Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (7): 1062-1070.doi: 10.12307/2023.103
Previous Articles Next Articles
Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant
Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang
- School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-08-30Accepted:2021-10-28Online:2023-03-08Published:2022-07-19 -
Contact:Dong Qiang, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Xu Xingxing, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860192 (to DQ); Guiyang Science and Technology Plan Project, No. [2017]3040 (to DQ); the Scientific Research Fund of Stomatological College of Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Guizhou Medical University (to WCJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
2.1.1 石墨烯 石墨烯其定义是从其三维原材料石墨中分离出来的六边形排列的二维碳原子片,它具有良好的生物相容性和机械性能[12],研究表明将石墨烯及其衍生物应用于种植体材料表面涂层研究中,可以明显促进细胞成骨分化和具有良好的抗菌作用。 石墨烯及其衍生物是最具有代表性的二维碳纳米材料,石墨烯氧化可以获得氧化石墨烯(graphene oxide,GO),氧化石墨烯可以合成还原氧化石墨烯。此外,石墨烯衍生物表面积大、活性位点多,是药物和生物活性因子的良好载体[13],可以广泛应用在口腔种植体组织工程研究中。其中氧化石墨烯由于在生物应用中具有更好的机械性能和生物活性,近年来在口腔种植领域中应用较为广泛。 2.1.2 碳纳米纤维 碳纳米纤维是由多层石墨片卷曲而成的纤维状纳米碳材料,具有良好生物相容性,可作为口腔骨组织工程修复中的增强材料[14]。 2.1.3 碳纳米管 碳纳米管是具良好的机械性能和官能团可修饰性的一维碳纳米材料,主要有单壁纳米管、多壁纳米管2种类型[15]。碳纳米管还可以释放骨生成药物、抗炎药物和生长因子,其可常用于作为口腔组织工程支架材料。 2.1.4 其他碳纳米材料 纳米金刚石是指直径为4.0-5.0 nm的碳纳米颗粒,是零维碳纳米材料的典型代表,它具有良好的机械性能、化学惰性、生物相容性和耐磨性。纳米金刚石还能够同时递送骨形态发生蛋白2和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2种蛋白,促进成骨细胞增殖和分化[16]。 2.2 碳纳米材料的特点 由于种植体周围病和植入材料骨愈合不佳的问题,将明显增加临床种植体植入的失败率,学者们不断研究具有良好生物相容性和机械性能的植入体材料,以提高种植体骨结合的质量和速度。此外,在植入物材料上用抗菌材料薄膜和药物对植入物表面进行功能化,为制造新型植入材料提供了新的机会。研究发现碳纳米材料具有成骨、抗菌、靶向位点吸附药物的特点,这类具有抗菌性能的骨组织移植物既可修复骨缺损又对种植体周围炎治疗或预防具有一定意义。 "

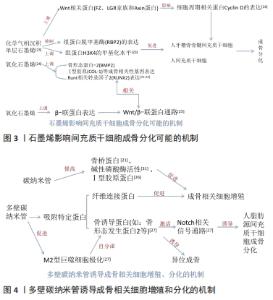
2.2.1 碳纳米材料的成骨作用 大量研究表明,氧化石墨烯能够促进人间充质干细胞成骨向分化、成骨细胞和MC3T3-E1 细胞黏附和增殖及牙周膜干细胞增殖及成骨分化[17-22],具有很强的骨传导和骨源性细胞生长诱导能力。其中单层石墨烯可以促进人间充质干细胞和人牙槽骨骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,这可能与抑制组蛋白脱甲基酶(retinoblastoma binding protein 2,RBP2)的表达上调H3K4的甲基化水平机制相关,也可能与石墨烯能够上调骨形成蛋白2、Runt相关转录因子2、Ⅰ型胶原等成骨相关性基因表达水平有关[23]。化学气相沉积的石墨烯通过上调Wnt相关蛋白,包括FZ、LGR家族和Axin蛋白,最终影响细胞周期、增殖和分化相关蛋白Cyclin D的表达,从而促进人间充质干细胞的成骨[24]。有实验表明,氧化石墨烯可以上调β-联蛋白表达,并通过Wnt/β-联蛋白通路使Runt相关转录因子2(RUNX2)表达上调[25]。同样碳纳米管对成骨细胞的附着和增殖有促进作用,还可以促进间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化[26]。碳纳米管在骨修复过程中控制成骨细胞、破骨细胞等细胞的行为以及分化,从而促进骨修复进程[26]。碳纳米管还可以促进小鼠胚胎干细胞的成骨分化和M2型巨噬细胞极化[21],即在损伤部位细胞大量分泌重组人骨形态发生蛋白、血小板衍生生长因子、转化生长因子等物质,引发一系列促进骨组织再生的细胞反应[27-28]。碳纳米管还可以通过T转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路促进成牙骨质细胞的分化与矿化[12,22]。 氧化石墨烯、碳纳米管通过控制成骨细胞[29]、破骨细胞等细胞黏附和增殖以及分化[20],从而促进骨修复进程,还能促进间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化[27]。大量研究还将氧化石墨烯、碳纳米管等碳纳米材料与其他生物分子材料功能化组合成复合材料,从而可以获得某种特性[29-30]。还原氧化石墨烯和多壁碳纳米管在一定程度也能促进小鼠前成骨细胞黏附和增殖及分化[21]。与纳米羟基磷灰石相比,多壁碳纳米管能诱导人脂肪间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,体内诱导异位成骨其机制可能是多壁碳纳米管通过聚集更多的蛋白质(包括M2巨噬细胞分泌的特异性骨诱导蛋白)来激活Notch相关的信号通路[27]。实验发现碳纳米管可以通过提高成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨唾液酸蛋白和骨钙素所有基因的mRNA表达水平均显著上调,有利于进而促进成骨相关细胞增殖分化[26,31]。多壁碳纳米管作为填料应用于活骨组织生物复合材料中,其具有良好的生物相容性,可以促进骨整合的发生。大量研究碳纳米管表面功能化在牙科植入物纳米复合材料中(如羟基磷灰石、氧化锆和钛),可以更好地促进成骨细胞增殖,其中碳纳米管与羟基磷灰石的结合表现出的细胞相容性,被认为是一种有吸引力的骨填充材料[30]。 氧化石墨烯改性的碳纳米纤维复合材料可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖及成骨分化,碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化潜力具有积极影响[32]。涂有纳米金刚石薄膜的生物材料提高骨导电性和生物活性,也能刺激骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞黏附、增殖及成骨分化[33-34],实验发现,成骨细胞特异性因子2、骨唾液蛋白和骨形态发生蛋白2 mRNA表达显著增加,并增强了体内骨形成的发生[34-35]。 文章总结了石墨烯影响间充质干细胞成骨分化可能的机制,以及多壁碳纳米管诱导成骨相关细胞增殖、分化的机制,见图3,4。 "
