Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (17): 2776-2781.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1693
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research progress in the roles of exosomal miRNA in leukemia
Zhang Juanjuan1, Li Ruiwei1, He Jigang2, Sa Yalian1
- 1The Affiliated Hospital of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Institute of Clinical and Basic Medical Sciences, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory for Birth Defects and Genetic Diseases, Key Laboratory for Clinical Virology), Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Cardiothoracic-Vascular Surgery, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China
-
Revised:2019-01-13Online:2019-06-18Published:2019-06-18 -
Contact:Sa Yalian, PhD, Chief technician, the Affiliated Hospital of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Institute of Clinical and Basic Medical Sciences, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory for Birth Defects and Genetic Diseases, Key Laboratory for Clinical Virology), Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
About author:Zhang Juanjuan, Master candidate, the Affiliated Hospital of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Institute of Clinical and Basic Medical Sciences, the First People’s Hospital of Yunnan Province, Yunnan Provincial Key Laboratory for Birth Defects and Genetic Diseases, Key Laboratory for Clinical Virology), Kunming 650032, Yunnan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 31460298 (to SYL) and 81460073 (to HJG); Institutional Funding Project of Yunnan Provincial Health Department, No. 2017NS228 (to SYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Juanjuan, Li Ruiwei, He Jigang, Sa Yalian. Research progress in the roles of exosomal miRNA in leukemia[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(17): 2776-2781.
share this article
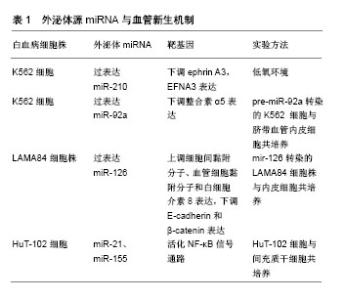
2.1 外泌体源miRNA与血管新生 白血病细胞的浸润转移与肿瘤微环境中的内皮细胞、成纤维细胞、间充质干细胞、基质等成分有关,其中内皮细胞是血管新生的关键成员。已有的研究表明,外泌体源miRNA在白血病细胞与内皮细胞对话中扮演着重要角色,介导骨髓血管化。Tadokoro等[12]报道,在低氧环境(体积分数为1%O2,24 h)中,白血病K562细胞释放富载miR-210的外泌体增多,通过下调抑制血管生成靶基因(ephrin A3、EFNA3)在脐带血管内皮细胞中的表达,从而促进管腔样结构的形成,见表1。研究发现白血病细胞株K562细胞源外泌体富集表达miR-92a,通过Cy3标记pre-miR-92a转染的K562细胞与脐带血管内皮细胞共培养,结果下调了miR-92a靶基因整合素α5在血管内皮细胞中的表达,使内皮细胞的黏附性下降,而迁移以及形成管腔样结构的能力增强[13],见表1。Paggetti等[14]观察到内皮细胞摄取慢性淋巴细胞白血病源外泌体后,形成管腔样结构的能力增强,其机制与外泌体富载miR-146a、miR-150、miR-155的调控作用有关。Taverna等[15-16]观察到慢性髓系白血病患者血液、LAMA84细胞株培养上清来源外泌体富载miR-126,其呈剂量依赖性上调细胞间黏附分子、血管细胞黏附分子和白细胞介素8在脐带血管内皮细胞的表达,而下调E-cadherin和β-catenin的表达,从而使脐带血管内皮细胞迁移能力以及形成管腔样结构的能力增强,见表1。人类嗜T细胞白血病Ⅰ型病毒(HTLV-Ⅰ)是成人T细胞白血病的致病因子,其编码的TAX蛋白可与IKB激酶γ(IKKγ)直接结合,使NF-κB通路中抑制性蛋白IKB降解,从而使NF-κB通路活化,使细胞抗凋亡的能力增强,发挥促癌作用。El-Saghir等[17]研究表明,成人型T细胞白血病/淋巴瘤细胞C81和HuT-102源外泌体富载致癌因子病毒源TAX蛋白,其中HuT-102细胞源外泌体还携载有miR-21、miR-155和血管内皮生长因子,由骨髓间充质干细胞摄取后活化NF-κB信号通路,调控细胞增殖迁移、抵抗凋亡和促血管形成基因的表达,见表1。骨髓来源的抑制性细胞有免疫抑制作用,促进肿瘤的发生发展。Bruns等[18]报道,慢性淋巴细胞白血病外泌体携载的miR-155诱导骨髓来源的抑制性细胞增多,参与肿瘤的浸润转移和血管形成等病理过程。总而言之,外泌体源miRNA介导白血病细胞的浸润转移和血管形成等病理过程,干预外泌体源miRNA可能是治疗白血病的新思路。"

| [1] Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659.[2] 刘儒涛,王世伟,刘晶.细胞间信息交流的新载体——外泌体[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2013,40(8):719-727.[3] Tickner JA, Richard DJ, O'Byrne KJ. EV, Microvesicles/MicroRNAs and Stem Cells in Cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1056:123-135.[4] DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(4):252-271.[5] 陈万青,李贺,孙可欣,等.2014年中国恶性肿瘤发病和死亡分析[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2018,40(1):5-13.[6] Mirzaei H, Fathullahzadeh S, Khanmohammadi R, et al. State of the art in microRNA as diagnostic and therapeutic biomarkers in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(2):888-900.[7] Nawaz M. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transport of non-coding RNAs between stem cells and cancer cells: implications in tumor progression and therapeutic resistance. Stem Cell Investig. 2017; 4:83.[8] Barrera-Ramirez J, Lavoie JR, Maganti HB, et al. Micro-RNA Profiling of Exosomes from Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Implications in Leukemogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 2017;13(6):817-825.[9] Bayraktar R, Van Roosbroeck K, Calin GA. Cell-to-cell communication: microRNAs as hormones. Mol Oncol. 2017;11(12): 1673-1686.[10] Ohno S, Kuroda M. Exosome-Mediated Targeted Delivery of miRNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1448:261-270.[11] Caivano A, Laurenzana I, De Luca L, et al. High serum levels of extracellular vesicles expressing malignancy-related markers are released in patients with various types of hematological neoplastic disorders. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(12):9739-9752.