Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5214-5218.doi: 10.12307/2023.817
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of astragalus polysaccharides on orthodontic bone remodeling
Wang Huida, Sun Xiaotong, Bi Lan, Wang Zixuan, Zhang Ronghe
- Department of Orthodontics, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-10-26Accepted:2022-11-30Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:Zhang Ronghe, Master, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthodontics, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Wang Huida, Master candidate, Department of Orthodontics, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256600, Shandong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Huida, Sun Xiaotong, Bi Lan, Wang Zixuan, Zhang Ronghe. Effect of astragalus polysaccharides on orthodontic bone remodeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5214-5218.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
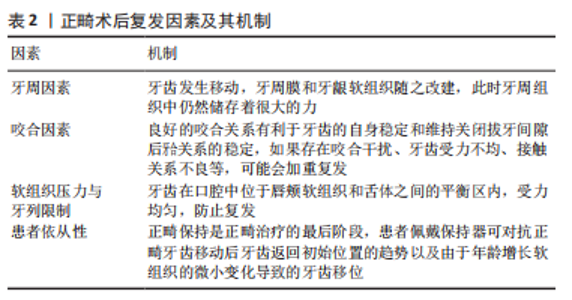
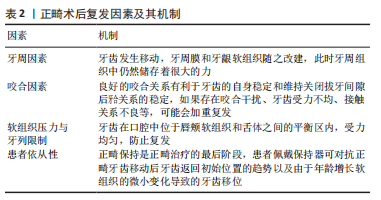
牙槽骨是牙齿的支持组织,是人体骨骼代谢最活跃的部分,可依据牙齿功能形态的改变而改变。牙骨质较牙槽骨抗吸收性更强,且随年龄的增长而逐渐沉积。牙与牙槽骨通过牙周膜相连,牙周膜具有形成、营养、感觉和支持的功能,可进行自我更新和改建。当受到刺激时,牙齿、牙周膜以及牙槽骨可作为一个整体对刺激做出应答,并保持自身的相对稳定。所以当矫治力作用于牙齿上,牙槽骨的可塑性、牙骨质的抗压性以及牙周膜内环境的稳定性是牙齿正畸运动中最基本的生物学基础,也是牙周组织重建的基础[10]。 正畸治疗的任何阶段都可能诱发牙根吸收,是仅次于牙釉质白斑病变的第二大正畸并发症,会引起牙冠根比降低,造成牙齿松动、脱落,对牙齿寿命以及治疗结果稳定性造成损害。当正畸压力超过局部毛细血管压力时,由于塌陷和局部供血不足,牙周韧带会发生缺血性坏死,导致牙齿外部透明层的退化。由于前牙骨质及其形成的成牙骨质细胞层的缺损,破骨细胞被激活,并且在去除透明液化坏死组织期间开始进行牙根吸收。因此,当损害超过牙骨质自身修复能力时,牙本质就会暴露,破牙细胞导致牙根结构产生不可逆转的损失[11]。临床医生多通过数字化根尖片、锥形术CT等对牙根吸收监测评估[12]。有研究显示,正畸导致的牙根吸收可能与患者年龄、种族、牙位前后、拔牙与否、牙齿移动方式、矫治力大小、作用时间和矫治方式等有关[13-14]。牙根吸收最终由成牙骨质细胞修复,但仍可能导致牙根长度的永久性缺失,正常牙齿和根管治疗后的牙齿会受到同样的影响[15]。如果在牙齿矫正时监测到牙根的吸收,应立即停止治疗两三个月,防止进一步吸收并希望牙骨质愈合。若愈合后再次发生牙根吸收,应修改治疗计划[16]。很多患者因为初戴矫治器,口腔环境发生了变化,弓丝、颊管、带环、结扎丝等会造成黏膜溃疡。一般溃疡多发生于前2周,2周之后,口腔内环境稳定、患者适应性增强,溃疡发生率降低。 正畸牙齿移动会导致牙齿周围的牙龈和牙周组织平衡被打破并需要一段时间才能得到修复,拉伸的牙周纤维中仍然存在残余应力促使牙齿回复到最初位置,最终导致正畸术后复发[17]。有研究显示,正畸术后复发与多方面因素有关[18-19],见表2。正畸治疗后患者的依从性与术后复发的OR值为0.86,同样也是复发的重要因素[20]。"

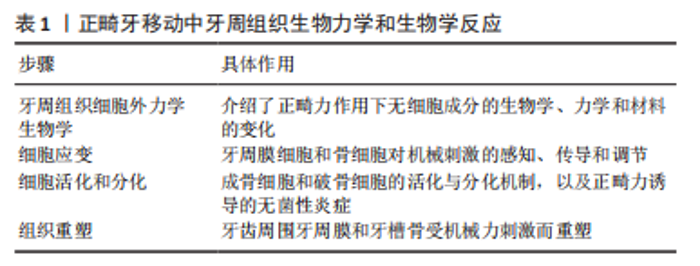
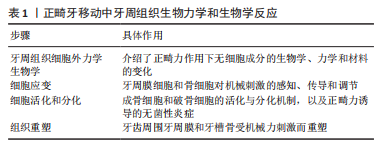
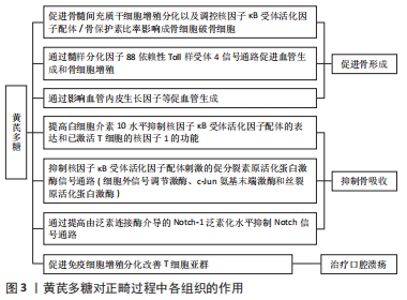
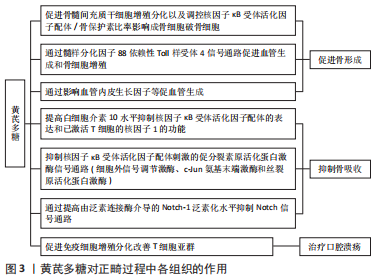
2.2.1 对牙周组织改建的作用 牙周组织改建是正畸过程中牙齿移动的生物学基础。牙齿受到矫治力,会引起牙周组织的炎性反应,从而刺激各种生化介质和信号的释放,最终造成牙槽骨及牙周韧带重塑[21],骨髓间充质干细胞在一定条件下可分化为成纤维细胞、破骨细胞、成骨细胞、脂肪细胞等,还可分化为有特定功能的器官或组织[22-23],此外,骨髓间充质干细胞的特点是易采样、易分离、体外扩增等,已成为组织工程常用的种子细胞[24],能支持骨微环境稳态并保持骨改建平衡[25-27]。黄芪多糖作为黄芪主要成分,其促血管生成、修复创面和抗炎作用等已经被广泛研究[28],同时又能改善微循环障碍,抗氧化,抑制细胞凋亡[29]。据报道,黄芪多糖能通过血管内皮生长因子分泌促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[30],YANG等[31]发现骨髓间充质干细胞暴露于柠檬酸铁铵中活性会降低,而黄芪多糖可部分减弱这些细胞的凋亡和衰老,在柠檬酸铁铵处理后,多能基因Nanog、Sox2和Oct4在骨髓间充质干细胞中被下调,但黄芪多糖抑制Nanog、Sox2和Oct4表达的降低。