Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (15): 2433-2439.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2569
Previous Articles Next Articles
Debridement antibiotics irrigation and implant retention for the treatment
of acute infection after total knee arthroplasty
Xu Changbo, Yin Li, Wang Haitao, Zhang Yi
- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2019-09-05Revised:2019-09-07Accepted:2019-10-31Online:2020-05-28Published:2020-03-23 -
Contact:Yin Li, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Xu Changbo, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Changbo, Yin Li, Wang Haitao, Zhang Yi .
Debridement antibiotics irrigation and implant retention for the treatment
of acute infection after total knee arthroplasty
share this article
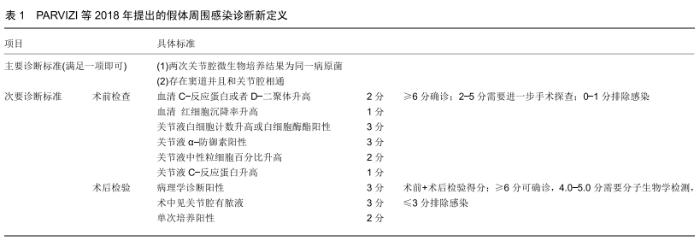
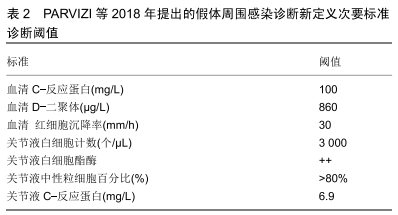
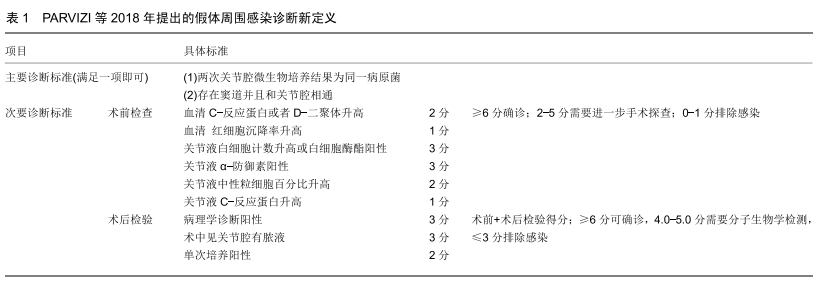
2.1 假体周围感染的分型及诊断 假体周围感染的分型目前多采用Tsukayama分型,其标准为:Ⅰ型,术中培养阳性的感染;Ⅱ型,术后早期感染包括浅表感染和深部感染(术后4周以内);Ⅲ型,急性血源性感染;Ⅳ,型晚期慢性感染[7],急性假体周围感染包括术后早期感染和急性血源性感染。假体周围感染的治疗包括:敏感抗生素保守治疗、保留假体清创、一期或二期关节翻修术、关节融合、关节切除及截肢术。 关于假体周围感染的诊断没有统一的标准,国际上有很多共识和指南,比如美国骨科医师协会、美国肌肉骨骼感染协会、假体周围感染国际共识会议都提出了很多标准。这些标准都是根据患者病史体征、炎症指标、细菌培养、关节液生化检查、组织病理等做出的综合判断。 PARVIZI等[8]综合其他共识和指南提出了新的假体周围感染诊断标准,其敏感性和特异性都较高,得到了大多数人的认可,见表1,2。 "
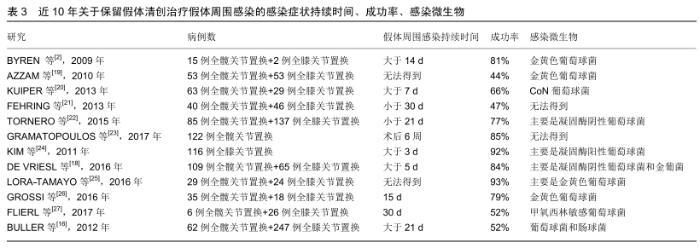
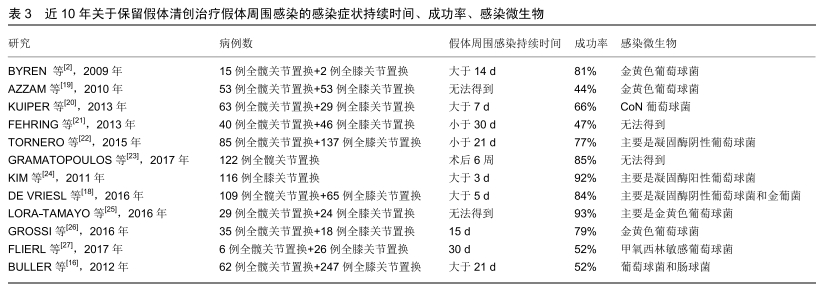
关于假体周围感染术后治疗成功的标准目前还没有达成共识,DIAZ-LEDEZMA等[9]综合其他治愈标准并邀请159名该领域国际知名专家经过研究达成共识:无复发或持续性假体周围感染;无需长期抗生素抑制;无需翻修;股骨和胫骨假体保留;无假体周围感染导致的死亡。 2.2 保留假体清创术前注意事项 保留假体清创适用于稳定且固定良好的假体、症状持续时间短、软组织良好且无窦道形成。窦道的存在表明是一种更为慢性的感染,是保留假体清创失败的危险因素[10]。进行过多次清创手术的也不建议行保留假体清创治疗,因为再感染率明显较高,可能是由于每次手术都可能带入新的病菌,多次手术后周围软组织包膜减少,伤口闭合困难、张力高、愈合困难[11-12]。对于那些关节肿胀明显关节腔内脓液较多及合并耐药性较强的菌种,也不建议进行保留假体清创。 为提高假体周围关节感染治疗的成功率,必须对患者进行全面的病史采集和术前检查,将患者机体调整至最佳状态,明确患者感染原因和发生感染的时间,培养出致病菌,这将会显著提高手术成功率。术前影响手术成功的因素有很多,如术前症状持续的时间、病原菌种类、患者合并的其他疾病。 2.2.1 症状持续的时间 症状持续时间是影响保留假体清创预后的主要因素,尽管有大量文献报道症状持续时间短暂在保留假体清创治疗成功率中的重要性,但是最佳持续时间阈值还存在争议。自DAVIE[13]提出生物膜概念以后,关于假体周围感染的治疗观念开始转变,强调在成熟的生物膜成熟前进行敏感抗生素和保留假体清创治疗的成功率更高。生物膜的形成是从接触细菌后的最初几分钟和几个小时内开始的,有一个渐进的成熟过程,形成成熟的生物膜分为4个步骤:细胞黏附、细胞聚集、生物膜成熟、细胞分离[14]。ZIMMERIL等[15]提出症状持续时间3周以内进行保留假体清创的成功率更高,这也被其他文献所证实[16-17]。BULLER等[16]发现症状大于21 d的患者比症状小于21 d的患者有更高的失败率。GRAMATOPOLOUS等[17]研究发现与症状持续时间较长的患者相比,6周内治疗患者的感染根除率有所提高。DE VRIES等[18]发现症状持续时间超过5 d是保留假体清创失败的独立风险。尽管不同作者报道的时间阈值不同,但是总体趋势是越早手术成功率越高,这可能和生物膜形成有关,见表3。一些作者描述了急性血源性和术后急性假体周围感染之间的失败率没有显著差异,而其他人则认为急性血源性感染导致感染复发的风险更高,比术后急性假体周围感染复发风险高8倍[28-29]。在临床实践中如何识别血源性感染确实是急性感染而不是慢性感染的恶化很关键,并非所有慢性感染患者都会有长期症状,有许多无菌性松动的患者本身可能就是隐匿性的假体周围感染。 "

