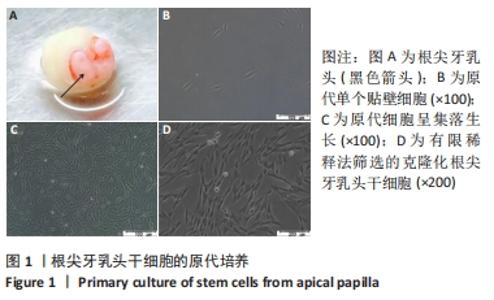
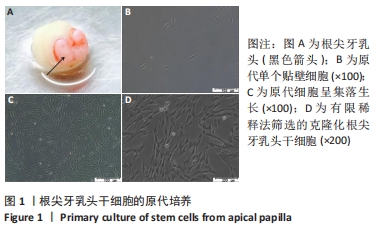
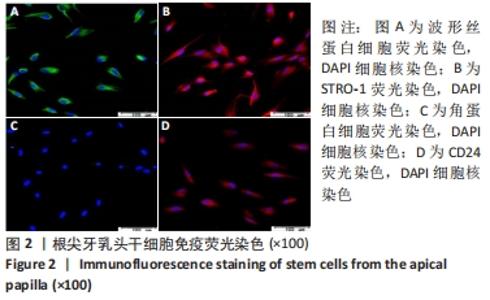
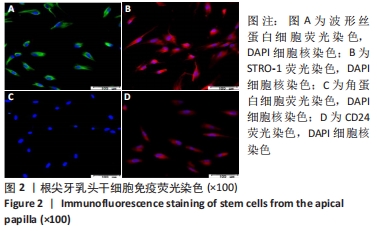
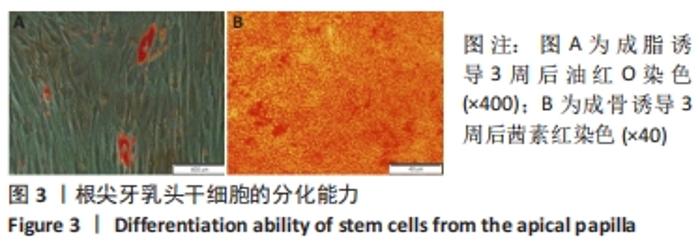
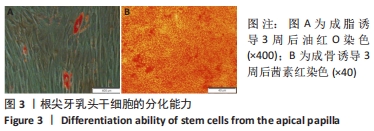
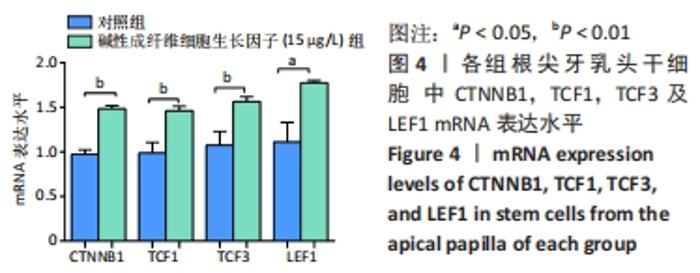
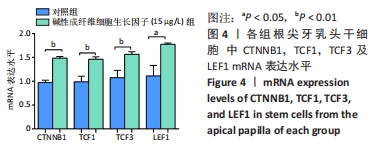
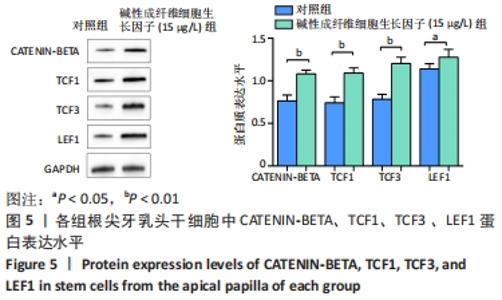
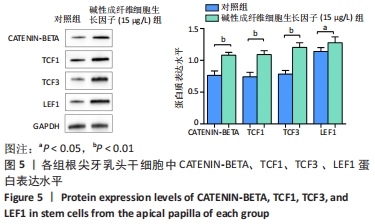
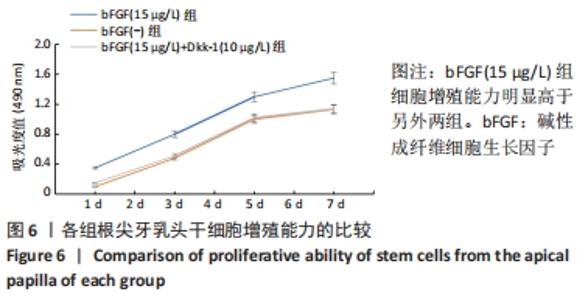
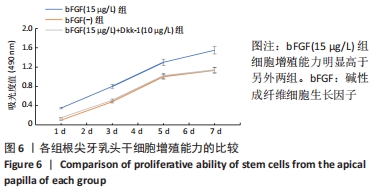
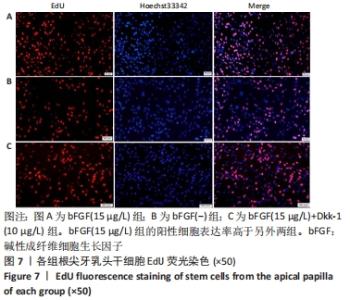
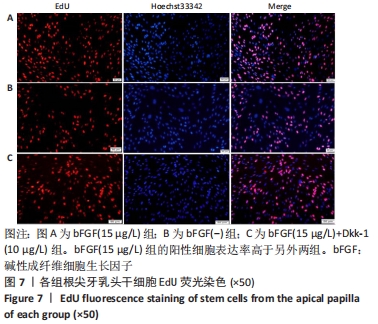
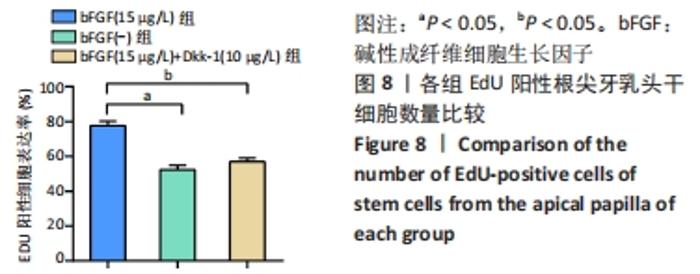
[1] 王恒心,王思拓,伍美玲,等.牙源性干细胞及牙髓再生的研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2019,12(5):312-316.
[2] AURREKOETXEA M, IRASTORZA I, GARCÍA-GALLASTEGUI P, et al. Wnt/β-Catenin Regulates the Activity of Epiprofin/Sp6, SHH, FGF, and BMP to Coordinate the Stages of Odontogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2016;4:25.
[3] YUN CY, CHOI H, YOU YJ, et al. Requirement of Smad4-mediated signaling in odontoblast differentiation and dentin matrix formation. Anat Cell Biol. 2016;49(3):199-205.
[4] ZHAI Q, DONG Z, WANG W, et al. Dental stem cell and dental tissue regeneration. Front Med. 2019;13(2):152-159.