进一步的研究发现,黄芪多糖治疗消除了柠檬酸铁铵处理的骨髓间充质干细胞中细胞内线粒体活性氧水平增加,增加的活性氧水平在细胞凋亡的发展中起关键作用[32-33]。所以,黄芪多糖可通过调控骨髓间充质干细胞中线粒体活性氧的水平控制细胞的凋亡和衰老来影响骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞、破骨细胞的能力,从而实现对牙周组织改建的调控。 以往有研究提出,基质金属蛋白酶在正畸治疗中起着关键作用,导致牙周重塑和牙齿移动,基质金属蛋白酶可由机械力诱导。LISBOA等[34]将原代培养的人牙周成纤维细胞置于脂多糖和Pam3Cys的作用下离心,Toll样受体4和Toll样受体2分别为其配体,采用抗体列阵、酶联免疫吸附实验以及免疫印迹法检测基质金属蛋白酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、c-jun氨基末端激酶以及核因子κB,发现与离心相关的Toll样受体激活后,基质金属蛋白酶1,3,10分泌增加,丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、c-jun氨基末端激酶以及核因子κB磷酸化增加,这些结果表明,Toll样受体激活和机械力刺激联合诱导培养的牙周成纤维细胞分泌基质金属蛋白酶是通过丝裂原活化蛋白激酶、c-jun氨基末端激酶以及核因子κB途径调节的。Toll样受体激活引起基质金属蛋白酶增加可能是正畸治疗中的重要因素。由于牙移动是一个复杂的生物学反应,因此对于Toll样受体参与牙周组织改建的具体机制,还需进一步深入研究。 QIU等[35]通过实验探讨黄芪多糖是否通过Toll样受体4信号通路在生长内皮细胞和原代人成骨细胞的共培养中促进血管生成或血管形成;他们用不同浓度的黄芪多糖处理共培养物24 h,然后又处理7 d,随后进行测量;又将黄芪多糖添加到生长内皮细胞和原代人成骨细胞的单一培养基中,以评估增殖、细胞凋亡、血管生成、成骨、Toll样受体4信号通路和炎症细胞因子释放。最终发现黄芪多糖在0.4 mg/mL的最佳浓度下促进了共培养物中的血管生成,黄芪多糖激活Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88提高了Toll样受体4/髓样分化因子88的表达水平,并增强了生长内皮细胞和原代人成骨细胞单一培养中的血管生成和成骨作用;在黄芪多糖处理后,E-选择蛋白黏附分子,3种细胞因子(白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、γ-干扰素)以及血管内皮生长因子和血小板源生长因子的水平显著增加,因此,黄芪多糖似乎通过Toll样受体4信号通路促进共培养系统中的血管生成和骨化。HUO等[36]通过研究证实黄芪多糖具有抗去卵巢小鼠骨质疏松症的作用,并呈剂量依赖关系。黄芪多糖通过增加小鼠骨保护素(osteoprotegerin,OPG)的产生和下调细胞核因子 κB 受体活化因子配体(receptor activator ofnuclear factor-κB ligand,RANKL)的表达,使得RANKL/OPG比值降低,对小鼠的骨丢失产生保护作用,这种作用的分子机制是黄芪多糖可减少骨吸收并抑制破骨细胞的合成。YANG等[37]经研究证实,黄芪多糖能够促进血管再生以及骨形成,其机制可能与黄芪多糖通过影响血管内皮生长因子等物质促进血管生成有关。以上多个研究证实黄芪多糖能通过多途径作用于成骨细胞,促进成骨,加快牙周骨组织改建,见图4。"

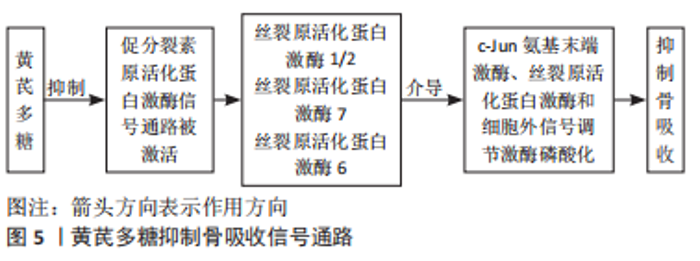
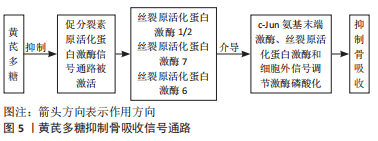
2.2.2 对牙根吸收的作用 正畸诱导性炎性牙根吸收是正畸治疗中常见的不良反应,发生率可高达20%-100%,深受学者们关注[38]。 黄芪可抑制牙根吸收。牙根吸收已被证明是由Notch信号传导介导的[39],通过白细胞介素6刺激牙根表面进行吸收以及牙周膜细胞产生RANKL,以响应高强度的正畸力。Notch信号通过直接作用于破骨细胞前体细胞和间接作用于成骨细胞来抑制破骨细胞的分化[40]。史桂荣等[41]经实验证实,黄芪抑制Notch信号通路是通过提高由泛素连接酶介导的Notch-1泛素化水平实现的。也有许多研究提出,破骨细胞的分化和功能主要受RANKL调节[42]。经RANKL刺激后,TRAF2/6信号被RANK激活,导致丝裂原活化蛋白激酶1/2,7,6介导的3条促分裂素原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(细胞外信号调节激酶、c-Jun氨基末端激酶和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)的磷酸化。此外,c-Fos水平的增加是已激活T细胞的核因子1产生调控破骨细胞分化所必需的。已激活T细胞的核因子1被认为是激活破骨细胞特异性基因的重要转录因子,包括CTSK、TRAP、DC-STAMP、MMP9和ATP6V0D2,这些基因在破骨细胞的增殖、分化、成熟和破骨细胞性骨吸收中起重要作用。黄芪多糖通过广谱抑制RANKL刺激的促分裂素原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(细胞外信号调节激酶、c-Jun氨基末端激酶和丝裂原活化蛋白激酶)来抑制破骨细胞的形成和牙根吸收[43]。见图5。"