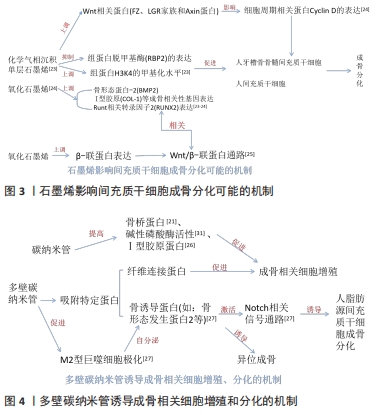
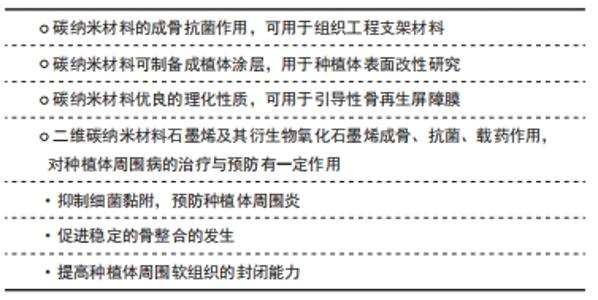
2.2.2 碳纳米材料抗菌机制与抗菌效果 有研究提出,石墨烯及其衍生物的抗菌机制主要有膜应激、氧化应激和电子转移等多种假说[35],氧化石墨烯对革兰阳性与阴性菌均有良好的抑制作用,研究发现,氧化石墨烯纳米片层在一定浓度和作用时间的条件下,能抑制细菌生物膜的形成[36]。钛表面氧化石墨烯涂层可以有效抑制细菌黏附及生物膜的形成,并随着氧化石墨烯层数的增加,抗菌和成骨作用将增加[37]。碳纳米管也已被证明对广泛的病原体具有很强的抗菌活性[38]。氧化石墨烯和碳纳米管均可通过活性氧的氧化压力杀死细菌[37-39]。 碳纳米材料的抗菌效果与材料自身的物理性能和化学结构相关。石墨烯的独特物理化学特性依赖于合成方法。碳纳米管的抗菌效果也受表面化学,纳米管的直径、长度和电子结构等多种因素的影响,其中纳米管的长度影响与细胞膜的相互作用[36-38]。 2.2.3 碳纳米材料因其独特的空间结构可作为药物、蛋白等分子物质载体 纳米材料的应用对牙种植术具有积极的影响,并改善了骨整合等临床实践。纳米级药物输送工具在组织再生和生物分子控制释放中具有很大的应用潜力,对碳纳米粒子药物输送平台的许多研究已经验证了碳纳米材料可用于组织修复[16]。石墨烯层内碳原子共同形成大π键,可通过π-π非共价的堆积结合疏水相互作用吸附客体药物分子,可实现难溶药物的高载药率、良好的水溶性和靶向性[25,40]。石墨烯涂层具有良好的蛋白质吸附和细胞黏附能力,可以扩大钛种植体表面的成骨活性。此外石墨烯及其衍生物通过大量吸附胞外基质蛋白,从而促进细胞黏附[40]。它还可以吸附骨形态发生蛋白及其他成骨诱导剂(如地塞米松、抗坏血酸等)[41-42],使局部成骨相关因子浓度升高,加速成骨过程[43]。植入物的氧化石墨烯涂层还可以输送地塞米松,用于促进大鼠骨髓干细胞的成骨分化[42]。氧化石墨烯是一种新型的纳米基因载体,应用于种植体表面siRNA 分子递送方面显示出巨大的应用潜力[44]。新的骨再生候选药物辛伐他汀(Sim,一种降脂类药物)与氧化石墨烯也可作为一种给药方式相结合,制备出一种有效的骨再生复合物,具有良好的成骨分化潜力[45]。 碳纳米管可以释放骨生成药物、抗炎药物、生长因子。碳纳米管的大比表面积及空心结构使其具有较强的药物携带能力,并可调节药物释放行为,从而改善药物的渗透性以及药物滞留。早期科学家成功地将抗炎症药物地塞米松吸附在碳纳米管内,实验证实了碳纳米管的独特结构能够缓慢释放药物,并有利于骨再生。研究表明,碳纳米管表面可以良好地吸附氨基酸、Ⅰ型胶原、骨形态发生蛋白及地塞米松,因此碳纳米管促进成骨方面应用潜力巨大[46]。纳米金刚石是具有生物相容性的4.0-5.0 nm碳纳米颗粒,已用于传递各种生长因子,包括蛋白质和肽。碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对于促进成骨细胞祖细胞的增殖至关重要,而骨形态发生蛋白对于刺激成骨细胞的分化和矿物质生成是必不可少的。MOORE等[16]证明了纳米金刚石同时递送骨形态发生蛋白2和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子会诱导成骨祖细胞的分化和增殖。临床如果种植体发生不愈合或植入失败,可以通过注射或冲洗ND-BMP+bFGF(一种可注射性骨替代物)解决方案避免再次手术。 2.3 新型碳纳米材料在口腔种植中的研究进展 "
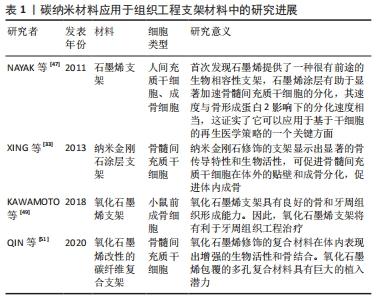
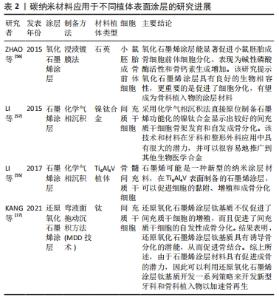
2.3.1 碳纳米材料的成骨抗菌作用,可用于组织工程支架材料 组织工程学在牙种植体方面的研究主要集中在伤口愈合与骨组织的再生,主要包括种植体周骨的再生、相关生长因子和信号通路的调控、骨与软组织的种子细胞与支架材料、组织工程技术增强的各种骨增量技术等领域。生物支架材料在组织工程中,起着替代组织或器官的细胞外基质的作用。目前对支架材料的研究中发现碳纳米材料具有良好的生物相容性,可以促进骨组织工程中相关细胞增殖、黏附及分化[20,22]。 NAYAK等[47]首先报告说,具有良好生物相容性的石墨烯作为一个有希望的骨组织工程支架,不抑制人类间质干细胞的细胞增殖,并可以促进其向成骨细胞的特异性分化,其分化速率可与普通生长因子所达到的分化速率相比,部分情况下甚至优于成骨诱导因子。石墨烯可以改善复合材料的力学性能及其生物相容性,作为骨增强复合材料在骨组织工程中具有一定的应用前景。氧化石墨烯涂敷的骨组织工程支架明显刺激了成骨细胞和牙周韧带细胞增殖及成骨分化[22,48],KAWAMOTO等[49]实验发现,氧化石墨烯支架能够增加牙周附着、类牙骨质和牙周韧带的形成。而碳纳米纤维常用来提高组织工程复合材料支架的力学性能,可为黏附在支架上面的细胞提供营养物质并排泄代谢物[50]。研究发现,氧化石墨烯改性的碳纤维复合支架有利于骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖、黏附和骨整合[51]。与石墨烯衍生物一样,碳纳米管的主要应用之一是组织工程,作为支架,为细胞的合并或生长因子提供合适的环境,以再生受损组织[52]。碳纳米管同样也可以应用于组织工程支架,尤其是骨组织工程领域,碳纳米管支架与成骨细胞、破骨细胞,骨髓间充质干细胞之间有相互作用[20]。研究显示,这种多孔结构的支架材料有利于干细胞和成骨细胞黏附,从而促进骨再生[46]。该支架植入大鼠4周后还可明显促进缺损部位的血管再生,将有利于骨组织缺损的修复[53]。XING等[33]研究发现,纳米金刚石涂层支架促进了骨骼形成过程中涉及基因的表达,即骨唾液酸蛋白 和 骨形态发生蛋白显著增加。 2.3.2 碳纳米材料可制备成植体涂层,用于种植体表面改性研究 钛种植体目前被认为是天然牙齿的最佳替代品,因为它们具有良好的生物相容性,使钛种植体成为最佳选择。然而,钛固有的惰性,且缺少刺激骨源性细胞生长和诱导的能力,这些都可能会导致种植体失败。为了尽量减少种植体术后并发症,获得迅速而稳定的骨整合,大量研究开始探索种植体不同的表面处理方式及其效果。其中许多实验将碳纳米材料用于种植体表面涂层,以加速种植体骨结合过程[5-6]。 基于对石墨烯及其衍生物成骨性能的研究,学者们发现将其用于种植体表面涂层可以显著促进骨整合的发生。有研究表明钛表面的氧化石墨烯涂层加速了成骨分化,与成骨相关的基因和蛋白(例骨钙素和骨桥蛋白等)增多,并增加矿化结核沉积[5,54]。石墨烯涂层钛表面的骨髓间充质干细胞形态扁平,表达更多的成骨相关基因和蛋白,涂层表面促进和加速了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化能力[55]。将氧化石墨烯作用于不同的种植体材料中发现,Ti6Al4V植体上的氧化石墨烯涂层增加了材料表面粗糙度和亲水性,并通过促进碱性磷酸酶活性、钙沉积以及骨形态发生蛋白、α1-Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素和成骨转录因子RUNX2基因的表达,促进间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖和骨分化[55]。