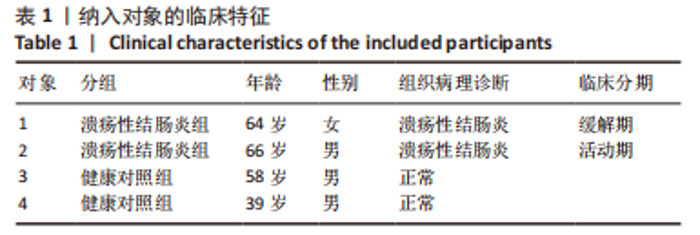
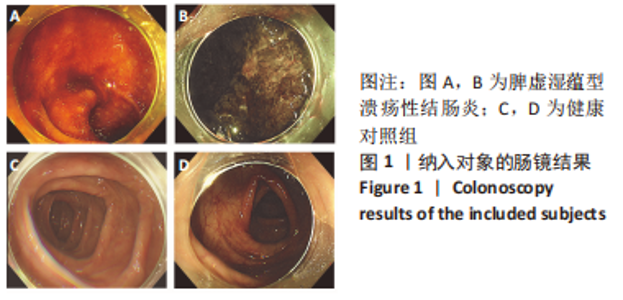
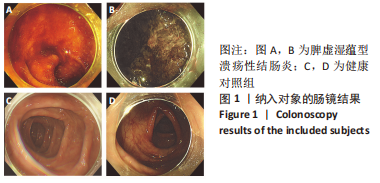
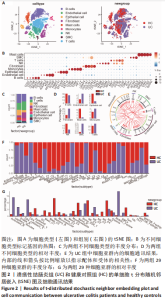
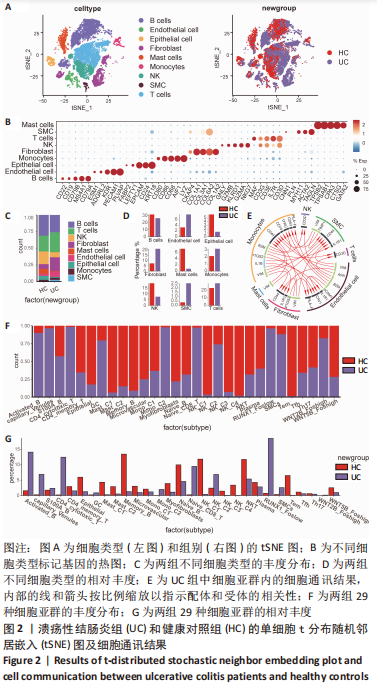
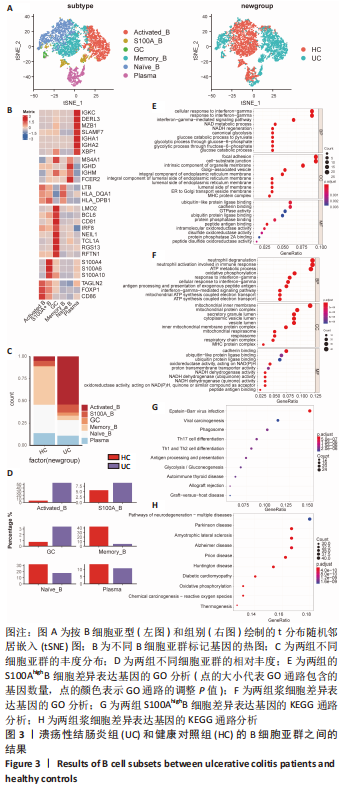
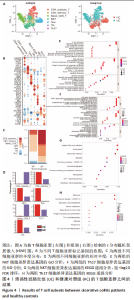
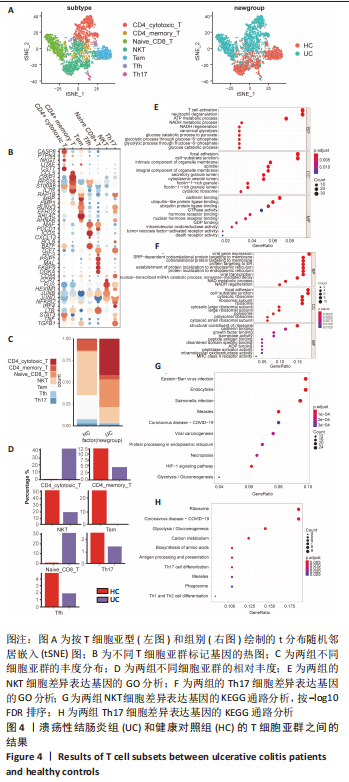
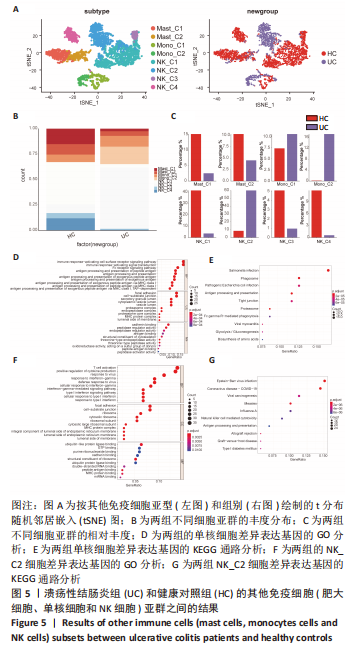
[1] UNGARO R, MEHANDRU S, ALLEN PB, et al. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2017; 389(10080):1756-1770.
[2] 梁园,江小柯,白阳秋,等.间充质干细胞治疗溃疡性结肠炎:可能与可行[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):4065-4069.
[3] 崔世超,柳越冬.溃疡性结肠炎的中医治疗思路[J].辽宁中医杂志,2017,44(7): 1381-1384.
[4] 张天涵,沈洪.溃疡性结肠炎及其中医辨证分型与炎症活动性指标的相关性分析[J].北京中医药大学学报,2019,42(8):685-690.
[5] 余今菁,李欢,胡邱宇,等.基于高通量测序技术的溃疡性结肠炎患者肠道菌群多样性研究[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2018,47(4):460-465.
[6] 梁艳妮,程雯,吴柯楠,等.基于高通量测序技术研究靛玉红对溃疡性结肠炎小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J].中草药,2021,52(13):3896-3904.
[7] 吴小倩,黄伟芳,孔德松,等.基于生物信息学探讨丹参酮ⅡA治疗溃疡性结肠炎及其机制[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(12):1750-1756.
[8] 胡宗仁,郑文江,严倩,等.溃疡性结肠炎差异表达基因及中药预测的生物信息学分析[J].中国中药杂志,2020,45(7):1684-1690.
[9] OLSEN TK, BARYAWNO N. Introduction to Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2018;122(1):e57.
[10] ZIEGENHAIN C, VIETH B, PAREKH S, et al. Comparative Analysis of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Methods. Mol Cell. 2017;65(4):631-643.e4.
[11] LEE TL. Single cell genomics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019;116:105596.
[12] LEI Y, TANG R, XU J, et al. Applications of single-cell sequencing in cancer research: progress and perspectives. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14(1):91.
[13] HEDLUND E, DENG Q. Single-cell RNA sequencing: Technical advancements and biological applications. Mol Aspects Med. 2018;59:36-46.
[14] LUO Y, LIU S, LI H, et al. Mass Cytometry and Single-Cell Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Immune Cell Characteristics of Ulcerative Colitis. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:859645.
[15] 吴开春,梁洁,冉志华,等.炎症性肠病诊断与治疗的共识意见(2018年,北京)[J].中华消化杂志,2018,38(5):292-311.
[16] 张声生,沈洪,郑凯,等.溃疡性结肠炎中医诊疗专家共识意见(2017)[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(8):3585-3589.