[12] Tadokoro H, Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, et al. Exosomes derived from hypoxic leukemia cells enhance tube formation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(48):34343-34351.[13] Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, Kuroda M, et al. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene. 2013;32(22): 2747-2755.[14] Paggetti J, Haderk F, Seiffert M, et al. Exosomes released by chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce the transition of stromal cells into cancer-associated fibroblasts. Blood. 2015;126(9): 1106-1117.[15] Taverna S, Flugy A, Saieva L, et al. Role of exosomes released by chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in angiogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2012;130(9):2033-2043.[16] Taverna S, Amodeo V, Saieva L, et al. Exosomal shuttling of miR-126 in endothelial cells modulates adhesive and migratory abilities of chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Mol Cancer. 2014; 13:169.[17] El-Saghir J, Nassar F, Tawil N, et al. ATL-derived exosomes modulate mesenchymal stem cells: potential role in leukemia progression. Retrovirology. 2016;13(1):73.[18] Bruns H, Böttcher M, Qorraj M, et al. CLL-cell-mediated MDSC induction by exosomal miR-155 transfer is disrupted by vitamin D. Leukemia. 2017;31(4):985-988.[19] Habiel DM, Krepostman N, Lilly M, et al. Senescent stromal cell-induced divergence and therapeutic resistance in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7(50): 83514-83529.[20] Viola S, Traer E, Huan J, et al. Alterations in acute myeloid leukaemia bone marrow stromal cell exosome content coincide with gains in tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance. Br J Haematol. 2016; 172(6):983-986.[21] Farahani M, Rubbi C, Liu L, et al. CLL Exosomes Modulate the Transcriptome and Behaviour of Recipient Stromal Cells and Are Selectively Enriched in miR-202-3p. PLoS One. 2015;10(10): e0141429.[22] Ohyashiki K, Umezu T, Katagiri S, et al. Downregulation of Plasma miR-215 in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Successful Discontinuation of Imatinib. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4):570.[23] 郭敏,李育敏,费嘉.以microRNA-21为靶标反义寡核苷酸对人白血病K562细胞的抑制作用[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2009,25(6):1127-1131.[24] Fraser M, Leung BM, Yan X, et al. p53 is a determinant of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein/Akt-mediated chemoresistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2003;63(21):7081-7088.[25] Hornick NI, Huan J, Doron B, et al. Serum Exosome MicroRNA as a Minimally-Invasive Early Biomarker of AML. Sci Rep. 2015;5:11295.[26] Hornick NI, Doron B, Abdelhamed S, et al. AML suppresses hematopoiesis by releasing exosomes that contain microRNAs targeting c-MYB. Sci Signal. 2016;9(444):ra88.[27] Barrera-Ramirez J, Lavoie JR, Maganti HB, et al. Micro-RNA Profiling of Exosomes from Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Implications in Leukemogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 2017;13(6):817-825.[28] Peng D, Wang H, Li L, et al. miR-34c-5p promotes eradication of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells by inducing senescence through selective RAB27B targeting to inhibit exosome shedding. Leukemia. 2018;32(5):1180-1188.[29] Asano M, Umezu T, Katagiri S, et al. Up-regulated exosomal miRNA-140-3p in CML patients with musculoskeletal pain associated with discontinuation of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int J Hematol. 2017;105(4):419-422.[30] Yeh YY, Ozer HG, Lehman AM, et al. Characterization of CLL exosomes reveals a distinct microRNA signature and enhanced secretion by activation of BCR signaling. Blood. 2015;125(21): 3297-3305.[31] Taverna S, Giallombardo M, Pucci M, et al. Curcumin inhibits in vitro and in vivo chronic myelogenous leukemia cells growth: a possible role for exosomal disposal of miR-21. Oncotarget. 2015;6(26): 21918-21933.[32] Lim JH, Song MK, Cho Y, et al. Comparative analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression profiles in cells and exosomes under toluene exposure. Toxicol In Vitro. 2017;41:92-101.[33] Boyiadzis M, Whiteside TL. Information transfer by exosomes: A new frontier in hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev. 2015;29(5): 281-290.[34] Yao Y, Wang C, Wei W, et al. Dendritic cells pulsed with leukemia cell-derived exosomes more efficiently induce antileukemic immunities. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e91463. [35] 郭芳,常春康,范华骅,等. 环磷酰胺联合树突状细胞分泌的外泌体和Poly Ⅰ∶C的抗肿瘤作用研究[J].中国输血杂志, 2008, 21(10): 759-762.[36] 范震,蔡国龙,严静,等.MicroRNA对脓毒症炎症因子的调控[J].中国急救医学,2010,30(3):271-274.