在钛基底上涂布用于引导性骨再生的氧化石墨烯薄膜,可以显著刺激小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞中的碱性磷酸酶活性,并在骨缺损大鼠模型中8周后形成更大的钙化骨结节[56]。镍钛合金涂布氧化石墨烯或明胶-氧化石墨烯,也可以改进蛋白质吸附功能,以及促进小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞黏附、增殖及细胞分化[56]。一项研究通过化学气相沉积在镍钛合金上制备石墨烯涂层,发现形成的石墨烯涂层通过增加骨形态发生蛋白、α-Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素和成骨转录因子RUNX2基因的表达,增加了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[57]。研究发现氧化石墨烯还与无机材料结合作为涂层,以协同提高植入物的表面特性。在钛材料上添加氧化石墨烯和羟基磷灰石复合涂层,可增强涂层黏附性和植入涂层粘结强度。与纯羟基磷灰石涂层相比,氧化石墨烯和羟基磷灰石复合涂层可以防止表面裂缝的形成,提高了植入物的耐腐蚀性能[12,58]。钛植入物表面的氧化石墨烯涂层可通过FAK/P38信号通路的介导来实现快速的骨植入物整合[6],同样钛表面还原氧化石墨烯涂层也具备较强的促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用,通过提高细胞碱性磷酸酶活性和促进基质矿化,具有良好的生物活性和成骨潜能,是一种有效的牙科和骨科骨替代材料[17]。氧化石墨烯涂层的钛改性表面具有多孔结构,结合氧化石墨烯的物理和化学性质还可以促进人牙髓干细胞矿化组织形成并具有抗感染性能,有利于牙本质整合[29]。带氧化石墨烯涂层的胶原蛋白海绵植入小猎犬拔牙后的牙槽窝中,实验发现可在2周内促进新骨的形成。在小猎犬Ⅱ类骨缺陷动物体内实验中,进一步证实了氧化石墨烯涂层改善骨愈合和牙周附着[12,49]。 文章将碳纳米材料应用于组织工程支架材料中和应用于组织工程支架材料中的研究进展作一汇总,见表1,2。 "
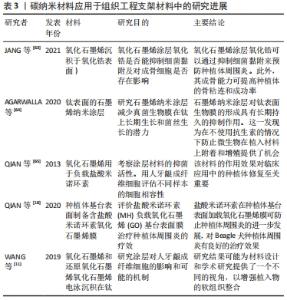
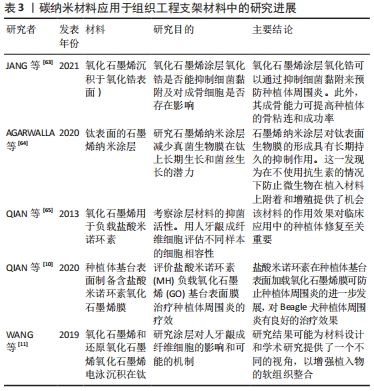
2.3.3 碳纳米材料优良的理化性质,可用于引导性骨再生屏障膜 引导骨再生是在牙科植入物放置之前应用的治疗方式,用于在骨缺陷部位或在引导植入物周围骨组织生长的过程中增加骨密度[59]。这种人造屏障还可作为支架,促进成骨细胞以比周围结缔组织更高的速率刺激骨形成,并在用于牙科植入物时防止感染。引导骨再生屏障膜可分为可降解膜和不可降解膜,在临床应用中,较为常用的可吸收膜常面临力学性能不足的问题,易发生穿孔与破裂[60-61]。 氧化石墨烯是应用较为广泛的一类石墨烯衍生物材料,具有良好的理化性质。添加氧化石墨烯的复合屏障膜在引导骨再生中同样有着良好的应用前景。在口腔手术中,将石墨烯添加到膜中,这种复合材料可以防止软组织细胞渗入生长[29]。实验表明,氧化石墨烯添加的胶原蛋白膜可减少炎症反应,还有利于人牙龈成纤维细胞的增殖[20]。3D还原氧化石墨烯多孔膜也可以促进细胞的活力和增殖,并能显著增强碱性磷酸酶活性和成骨相关基因的表达[61]。QI 等[62]研究氧化石墨烯-赖氨酸复合膜可以促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化,而不会影响间充质干细胞的形状和生长。张开润等[60]发现,氧化石墨烯-壳聚糖这种新型复合膜有较好的抗拉强度且生物相容性良好,但关于氧化石墨烯-壳聚糖的交联关系及机制,尚待深入研究。当石墨烯纳米片被添加到聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物上(一种牙周引导组织再生膜)薄膜中,复合薄膜促进了大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞细胞黏附、增殖和成骨分化,正因添加了石墨烯纳米片,实验发现碱性磷酸酶活性增强,钙矿物质沉积增加以及骨形态发生蛋白、α1-Ⅰ型胶原、骨钙素和成骨转录因子RUNX2基因等成骨相关基因表达增加[12]。 2.3.4 二维碳纳米材料石墨烯及其衍生物氧化石墨烯成骨、抗菌、载药作用,对种植体周围病的治疗与预防有一定作用 牙种植术因其美观舒适、固位支持作用好而获得医生和患者的广泛认可,已成为牙齿缺失修复的主要方法。虽然牙种植成功率很高,但也存在失败病例和并发症。其中,临床上种植体周围炎导致的植入体损失(脱落或彻底失败)接近4%,是种植体失败的主要原因之一。种植体周围病是发生在牙种植体周围软硬组织的感染性炎症,包括种植体周围黏膜炎和种植体周围炎2类疾病[4]。 抑制细菌黏附,预防种植体周围炎:一些研究利用碳纳米材料的载药抗菌、促进成骨的特性,在种植体周围炎的预防中有一定的研究意义。石墨烯和氧化石墨烯涂层都可以通过抑制细菌黏附来预防种植体周围炎。JANG等[63]研究氧化石墨烯沉积(氧化锆表面)对细菌黏附和成骨细胞活化的影响,实验发现氧化锆表面的氧化石墨烯涂层可以抑制变形链球菌的黏附,刺激成骨细胞的增殖和分化;其成骨能力可促进骨整合的发生,提高种植体的成功率。AGARWALLA 等[64]也发现石墨烯纳米涂层对钛表面生物膜的形成具有长期持久的抑制作用,研究发现能够附着在石墨烯涂层钛片组的细菌数量较少,且分散在各处,无法形成成熟的菌斑生物膜;在不使用抗生素的情况下,石墨烯涂层也可以有效防止微生物在植入材料上附着和增殖。 促进稳定的骨整合的发生:此外,石墨烯及其衍生物当应用于种植体表面改性时,利用碳纳米材料的载药抗菌和促进成纤维细胞黏附的作用,可以促进稳定的骨整合和提高植体周围软组织的封闭能力,这对于种植体周围炎的治疗和预防也有一定的研究意义。种植体的长期功能依赖于形成良好而稳定的骨整合,而种植体周围炎是一种不可逆的炎症行为,常伴有种植体周围支撑骨的丢失,这将会导致种植体松动甚至脱落。QIAN 等[65]前期研究发现,在纯钛表面负载盐酸米诺环素(MH)的氧化石墨烯(GO)薄膜对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和变形链球菌具有良好的抗菌性能。后续研究在钛种植体基牙上构建了载盐酸米诺环素的氧化石墨烯薄膜,并将其对Beagle犬种植体周围炎的治疗效果进行了系统的研究。在种植体周围炎模型的Beagle犬中实验发现,X射线片评价和Micro-CT断层分析结果都显示,钛和载盐酸米诺环素的钛组的边缘骨丢失较多,氧化石墨烯薄膜的钛组的边缘骨丢失很小,负载盐酸米诺环素的氧化石墨烯薄膜钛组的骨丢失可以忽略不计。该研究发现载盐酸米诺环素的氧化石墨烯薄膜钛片组具有较好的抗菌活性,能有效杀灭种植体周围细菌,防止种植体周围炎的进一步发展,这对种植体周围炎具有良好的治疗效果[10]。 提高种植体周围软组织的封闭能力:种植体的长期功能不仅依赖于稳定的骨整合,还依赖于强大的软组织黏附能力。理想的种植体周围软组织封闭是外部环境和牙槽骨之间的有效保护屏障,防止细菌的入侵。且稳定的软组织附着可保证结合上皮的封闭不脱离,甚至可以限制牙龈的边缘性炎症病损向根方扩散,从而避免发生骨丧失和降低种植体的失败率[4]。已有报道称碳纳米材料有利于软组织封闭,可通过碳原子杂化类型(sp2或sp3)进行调节,但其内在机制尚不清楚。WANG等[11]将氧化石墨烯电泳沉积在钛表面上,即获得GO-Ti组,并探讨其对人牙龈成纤维细胞的作用及其可能机制;并用硼氢化钠溶液和水合肼溶液(体积分数5%)去还原GO-Ti,将样品标记为rGO-1和rGO-2。