IGLESIAS-LINARES等[44]还通过综合多项研究得出结论:牙根吸收是多细胞参与调节的复杂过程,不仅受破骨细胞、破牙细胞影响,还受白细胞介素等因子的调控。HAN等[45]建立了大鼠牙周炎症模型,局部注射黄芪多糖,结果显示黄芪多糖可显著增加白细胞介素10的水平。白细胞介素10还可通过抑制RANKL的表达和已激活T细胞的核因子1的功能来抑制破骨细胞的形成[46]。此外,白细胞介素10通过抑制转化生长因子β的表达促进成骨细胞分化[47],当研究人员在动物体内敲除白细胞介素10基因时,可以看到成骨细胞缺陷和牙槽骨吸收[48]。林鹏等[49]通过实验,将200 mg/kg的黄芪多糖提取液注射到建模并加力的大鼠上颌第一磨牙附近,定期注射等量的黄芪多糖提取液,14 d后处死并制取标本发现,黄芪多糖提取液组牙根近中面骨吸收陷窝少,对照组骨吸收陷窝多,该实验证实了黄芪多糖可轻度抑制由正畸导致的牙根吸收,免疫组化显示压力侧黄芪多糖提取液组肿瘤坏死因子α表达低于对照组,推测可能由于黄芪多糖减弱了压力侧肿瘤坏死因子α表达从而炎性牙根吸收被抑制。这些机制进一步证实了黄芪多糖在正畸过程中对牙根吸收的抑制作用。 2.2.3 对防止正畸术后复发的影响 正畸术后牙齿回到初始位置的趋势视为正畸复发,会影响矫治效果,深受正畸医生的重视。不仅越隔纤维产生的机械张力和咬合不稳定会导致复发,牙周膜和牙槽骨改建的内在因素也会导致正畸复发。明确牙齿复发之后牙周组织改建以及细胞因子调控的情况,对于抑制复发并长期保持疗效具有重要意义。骨形成蛋白2是通过诱导间质干细胞分化为骨前体细胞来促骨形成的一类细胞因子。XUE等[50]经研究证实,骨形成蛋白2在牙移动中可参与骨增生与骨吸收的骨重建过程,并发挥着重要作用。林鹏等[51]将处于正畸牙齿保持阶段的大鼠建模,并在右上颌第一磨牙远中侧局部注射黄芪多糖,一段时间后发现,相较于对照组,黄芪多糖组注射区骨形成蛋白2表达量显著增多。通过研究证实,黄芪多糖局部注射可显著加强正畸术后牙周组织中骨形成蛋白2的表达,促进牙槽骨重建,对牙齿矫正后的保持、防止复发都有好处。 2.2.4 对正畸性口腔溃疡的作用 在固定矫治过程中,患者因长期佩戴固定矫治器,刺激角化较差甚至未发生角化的牙龈或黏膜,这种溃疡称为正畸性口腔溃疡[52]。目前关于其发病原因尚无统一明确的认知,一般认为与机体免疫力、刺激等有关。黄芪多糖因其具有直接杀伤作用和提高免疫功能近年来越来越受到关注[53]。邵玲玲等[54]通过临床试验随机将口腔溃疡患者分为对照组和实验组,对照组采用传统的西药治疗,用双氧水冲洗溃疡表面,地塞米松片+甲硝唑片研磨调糊涂抹于表面;在对照组基础上,实验组又加用黄芪多糖注射液静滴,结果发现,加用黄芪多糖注射液静滴可显著促进溃疡的愈合,并延缓复发,其机制可能与改善T细胞亚群的失衡有关。"

| [1] LI Z, YU M, JIN S, et al. Stress Distribution and Collagen Remodeling of Periodontal Ligament During Orthodontic Tooth Movement. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1263. [2] KITAURA H, MARAHELE A, OHORI F, et al. Osteocyte-Related Cytokines Regulate Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14):5169. [3] BALAKRISHNAN B, LIANG Q, FENIX K, et al. Combining the Anticancer and Immunomodulatory Effects of Astragalus and Shiitake as an Integrated Therapeutic Approach. Nutrients. 2021;13(8):2564. [4] 张淑娟,张育贵,牛江涛,等.黄芪的研究进展及其质量标志物预测分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2022,40(2):151-155. [5] 刘颖,张金莲,邓亚羚,等.黄芪多糖提取、分离纯化及其药理作用研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志,2021,36(10):6035-6038. [6] ABD E, ESSAWY AE, AL-SHAMI AS. Astragalus species: Phytochemistry, biological actions and molecular mechanisms underlying their potential neuroprotective effects on neurological diseases. Phytochemistry. 2022;202:113293. [7] 邹净亭,赵静辉,王佳,等.黄芪在口腔医学中的应用研究进展[J].口腔医学,2018,38(2):189-192. [8] WILL LA. Orthodontic Tooth Movement: A Historic Prospective. Front Oral Biol. 2016;18:46-55. [9] LI Y, ZHAN Q, BAO M, et al. Biomechanical and biological responses of periodontium in orthodontic tooth movement: up-date in a new decade. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):20. [10] 陈雅竹,管晓燕,肖茜文,等.中草药在正畸牙移动牙周组织改建中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(46):7477-7481. [11] YASSIR YA, MCINTYRE GT, BEARN DR. Orthodontic treatment and root resorption: an overview of systematic reviews. Eur J Orthod. 2021;43(4):442-456. [12] BELLINI SA, ALMEIDA J, ALIAGA-Del CA, et al. Evaluation of root resorption following orthodontic intrusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2021;43(4):432-441. [13] BAYIR F, BOLAT GU. External apical root resorption after orthodontic treatment: Incidence, severity and risk factors. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2021; 15(2):100-105. [14] PINHERIRO LHM, GUIMARAES LS, ANTUNES LS, et al. Genetic variation involved in the risk to external apical root resorption in orthodontic patients: a systematic review. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25(10):5613-5627. [15] ALVES O, MAGNO G, MARQUES B, et al. Comparison of orthodontic root resorption of root-filled and vital teeth: A meta-analysis. J Am Dent Assoc. 2022;153(6):532-541.e7. [16] KALRA S, GUPTA P, TRIPATHI T,et al. External apical root resorption in orthodontic patients: molecular and genetic basis. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020;9(8):3872-3882. [17] MILLETT D. The rationale for orthodontic retention:piecing together the jigsaw. Br Dent J. 2021;230(11):739-749. [18] JEDLINSKI M, GROCHOLEWICZ K, MAZUR M, et al. What causes failure of fixed orthodontic retention? - systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical studies. Head Face Med. 2021;17(1):32. [19] 汪益益,梅梅,张疆弢.固定正畸术后复发与保持的研究进展[J].新疆医学, 2020,50(4):401-404. [20] MILLETT D. The rationale for orthodontic retention: piecing together the jigsaw. Br Dent J. 2021;230(11):739-749. [21] AMAGUCHI M, FUKASAWA S. Is Inflammation a Friend or Foe for Orthodontic Treatment: Inflammation in Orthodontically Induced Inflammatory Root Resorption and Accelerating Tooth Movement. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2388. [22] ZHENG J, LIN Y, TANG F, et al. Promotive Role of CircATRNL1 on Chondrogenic Differentiation of BMSCs Mediated by miR-338-3p. Arch Med Res. 2021;52(5): 514-522. [23] LIU GY, WU Y, KONG FY, et al. BMSCs differentiated into neurons, astrocytes and oligodendrocytes alleviated the inflammation and demyelination of EAE mice models. PLoS One. 2021;16(5):e0243014. [24] XUE K, ZHANG X, GAO Z,et al. Cartilage progenitor cells combined with PHBV in cartilage tissue engineering. J Transl Med. 2019;17(1):104. [25] GUO Y, JIA X, CUI Y, et al. Sirt3-mediated mitophagy regulates AGEs-induced BMSCs senescence and senile osteoporosis. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101915. [26] ZHOU Y, GUAN XX, ZHU ZL, et al. Caffeine inhibits the viability and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Br J Pharmacol. 2010;161(7):1542-1552. [27] XIAN L, WU X, PANG L, et al. Matrix IGF-1 maintains bone mass by activation of mTOR in mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med. 2012;18(7):1095-1101. [28] 范丽娜,陈丽娟,刘芳.