Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3883-3891.doi: 10.12307/2023.680
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exosome-mediated cellular communication: a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease
Wang Yiying1, Li Ruiqing1, 2, Li Jingwen1, Mei Jinjin1, Zhang Jianyun1, Zhang Lihong1, Fan Yongfu1, Guo Jian1, 2
- 1School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Rehabilitation Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-09-05Accepted:2022-10-20Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-19 -
Contact:Li Ruiqing, Attending physician, Master’s supervisor, School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; Rehabilitation Center, The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Yiying, Master candidate, School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation for Youth Program, No. 81503630 (to LRQ); Key Scientific Research Project of Colleges and Universities in Henan Province, No. 21A360023 (to LRQ); Henan Province Scientific Research Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 2019ZY2129 (to LRQ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yiying, Li Ruiqing, Li Jingwen, Mei Jinjin, Zhang Jianyun, Zhang Lihong, Fan Yongfu, Guo Jian. Exosome-mediated cellular communication: a potential biomarker for Parkinson’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3883-3891.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
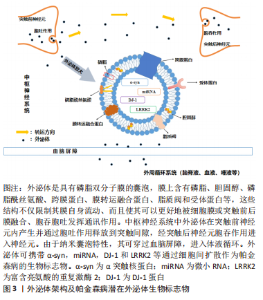
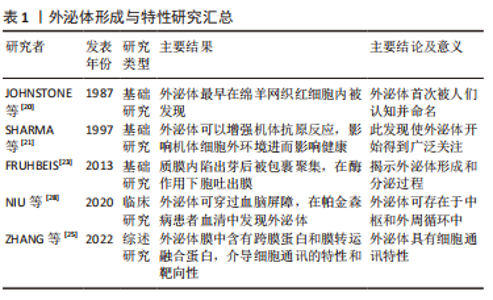
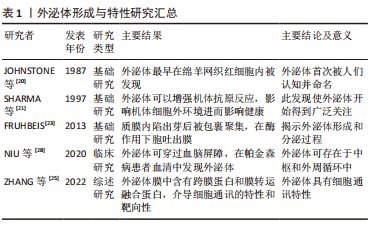
2.1 外泌体形成与特性 2.1.1 外泌体的形成 细胞外囊泡是由磷脂双分子层膜组成的小颗粒,由不同细胞在生理和病理状态下释放。根据它们的生物起源,细胞外囊泡主要分为3类,即凋亡小体(直径1 000-5 000 nm)、微泡(直径200-1 000 nm)和外泌体(直径30-150 nm)[17-18],其中外泌体最早是1983年在绵羊网织红细胞内被发现的[19-20]。有研究表明,外泌体可以刺激T细胞增殖,增强人体抗原和免疫反应[21]。几乎所有类型的细胞都会产生和释放外泌体,其可以通过微生物攻击、细胞外刺激和其他应激的诱导生成。目前多数观点认为外泌体的形成是由于质膜首先向内发生凹陷和出芽形成早期的内体,早期内体再经过出芽包裹细胞内容物,形成多个腔内小囊泡,由这些腔内小囊泡构成多泡体,后者最后在鸟苷三磷酸酶家族中Rab酶的调节下与细胞膜融合通过胞吐的模式向细胞膜外分泌腔内囊泡,这些细胞外囊泡即是外泌体[22-23]。 2.1.2 外泌体的细胞通讯特性及作为帕金森病生物标志物的细胞通讯方式 外泌体几乎存在于所有的组织、细胞间隙和体液中,在电镜下呈杯状或双凹碟形,其磷脂双分子层膜中有跨膜蛋白和膜转运融合蛋白以及受体蛋白使其更好地被膜融合、胞吞胞吐发挥通讯作用。膜上有脂质筏,且富含胆固醇及磷脂酰丝氨酸等物质,限制膜的流动,并参与包括跨膜信号转导、物质内吞、脂质及蛋白定向分选等多种功能[24]。外泌体可将携带的物质分子从供体细胞转移到受体细胞,从而引发后者产生变化的特性称为外泌体的细胞通讯作用,同时该物质也被认为参与细胞通讯并传递信息至另一受体细胞。外泌体可以具有不同的内容物和生理功能,其内可含有核酸、蛋白质、脂质和其他物质,可以循环传递到相邻和远处的细胞,但是外泌体都具有细胞间通讯的特性和靶向性[25]。 外泌体介导的细胞通讯主要有3种模式:①通过膜融合将携带的内容物释放至受体细胞内完成信息转运交流;②膜表面携带和产生的信号分子进行细胞信息的交流转运;③信号分子在细胞外即被释放从而进行信息交流。而现阶段研究发现外泌体携带帕金森病生物标志物的细胞通讯方式大多数是通过第一种膜融合释放至受体细胞的机制发挥作用。 2.1.3 外泌体与血脑屏障 由于外泌体的外周可用性、胶囊囊泡的特性以及穿越血脑屏障的通讯能力和优越的靶向性,在脑脊液、血液和唾液中均发现其踪迹[26-28],因此增加了用作帕金森病生物标志物的可能性,从而证明其在帕金森病诊断中的应用价值[29-30]。JIANG等[31]从血清中分离出帕金森病患者和健康对照组的外泌体,用无标记定量蛋白质组学通过质谱法分析外泌体蛋白,共鉴定出429种蛋白质,其中帕金森病患者中色素上皮因子、载脂蛋白D和J等7种蛋白的表达水平显著升高,补体C1q和蛋白质免疫球蛋白Lambda变量1-33(IGLV1-33)等7种蛋白的表达水平均有所下降,通过基因本体学和京都基因与基因组富集百科全书分析这些差异表达的蛋白质被证实其可作为早期帕金森病诊断的潜在生物标志物。外泌体的这种纳米囊泡特性、优越的血脑屏障穿透能力和靶向性都证明了其可作为诊断帕金森病的生物标志物,从而为帕金森病患者的早发现、早诊断提供基础和保障。 外泌体架构及帕金森病潜在外泌体生物标志物,见图3;外泌体形成与特性研究,见表1。"
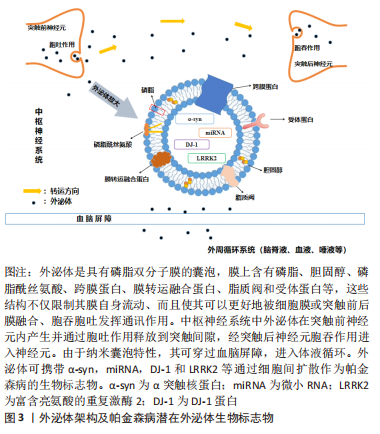

因此,外泌体在供体细胞中形成,通过细胞间通讯、物质运输交换、细胞间信号释放等方式,传递信号并向受体细胞靶向扩散,完成神经元之间或胶质细胞与神经元之间的细胞通讯。同时由于其纳米囊泡的特性,可以透过血脑屏障,进入外周循环中,使其能够在体液中被检测出来,增加其成为临床诊断生物标志物的可行性。 2.2 外泌体可作为帕金森病生物标志物 目前帕金森病的诊断方法主要是基于神经系统症状和大脑成像技术,但这些方法通常不精确并且耗时过长,医生在确诊之前需要对患者进行一段时间的监测。从症状发作到神经系统的诊断之间大约滞后12个月,大部分帕金森病在出现运动症状时才被发现和诊断,但此时几乎70%的多巴胺神经元已经丢失[32]。因此,具有高度可靠性的生物标志物对于帕金森病的诊断、疾病进展监测和治疗反应评估是十分必要的。而识别可靠生物标志物最具挑战性的是帕金森病受限于中枢神经系统特定位置的特定神经元[33-34]。基于这一观点,这些特定神经细胞释放的外泌体及其所携带的因子介导细胞通讯作为帕金森病生物标志物就成为目前研究的重点。研究外泌体作为帕金森病诊断的生物标志物至关重要的一点是其参与帕金森病中的各种病理机制。图4为帕金森病的主要外泌体生物标志物及其不同的病理机制。"
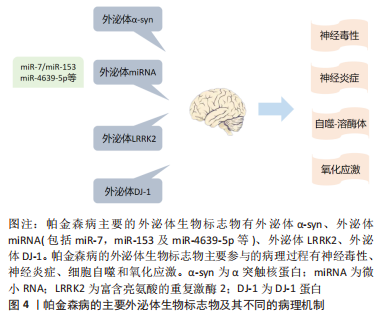
