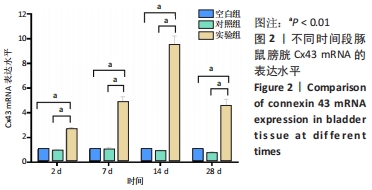
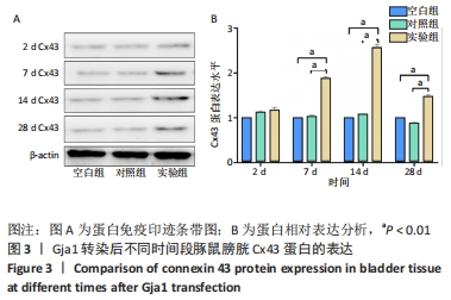
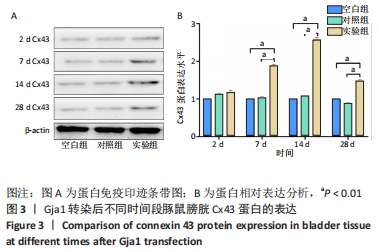
[1] OGURTSOVA K, DA ROCHA FERNANDES JD, HUANG Y, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40-50.
[2] YUAN Z, TANG Z, HE C, et al. Diabetic cystopathy: A review.J Diabetes. 2015;7(4):442-447.
[3] 郭文敏, 孙李斌, 王东文. 糖尿病膀胱研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020,23(17):2095-2101.
[4] NICHOLS GA, BRODOVICZ KG, KIMES TM, et al. Prevalence and incidence of urinary tract and genital infections among patients with and without type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complications. 2017;31(11): 1587-1591.
[5] LIU Y, WANG X, WANG L, et al. Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts the Presence of Diabetic Neurogenic Bladder. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022;15:7-13.
[6] BOLGEO T, MACONI A, BERTOLOTTI M, et al. Physiopathology of the diabetic bladder. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2020;92(4). doi: 10.4081/aiua.2020.4.314.
[7] 乔颜春,孙青. 连接蛋白Connexin43的研究进展[J]. 国际病理科学与临床杂志,2005,25(4):345-347.
[8] 石瑶瑶, 崔玉双, 高宏程, 等. 缝隙连接蛋白43在糖尿病视网膜病变中的作用[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2021,21(2):144-147.
[9] MOLICA F, FIGUEROA XF, KWAK BR, et al. Connexins and Pannexins in Vascular Function and Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1663.
[10] TAŞDELEN E, DURMAZ CD, KARABULUT HG. Autosomal Recessive Oculodentodigital Dysplasia: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2018;154(4):181-186.
[11] 李朋, 钱彪, 申茂磊, 等. 缝隙连接蛋白-43在糖尿病膀胱豚鼠模型中的表达及意义[J]. 天津医药,2020,48(1):25-29.
[12] Poladia DP, Schanbacher B, Wallace LJ, et al. Innervation and connexin isoform expression during diabetes-related bladder dysfunction: early structural vs. neuronal remodelling. Acta Diabetol. 2005;42(3):147-152.
[13] Rizk D, Padmanabhan RK, Tariq S, et al. Ultra-structural morphological abnormalities of the urinary bladder in streptozotocin-induced diabetic female rats. Int Urogynecol J Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2006;17(2):143-154.
[14] KONO J, UEDA M, SENGIKU A, et al. Urothelium-Specific Deletion of Connexin43 in the Mouse Urinary Bladder Alters Distension-Induced ATP Release and Voiding Behavior. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1594.
[15] COLE JB, FLOREZ JC. Genetics of diabetes mellitus and diabetes complications. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16(7):377-390.
[16] EID S, SAS KM, ABCOUWER SF, et al. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications: role of lipids and lipid metabolism. Diabetologia. 2019;62(9):1539-1549.
[17] POWELL CR. Is the Diabetic Bladder a Neurogenic Bladder? Evidence from the Literature. Curr Bladder Dysfunct Rep. 2014;9(4):261-267.
[18] ESTEGHAMATI A, RASHIDI A, NIKFALLAH A, et al. The association between urodynamic findings and microvascular complications in patients with long-term type 2 diabetes but without voiding symptoms. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2007;78(1):42-50.
[19] OSHIRO T, MIYAZATO M, SAITO S. Relationship between connexin43-derived gap junction proteins in the bladder and age-related detrusor underactivity in rats. Life Sci. 2014;116(1):37-42.
[20] HARRIS AL. Electrical coupling and its channels. J Gen Physiol. 2018; 150(12):1606-1639.
[21] BEYER EC, BERTHOUD VM. Gap junction gene and protein families: Connexins, innexins, and pannexins. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018;1860(1):5-8.
[22] GÜIZA J, BARRÍA I, SÁEZ JC, et al. Innexins: Expression, Regulation, and Functions. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1414.
[23] SCHULZ R, GORGE PM, GORBE A, et al. Connexin 43 is an emerging therapeutic target in ischemia/reperfusion injury, cardioprotection and neuroprotection. Pharmacol Ther. 2015;153:90-106.
[24] LEITHE E. Regulation of connexins by the ubiquitin system: Implications for intercellular communication and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1865(2):133-146.
[25] HULSMANS M, CLAUSS S, XIAO L, et al. Macrophages Facilitate Electrical Conduction in the Heart. Cell. 2017;169(3):510.
[26] MUGISHO O, GREEN C, ZHANG J, et al. Immunohistochemical Characterization of Connexin43 Expression in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Retinopathy and in Human Donor Retinas. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(12):2567.
[27] FANIKU C, O SHAUGHNESSY E, LORRAINE C, et al. The Connexin Mimetic Peptide Gap27 and Cx43-Knockdown Reveal Differential Roles for Connexin43 in Wound Closure Events in Skin Model Systems. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):604.
[28] SEKIDO N, OTSUKI T, KIDA J, et al. EP2 and EP3 receptors as therapeutic targets for underactive bladder/detrusor underactivity due to diabetic cystopathy in a type 1 diabetic rat model. Lower Urin Tract Symptoms. 2020;12(3):285-291.
[29] LI K, YAO J, SAWADA N, et al. beta-Catenin signaling contributes to platelet derived growth factor elicited bladder smooth muscle cell contraction through up-regulation of Cx43 expression. J Urol. 2012; 188(1):307-315.
[30] IMAMURA M, NEGORO H, KANEMATSU A, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor causes urinary bladder overactivity through gap junction generation in the smooth muscle. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 297(1):F46-F54.
[31] HUANG Y, GAO J, ZHOU Y, et al. Therapeutic effect of integrin-linked kinase gene-modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for streptozotocin-induced diabetic cystopathy in a rat model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):278.
[32] 罗广承, 何志华, 罗建珍, 等. 构建糖尿病膀胱病豚鼠模型及其尿动力学评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(7):1063-1068.
[33] PODELL BK, ACKART DF, RICHARDSON MA, et al. A model of type 2 diabetes in the guinea pig using sequential diet-induced glucose intolerance and streptozotocin treatment.Dis Model Mech. 2017;10(2): 151-162.
[34] 魏艳青, 王江平, 王勤章, 等. 经尿道灌注慢病毒转染豚鼠膀胱的研究[J]. 天津医药,2015,43(11):1275-1277.
|