黄芪多糖对大鼠慢性难愈合创面的作用及其对PTEN、AKT和VEGF蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医药科技,2022,29(1):36-40. [29] ZHANG YW, WU CY, CHENG JT. Merit of Astragalus polysaccharide in the improvement of early diabetic nephropathy with an effect on mRNA expressions of NF-kappaB and IkappaB in renal cortex of streptozotoxin-induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;114(3):387-392. [30] ZHAO L, ZHONG Y, LIANG J, et al. Effect of Astragalus Polysaccharide on the Expression of VEGF and EGFR in Mice with Lewis Transplantable Lung Cancer. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2019;29(4):392-394. [31] YANG F, YAN G, LI Y, et al. Astragalus Polysaccharide Attenuated Iron Overload-Induced Dysfunction of Mesenchymal Stem Cells via Suppressing Mitochondrial ROS. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4):1369-1379. [32] SUN L, ZANG WJ, WANG H, et al. Acetylcholine promotes ROS detoxification against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced oxidative stress through FoxO3a/PGC-1α dependent superoxide dismutase. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;34(5):1614-1625. [33] PATKOVA J, ANDEL M, TRNKA J. Palmitate-induced cell death and mitochondrial respiratory dysfunction in myoblasts are not prevented by mitochondria-targeted antioxidants. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2014;33(5):1439-1451. [34] LISBOA RA, ANDRADE MV, CUNHA-MELO JR. Toll-like receptor activation and mechanical force stimulation promote the secretion of matrix metalloproteinases 1, 3 and 10 of human periodontal fibroblasts via p38, JNK and NF-kB. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(6):731-739. [35] QIU H, ZHANG L, HE X, et al. Promotion of angiogenesis in vitro by Astragalus polysaccharide via activation of TLR4 signaling pathway. J Food Biochem. 2022; 46(10):e14329. [36] HUO J, SUN X. Effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Genet Mol Res. 2016;15(4):10.4238. [37] YANG Y, CHIN A, ZHANG L, et al. The role of traditional Chinese medicines in osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Phytother Res. 2014;28(1):1-8. [38] ROSCOE MG, CATTANEO PM, DALSTRA M, et al. Orthodontically induced root resorption: A critical analysis of finite element studies’ input and output. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2021;159(6):779-789. [39] LI X, XU J, YIN Y, et al. Notch signaling inhibition protects against root resorption in experimental immature tooth movement in rats. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2021;159(4):426-434.e5. [40] YU J, CANALIS E. Notch and the regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. Bone. 2020;138:115474. [41] 史桂荣,任博文,张仲博,等.