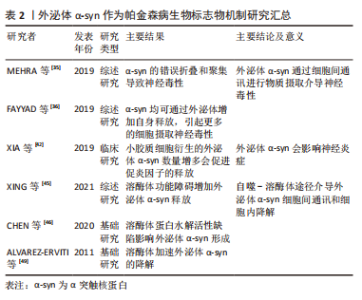
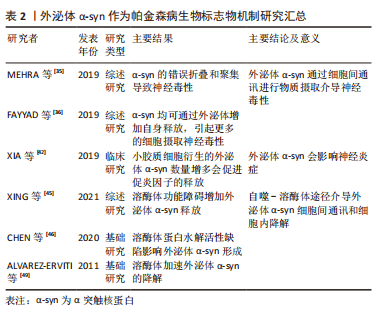
2.2.1 外泌体α-syn 外泌体α-syn与神经毒性:帕金森病认可度较高的生物标志物为α-syn,并且由于外泌体胶囊囊泡的特性,在脑脊液、血液等体液中均可发现其踪迹[26-27]。α-syn单体在氨基末端被酰化,因此可以拼凑成紧凑的构象即低聚物,后者聚集形成可溶性原纤维或细丝,若结构发生变化就会变为不溶性原纤维,纤维前低聚物播种和加速α-syn单体的聚集形成寡聚体,其毒性远大于成熟的聚集纤维。较大的寡聚体或原纤维已被证明会损害线粒体和内质网等几种胞质细胞器的功能,从而破坏突触的电生理功能。α-syn的错误折叠和聚集及其在路易体中的沉积导致了与帕金森病相关的自主介导的神经毒性[35]。研究表明,在外泌体内部可以检测到单体和低聚物α-syn,无论α-syn结构的大小均可通过外泌体进行神经元之间的交换从而导致神经毒性[36],α-syn在神经母细胞瘤细胞中的过度表达导致其外泌体释放就证明了这一观点。 外泌体介导的细胞间通讯是不同疾病致病机制中的必要组成部分,也是帕金森病发病和进展中作用的基础之一,它们可能通过调节、摄取和转移异常的α-syn至邻近细胞从而促进帕金森病进展。此外,外泌体可能增加α-syn介导的神经毒性,因为这些与外泌体相关的低聚物比非细胞外囊泡低聚物具有更高的细胞摄取和神经毒性[37]。有研究表明,外泌体可以将α-syn低聚物从受损神经元转运到正常神经元[38],诱导聚集体形成和细胞死亡。体外研究表明,当从帕金森病患者脑脊液中分离外泌体时,外泌体可加速α-syn的聚集[39];相反,从对照患者脑脊液中分离的外泌体不会以任何方式影响α-syn的聚集。一些研究发现,非震颤患者血浆神经源性外泌体中α-syn的含量高于震颤患者[40],因此它也可用于识别帕金森病中运动与非运动障碍等不同的类型。以上研究结果均说明,神经元来源的外泌体能够通过调节、转移和摄取α-syn影响细胞间通讯和信息转移,进而调节细胞的神经毒性和帕金森病的发生进展。因此,外泌体α-syn作为早发现早诊断帕金森病的生物标志物,在很大程度上能够减缓神经毒性的侵袭,延缓帕金森病的进程。 外泌体α-syn与神经炎症:外泌体介导细胞通讯特性揭示了外泌体α-syn可以在神经元之间以及从神经元扩散到神经胶质细胞的潜在机制,而这种扩散通讯的机制反过来会增加促炎因子的释放,进一步加剧细胞毒性和神经炎症。小胶质细胞是大脑中的主要吞噬细胞,主要功能是通过吞噬作用降解细胞外α-syn并去除不同大脑区域中的聚集蛋白,其已被充分证明是神经炎症的诱导剂,在通过外泌体途径传递α-syn中也起着至关重要的作用[41-42]。小胶质细胞介导的神经炎症是由α-syn诱导促炎细胞因子释放引起的,这些促炎细胞因子被证明参与帕金森病进展和发病机制[43],小胶质细胞释放的外泌体α-syn通过胞吐作用被释放至细胞间隙,后被受体神经元胞吞重新摄入并能够在受体神经元中诱导蛋白质聚集,并且帕金森病患者的脑脊液中小胶质细胞衍生的外泌体总α-syn水平更高,介导和促进炎症递质白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18和肿瘤坏死因子α的信息交流,使促炎因子进一步释放导致神经炎症和神经变性显著增加进而影响帕金森病进展[44]。小胶质细胞介导神经炎症释放的外泌体α-syn成为诊断帕金森病的生物标志物,这提示研究者从介导细胞通讯过程减轻神经炎症反应进而减缓帕金森病发生进展这一角度思考,因此还可作为帕金森病新的诊疗靶点,对帕金森病实现早发现早干预。 外泌体α-syn与自噬-溶酶体:外泌体α-syn的发生和自噬是通过溶酶体途径连接,自噬是溶酶体依赖性降解和循环途径,溶酶体功能障碍可增加外泌体介导的α-syn释放和传播[45]。外泌体α-syn的堆积可能是由于溶酶体的蛋白水解活性缺陷引起的[46],为了避免其细胞内积累,α-syn依赖外泌体细胞通讯的特性在供体细胞(神经元或神经胶质细胞)内加载并随外泌体向外部及受体细胞分泌[47]。通过自噬-溶酶体途径这种方式,外泌体介导了两个过程:一方面,它们在细胞之间传播α-syn,而另一方面,一旦进入靶细胞外泌体就会被输送到溶酶体,在那里α-syn最终可以被降解[48-49]。过度自噬或是溶酶体功能障碍导致的机体微环境失衡都会调控外泌体α-syn在细胞通讯中的释放进而影响帕金森病的病理进展。因此以上发现均证明外泌体α-syn通过自噬-溶酶体途径在帕金森病病理学中发挥的关键作用,不仅能作为生物标志物的可能来源,而且可作为治疗干预的合适靶标。 文章总结了外泌体α-syn作为帕金森病生物标志物机制研究进展,见表2。"
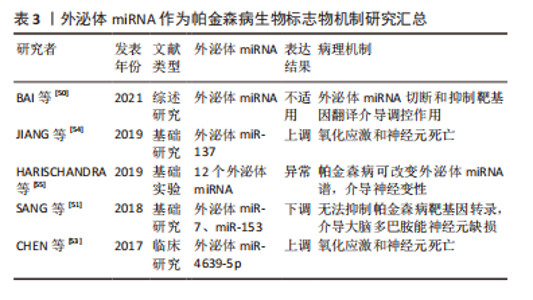
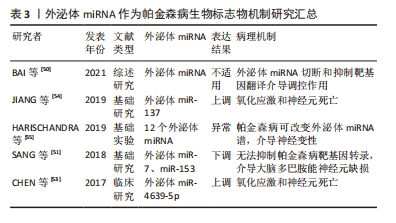
2.2.2 外泌体miRNA 外泌体miRNA靶向帕金森病相关基因:外泌体还可通过介导其在细胞通讯之间转移遗传物质和进行遗传信息交换或输入的能力参与到帕金森病的发病机制中。miRNAs(Micro RNAs)是由内源基因编码的单链小RNA分子,被称为转录后的基因调节器。一个miRNA可以调控多个基因的表达,人类机体内1/3的基因都被miRNA调节。miRNA发挥调控作用主要是通过切断靶基因的信使RNA(message RNA,mRNA)分子、抑制靶基因翻译的方式[50]。神经元将miRNA包裹到外泌体中,并运输至胶质细胞参与帕金森病的生理病理过程。这些神经元性外泌体miRNA通过胞吐胞吞作用在细胞间传递遗传物质并靶向至帕金森病相关基因,如miR-7和miR-153可与SNCA mRNA的3’-端非编码区结合,抑制其转录。因此,miR-7和miR-153的缺失无法抑制SNCA mRNA的转录,会导致帕金森病患者大脑中α-syn上调、聚集和多巴胺能神经元损失增加,反之则可以发挥保护细胞的作用[51-52]。以上研究提示,外泌体miRNA不仅可作为诊断帕金森病的生物标志物,而且可以通过细胞通讯作用被运输至胶质细胞上调其外泌体miRNA的表达,进而调控帕金森病的相关靶基因对帕金森病发生发展起到延缓和发挥脑保护的作用,可作为治疗的新靶点。 外泌体miRNA与氧化应激:有一些外泌体miRNA影响细胞的氧化应激,促进帕金森病病理机制的进展。CHEN等[53]研究证明,外泌体包裹miR-4639-5p在转录后水平上负调节DJ-1,DJ-1是一种众所周知的在细胞氧化应激反应中起着至关重要的作用的因子。miR-4639-5p的异常上调导致DJ-1蛋白水平下调,从而造成严重的氧化应激和神经元死亡。同时,还有研究发现,外泌体相关的miR-137在帕金森病的神经元中上调,其直接靶向氧化抗性1(oxidation resistance gene 1,OXR-1)蛋白对其表达进行负调节,从而诱导氧化应激的发生,促进神经元的毒性和死亡[54]。外泌体miRNA通过神经元之间的细胞交流通讯和信息转移调节氧化应激系统中重要的关键蛋白,影响细胞内脂质氧化程度进而调控细胞的生存与死亡。因此,早期发现神经元之间外泌体miRNA的转移和表达变化或许可以防止脂质过氧化,恢复氧化还原平衡,保护细胞并减缓帕金森病的进展。 长期暴露于神经毒性物质(锰)环境会导致伴有运动功能障碍的帕金森病发生[55]。HARISCHANDRA等[56]利用体外细胞模型,进行锰暴露处理后发现,细胞外泌体分泌显著增加,且改变了细胞分泌的外泌体miRNA谱,其中发现了12个miRNA(miR-210-5p,miR-128-1-5p,miR-450b-3p,miR-24-2-5p,miR-505,miR-325-5p,miR-669b-5p,miR-125b-5p,miR-16-5p,miR-1306-5p,miR-6516-3p和miR-1291)富集在细胞衍生的外泌体中。筛查出的miRNA会通过外泌体进行细胞间的交流和信息输入,调控如氧化应激、自噬及炎症等几种与神经变性相关的关键生物学途径。作为帕金森病潜在的生物标志物,可进一步在体内帕金森病研究中经过评估后应用于帕金森病的诊疗,成为帕金森病诊疗的新靶点。 文章总结了外泌体miRNA作为帕金森病生物标志物机制研究进展,见表3。"