研究发现Go-Ti,rGO-1和rGO-2上培养的细胞比在钛上培养的细胞有更多的丝状伪足和更高的纤维状肌动蛋白(F-actin)表达。其中rGO-2表面的细胞数量最多,表达的肌动蛋白量最多;随着培养时间的延长,GO-Ti,rGO-1和rGO-2的细胞增殖率均高于Ti;培养4,7 d后,所有样品的细胞数量均呈RGO-2>RGO-1>GO-Ti>Ti的趋势,rGO-2上的细胞增殖率最高。这项研究表明,与钛相比,氧化石墨烯和还原氧化石墨烯更有利于人牙龈成纤维细胞的迁移,其中rGO-2上的人牙龈成纤维细胞的迁移能力最强;GO-Ti,rGO-1和RGO-2都表现出比钛有更高的蛋白质吸附量;在所有样品中,SP2结构域数量最多、尺寸最小的rGO-2对人牙龈成纤维细胞的行为有最积极的影响。该实验证明了氧化石墨烯和还原氧化石墨烯可以为优化金属生物材料的软组织封闭能力提供了一种较好的策略,良好的软组织封闭能力可以显著降低种植体周围炎的发生率。 碳纳米材料中石墨烯作为典型的二维碳纳米材料,一直也是口腔种植及其他领域研究的热点。其中氧化石墨烯是应用较为广泛的一类石墨烯衍生物材料,具有良好的理化性质。研究发现钛表面氧化石墨烯涂层可以显著促进骨整合的发生,在种植体表面改性方面有一定的研究意义。此外石墨烯及其衍生物独特的空间结构,具有运载药物、蛋白和小分子物质的能力。载有盐酸米诺环素的氧化石墨烯薄膜钛片组具有较好的抗菌活性和减少边缘骨丢失的能力。氧化石墨烯和还原氧化石墨烯还有利于牙龈成纤维细胞的迁移与增殖,这能显著增强种植体周围的软组织封闭作用。有2个研究支持验证了石墨烯及其衍生物当应用于种植体表面改性时,可以促进稳定的骨整合和提高植体周围软组织的封闭能力,这对种植体周围炎的治疗及预防方面有一定的研究意义[10,17]。添加氧化石墨烯的复合屏障膜在引导性骨再生术中同样有着良好的应用前景。氧化石墨烯添加的胶原蛋白膜可减少炎症反应,还有利于人牙龈成纤维细胞的增殖,可以防止软组织细胞渗入生长。并有利于细胞增殖、黏附及成骨分化[20]。 文章将碳纳米材料在口腔种植体周围疾病中的研究应用进展作一汇总,见表3。 "
| [1] CHUNG C, KIM YK, SHIN D, et al. Biomedical applications of graphene and graphene oxide. Acc Chem Res. 2013;46(10):2211-2224. [2] VENKATESAN J, PALLELA R, KIM SK. Applications of carbon nanomaterials in bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(10):3105-3123. [3] 张超,张利,刘兴华,等.碳纳米材料的抗菌性及在生物医学中的应用研究进展[J].材料导报,2020,34(S1):53-57. [4] 刘宝林.口腔种植学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2010:18-27. [5] LI Q, WANG Z. Involvement of FAK/P38 signaling pathways in mediating the enhanced osteogenesis induced by nano-graphene oxide modification on titanium implant surface. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:4659-4676. [6] PASSERI D, RINALDI F, INGALLINA C, et al. Biomedical applications of nanodiamonds: an overview. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2015;15(2):972-988. [7] 王倩云,张元杰,买热叶木姑·艾沙,等.石墨烯及氧化石墨烯在口腔组织再生领域的研究进展[J].西北国防医学杂志,2021,42(2): 123-129. [8] 王楠,周延民.石墨烯材料在口腔医学领域的应用及生物安全性研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(5):410-412. [9] 魏常博,余东升. 石墨烯在口腔种植中的应用前景[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志(电子版),2016,10(2):151-154. [10] QIAN W, QIU J, LIU X. Minocycline hydrochloride-loaded graphene oxide films on implant abutments for peri-implantitis treatment in beagle dogs. J Periodontol. 2020;91:792-799. [11] WANG L, QIU JN, GUO J, et al. Regulating the behavior of human gingival fibroblasts by sp domains in reduced graphene oxide. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5:6414-6424. [12] DANESHMANDI L, BARAJAA M, TAHMASBI RAD A, et al. Graphene-based biomaterials for bone regenerative engineering:a comprehensive review of the field and considerations regarding biocompatibility and biodegradation. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(1):2001414. [13] CHENG X, WAN Q, PEI X. Graphene family materials in bone tissue regeneration: perspectives and challenges. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2018; 13:289. [14] SAMADIAN H, MOBASHERI H, AZAMI M, et al. Osteoconductive and electroactive carbon nanofibers/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite tailored for bone tissue engineering: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14853. [15] PATEL DK, DUTTA SD, GANGULY K, et al. Enhanced osteogenic potential of unzipped carbon nanotubes for tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2021;109(10):1869-1880. [16] MOORE L, GATICA