黄芪多糖干预对骨关节炎模型小鼠关节软骨损伤的修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(20):3236-3242. [42] TSUKASAKI M. RANKL and osteoimmunology in periodontitis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):82-90. [43] YANG J, QIN L, HUANG J, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide attenuates LPS-related inflammatory osteolysis by suppressing osteoclastogenesis by reducing the MAPK signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(14):6800-6814. [44] IGLESIAS-LINARES A, HARTSFIELD JK. Cellular and Molecular Pathways Leading to External Root Resorption. J Dent Res. 2017;96(2):145-152. [45] HAN Y, YU C, YU Y. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates alveolar bone destruction by regulating local osteoclastogenesis during periodontitis. J Appl Biomed. 2021; 19(2):97-104. [46] KAWAMOTO D, ANDO-SUGUIMOTO ES, BUENO-SILVA B, et al. Alteration of Homeostasis in Pre-osteoclasts Induced by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans CDT. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016;6:33. [47] ZHANG Q, CHEN B, YAN F, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits bone resorption:a potential therapeutic strategy in periodontitis and other bone loss diseases. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:284836. [48] CLAUDINO M, GARLET TP, CSRDOSO CR, et al. Down-regulation of expression of osteoblast and osteocyte markers in periodontal tissues associated with the spontaneous alveolar bone loss of interleukin-10 knockout mice. Eur J Oral Sci. 2010;118(1):19-28. [49] 林鹏,辛海燕,王以玲,等.黄芪多糖对正畸所致牙根吸收的实验研究[J]. 临床口腔医学杂志,2020,36(1):15-18. [50] XUE H, ZHENG J, CUI Z, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates tooth movement via activation of the BMP-2 signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2013;8(7): e68926. [51] 林鹏,郭新星,魏竹亮.局部注射黄芪多糖对大鼠正畸牙保持阶段BMP-2表达的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究,2017,33(5):520-524. [52] ALDAHASH F, AISHAMALI D, AIBANDER W, et al. Oral mucosal ulceration during orthodontic treatment:The perception of patients and knowledge and attitude of the orthodontic practitioners. J Family Med Prim Care. 2020;9(11):5537-5541. [53] ZHOU Y, ZONG Y, LIU Z, et al. Astragalus Polysaccharides Enhance the Immune Response to OVA Antigen in BALB/c Mice. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9976079. [54] 邵玲玲,邵丽黎,贾向东.黄芪注射液治疗复发性口腔溃疡的临床效果及机制探讨[J]. 中国中医药科技,2015,22(4):419-420. |
| [1] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [2] | Long Guiyue, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Calcium phosphate cement/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degradation products promote osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1193-1198. |
