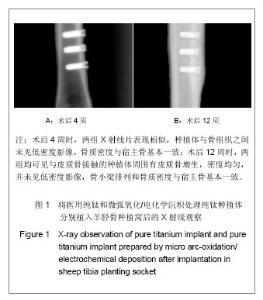
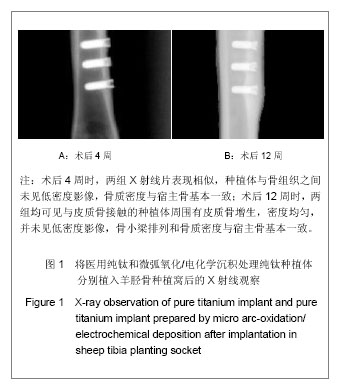
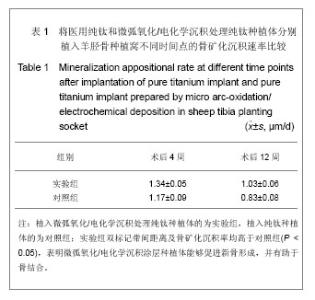
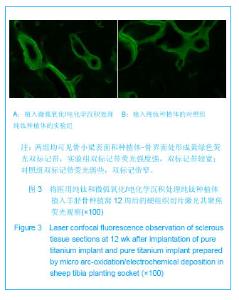
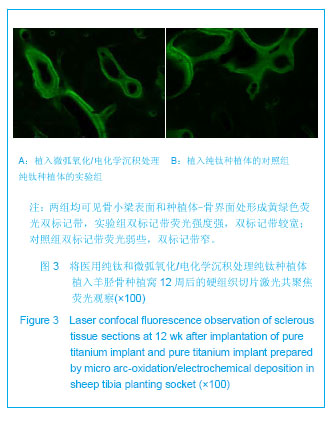
| [1] Jia Y, Deng JY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu.2009; 13(12):2321-2324.贾彦,邓嘉胤.钛种植体表面改性的研究现状及应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(12):2321-2324.[2] Cheng W,Chen JH,Ma CF,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2007; 16(1):107-110.成炜,陈吉华,马楚凡,等.纯钛种植体表面不同化学组成微弧氧化膜的结构与成分分析[J].中国美容医学,2007,16(1):107-110.[3] Jia GD,Wang Y,Pan KF.Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi.2004; 14 (1):74-78.贾国栋,王艺,潘可风.金属基底牙种植体表面陶瓷类涂层的材料学研究进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2004,14(1):74-78.[4] Rupp F,Scheideler L,Rehbein D,et al.Roughness induced dynamic changes of wettability of acid etched titanium implant modifications. Biomaterilas. 2004;25:1429-1438.[5] Kanagaraja S,Wennerberg A,Eriksson C,et al.Cellular re- actions and bone apposition to titanium surfaces with different surface roughness and oxide thickness cleaned by oxidation. Biomaterials.2001;22:1809-1818.[6] Zhang YY,Tao J,Pang YC.Electrochemical deposition of hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium.Nonferrous Met.2006; 16: 633-637.[7] Wang YQ,Tao J,Wang L,et al.HA coating on titanium with nanotubular anodized TiO2 intermediate layer via electrochemical deposition.T Nonferr Metal Soc. 2008;(18): 731-635.[8] Nie RR,Zhu F,Shen LR,et al.Shengwu Yixue Gongchengxue Zhazi. 2010;27(2):334-357.聂蓉蓉,朱锋,沈丽茹,等.纯钛表面不同厚度微弧氧化膜的形貌及相结构分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2010,27(2):334-357.[9] Yao ZhP,Jiang ZH,Sun XT.Influences of current density on Structure and corrosion resistance of ceramic coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by micro-plasma oxidation. Thin Solid Films. 2004;468(1-2):120-124.[10] Ma W,Wei JH,Li YZ,et al.Histological evaluation and surface componential analysis of modified micro-arc oxidation treated titanium implants.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2008; 86(1): 162-169. [11] Zhao Q,Guo X,Dang X,et al.Preparation and properties of Composite MAO/ECD coatings on magnesium alloy. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;102C:321-326.[12] Liu LX,Wu FM,Zhu ZJ,et al.Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu. 2010; 30(5):261-263.柳麟翔,吴凤鸣,朱志军,等.微弧氧化AZ91D镁合金骨结合性能的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2010,30(5):261-263.[13] Liu ZM,Gao B,Zhang LZ. Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2008; 26(6):595-598.柳正明,高勃,张立钊.经微弧氧化处理的钛铌锆锡合金种植体的动物实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2008,26(6):595-598.[14] Han X,Tao XJ,Li SJ,et al.shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2006; 22(2):252-254.韩雪,陶晓杰,李述军,等.新型钛合金阳极氧化后对成骨细胞增殖、分化的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2006,22(2):252-254.[15] Fan X,Jia S,Su JS. Kouqiang Hemian Waike Zazhi.2009; 19(2):128-131.范霞,贾爽,苏剑生.种植体表面粗糙度对成骨细胞增殖及ALP含量的影响[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2009,19(2):128-131.[16] Park YS,Yi KY,Lee IS,et al. The effects of ion beam-assisted deposition of hydroxyapatite on the grit-blasted surface of endosseous implants in rabbit tibiae.