kan. Bioinformatic analysis and experimental validation of ferroptosis in osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(17): 2637-2643.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
|
[1] STOCKWELL BR, JIANG X, GU W. Emerging mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosi. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30(6):478-490. |
| [1] | He Xi, Wan Yu, Tang Yuting, Yang Anning, Wu Kai, Jiao Yun, Bai Zhigang, Jiang Yideng, Shen Jiangyong. Erastin inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [3] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [4] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [5] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [6] | Cao Sheng, Kong Lingwei, Xu Kun, Sun Zhijie. Correlation of cervical sagittal force line parameters with degenerative segment and Pfirrmann classification in patients with cervical intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1319-1324. |
| [7] | Li Xiaomin, Tian Xiangdong, Tan Yetong, Zhu Guangyu, Wang Rongtian, Wang Jian, Xue Zhipeng, Ma Sheng, Hu Yuanyi, Huang Ye, Ding Tiansong. Changes of lower limb force line and knee function after high tibial osteotomy in osteoporotic medial ventricular knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [8] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [9] | Tang Liang, Li Xiheng, Niu Ruijuan, Li Xinyue, Zou Xinying, Mao Tianjiao, Li Jiang. Naringin regulates the function of RAW264.7 macrophages to affect the osteogenic differentiation of MC-3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1205-1210. |
| [10] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [11] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [12] | Zhang Yongqiang, Pan Feng, Sun Peng, Tan Minghui, Xuan Liuming, Wang Qinzhang. Effect of Gja1 gene recombinant lentivirus on Cx43 protein and mRNA expression in a diabetic guinea pig bladder model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1161-1165. |
| [13] | Zhao Lu, Zhao Yifei, Gao Da, Liu Yanfang, Fu Tingting, Xu Jiangyan. Expression of suppressor of Zeste 12 in kidney tissues of rats with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1179-1186. |
| [14] | Lian Shilin, Zhang Yan, Jiang Qiang, Zhang Hanshuo, Li Tusheng, Ding Yu. Interventional effects of whole blood and platelet-rich plasma with different preparation methods on nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1199-1204. |
| [15] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||