2.2.2 患者自身合并的疾病 患者自身合并症也是保留假体清创术前重要的注意事项,多项研究表明肥胖和人工全膝关节置换后假体周围感染有关[30-31]。EVERHART 等[32]研究发现在初次关节置换后,体质量指数作为一个连续变量与术后假体周围感染显著相关,体质量指数> 45 kg/m2的患者在其预测模型中有8.6%的感染风险,而体质量指数>60 kg/m2的患者有30%的感染概率。体质量指数与保留假体清创失败之间的关系还不太清楚。大型学术中心的多项研究发现,当使用体质量指数作为一个连续变量时,体质量指数与保留假体清创治疗失败之间没有联系[16,33]。但TRIATAFYLLOPOULOS等[34]确实发现体质量指数>30 kg/m2与髋部深部假体周围感染的保留假体清创失败相关。考虑到肥胖与原发性假体周围感染的关系,由于样本量小,其中一些研究可能在检测这种差异方面力度不够,需要进一步的研究来确定肥胖对保留假体清创的影响。 宿主免疫受损可能导致保留假体清创失败。与其他治疗假体周围感染的方法相比,保留假体清创可能更依赖于患者自身的免疫来清除潜在感染。糖尿病和其他应用免疫抑制剂的疾病会增加原发性假体周围感染的风险,然而它们与保留假体清创失败之间的联系却不那么明确。某些研究发现免疫抑制疗法、类风湿关节炎和糖尿病与保留假体清创失败有相关性,但这些相关性较弱[12,35],部分原因可能是选择偏倚,即患有较难控制的糖尿病或免疫抑制的患者不易选择保留假体清创治疗。综上所述,一个优化的宿主可以使保留假体清创成功的机会最大化,但是单独的合并症本身并不能成为保留假体清创的禁忌证。 2.2.3 感染微生物种类 虽然这是非常重要的信息,但在选择进行手术时有关感染微生物的种类及其敏感抗生素的往往还不清楚。 葡萄球菌感染常与保留假体清创后的不良结果有关[16,19],特别是耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌,传统上被认为即使在急性感染中也存在细菌成分残留,增加了清创失败的风险[36]。BRADBURY等[37]甚至提出如果遇到耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌则应考虑采用翻修术。这可能与葡萄球菌更容易形成生物膜,清除较困难,抗生素治疗效果差有关[37]。 革兰阴性杆菌也是影响保留假体清创成功的重要微生物,因为它们通常被认为与保留假体清创的不良结果有关[38-39]。尽管如此,如果症状持续时间短和敏感抗生物膜抗生素治疗,保留假体清创手术的成功率在该类患者中也比较良好[40]。关于革兰阴性假体周围感染的关键问题是不断增长的抗生素耐药性,特别是在中东和亚洲以及欧洲地中海地区[41]。研究表明当发现氟喹诺酮耐药时,保留假体清创后的预后显著下降[42]。更严重的问题是如对第三代头孢菌素类、氟喹诺酮类和氨基糖苷类的联合耐药性,将显著减少抗生素治疗的选择[41]。 肠球菌感染虽然不常见,但也应受到特别关注,因为它们与不良结果有关,当肠球菌合并其他微生物感染或者出现万古霉素耐药性时治疗效果会更差[43]。一项欧洲多中心研究包括来自6个不同国家的18家医院数据,专门针对肠球菌引起的假体周围感染术后至少随访1年的治疗总成功率为56%(100/178),植入物移除显示出比保留假体清创更高的成功率,但这仅在关节置换2年以后出现感染的患者中有统计学意义[44]。 链球菌感染的预后据大多数文献报道都较为良 好[5,45-46]。尽管如此,最近的一项回顾性、观察性、多中心、国际性研究显示,由保留假体清创疗的最大系列链球菌假体周围感染462例,其预后比以前报道的更 差[47],其中一部分原因可能与链球菌耐药及研究设计的差异和作者自己的纳入标准不同,许多患者并不严格满足理想病例选择的标准,单个医疗组根据自己习惯进行保留假体清创有关。 2.3 保留假体清创术中注意事项 保留假体清创的主要操作步骤包括开放式关节切开术、广泛的滑膜及疑似感染坏死组织切除清创术、彻底的冲洗、固定部件的保留及垫片的更换。为了改善局部感染和减少生物膜,同时使用了各种辅助治疗,包括使用局部抗生素(如抗生素珠、海绵和粉末)、化学清创(如倍他定、氯己定、过氧化物等)冲洗和物理治疗。 2.3.1 可移动垫片更换 保留假体清创术中应常规更换垫片,由于在软组织和假体之间会形成纤维蛋白层,保留垫片可能导致持续感染和更高的失败率。此外,移除垫片能扩大手术视野,能接触到关节囊后窝,使清创更加彻底。GRAMATOPOULOS等[23]报告称可移动垫片交换是提高感染根除率的独立风险因素,垫片交换患者的10年总生存率为86%,而非垫片交换患者的生存率为68%,更换垫片远期疗效更优。 2.3.2 疑似感染软组织切除和冲洗 应该对所有感染和潜在感染组织进行彻底清创及滑膜切除,伤口边缘应仔细清创,清除任何坏死的软组织碎片。一项研究发现关节腔有脓性物质与较高的失败率有关,因此这种情况下考虑进行翻修来移除关节假体是有必要的[19]。同时应从不同地点采集多个组织样本并送去进行培养和组织病理研究。清创后用大量液体彻底冲洗关节腔,虽然冲洗液体具体用量多少还存在争议,但大多数研究报告的冲洗液体范围为3-9 L[48]。 生理盐水是最常用的冲洗液,与化学消毒液联合起来冲洗效果会更好,目前所使用冲洗液包括碘伏、氯己定、辛替尼定、聚己定、稀倍他定和过氧化氢溶液[2,38]。尽管有人担心高压脉冲冲洗枪可能导致医源性细菌播撒到更深的组织层[49],但有研究证明低压或高压灌洗均可使用,临床实践中无明显差异。在体外钛盘生物膜模型中,葡萄糖酸氯己定(0.05%)溶液在减少细菌菌落计数方面优于脉冲盐水冲洗[50]。辛烯啶和聚己烷在欧洲的研究中已被用于对抗革兰阳性和革兰阴性细菌的抗菌活性[33,51]。与生理盐水、聚维酮碘冲洗相比,葡萄糖酸洗必泰被证明减少细菌菌落计数更有效[50]。体外实验表明醋酸对革兰阳性和革兰阴性生物膜都有很高的抑制效果[52]。目前还没有一种冲洗方法被证明是绝对有效的,采用哪一种冲洗液通常取决于外科医生自己的偏好。需要进一步的研究来确定辅助冲洗剂在保留假体清创中到底起多大作用。 2.3.3 局部抗生素治疗 局部抗生素也可用作保留假体清创术中的辅助药物。以珠子、海绵或粉末形式存在的抗生素载体增加了抗生素的局部浓度,并使其缓慢释放到周围组织中。不同的抗生素载体已被用于改善保留假体清创治疗的成功率,尽管他们的有效性还存在争议。比较常见的抗生素载体有骨水泥抗生素链珠、硫酸钙颗粒、胶原纤维。骨水泥抗生素链珠在骨败血症手术中有着悠久的传统,有一些论文探讨其在保留假体清创后用于关节感染的应用,然而它们需要第二次手术移除[53],这将焦点转移到了可吸收材料上,如胶原纤维或硫酸钙颗粒。尽管小样本研究显示了不错的结果,但没有随机对照研究清楚地证明使用这些材料可以提高正确操作的结果[54]。另外可吸收的抗生素载体增加成本、局部反应和是否需要持续的伤口引流等也是需要考虑的问题。 2.4 保留假体清创术后抗生素应用时间 充分清创后正确的抗生素治疗对感染根除至关重要。