M, KIM H, et al. Multi-protein delivery by nanodiamonds promotes bone formation. J Dent Res. 2013;92(11):976-981. [17] KANG MS, JEONG SJ, LEE SH, et al. Reduced graphene oxide coating enhances osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on Ti surfaces. Biomater Res. 2021;25:4. [18] LUO Y, SHEN H, FANG Y, et al. Enhanced proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on graphene oxide-incorporated electrospun poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibrous mats. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(11):6331-6339. [19] KANAYAMA I, MIYAJI H, TAKITA H, et al. Comparative study of bioactivity of collagen scaffolds coated with graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:3363-3373. [20] BONILLA-REPRESA V, ABALOS-LABRUZZI C, HERRERA-MARTINEZ M, et al. Nanomaterials in dentistry: state of the art and future challenges. Nanomaterials. 2020;10(9):1770. [21] BARRIENTOS-DURÁN A, CARPENTER EM, ZUR NIEDEN NI, et al. Carboxyl-modified single-wall carbon nanotubes improve bone tissue formation in vitro and repair in an in vivo rat model. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:4277-4291. [22] LI L, ZHU Z, XIAO W, et al. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes promote cementoblast differentiation and mineralization through the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:3188-201. [23] LIU Y, CHEN T, DU F, et al. Single-layer graphene enhances the osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2016;12(6):1270-1284. [24] KANG ES, KIM H, HAN Y, et al. Enhancing osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells using gold nanostructure/peptide-nanopatterned graphene oxide. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021; 204:111807. [25] WEI C, LIU Z, JIANG F, et al. Cellular behaviours of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards pristine graphene oxide nanosheets. Cell Prolif. 2017,50(5):e12367. [26] PATEL KD, KIM TH, MANDAKHBAYAR N, et al. Coating biopolymer nanofibers with carbon nanotubes accelerates tissue healing and bone regeneration through orchestrated cell- and tissue-regulatory responses. Acta Biomater. 2020;108:97-110. [27] DU Z, FENG X, CAO G, et al. in vitro The effect of carbon nanotubes on osteogenic functions of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone formation compared with that of nano-hydroxyapatite and the possible mechanism. Bioact Mater. 2021;6:333-345. [28] 田江雪,莫龙义,贾小玥,等.转化生长因子β在牙周炎发生发展中的作用及其机制[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2018,45(5):553-559. [29] TAHRIRI M, DEL MONICO M, MOGHANIAN A, et al. Graphene and its derivatives: opportunities and challenges in dentistry. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;102:171-185. [30] CASTRO-ROJAS MA, VEGA-CANTU YI, CORDELL GA, et al. Dental Applications of Carbon Nanotubes. Molecules. 2021;26(15):4423. [31] MUNIR KS, WEN C, LI Y. Carbon nanotubes and graphene as nanoreinforcements in metallic biomaterials: a review. Adv Biosyst. 2019,3(3):1800212. [32] SKOOG SA, KUMAR G, ZHENG J, et al. Biological evaluation of ultrananocrystalline and nanocrystalline diamond coatings. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27:187. [33] XING Z, PEDERSEN TO, WU X, et al. Biological effects of functionalizing copolymer scaffolds with nanodiamond particles. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(15-16):1783-1791. [34] KLOSS FR, GASSNER R, PREINER J, et al. The role of oxygen termination of nanocrystalline diamond on immobilisation of BMP-2 and subsequent bone formation. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2433-2442. [35] SHI L, CHEN J, TENG L, et al. The antibacterial applications of graphene and its derivatives. Small. 2016;12:4165-4184. [36] QIU J, GENG H, WANG D, et al. Layer-number dependent antibacterial and osteogenic behaviors of graphene oxide electrophoretic deposited on titanium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(4):12253-12263. [37] MOHAMMED H, KUMAR A, BEKYAROVA E, et al. Antimicrobial mechanisms and effectiveness of graphene and graphene-functionalized biomaterials. A Scope Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:465. [38] ARIAS LR, YANG L. Inactivation of bacterial pathogens by carbon nanotubes in suspensions. Langmuir. 2009;25(5):3003-3012. [39] 汪秀南,刘轶,徐京城,等.石墨烯基药物传输系统结合强度和药物扩散的分子动力学研究[J].功能材料,2015,46(16):16052-16058. [40] PARK J, KIM B, HAN J, et al. Graphene oxide flakes as a cellular adhesive: prevention of reactive oxygen species mediated death of implanted cells for cardiac repair. ACS Nano. 2015;9(5):4987-4999. [41] HAN L, SUN H, TANG P, et al. Mussel-inspired graphene oxide nanosheet-enwrapped Ti scaffolds with drug-encapsulated gelatin microspheres for bone regeneration. Biomater Sci. 2018;6:538-549. [42] PARK J, PARK S, KIM JE, et al. Enhanced osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells using a graphene oxide-coated poly (ε-caprolactone) scaffold. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(5):797. [43] KUMAR S, RAJ S, SARKAR K, et al. Engineering a multi-biofunctional composite using poly(ethylenimine) decorated graphene oxide for bone tissue regeneration. Nanoscale. 201;8:6820-6836. [44] ZHANG L, ZHOU Q, SONG W, et al. Dual-functionalized graphene oxide based sirna delivery system for implant surface biomodification with enhanced osteogenesis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9:34722-34735. [45] OH JS, LEE EJ. Enhanced effect of polyethyleneimine-modified graphene oxide and simvastatin on osteogenic differentiation of murine bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biomedicines. 2021;9(5):501. [46] 任义行,黄若愚,王存阳,等.碳纳米管作为骨修复材料的优势和挑战[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(3):271-277. [47] NAYAK TR, ANDERSEN H, MAKAM VS, et al. Graphene for controlled and accelerated osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Nano. 2011;5(6):4670-4678. [48] KANG Y,SCULLY A,YOUNG DA, et al. Enhanced mechanical performance and biological evaluation of a PLGA coated β-TCP composite scaffold for load-bearing applications. Eur Polym J. 2011;47:1569-1577. [49] KAWAMOTO K, MIYAJI H, NISHIDA E, et al. Characterization and evaluation of graphene oxide scaffold for periodontal wound healing of class II furcation defects in dog. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13: 2365-2376. [50] VELIOGLU N, AKOVA T, OZKOMUR A. Effects of hard thin-film coatings on adhesion of early colonizer bacteria over titanium surfaces. Implant Dent. 2016;25(1):114-121. [51] QIN W, LI Y, MA J, et al. Osseointegration and biosafety of graphene oxide wrapped porous CF/PEEK composites as implantable materials: the role of surface structure and chemistry. Dent Mater. 