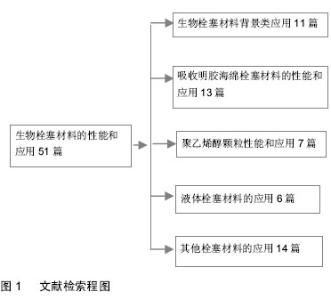
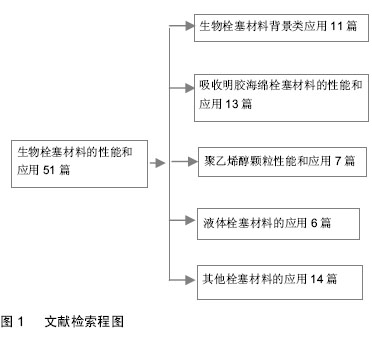
| [1] |
Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing .
MicroRNA-214 is involved in the regulation of bone metabolism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1779-1784.
|
| [2] |
Qin Wenpin, Yang Yujie, Zhao Laihe, Shi Xiaowei, Lu Lei, Yang Hongxu, Huang Jinghui.
Hemorrhage control of fluid gelatin SurgifloTM versus gelatin sponge in lumbar spine
fusion surgery
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 561-565.
|
| [3] |
Li Xuewei, Hu Beibei, Zhang Dawei, Quan Lulu, Liang Yongqiang.
Calcium hydrogen phosphate dehydrate combined with gelatin and recombinant human bone morphologic protein 2/7 for repair of bone defects in rabbits
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4533-4539.
|
| [4] |
Zhang Helong, Wang Huiyan, Li Zhuo, Gao Jianguo, Zhai Qian.
In vitro anti-tuberculosis effect of chitosan-gelatin/poly(lactic acid co-glycolic acid) combined with
drug-loaded hydrogel
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3480-3485.
|
| [5] |
Zhou Jian, Tian Zhuang, Tian Qinyu, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Kun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi, Yao Qi.
Properties of gelatin methacrylate/decellularized meniscus
extracellular matrix composite hydrogel with different crosslinking densities
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2493-2499.
|
| [6] |
Yuan Bo, Wang Zhiwei, Tang Yifan, Zhou Shengyuan, Chen Xiongsheng, Jia Lianshun.
Construction of polycaprolactone-tricalcium phosphate with different mixture ratios using three-dimensional printing technology and its osteoinductivity in vitro
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(6): 821-826.
|
| [7] |
Chen Hongrang, Shen Yun, Zhang Haitao, Deng Kunxue, Xu Yuanling, Dai Xingliang, Li Yongsheng, Zhang Xinqiong, Xu Tao.
Bionic polylactic acid/gelatin nanofiber membrane for repairing varicose ulcers in the lower extremities
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(26): 4217-4224.
|
| [8] |
Wei Wei, Liu Yanfei, Zhang Ling, Xiong Na .
Self-assembling peptide hydrogel: hemostatic effect and mechanism
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 310-316.
|
| [9] |
Chen Hongrang, Zhang Haitao, Deng Kunxue, Li Yongsheng, Shen Yun, Xu Tao, Zhang Xinqiong.
In situ repair of full-thickness skin defects by handheld electrospun biodegradable nanofibers
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 257-264.
|
| [10] |
Chen Dongdong, Zhang Qi, Zhang Pengfei, Zhou Jiping, Jiang Yani.
3D bioprinted nozzle for skin scaffolds: CFD simulation and experiments
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 245-250.
|
| [11] |
Li Jingjing, Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Huang Lei, Suo Jinrong, Fu Songtao.
Preparation of agarose/gelatin/hyaluronic acid/extracellular matrix hydrogel and its property characterization
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2900-2908.
|
| [12] |
Zhang Minbo, Peng Qifeng, Ma Yaping, Kong Weijun, Liao Wenbo.
Physical properties and biocompatibility of 3D printed bone microparticle/poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffold
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2215-2222.
|
| [13] |
Li Zhi, Tan Chunhua, Cai Xianhua, Wang Huasong, Ding Xiaoming, Zhao Yanhong.
Fabrication and biocompatibility assessment of the scaffold with biomimetic interconnected macropore structure
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2223-2227.
|
| [14] |
Bai Yulong, Gao Yufeng, Zhong Hongbin, Zhao Yantao, Guo Ruizhou, Li Li.
Allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue repair materials: how to choose a suitable virus inactivation process
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(14): 2261-2268.
|
| [15] |
Luo Kai, Yang Yafeng, Ma Teng, Xia Bing, Huang Liangliang, Huang Jinghui, Luo Zhuojing.
Effects of perfluorotributylamine/alginate/bioglass biomaterials on viability and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(13): 1995-2001.
|