大多数情况下,保留假体清创手术将在不知道病原菌的情况下进行,在等待术中培养结果的同时必须开始有效的经验性抗生素治疗。在急性假体周围感染早期浮游细菌占主导地位,因此治疗通常从静脉治疗开始。在术中和静脉注射抗生素引起的细菌负荷初步消除后,可以转而使用院外口服生物利用度高和抗生物膜活性高的抗生素,从而避免长期住院的相关并发症。传统上建议静脉注射2-6周的抗菌药物治疗[55]。感染微生物种类不同所用抗生素也会不同,保留假体清创术后的抗生素治疗也是影响手术成败的关键因素。与移除植入物的翻修手术不同,手术清创后在假体中自然会出现生物膜残留物,因此所选抗生素应具有抗生物膜活性。ZIMMERLI等[56]首次提出利福平用于抗生物膜后,利福平在生物膜相关葡萄球菌感染中发挥了非常大的作用。必须强调的是,由于细菌快速产生抗微生物性,利福平不应单独使用,而应联合使用。ACHERMANN等[57]发现手术清创不足或静脉抗生素治疗少于2周与利福平耐药性的出现独立相关。喹诺酮类抗生素在对抗革兰阴性的细菌中有重要作用。在一项包括242例革兰阴性假体周围感染的大型多中心研究中,环丙沙星治疗显示出了非常重要的作用,环丙沙星敏感假体周围感染患者应用环丙沙星的治疗成功率为79%[42]。 "

| [1] TANDE AJ, PATEL R. Prosthetic joint infection. Clin Microbiol Rev.2014;27(2):302-345. [2] BYREN I, BEJON P, ATKINS BL, et al.One hundred and twelve infected arthroplasties treated with \"DAIR\" (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention): antibiotic duration and outcome.J Antimicrob Chemother.2009;63(6): 1264-1271. [3] KUIPER JW, WILLINK RT, MOOJEN DJ, et al.Treatment of acute periprosthetic infections with prosthesis retention: Review of current concepts.World J Orthop. 2014;5(5): 667-676. [4] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, SORANOGLOU V, MEMTSOUDIS SG, et al.Implant retention after acute and hematogenous periprosthetic hip and knee infections: Whom, when and how? World J Orthop.2016;7(9):546. [5] GRAMMATOPOULOS G, KENDRICK B, MCNALLY M, et al. Outcome Following Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention in Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection—An 18-Year Experience.J Arthroplasty.2017;32(7):2248-2255. [6] ZARUTA DA, QIU B, LIU AY, et al.Indications and Guidelines for Debridement and Implant Retention for Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2018;11(3): 347-356. [7] TSUKAYAMA DT, GOLDBERG VM, KYLE R. Diagnosis and management of infection after total knee arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2003;85-A Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S75. [8] PARVIZI J, TAN TL, GOSWAMI K, et al. The 2018 Definition of Periprosthetic Hip and Knee Infection: An Evidence-Based and Validated Criteria. J Arthroplasty.2018;33(5):1309-1314, e1302. [9] DIAZ-LEDEZMA C, HIGUERA CA, PARVIZI J. Success after treatment of periprosthetic joint infection: a Delphi-based international multidisciplinary consensus.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(7):2374-2382. [10] MARCULESCU CE, BERBARI EF, HANSSEN AD, et al. Outcome of Prosthetic Joint Infections Treated with Debridement and Retention of Components.Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42(4):471-478. [11] KOH IJ, HAN SB, IN Y, et al.Open debridement and prosthesis retention is a viable treatment option for acute periprosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2015;135(6):847-855. [12] LORA-TAMAYO J, MURILLO O, IRIBARREN JA, et al.A Large Multicenter Study of Methicillin-Susceptible and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic Joint Infections Managed With Implant Retention.Clin Infect Dis. 2013;56(2):182-194. [13] DAVIES D. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents.Nat Rev Drug Discov.2003;2(2):114-122. [14] GBEJUADE HO, LOVERING AM, WEBB JC.The role of microbial biofilms in prosthetic joint infections.Acta Orthop. 2015;86(2):147-158. [15] ZIMMERLI W, TRAMPUZ A, OCHSNER PE. Prosthetic-Joint Infections. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1645-1654. [16] BULLER LT, SABRY FY, EASTON RW, et al.The Preoperative Prediction of Success Following Irrigation and Debridement With Polyethylene Exchange for Hip and Knee Prosthetic Joint Infections.J Arthroplasty.2012;27(6): 857-864.e854. [17] GRAMMATOPOULOS G, BOLDUC ME, ATKINS BL, et al. Functional outcome of debridement, antibiotics and implant retention in periprosthetic joint infection involving the hip. Bone Joint J.2017; 99-B(5):614-622. [18] DE VRIES L, VAN DER WEEGEN W, NEVE WC, et al. The Effectiveness of Debridement, Antibiotics and Irrigation for Periprosthetic Joint Infections after Primary Hip and Knee Arthroplasty. A 15 Years Retrospective Study in Two Community Hospitals in the Netherlands.J Bone Jt Infect.2016;1:20-24. [19] AZZAM KA, SEELEY M, GHANEM E, et al.Irrigation and Debridement in the Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Traditional Indications Revisited.J Arthroplasty.2010; 25(7): 1022-1027. [20] KUIPER JWP, VOS SJ, SAOUTI R, et al.Prosthetic joint-associated infections treated with DAIR (debridement, antibiotics, irrigation, and retention).Acta Orthopaedica.2013; 84(4):380-386. [21] FEHRING TK, ODUM SM, BEREND KR, et al.Failure of irrigation and debridement for early postoperative periprosthetic infection.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(1): 250-257. [22] TORNERO E, MORATA L, MARTíNEZ-PASTOR JC, et al. KLIC-score for predicting early failure in prosthetic joint infections treated with debridement, implant retention and antibiotics.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(8): 786.e789-786. e717. [23] GRAMMATOPOULOS G, KENDRICK B, MCNALLY M, et al. Outcome Following Debridement, Antibiotics, and Implant Retention in Hip Periprosthetic Joint Infection-An 18-Year Experience.J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(7): S0883540317301869. [24] KIM YH, CHOI Y, KIM JS. Treatment Based on the Type of Infected TKA Improves Infection Control.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(4):977-984. [25] LORA-TAMAYO J, EUBA G, COBO J, et al.Short- versus long-duration levofloxacin plus rifampicin for acute staphylococcal prosthetic joint infection managed with implant retention: a randomised clinical trial.