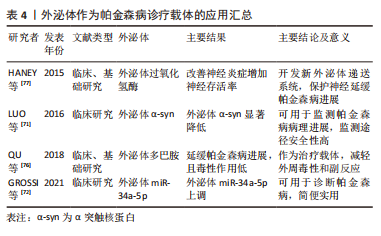
2.2.3 外泌体DJ-1 DJ-1是一种抗氧化蛋白,在氧化应激下发生自氧化,保护细胞内容物并调节抗氧化防御系统。DJ-1可通过分子伴侣样活性调节α-syn的聚集并保护神经元,其被敲低或敲除则会增加α-syn毒性,从而使神经元更容易受到多巴胺能选择性神经毒素的影响[57-58],但血浆神经源性外泌体DJ-1在帕金森病中的研究尚缺乏。ZHAO等[59]的研究首次指出帕金森病患者中血浆神经源性外泌体中的DJ-1水平显著增加,且血浆神经源性外泌体的DJ-1水平和α-syn之间存在显著的正相关关系,但此研究有一定的局限性,即敏感性和特异性不够高,应与更大的患者队列进行进一步研究,以证实血浆神经源性外泌体α-syn和DJ-1作为生物标志物与疾病进展的关系,但仍可认为二者通过外泌体介导细胞通讯,透过血脑屏障进入外周循环,并可作为帕金森病的潜在生物标志物。由此可认为,外泌体可介导细胞通讯完成物质转移,透过血脑屏障在帕金森病患者的不同体液中外泌体携带标志物表达亦可能有差异,因此,应开展更多大样本的临床试验探究不同来源外泌体携带DJ-1含量以及其对α-syn的调控在帕金森病诊治中的敏感度和特异度。 2.2.4 外泌体富亮氨酸重复激酶基因(Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2,LRRK2) LRRK2基因突变是帕金森病最常见的遗传原因,可提高自磷酸化LRRK2蛋白的水平,其会加速路易体的聚集,导致遗传性家族帕金森病,目前检测到的所有LRRK2蛋白都完全局限于外泌体部分[60]。星形胶质细胞分泌含α-syn的外泌体,通过对遗传性帕金森病的体外细胞实验研究发现,LRRK2基因突变增加了多泡体内的磷酸化α-syn的量,多泡体过度积累帕金森病相关蛋白LRRK2和磷酸化α-syn,会改变分泌的外泌体表型进而影响细胞间信息通讯[61]。以上研究表明,外泌体LRRK2会发生自磷酸化增加外泌体中LRRK2蛋白和α-syn,导致胶质细胞与神经元之间或神经元相互之间的细胞通讯和信息交流的病理性失调,诱导帕金森病的病理发生发展[62]。 综上可知,外泌体携带生物标志物可通过胞吐胞吞作用方式完成细胞间的通讯和物质输送,介导不同机制途径参与帕金森病的病理进展。目前公认的、研究最多的帕金森病外泌体生物标志物是外泌体α-syn,其通过神经毒性、神经炎症、氧化应激及细胞自噬等多途径参与介导帕金森病的病理进展;外泌体miRNA是近些年研究较热的帕金森病外泌体生物标志物,其可直接靶向帕金森病相关基因影响其转录功能导致α-syn上调、聚集和多巴胺能神经元损失增加而参与帕金森病的病理进展,外泌体miRNA也参与了细胞氧化应激调节;外泌体DJ-1则是直接的氧化应激关键蛋白,可影响细胞的脂质过氧化程度;而外泌体LRRK2可上调自身磷酸化表达,介导α-syn细胞通讯增加其堆积,参与帕金森病病理进展。因此,外泌体及其携带生物标志物仍是诊断和延缓帕金森病的研究热点,具有广阔前景。 2.3 外泌体可作为区分帕金森病与相似疾病的生物标志物 帕金森病与其他神经退行性疾病症状等方面有一定的重叠,使得诊断变得有些困难,而外泌体作为生物标志物可以将帕金森病和其他相似疾病区分开。MANNA等[63]通过TaqMan测定33名健康对照者、40例帕金森病和20例进行性核上麻痹(Progressive Supranuclear Paralysis,PSP)患者的血清miRNA水平,筛选出miR-21-3p,miR-22-3p,miR-223-5p,miR-425-5p和miR-199a-5p这5个外泌体miRNA可以作为生物标志物来区分帕金森病和PSP。血清神经元外泌体中α-syn分泌增加在帕金森病诊断之前,持续存在疾病进展中,并与聚类蛋白联合预测和区分帕金森病和非典型帕金森综合征[64]。使用神经元和少突胶质细胞标志物免疫沉淀的血液外泌体中的α-syn可将帕金森病与多系统萎缩区分开来[65]。以上研究数据均证实,外泌体携带生物标志物通过细胞通讯进行细胞间的转运和交流可作为帕金森病的生物标志物,甚至有些还具有特异性检测诊断的特点,但仍有大量待临床验证的潜在生物标志物,或可成为未来的研究热点,为帕金森病的早期精准诊断和预防提供新靶点。 2.4 外泌体可作为帕金森病诊疗载体的应用前景和临床应用 2.4.1 外泌体作为帕金森病诊疗载体的应用前景 近年来,外泌体是一种非常有效的帕金森病诊断生物标志物类型,通过分离提取外泌体对其携带标志物进行检测以此诊断帕金森病,从而能够在疾病发生进展的早期即可发现甄别,并采取对应治疗手段延缓帕金森病进展。外泌体同时也是一种很有前途的药物载体,具有载体体积小(纳米囊泡)、细胞间通讯交流输入、穿透血脑屏障能力强、靶向性强、外周稳定性好、药物清除率低等特点。外泌体作为纳米囊泡,其穿越血脑屏障的能力可以作为药物输送载体进入大脑[66-67],并且,由于外泌体的靶向作用、免疫抗性(外周稳定性)和药物清除率低,它们作为药物载体可以进一步减少由于药物在转运过程中在外周滞留而产生的药物不良反应,并减少传统药物治疗的不良反应,进一步增加药物递送的益处[68-69]。外泌体由于固有的小尺寸和自然本身的细胞产物,作为载体可以避免巨噬细胞的吞噬作用或降解,在体内长时间循环,可以潜在地避免内体途径和溶酶体降解,并且还可以将运载物质生物因子直接输送到细胞质中。通过使用血液外泌体作为递送系统,多巴胺在大脑中的分布可以增加15倍以上,与静脉内给药后的游离多巴胺相比,负载多巴胺的外泌体显示出更准确的靶向、更好的治疗效果和更低的全身毒性,极大程度上减轻帕金森病相关神经毒性和神经炎症[70]。虽然仍需要进一步的临床试验来探索,但逐渐增多的证据表明应用外泌体在帕金森病诊疗中的可行性,这将是帕金森病诊疗的一种新的思路与方向。 2.4.2 外泌体作为帕金森病诊疗载体的临床应用 外泌体更敏感、更可靠以及细胞间通讯的特性使其能够作为帕金森病的生物标志物。它可以反映帕金森病的病理情况并监测疾病进展。LUO等[71]开展了应用普拉克索治疗帕金森病患者的临床试验,他们对治疗后血清外泌体α-syn的水平进行评估,研究结果显示有效治疗组的患者血清外泌体α-syn显著降低,这些发现表明,对帕金森病治疗的疗效可以通过基于外泌体α-syn水平测量的非侵入性分析来监测。GROSSI等[72]分析了来自帕金森病患者血浆样本的外泌体发现,与正常组血浆外泌体相比,帕金森病发病后5年内患者血浆中的外泌体miR-34a-5p显著增加。以上外泌体生物标志物临床应用证明使用外周来源获得外泌体为阐明目标参与提供了一种简单实用的方法,可在推定帕金森病病理进展改变干预措施的前瞻性临床试验中进一步应用。临床中最常用的检测帕金森病的生物标志物为外泌体α-syn,其表达增多会产生神经毒性,检测的敏感度和特异性较高;其次为外泌体miRNA,较多在体液中被检测到。临床诊断检测中的外泌体可来自脑脊液、血浆、血清、唾液和尿液,其中脑脊液是帕金森病中生物标志物的准确可靠来源[73]。然而,与常规临床环境中的血液采样相比,获得脑脊液是一个复杂、繁琐且有一定危险性的过程。因为外泌体可穿过血脑屏障,且具有优越的细胞间通讯、传输和信息交换等特性,血液成为临床环境中应用采集外泌体及其携带标志物的可靠来源[74]。然而,血液生物标志物的一个主要缺点是它们不能直接反映中枢神经系统的状况,并且更容易受到周围环境的影响,而尿液中的一些外泌体来源尚不清楚。一些血液来源的外泌体miRNA被证明是帕金森病认知障碍的生物标志物[75]。以上研究均说明外泌体在临床诊断帕金森病中的应用仍有很大的研究空间和发展前景。 外泌体利用其细胞间通讯特性,可以靶向输送治疗物质和因子,这一点可在临床上尝试和应用来治疗帕金森病。QU等[76]从人体血液中分离出外泌体,并用饱和的多巴胺溶液加载外泌体,在体内和体外实验中发现,血液外泌体可以穿过血脑屏障并通过转铁蛋白和转铁蛋白受体之间相互作用将外泌体携带的多巴胺传递到大脑中,负载多巴胺的外泌体在帕金森病小鼠模型中具有更好的治疗效果,并且比静脉内全身给药的游离多巴胺毒性更低。HANEY等[77]利用单核细胞和巨噬细胞开发了一种负载过氧化氢酶的新外泌体递送系统,在体内或体外帕金森病模型中这些外泌体被神经元摄取,有效地积聚在大脑中的神经元和小胶质细胞中,过氧化氢酶是一种强效抗氧化剂,其被摄取后释放可改善神经炎症并增加神经存活率起到神经保护作用,进而缓解帕金森病进展。外泌体作为帕金森病的诊疗载体优点是与纳米颗粒相比更容易运送其内容物,并且作为细胞通讯的载体可以出现在体液中,更好地透过血脑屏障将治疗药物直接运送至大脑特定区域。外泌体携带药物治疗帕金森病大多还限制于动物实验,临床试验的开展有许多限制因素:目前还没有成熟的纯化技术来分离高纯度的外泌体;分离方法产生的外泌体量较低,其用于临床研究和药物后批准的大规模生产价格昂贵;与治疗性药物结合时可能会存在不良反应;外泌体功能化的主动靶向特定细胞修饰仍需进一步探索等[78]。因此,基于临床试验开展外泌体在帕金森病治疗中的应用是未来研究的重点和亟待突破点。表4为外泌体作为帕金森病诊疗载体的应用情况。"