[37] Fu C, Jiang L, Xu X, et al. STAT4 knockout protects LPS-induced lung injury by increasing of MDSC and promoting of macrophage differentiation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2016;223:16-22.[38] 苏强,李浪.PTEN与炎症关系的研究进展[J].重庆医学, 2014,43(4): 494-497.[39] Luyendyk JP, Schabbauer GA, Tencati M, et al. Genetic analysis of the role of the PI3K-Akt pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine and tissue factor gene expression in monocytes/macrophages. J Immunol. 2008;180(6):4218-4226.[40] Ufkin ML, Peterson S, Yang X, et al. miR-125a regulates cell cycle, proliferation, and apoptosis by targeting the ErbB pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 2014;38(3):402-410.[41] Bai H, Zhou L, Wang C, et al. Involvement of miR-125a in resistance to daunorubicin by inhibiting apoptosis in leukemia cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2017;39(4):1010428317695964.[42] Puissegur MP, Eichner R, Quelen C, et al. B-cell regulator of immunoglobulin heavy-chain transcription (Bright)/ARID3a is a direct target of the oncomir microRNA-125b in progenitor B-cells. Leukemia. 2012;26(10):2224-2232.[43] Due H, Svendsen P, Bødker JS, et al. miR-155 as a Biomarker in B-Cell Malignancies. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:9513037.[44] Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, et al. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol. 2005;207(2):243-249.[45] Zhang X, Zeng J, Zhou M, et al. The tumor suppressive role of miRNA-370 by targeting FoxM1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:56.[46] Yan-Fang T, Jian N, Jun L, et al. The promoter of miR-663 is hypermethylated in Chinese pediatric acute myeloid leukemia (AML). BMC Med Genet. 2013;14:74.[47] Akao Y, Iio A, Itoh T, et al. Microvesicle-mediated RNA molecule delivery system using monocytes/macrophages. Mol Ther. 2011; 19(2):395-399.[48] 张娟娟,李瑞玮,贺继刚,等. 白血病细胞源外泌体的作用研究进展[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2017, 33(12):2287-2292. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [3] | Liu Cong, Liu Su. Molecular mechanism of miR-17-5p regulation of hypoxia inducible factor-1α mediated adipocyte differentiation and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1069-1074. |
| [4] | Zhao Min, Feng Liuxiang, Chen Yao, Gu Xia, Wang Pingyi, Li Yimei, Li Wenhua. Exosomes as a disease marker under hypoxic conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1104-1108. |
| [5] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [6] | Lu Yuyun, Huang Mei, Shi Xinlei, Chen Baoyan. Bibliometric and visualization analysis of breast cancer stem cell literature from 2011 to 2020 based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4001-4008. |
| [7] | Gao Kun, Chen Dayu, Zhang Yong, Liu Weidong, Sun Shufen, Lai Wenqiang, Ma Dujun, Wu Yihong, Lin Zhanpeng, Jiang Yinglu, Yu Weiji. Achyranthes bidentata alcohol extract inhibits extracellular matrix degradation of the cartilage by regulating synovial fibroblast exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3636-3640. |
| [8] | Lin Haiqi, Chen Liang, Tang Lu, Weng Xiquan, Lin Wentao. Significance of urinary proteomics assessing pathological changes in the body [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3259-3266. |
| [9] | Zhao Shuangdan, Zheng Jiahua, Qi Wenbo, Huang Xianghua. Role and mechanism of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells in reproductive system diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3097-3102. |
| [10] | Wang Kang, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Effect of stem cell derived exosomes on repairing peripheral nerve injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3083-3089. |
| [11] | Yuan Changshen, Rong Weiming, Lu Zhixian, Duan Kan, Guo Jinrong, Mei Qijie. Construction of osteosarcoma miRNA-mRNA regulatory network based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2740-2746. |
| [12] | Liu Feng, Zhang Yu, Wang Yanli, Luo Wei, Han Chaoshan, Li Yangxin. Application of temperature-sensitive chitosan hydrogel encapsulated exosomes in ischemic diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2479-2487. |
| [13] | Cai Yuan, Deng Chengliang. Therapeutic application of adipose stem cell-free liquid extracts: skin aging, wound healing, scar recovery and nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2097-2102. |
| [14] | Liu Tao, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin . Relationship between extracellular vesicles and radiation-induced tissue injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2121-2126. |
| [15] | Zhao Chuntao, Qing Mingsong, Yu Langbo, Peng Jiachen . Meta-analysis of total knee arthroplasty guided by kinematic alignment and mechanical alignment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||