| [3] | Huang Linke, Wei Linhua, Jiang Jie, Liu Qian, Chen Weiwei. Effects of estrogen combined with treadmill exercise on bone mass and articular cartilage in ovariectomized mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | Yang Zhishan, Tang Zhenglong. YAP/TAZ, a core factor of the Hippo signaling pathway, is involved in bone formation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [5] | Liu Xiaolin, Mu Xinyue, Ma Ziyu, Liu Shutai, Wang Wenlong, Han Xiaoqian, Dong Zhiheng. Effect of hydrogel-loaded simvastatin microspheres on osteoblast proliferation and differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 998-1003. |
| [6] | Liu Wentao, Feng Xingchao, Yang Yi, Bai Shengbin. Effect of M2 macrophage-derived exosomes on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [7] | Qiao Luhui, Ma Ziyu, Guo Haoyu, Hou Yudong. Comparison of puerarin and icariin on the biological properties of mouse preosteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 872-877. |
| [8] | Wu Yujie, Wan Xiaofang, Wei Mianxing, Peng Shiyuan, Xu Xiaomei. Correlation between autophagy and the Hippo-YAP protein pathway in periodental ligament cells on the pressure side of a mouse model of orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 683-689. |
| [9] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [10] | Liu Chunli, Yan Yujuan, Mo Liwen, Wu Zhijie, Zhang Li. Effects of puerarin on osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5114-5119. |
| [11] | Mo Yaomin, Liu Pan, Ma Ruixin, Zeng Gaofeng, Zong Shaohui. Mechanism of paroxetine on osteoclast differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5184-5190. |
| [12] | Han Jie, Lin Zhiyu, Xu Zhiwei, Zhang Xiaoyun, Shang Yuzhi, Liu Hao. Interventional effect of microRNA on osteonecrosis of the femoral head through bone metabolism mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5238-5248. |
| [13] | Liu Guanjuan, Xia Qianxi, Song Na, Huo Hua, Hong Wei, Liao Jian. Role of pyruvic acid in osteoclast differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(31): 5015-5021. |
| [14] | Shen Mengran, Ren Yansong, Zhou Yu, Yue Debo, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang. Interleukin-33-mediated bone immunity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4723-4728. |
| [15] | Wei Zongbo, Su Yunyu, Zhang Xiaoyun, Huang Wei, Xu Hang, Liu Rongfa. Role and mechanism by which long non-coding RNAs regulate subchondral bone homeostasis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(29): 4736-4744. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||