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2005; 20(1):31-38.[17] Yeon HK,Jai YK,Ik-Tae Chang,et al. A histomorphometric analysis of the effects of various surface treatment methods on osseointegration.Oral Maxillofac Implants.2003;18: 349-356.[18] Li XC,Dong FS.Xiandai Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu, 2007;21(6): 645-646.栗兴超,董福生.种植体表面优化处理对其骨结合促进的研究进展[J].现代口腔医学研杂志,2007,21(6):645-646.[19] Ma W,Jia BL,Wei JH,et al. Kouqiang Yixue Yanjiu.2004;20(4): 376-378.马威,刘宝林,魏建华,等.微弧氧化处理后纯钛植入体的皮下埋置实验及表面元素成分研究[J].口腔医学研究, 2004,20(4): 376-378.[20] Liu Y,Zhao BH. Zhongguo Shiyong Kouqiangke Zazhi.2010; 3(6):373-375.刘阳,赵宝红.种植体表面改性方法研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(6):373-375.[21] Hu R,Lin CJ,Shi HY.A noval ordered nano hydroxyapatite coating electrochemically deposited on titanium substrate.J Biomer Mater Res A,2007;80(3):687-692.[22] Gao YP,Hu B.Kouqiang Cailiao Qixie Zazhi. 2008; 17(4): 189-202.高颖萍,胡滨.牙用合金表面改性技术的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2008,17(4):189-202.[23] Liang W. Xiandai Yiyao Weisheng.2012; 28(13):2016-2018.梁伟.种植体表面处理的研究进展[J].现代医药卫生,2012, 28(13): 2016-2018.[24] Yu KT,Shu Y,Zhou JC. Hunan Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao. 2012;32(4):74-75.于开涛,舒瑶,邹敬才.牙种植体表面处理技术的新进展[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,32(4):74-75.[25] Kokubo T,Kim HM,Kawashita M,et al.Bioactive metals: preparation and properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2004; 15(2):99-107.[26] Zhou CR,Luo CX,Li LH.Cailiao Daobao.2011;25(5):81-84.周长忍,罗传旭,李立华.电沉积羟基磷灰石及其复合物涂层的研究进展[J].材料导报,2011,25(5):81-84.[27] Narayanan R,Kim SY,Kwon TY,et al. Nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite coatings from ultrasonated electrolyte: preparation, characterization, and osteoblast responses.J Biomed Mater Res A.2008;87:1053.[28] Li Y,Lee IS,Cui FZ,et al. The biocompatibility of nanostructured calcium phosphate coated on micro-arc oxidized titanium.Biomaterials.2008; 29(13):2025-2032.[29] Qu LJ,WANG YH,Ma C.Jiamusi Daxue Xuebao.2009; 27(2): 240-241.曲立杰,王颖慧,马臣.微弧氧化-电化学共沉积磷酸钙类涂层的研究[J].佳木斯大学学报,2009,27(2):240-241.[30] Li F,Wang CY,Tao SQ,et al. Haerbin Yiyao.2009;29(4):1-3.李锋,王春阳,陶树清,等. 羟基磷灰石/40%氧化锆与骨组织相容性和生物活性的体内研究[J].哈尔滨医药,2009,29(4):1-3.[31] Zhang YM,Fu T,Xu KW,et al.Zhongguo Kouqiang Zhongzhixue Zazhi.2000;5(4):154-157.张玉梅,付涛,徐可为,等.水热合成法制备羟基磷灰石生物涂层的体内及体外实验研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2000,5(4): 154-157.[32] Wang YQ,Tao J,Wang L,et al.Nanjing Hangkong Hangtian Daxue Xuebao.2007; 39(5): 659-664.王月勤,陶杰,王玲,等.钛基材上羟基磷灰石生物活性研究[J].南京航空航天大学学报,2007,39(5) : 659-664.[33] Gottlander M,Johansson CB,Albrektsson T.Short and long -term animal studies with a plasma-sprayed calcium phosphate-coated implant. Clin Oral Impl Res.1997;8:345-351.[34] Tetsuo I,Katsuhiko H,Hideo K,et al.Rapid bone resorption adjacent to hydroxyapatite -coated implants.J Oral Impl. 1996; 22: 232-235.[35] Watson CJ,Tinsley D,Ogden AR,et al. A 3 to 4 year study of single tooth hydroxylapatite coated endosseous dental implants. Br Dent J.1999; 187: 90-94.[36] Wang DS,Liu HC,Lv Y,et al.Zhonghua Laonian Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi.2008; 6(4):203-205.王东胜,刘洪臣,吕燕,等.带种植体骨磨片的标准化制作[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2008,6(4):203-205. |