| [1] GUPTA R, AMBASTA RK, KUMAR P. Multifaced role of protein deacetylase sirtuins in neurodegenerative disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022;132:976-997. [2] WANG J, ZHANG XN, FANG JN, et al. The mechanism behind activation of the Nod-like receptor family protein 3 inflammasome in Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):898-904. [3] WALDTHALER J, VINDING MC, ERIKSSON A, et al. Neural correlates of impaired response inhibition in the antisaccade task in Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2022;422:113763. [4] MIZRAHI-KLIGER AD, FELDMANN LK, KUHN AA, et al. Etiologies of insomnia in Parkinson’s disease -Lessons from human studies and animal models. Exp Neurol. 2022;350:113976. [5] SCHRAG A, ZHELEV SS, HOTHAM S, et al. Heterogeneity in progression of prodromal features in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2019;64:275-279. [6] MARRAS C, BECK JC, BOWER JH, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease across North America. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2018;4:21. [7] QIU J, CHEN Y, ZHUO J, et al. Urolithin A promotes mitophagy and suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglial cells and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Neuropharmacology. 2022;207:108963. [8] OZGEN S, KRIGMAN J, ZHANG R, et al. Significance of mitochondrial activity in neurogenesis and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(4):741-747. [9] CHAU E, KIM J R. alpha-synuclein-assisted oligomerization of beta-amyloid (1-42). Arch Biochem Biophys. 2022;717:109120. [10] NGUYEN TT, NGUYEN TTD, TRAN NM, et al. Lipid-based nanocarriers via nose-to-brain pathway for central nervous system disorders. Neurochem Res. 2022;47(3):552-573. [11] YU H, SUN T, AN J, et al. Potential roles of exosomes in Parkinson’s disease:from pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment to prognosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:86. [12] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020. doi:10.1126/science.aau6977. [13] ARAUJO-ABAD S, SACEDA M, DE JUAN ROMERO C. Biomedical application of small extracellular vesicles in cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;182:114117. [14] SIDORYK-WEGRZYNOWICZ M, DABROWSKA-BOUTA B, SULKOWSKI G, et al. Nanosystems and exosomes as future approaches in treating multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;54(9):7377-404. [15] 卫宇帆,樊飞燕,李双利,等.外泌体及间充质干细胞源性外泌体在帕金森病诊治中的未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25): 4076-4083. [16] 周丽娜,王洪新.外泌体在帕金森病中的研究进展[J].中华神经医学杂志,2021,20(12):1270-1274. [17] WAN Y, LIU B, LEI H, et al. Nanoscale extracellular vesicle-derived DNA is superior to circulating cell-free DNA for mutation detection in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2018;29(12):2379-2383. [18] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, LIU H, et al. Exosomes: biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019;9:19. [19] GAO P, LI X, DU X, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic potential of exosomes in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021; 13:790863. [20] JOHNSTONE RM, ADAM M, HAMMOND JR, et al. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J Biol Chem. 1987;262(19): 9412-9420. [21] SHARMA S, MILLER PW, STOLINA M, et al. Multicomponent gene therapy vaccines for lung cancer:effective eradication of established murine tumors in vivo with interleukin-7/herpes simplex thymidine kinase-transduced autologous tumor and ex vivo activated dendritic cells. Gene Ther. 1997;4(12):1361-1370. [22] LI S, CHEN L. Exosomes in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2022;12:793432. [23] FRUHBEIS C, FROHLICH D, KUO WP, et al. Extracellular vesicles as mediators of neuron-glia communication. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013; 7:182. [24] SOARES MARTINS T, MARCALO R, DA CRUZ ESCB, et al. Novel exosome biomarker candidates for alzheimer’s disease unravelled through mass spectrometry analysis. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. doi:10.1007/s12035-022-02762-1. [25] ZHANG H, XING J, DAI Z, et al. Exosomes: the key of sophisticated cell-cell communication and targeted metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):9. [26] AGLIARDI C, GUERINI FR, MELONI M, et al. Alpha-synuclein as a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease:focus on neural derived extracelluar vesicles. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(7):1503-1504. [27] FU Y, JIANG C, TOFARIS G K, et al. Facile impedimetric analysis of neuronal exosome markers in parkinson’s disease diagnostics. Anal Chem. 2020;92(20):13647-13651. [28] NIU M, LI Y, LI G, et al. A longitudinal study on alpha-synuclein in plasma neuronal exosomes as a biomarker for Parkinson’s disease development and progression. Eur J Neurol. 2020;27(6):967-974. [29] YOUSIF G, QADRI S, HAIK M, et al. Circulating exosomes of neuronal origin as potential early biomarkers for development of stroke. Mol Diagn Ther. 2021;25(2):163-180. [30] WEI Z X, XIE G J, MAO X, et al. Exosomes from patients with major depression cause depressive-like behaviors in mice with involvement of miR-139-5p-regulated neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020;45(6):1050-1058. [31] JIANG R, RONG C, KE R, et al. Differential proteomic analysis of serum exosomes reveals alterations in progression of Parkinson disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(41):e17478. [32] CHOI WS, KIM HW, TRONCHE F, et al. Conditional deletion of Ndufs4 in dopaminergic neurons promotes Parkinson’s disease-like non-motor symptoms without loss of dopamine neurons. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44989. [33] JANKOVIC J, TAN EK. Parkinson’s disease:etiopathogenesis and treatment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(8):795-808. [34] LATIF S, JAHANGEER M, MAKNOON RAZIA D, et al. Dopamine in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;522:114-126. [35] MEHRA S, SAHAY S, MAJI SK. alpha-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation:Implications in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2019;1867(10):890-908. [36] FAYYAD M, SALIM S, MAJBOUR N, et al. Parkinson’s disease biomarkers based on alpha-synuclein. J Neurochem. 2019;150(5):626-636. [37] FAN RZ, GUO M, LUO S, et al. Exosome release and neuropathology induced by alpha-synuclein:new insights into protective mechanisms of Drp1 inhibition. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2019;7(1):184. [38] GUO M, WANG J, ZHAO Y, et al. Microglial exosomes facilitate alpha-synuclein transmission in Parkinson’s disease. Brain. 2020;143(5): 1476-1497. [39] HAN C, XIONG N, GUO X, et al. Exosomes from patients with Parkinson’s disease are pathological in mice. J Mol Med (Berl). 