[5] SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, YAMAZA T, et al. Characterization of the apical papilla and its residing stem cells from human immature permanent teeth: a pilot study. J Endod. 2008;34(2):166-171.
[6] 马玉,段子文,李淑慧,等.牙周膜干细胞与根尖乳头干细胞成骨及成牙本质能力比较的实验研究[J].口腔医学,2018,38(1):5-9.
[7] 赵璐,于莉,袁萍,等.根尖乳头干细胞与牙周膜干细胞的生物学行为比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):113-117.
[8] 谭小兵,郭宇,刘佳,等.人牙髓干细胞和根尖乳头干细胞体外分化能力的对比研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(5):586-589.
[9] 李林峰,李健.牙源性干细胞在组织工程中的研究与应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2019,35(3):179-183.
[10] DU J, LU Y, SONG M, et al. Effects of ERK/p38 MAPKs signaling pathways on MTA-mediated osteo/odontogenic differentiation of stem cells from apical papilla: a vitro study. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):S30-S43.
[11] SCHNEIDER R, HOLLAND GR, CHIEGO D JR, et al. White mineral trioxide aggregate induces migration and proliferation of stem cells from the apical papilla. J Endod. 2014;40(7):931-936.
[12] 王远锏.bFGF:碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的研究现状与应用[J].科技创新与应用,2019(26):165-166.
[13] WU J, HUANG GT, HE W, et al. Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances stemness of human stem cells from the apical papilla. J Endod. 2012; 38(5):614-622.
[14] 何梅. Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路和p38信号通路对bFGF维持人根尖牙乳头干细胞干性的影响[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2019.