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016;48(3):310-316. [26] GROSSI O, ASSERAY N, BOURIGAULT C, et al. Gram-negative prosthetic joint infections managed according to a multidisciplinary standardized approach: risk factors for failure and outcome with and without fluoroquinolones.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(9):2593-2597. [27] FLIERL MA, CULP BM, OKROJ KT, et al.Poor Outcomes of Irrigation and Debridement in Acute Periprosthetic Joint Infection With Antibiotic-Impregnated Calcium Sulfate Beads. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(8):S0883540317302887. [28] BETZ M, ABRASSART S,V AUDAUX P, et al.Increased risk of joint failure in hip prostheses infected with Staphylococcus aureus treated with debridement, antibiotics and implant retention compared to Streptococcus.Int Orthop. 2015;39(3): 397-401. [29] VILCHEZ F, MARTÍNEZ-PASTOR JC, GARCÍA-RAMIRO S, et al. Efficacy of Debridement in Hematogenous and Early Post-Surgical Prosthetic Joint Infections.Int J Artif Organs. 2011;34(9):863-869. [30] POULTSIDES LA, TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, SAKELLARIOU VI, et al.Infection risk assessment in patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty.Int Orthop. 2018; 42(1):87-94. [31] CHEN J, CUI Y, LI X, et al.Risk factors for deep infection after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2013;133(5):675-687. [32] EVERHART JS, ALTNEU E, CALHOUN JH. Medical comorbidities are independent preoperative risk factors for surgical infection after total joint arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(10):3112-3119. [33] SENDI, LöTSCHER PO, KESSLER B, et al.Debridement and implant retention in the management of hip periprosthetic joint infection: outcomes following guided and rapid treatment at a single centre.Bone Joint J.2017;99-B(3):330-336. [34] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS G, POULTSIDES L, SAKELLARIOU V, et al.Irrigation and debridement for periprosthetic infections of the hip and factors determining outcome.Int Orthop. 2015;39(6):1203-1209. [35] TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS GK, POULTSIDES LA, ZHANG W, et al.Periprosthetic Knee Infections Treated with Irrigation and Debridement: Outcomes and Preoperative Predictive Factors. J Arthroplasty.2015;30(4):649-657. [36] SALGADO CD, DASH S, CANTEY JR, et al.Higher Risk of Failure of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Prosthetic Joint Infections.