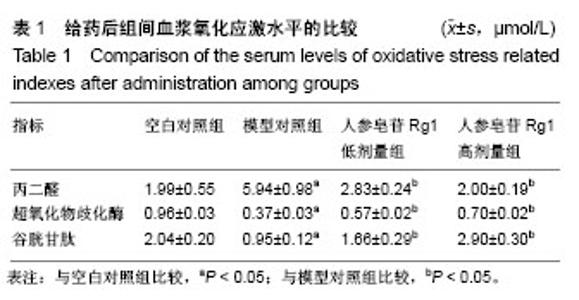
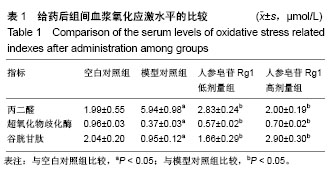
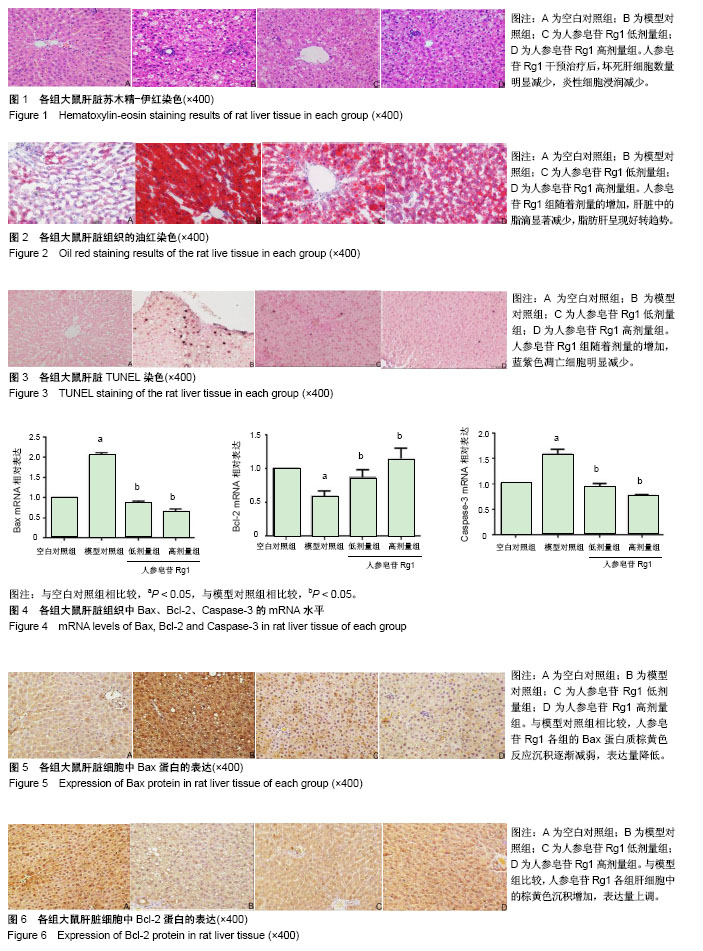
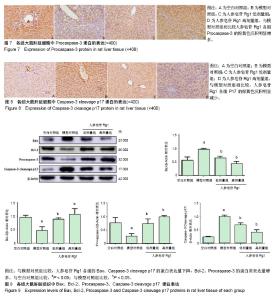
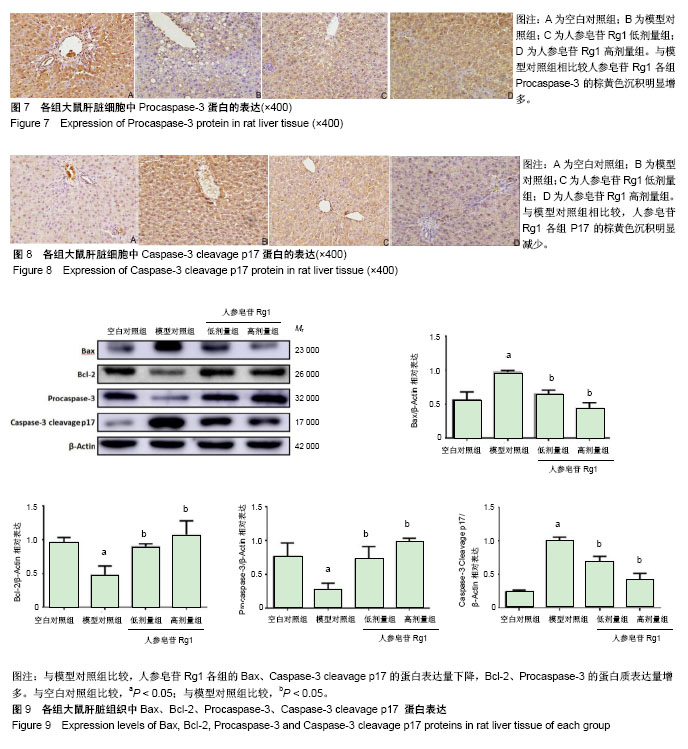
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (3): 384-390.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0597
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ginsenoside Rg1 protects against hepatocyte apoptosis in a rat model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Xiao Yang1, Hou Yunhe2, Yin Xin3, Kang Feng3, Li Shude2, Yang Shikun4, Tao Jianping1
- (1Department of Anesthesiology, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China; 2Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 32016 Medical Experimental Technology Class, Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650500, Yunnan Province, China; 4Department of Organ Transplantation, First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University, Kunming 650000, Yunnan Province, China)