[15] 何梅,吴家媛.Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路对牙根发育的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28):4556-4562.
[16] YANG ZH, LIU F. Wnt/β-catenin signaling for dentalregeneration. Regen Dent Implant Ther. 2014;1:3-8.
[17] WANG B, LI H, LIU Y, et al. Expression patterns of WNT/β-CATENIN signaling molecules during human tooth development. J Mol Histol. 2014;45(5):487-496.
[18] YOSHIOKA S, TAKAHASHI Y, ABE M, et al. Activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease 1 during tertiary dentinogenesis. J Biochem. 2013;153(1):43-50.
[19] JIN Y, WANG C, CHENG S, et al. MicroRNA control of tooth formation and eruption. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;73:302-310.
[20] MOON RT, SHAH K. Developmental biology: signalling polarity. Nature. 2002;417(6886):239-240.
[21] 冯晓宇,易昆,贾瑞芝,等.Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路对钟状晚期牙胚成釉器上皮调控的初步研究[J].北京口腔医学,2020,28(3):126-130.
[22] LI Z, XU Z, DUAN C, et al. Role of TCF/LEF Transcription Factors in Bone Development and Osteogenesis. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(12):1415-1422.
[23] WANG X, ZHU Y, SUN C, et al. Feedback Activation of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Signaling via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Skin Fibroblasts. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:32.
[24] 黄义彬.人根尖乳头干细胞与牙髓干细胞体外生物学特性的比较研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[25] SONOYAMA W, LIU Y, FANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated functional tooth regeneration in swine. PLoS One. 2006;1(1):e79.
[26] 苏尚,吴畏.Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路对靶基因转录的调控[J].中国科学:生命科学,2014,44(10):1029-1042.
[27] SCHWARZ-ROMOND T. Three decades of Wnt signalling. EMBO J. 2012; 31(12):2664.
[28] ROOSE J, HULS G, VAN BEEST M, et al. Synergy between tumor suppressor APC and the beta-catenin-Tcf4 target Tcf1. Science. 1999; 285(5435):1923-1926.
[29] CHEESMAN SE, NEAL JT, MITTGE E, et al. Epithelial cell proliferation in the developing zebrafish intestine is regulated by the Wnt pathway and microbial signaling via Myd88. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):4570-4577.
[30] HOVANES K, LI TW, MUNGUIA JE, et al. Beta-catenin-sensitive isoforms of lymphoid enhancer factor-1 are selectively expressed in colon cancer. Nat Genet. 2001;28(1):53-57.
[31] DAS J, KUMAR R. Plant Wnt: deciphering a novel signaling pathway in plants. Curr Sci. 2016;111(8):1319-1324.
[32] TAMURA M, NEMOTO E. Role of the Wnt signaling molecules in the tooth. Jpn Dent Sci Rev. 2016;52(4):75-83.
[33] NAYAK L, BHATTACHARYYA NP, DE RK. Wnt signal transduction pathways: modules, development and evolution. BMC Syst Biol. 2016; 10 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):44.
[34] TSENTIDIS C, GOURGIOTIS D, KOSSIVA L, et al. Increased levels of Dickkopf-1 are indicative of Wnt/β-catenin downregulation and lower osteoblast signaling in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus, contributing to lower bone mineral density. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(3):945-953.
[35] 颜露,袁晓娟,左婕,等.DKK-1在大鼠牙囊细胞体外的表达作用研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(10):902-906.
[36] 陈曦,孙延芳,NXUMALO W. Dickkopfs分泌蛋白调控肿瘤细胞机制[J].浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,43(2):253-261.
[37] HAN XL, LIU M, VOISEY A, et al. Post-natal effect of overexpressed DKK1 on mandibular molar formation. J Dent Res. 2011;90(11):1312-1317.
[38] 徐仑,聂嘉,陈冬冬,等.两种Wnt通路抑制剂对牙周膜干细胞作用的比较研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2016,16(2):253-256.
[39] 刘苹,李平,熊仁平,等.MTT法与BrdUELISA法检测成纤维细胞增殖的可靠性比较[J].第三军医大学学报,2006,28(11):1262-1263.
[40] 罗涛,王彤敏,李力燕.EdU与BrdU在检测细胞增殖中的特点及应用进展[J].重庆医学,2015,44(32):4581-4583.
|