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2007; 461(461): 48. [37] BRADBURY T, FEHRING TK, TAUNTON M, et al.The Fate of Acute Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Periprosthetic Knee Infections Treated by Open Debridement and Retention of Components.J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6): 101-104. [38] PEEL TN, CHENG AC, CHOONG PFM, et al.Early onset prosthetic hip and knee joint infection: treatment and outcomes in Victoria, Australia.J Hosp Infect. 2012;82(4) : 248-253. [39] HSIEH PH, LEE MS, HSU KY, et al.Gram‐Negative Prosthetic Joint Infections: Risk Factors and Outcome of Treatment.Clin Infect Dis.2009;49(7):1036-1043. [40] ABOLTINS CA, DOWSEY MM, BUISING KL, et al. Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection treated with debridement, prosthesis retention and antibiotic regimens including a fluoroquinolone.Clin MicrobiolInfect. 2011;17(6): 862-867. [41] RICCIARDI W, GIUBBINI G, LAURENTI P. Surveillance and control of antibiotic resistance in the mediterranean region. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis.2016;8(1):e2016036. [42] RODRíGUEZPARDO D, PIGRAU C, LORATAMAYO J, et al.Gram-negative prosthetic joint infection: outcome of a debridement, antibiotics and implant retention approach. A large multicentre study.Clin Microbiol Infect.2014; 20(11): O911-O919. [43] KHEIR MM, TAN TL, HIGUERA C, et al.Response to Letter to the Editor on “Periprosthetic Joint Infections Caused by Enterococci Have Poor Outcomes”.J Arthroplasty.2017; 2(3): 933-947. [44] TORNERO E, SENNEVILLE E, EUBA G, et al.Characteristics of prosthetic joint infections due to Enterococcus sp. and predictors of failure: a multi-national study.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;20(11):1219-1224. [45] MEEHAN AM, OSMON DR, DUFFY MCT, et al.Outcome of Penicillin‐Susceptible Streptococcal Prosthetic Joint Infection Treated with Debridement and Retention of the Prosthesis. Clin Infect Dis.2003;36(7):845-849. [46] ODUM SM, FEHRING TK, LOMBARDI AV, et al.Irrigation and Debridement for Periprosthetic Infections: Does the Organism Matter? J Arthroplasty.2011;26(6 Suppl):114-118. [47] LORATAMAYO J, SENNEVILLE É, RIBERA A, et al.The Not-So-Good Prognosis of Streptococcal Periprosthetic Joint Infection Managed by Implant Retention: The Results of a Large Multicenter Study.Clin Infect Dis.2017;64(12):1742. [48] AZZAM KA, SEELEY M, GHANEM E, et al.Irrigation and Debridement in the Management of Prosthetic Joint Infection: Traditional Indications Revisited. J Arthroplasty. 25(7): 1022-1027. [49] KALTEIS T, LEHN N, SCHRÖDER HJ, et al.Contaminant Seeding in Bone by Different Irrigation Methods.J Orthop Trauma. 2005; 19(9):591-596. [50] SCHWECHTER EM, FOLK D, VARSHNEY AK, et al.Optimal Irrigation and Debridement of Infected Joint Implants: An In Vitro Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Model. J Arthroplasty.2011;26(6):109-113. [51] FINK B, SCHUSTER P, SCHWENNINGER C, et al.A Standardized Regimen for the Treatment of Acute Postoperative Infections and Acute Hematogenous Infections Associated With Hip and Knee Arthroplasties.J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(4):1255. [52] BJARNSHOLT T, ALHEDE M, JENSEN PØ, et al.Antibiofilm Properties of Acetic Acid. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015;4(7):363. [53] ESTES CS, BEAUCHAMP CP, CLARKE HD, et al.A two-stage retention debridement protocol for acute periprosthetic joint infections.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(8):2029-2038. [54] TINTLE SM, FORSBERG JA, POTTER BK, et al.Prosthesis retention, serial debridement, and antibiotic bead use for the treatment of infection following total joint arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2009;32(2):87. [55] OSMON DR, BERBARI EF, BERENDT AR, et al.Diagnosis and management of prosthetic joint infection: clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis.2013;56(1):e1-e25. [56] ZIMMERLI W, WIDMER AF, BLATTER M, et al.Role of Rifampin for Treatment of Orthopedic Implant–Related Staphylococcal Infections A Randomized Controlled Trial. Jama.1998; 279(19):1537-1541. [57] ACHERMANN Y, EIGENMANN K, LEDERGERBER B, et al. Factors associated with rifampin resistance in staphylococcal periprosthetic joint infections (PJI): a matched case–control study.Infection.2013;41(2):431-437. [58] PARVIZI J, ALIJANIPOUR P, BARBERI EF, et al.Novel Developments in the Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Periprosthetic Joint Infections.J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2015; 23 Suppl:S32-43. [59] WANG X, SADOVSKAYA I, LETERME D, et al.A comparative study of antibodies against proteins extracted from staphylococcal biofilm for the diagnosis of orthopedic prosthesis–related infections in an animal model and in humans. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis.2013;75(2):124-129. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [4] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [5] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [6] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [7] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [8] | Yuan Mei, Zhang Xinxin, Guo Yisha, Bi Xia. Diagnostic potential of circulating microRNA in vascular cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1299-1304. |
| [9] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [10] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [11] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [12] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [13] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [14] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [15] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||