[17] VIETH B, PAREKH S, ZIEGENHAIN C, et al. A systematic evaluation of single cell RNA-seq analysis pipelines. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):4667.
[18] VAN DER MAATEN L. Accelerating t-SNE using Tree-Based Algorithms. J Mach Learn Res. 2014; 15(1):3221-3245.
[19] SMILLIE CS, BITON M, ORDOVAS-MONTANES J, et al. Intra- and Inter-cellular Rewiring of the Human Colon during Ulcerative Colitis. Cell. 2019;178(3):714-730.e22.
[20] BUTLER A, HOFFMAN P, SMIBERT P, et al. Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36(5):411-420.
[21] FRIEDRICH M, POHIN M, POWRIE F. Cytokine Networks in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Immunity. 2019;50(4):992-1006.
[22] BROZ F, NEHANIV CL, BELPAEME T, et al. The ITALK project: a developmental robotics approach to the study of individual, social, and linguistic learning. Top Cogn Sci. 2014;6(3):534-544.
[23] YU LC. Microbiota dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancers: exploring a common ground hypothesis. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):79.
[24] KHAN I, ULLAH N, ZHA L, et al. Alteration of Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Cause or Consequence? IBD Treatment Targeting the Gut Microbiome. Pathogens. 2019;8(3):126.
[25] CORRIDONI D, ANTANAVICIUTE A, GUPTA T, et al. Single-cell atlas of colonic CD8+ T cells in ulcerative colitis. Nat Med. 2020;26(9):1480-1490.
[26] 刘杰民,蔺晓源,王敏,等.基于肠道黏膜免疫的“脾为之卫”理论探讨[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2013,19(4):460-466.
[27] 孙莺.自然杀伤T细胞在溃疡性结肠炎不同证型患者的表达与意义[J].海南医学院学报,2013,19(10):1386-1389.
[28] MISKA J, LEE-CHANG C, RASHIDI A, et al. HIF-1α Is a Metabolic Switch between Glycolytic-Driven Migration and Oxidative Phosphorylation-Driven Immunosuppression of Tregs in Glioblastoma. Cell Rep. 2019;27(1):226-237.e4.
[29] SHI LZ, WANG R, HUANG G, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells. J Exp Med. 2011;208(7):1367-1376.
[30] SÁEZ DE GUINOA J, JIMENO R, GAYA M, et al. CD1d-mediated lipid presentation by CD11c+ cells regulates intestinal homeostasis. EMBO J. 2018;37(5):e97537.
[31] 张艺凡,沈倍奋,宋伦.生发中心B淋巴细胞活化机制研究进展[J].生物技术通讯,2020,31(2):209-213.
[32] ZENG ML, ZHU XJ, LIU J, et al. An Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis of the S100 Gene Family for the Prognosis of Colorectal Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:4746929.
[33] OLÉN O, ERICHSEN R, SACHS MC, et al. Colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a Scandinavian population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395(10218):123-131.
[34] SMIDS C, HORJUS TALABUR HORJE CS, DRYLEWICZ J, et al. Intestinal T Cell Profiling in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Linking T Cell Subsets to Disease Activity and Disease Course. J Crohns Colitis. 2018;12(4):465-475.
[35] DONNARUMMA T, YOUNG GR, MERKENSCHLAGER J, et al. Opposing Development of Cytotoxic and Follicular Helper CD4 T Cells Controlled by the TCF-1-Bcl6 Nexus. Cell Rep. 2016;17(6):1571-1583.
[36] SOHNI A, TAN K, SONG HW, et al. The Neonatal and Adult Human Testis Defined at the Single-Cell Level. Cell Rep. 2019;26(6):1501-1517.e4.
[37] PAULSON KG, VOILLET V, MCAFEE MS, et al. Acquired cancer resistance to combination immunotherapy from transcriptional loss of class I HLA. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3868.
|