2019; 97(9):1329-1344. [40] SI X, TIAN J, CHEN Y, et al. Central nervous system-derived exosomal alpha-synuclein in serum may be a biomarker in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience. 2019;413:308-316. [41] GUO M, HAO Y, FENG Y, et al. Microglial exosomes in neurodegenerative disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:630808. [42] XIA Y, ZHANG G, HAN C, et al. Microglia as modulators of exosomal alpha-synuclein transmission. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(3):174. [43] BRUCK D, WENNING GK, STEFANOVA N, et al. Glia and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration: a complex interaction. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;85:262-274. [44] SARKAR S, DAMMER EB, MALOVIC E, et al. Molecular signatures of neuroinflammation induced by alphasynuclein aggregates in microglial cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:33. [45] XING H, TAN J, MIAO Y, et al. Crosstalk between exosomes and autophagy: a review of molecular mechanisms and therapies. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(5):2297-308. [46] CHEN HX, LIANG FC, GU P, et al. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells repair a Parkinson’s disease model by inducing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(4):288. [47] FUSSI N, HOLLERHAGE M, CHAKROUN T, et al. Exosomal secretion of alpha-synuclein as protective mechanism after upstream blockage of macroautophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(7):757. [48] STEFANIS L, EMMANOUILIDOU E, PANTAZOPOULOU M, et al. How is alpha-synuclein cleared from the cell? J Neurochem. 2019;150(5):577-590. [49] ALVAREZ-ERVITI L, SEOW Y, SCHAPIRA AH, et al. Lysosomal dysfunction increases exosome-mediated alpha-synuclein release and transmission. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;42(3):360-367. [50] BAI Y, SU X, PIAO L, et al. Involvement of astrocytes and microrna dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: from pathogenesis to therapeutic potential. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021;14:556215. [51] SANG Q, LIU X, WANG L, et al. CircSNCA downregulation by pramipexole treatment mediates cell apoptosis and autophagy in Parkinson’s disease by targeting miR-7. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(6):1281-1293. [52] LU S, YANG X, WANG C, et al. Current status and potential role of circular RNAs in neurological disorders. J Neurochem. 2019;150(3): 237-248. [53] CHEN Y, GAO C, SUN Q, et al. MicroRNA-4639 Is a regulator of DJ-1 expression and a potential early diagnostic marker for parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:232. [54] JIANG Y, LIU J, CHEN L, et al. Serum secreted miR-137-containing exosomes affects oxidative stress of neurons by regulating OXR1 in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2019;1722:146331. [55] HARISCHANDRA DS, ROKAD D, NEAL ML, et al. Manganese promotes the aggregation and prion-like cell-to-cell exosomal transmission of alpha-synuclein. Sci Signal. 2019. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aau4543. [56] HARISCHANDRA DS, GHAISAS S, ROKAD D, et al. Environmental neurotoxicant manganese regulates exosome-mediated extracellular miRNAs in cell culture model of Parkinson’s disease: relevance to alpha-synuclein misfolding in metal neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology. 