2020;36: 1289-1302. [52] LOH QL, CHOONG C. Three-dimensional scaffolds for tissue engineering applications: role of porosity and pore size. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013; 19:485-502. [53] KHALID P, SUMAN VB. Carbon nanotube-hydroxyapatite composite for bone tissue engineering and their interaction with mouse fibroblast L929 in vitro. J Bionanosci. 2017;11(3):233-240. [54] LEE WC, LIM CH, SHI H, et al. Origin of enhanced stem cell growth and differentiation on graphene and graphene oxide. ACS Nano. 2011;5: 7334-7341. [55] LI K, YAN J, WANG C, et al. Graphene modified titanium alloy promote the adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;489: 187-192 [56] ZHAO C, LU X, ZANDEN C. The promising application of graphene oxide as coating materials in orthopedic implants: preparation, characterization and cell behavior. Biomed Mater. 2015;10:015019. [57] LI J, WANG G, GENG H, et al. CVD growth of graphene on niti alloy for enhanced biological activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7; 19876-19881. [58] XIE Y, LI H, DING C, et al. Effects of graphene plates’ adoption on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and in vivo biocompatibility of calcium silicate coating. Int J Nanomedicine. 2015;10:3855-3863. [59] WANG Y, HUA Y, ZHANG Q, et al. Using biomimetically mineralized collagen membranes with different surface stiffness to guide regeneration of bone defects. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12: 1545-1555. [60] 张开润,许瑞,邹多宏.氧化石墨烯-壳聚糖复合膜的抗拉强度及其对人牙龈成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2019, 54(5):322-327. [61] TIAN Z, HUANG L, PEI X, et al. Electrochemical synthesis of three-dimensional porous reduced graphene oxide film: preparation and in vitro osteogenic activity evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;155:150-158. [62] QI W, YUAN W, YAN J, et al. Growth and accelerated differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on graphene oxide/poly-l-lysine composite films. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2:5461-5467. [63] JANG W, KIM HS, ALAM K, et al. Direct-deposited graphene oxide on dental implants for antimicrobial activities and osteogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:5745-5754. [64] AGARWALLA SV, ELLEPOLA K, SILIKAS N, et al. Persistent inhibition of Candida albicans biofilm and hyphae growth on titanium by graphene nanocoating. Dent Mater. 2021;37:370-377. [65] QIAN W, QIU J, SU J, et al. Minocycline hydrochloride loaded on titanium by graphene oxide: an excellent antibacterial platform with the synergistic effect of contact-killing and release-killing. Biomater Sci. 2018;6:304-313. [66] DU Z, WANG C, ZHANG R, et al. Applications of graphene and its derivatives in bone repair: advantages for promoting bone formation and providing real-time detection, challenges and future prospects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:7523-7551. [67] JYOTI J, KIRAN A, SANDHU M, et al. Improved nanomechanical and in-vitro biocompatibility of graphene oxide-carbon nanotube hydroxyapatite hybrid composites by synergistic effect. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;117:104376. [68] ZHANG Z, WANG Y, TENG W, et al. An orthobiologics-free strategy for synergistic photocatalytic antibacterial and osseointegration. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120853. [69] DANTAS PCL, MARTINS-JÚNIOR PA, COUTINHO DCO, et al. Nanohybrid composed of graphene oxide functionalized with sodium hyaluronate accelerates bone healing in the tibia of rats. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123:111961. [70] ZOU M, SUN J, XIANG Z. Induction of M2-type macrophage differentiation for bone defect repair via an interpenetration network hydrogel with a go-based controlled release system. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10:e2001502. [71] AL RUGAIE O, JABIR M, KADHIM R, et al. Gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide flakes synergistic partaking in cytosolic bactericidal augmentation: role of ROS and NOX2 activity. Microorganisms. 2021; 9(1):101. [72] PANG L, DAI C, BI L, et al. Biosafety and antibacterial ability of graphene and graphene oxide in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2017;12: 564. [73] ZANCANELA DC, SIMÃO AM, FRANCISCO CG, et al. Graphene oxide and titanium: synergistic effects on the biomineralization ability of osteoblast cultures. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27:71. |
| [1] | Sun Kexin, Zeng Jinshi, Li Jia, Jiang Haiyue, Liu Xia. Mechanical stimulation enhances matrix formation of three-dimensional bioprinted cartilage constructs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | Pan Zhongjie, Qin Zhihong, Zheng Tiejun, Ding Xiaofei, Liao Shijie. Targeting of non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of the osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [3] | Cai Zhihao, Xie Zhaoyong. Femoral neck anteversion measurement assessment: how to establish a unified method and standard [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [4] | Dang Yi, Du Chengyan, Yao Honglin, Yuan Nenghua, Cao Jin, Xiong Shan, Zhang Dingmei, Wang Xin. Hormonal osteonecrosis and oxidative stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [5] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [6] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [7] | Chen Shisong, Liu Xiaohong, Xu Zhiyun. Current status and prospects of bioprosthetic heart valves [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1096-1102. |
| [8] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [9] | Shi Yehong, Wang Cheng, Chen Shijiu. Early thrombosis and prevention of small-diameter blood vessel prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1110-1116. |
| [10] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [11] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [12] | Tao Xin, Xu Yi, Song Zhiwen, Liu Jinbo. Hippo signaling pathway in the regulation of spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 619-625. |
| [13] | Li Shihao, Li Qi, Li Zhen, Zhang Yuanyuan, Liu Miaomiao, Ouyang Yi, Xu Weiguo. Plantar pressure and gait analysis in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury and reconstruction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhou Jie, Pei Xibo, Wan Qianbing. Advances and biological application of asymmetric dressings [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 434-440. |
| [15] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||