2018;64:267-277. [57] PANICKER N, GE P, DAWSON VL, et al. The cell biology of Parkinson’s disease. J Cell Biol. 2021. doi:10.1083/jcb.202012095. [58] ZHANG K, ZHU SO, LI JM, et al. Targeting autophagy using small-molecule compounds to improve potential therapy of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(10):3015-3034. [59] ZHAO ZH, CHEN ZT, ZHOU RL, et al. Increased DJ-1 and alpha-synuclein in plasma neural-derived exosomes as potential markers for Parkinson’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018;10:438. [60] FRASER KB, MOEHLE MS, ALCALAY RN, et al. Urinary LRRK2 phosphorylation predicts parkinsonian phenotypes in G2019S LRRK2 carriers. Neurology. 2016;86(11):994-999. [61] STREUBEL-GALLASCH L, GIUSTI V, SANDRE M, et al. Parkinson’s Disease-associated LRRK2 interferes with astrocyte-mediated alpha-synuclein clearance. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(7):3119-3140. [62] DE RUS JACQUET A, TANCREDI JL, LEMIRE AL, et al. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation alters astrocyte-to-neuron communication via extracellular vesicles and induces neuron atrophy in a human iPSC-derived model of Parkinson’s disease. Elife. 2021. doi:10.7554/eLife.73062. [63] MANNA I, QUATTRONE A, DE BENEDITTIS S, et al. Exosomal miRNA as peripheral biomarkers in Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: a pilot study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021;93: 77-84. [64] JIANG C, HOPFNER F, KATSIKOUDI A, et al. Serum neuronal exosomes predict and differentiate Parkinson’s disease from atypical parkinsonism. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2020;91(7):720-729. [65] DUTTA S, HORNUNG S, KRUAYATIDEE A, et al. alpha-Synuclein in blood exosomes immunoprecipitated using neuronal and oligodendroglial markers distinguishes Parkinson’s disease from multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 2021;142(3):495-511. [66] GOMEZ-MOLINA C, SANDOVAL M, HENZI R, et al. Small extracellular vesicles in rat serum contain astrocyte-derived protein biomarkers of repetitive stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019;22(3):232-246. [67] SAMANTA S, RAJASINGH S, DROSOS N, et al. Exosomes:new molecular targets of diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(4):501-513. [68] KALIMUTHU S, GANGADARAN P, RAJENDRAN RL, et al. A new approach for loading anticancer drugs into mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome mimetics for cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1116. [69] BUNGGULAWA EJ, WANG W, YIN T, et al. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J Nanobiotechnology. 2018;16(1):81. [70] KOJIMA R, BOJAR D, RIZZI G, et al. Designer exosomes produced by implanted cells intracerebrally deliver therapeutic cargo for Parkinson’s disease treatment. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1305. [71] LUO HT, ZHANG JP, MIAO F. Effects of pramipexole treatment on the alpha-synuclein content in serum exosomes of Parkinson’s disease patients. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1373-1376. [72] GROSSI I, RADEGHIERI A, PAOLINI L, et al. MicroRNA34a5p expression in the plasma and in its extracellular vesicle fractions in subjects with Parkinson’s disease: an exploratory study. Int J Mol Med. 2021; 47(2):533-546. [73] FAROTTI L, PACIOTTI S, TASEGIAN A, et al. Discovery, validation and optimization of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for use in Parkinson’s disease. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2017;17(8):771-780. [74] MEHTA SH, ADLER CH. Advances in biomarker research in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016;16(1):7. [75] ALAMRI Y, VOGEL R, MACASKILL M, et al. Plasma exosome concentration may correlate with cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 2016;4:107-108. [76] QU M, LIN Q, HUANG L, et al. Dopamine-loaded blood exosomes targeted to brain for better treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Control Release. 2018;287:156-166. [77] HANEY MJ, KLYACHKO NL, ZHAO Y, et al. Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Control Release. 2015;207: 18-30. [78] ARYANI A, DENECKE B. Exosomes as a nanodelivery system: a key to the future of neuromedicine? Mol Neurobiol. 2016;53(2):818-834. |
| [1] | Fang Xingyan, Tian Zhenli, Zhao Zheyi, Wen Ping, Xie Tingting. Effects of sodium arsenite on human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury and sphingosine kinases 1/sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling axis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Nong Fuxiang, Jiang Zhixiong, Li Yinghao, Xu Wencong, Shi Zhilan, Luo Hui, Zhang Qinglang, Zhong Shuang, Tang Meiwen. Bone cement augmented proximal femoral nail antirotation for type A3.3 intertrochanteric femoral fracturalysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [3] | Guo Shuhui, Yang Ye, Jiang Yangyang, Xu Jianwen. Screening and validation of neurogenic bladder miRNA-mRNA regulatory network [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-8. |
| [4] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [5] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | Ruan Ling, Wang Guanghua, Wu Rongping, Jin Zhan, Lyu Zhenqing, Zhang Nan, Li Shoubang. Correlation between exercise intensity and lipid metabolism disorder and oxidative stress in a high-diet rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [7] | Nie Chenchen, Su Kaiqi, Gao Jing, Fan Yongfu, Ruan Xiaodi, Yuan Jie, Duan Zhaoyuan, Feng Xiaodong. The regulatory role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [8] | Liang Jiaqi, Liu Hengxu, Yang Jinxin, Yang Yi, Deng Xuhui, Tan Mingjian, Luo Jiong. Health benefit relationship between exercise and intestinal bacteria [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [9] | Tian Qinyu, Tian Xinggui, Tian Zhuang, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Lu Xiaobo, Guo Quanyi. Protection of manganese oxide nanoparticles for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell spreading against oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 821-826. |
| [10] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [11] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [12] | Wang Min, Yin Xiushan, Wang Yingxi, Zhang Yan, Zhao Long, Xia Shuyue. Inhalation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviates inflammatory injury in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 827-834. |
| [13] | Zhang Houjun, Deng Bowen, Jiang Shengyuan, Zhao Yi, Ren Jingpei, Xu Lin, Mu Xiaohong. Proteomic analysis of cerebrospinal fluid exosomes derived from cerebral palsy children [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 903-908. |
| [14] | Gao Ting, Ma Xiaohong, Li Xiaorong. Extraction and identification of exosomes from three different sources of ovarian granulosa cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 860-865. |
| [15] | Yuan Bo, Xie Lide, Fu Xiumei. Schwann cell-derived exosomes promote the repair and regeneration of injured peripheral nerves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 935-940. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||