Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 257-264.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1513
Previous Articles Next Articles
In situ repair of full-thickness skin defects by handheld electrospun biodegradable nanofibers
Chen Hongrang1, 2, Zhang Haitao3, Deng Kunxue3, Li Yongsheng2, Shen Yun2, Xu Tao4, Zhang Xinqiong1
- 1Nursing College, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 2Department of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; 3Guangzhou Medprin Regenerative Medicine Technology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510663, Guangdong Province, China; 4Department of Mechanical Engineering, Biomanufacturing Center, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2018-08-13Online:2019-01-18Published:2019-01-18 -
Contact:Zhang Xinqiong, Associate professor, Nursing College, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Chen Hongrang, Master candidate, Nursing College, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China; Department of General Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program), No. 2015AA020303 (to XT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Hongrang, Zhang Haitao, Deng Kunxue, Li Yongsheng, Shen Yun, Xu Tao, Zhang Xinqiong. In situ repair of full-thickness skin defects by handheld electrospun biodegradable nanofibers[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 257-264.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
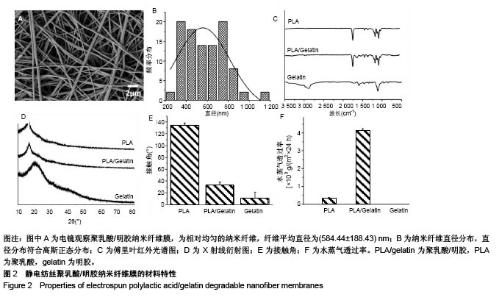
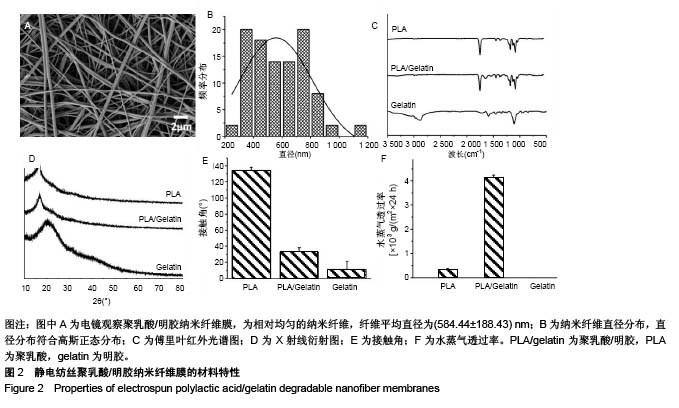
2.1 手持静电纺丝纳米纤维膜材料的特性 2.1.1 电镜观察 手持式静电纺丝装置原位电纺样品的电镜图,见图2A,可见经原位电纺后,聚乳酸/明胶纺丝液被拉伸、固化为相对均匀的纳米纤维,纤维平均直径为(584.44±188.43) nm。直径分布统计发现,其直径分布符合高斯正态分布,见图2B所示。 2.1.2 傅里叶变换红外光谱 聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜、聚乳酸纳米纤维膜及明胶纳米纤维膜的傅里叶变换红外光谱图,见图2C所示,可见聚乳酸纳米纤维在1 758,1 452,1 183,1 130,1 087 cm-1出现的吸收峰分,别对应C=O的伸缩振动吸收峰、-CH3的伸缩振动吸收峰、C-O反对称伸缩振动吸收峰、C-O-C伸缩振动吸收峰、C-O对称伸缩振动吸收峰;明胶纳米纤维在1 593,1 462,1 246 cm-1出现的吸收峰,对应酰胺Ⅰ带的N-H变形振动吸收峰、酰胺Ⅱ带的N-H伸缩振动吸收峰、酰胺Ⅲ 带的N-H伸缩振动吸收峰。当二者复合后,聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维基本遵从聚乳酸纳米纤维的红外特征,归属于明胶的特征吸收峰基本消失,证明少量明胶的加入,对聚乳酸的特征基团不产生大的影响;同时,还发现聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维在1 650 cm-1出现了吸收峰,对应酰胺Ⅰ带C=O伸缩振动吸收峰,说明明胶和聚乳酸之间产生了微弱的化学作用,这有助于明胶在聚乳酸中的均匀分布。 2.1.3 X射线衍射 聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜、聚乳酸纳米纤维膜及明胶纳米纤维膜的X射线衍射结果,见图2D所示,可见聚乳酸纳米纤维在16.6°位置出现结晶峰,对应聚乳酸的(200)晶面。明胶纳米纤维在20°左右出现馒头峰。当二者复合后,聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维也仅在16.6°位置出现结晶峰,并且X射线衍射曲线与聚乳酸纳米纤维没有明显差别,说明明胶的加入对复合材料结晶性能无影响。 2.1.4 水接触角 聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜、聚乳酸纳米纤维膜及明胶纳米纤维膜的水接触角,见图2E所示。聚乳酸纳米纤维的水接触角为(134.48±3.43)°,属于疏水材料范围。研究采用的明胶纳米纤维未经过交联处理,因此当水滴接触明胶纳米纤维膜后,会迅速弥散开来,且明胶纳米纤维易溶于水,所以无法得到正常的水接触角,增大明胶纳米纤维膜的厚度并缩短拍照时间,可得到明胶纳米纤维的水接触角为(11.02±10.34)°,属于亲水材料范围。当二者复合后,测得聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜的水接触角为(32.68± 5.68)°,属于亲水材料范围,而且这个水接触角在最适宜细胞黏附的30°-50°的范围内[24]。因此,聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜的水接触角满足细胞黏附需求。 2.1.5 水蒸气透过率 聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜、聚乳酸纳米纤维膜及明胶纳米纤维膜的水蒸气透过率,见图2F所示。作为皮肤上的外敷料,除需保护创面不受外界环境影响,原位电纺的纳米纤维膜还需要有一定的透气透湿性能。经测试发现,因聚乳酸纳米纤维为疏水性,24 h透湿率仅为(0.272±0.09)×103 g/m2。因明胶纳米纤维溶于水,当进行透湿测试时,膜片很快被水浸湿后破裂,无法得到透湿率,因此不具备原位电纺的实际应用价值。当二者复合后,聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜的24 h透湿率可达到(4.21±0.11)× 103 g/m2,可满足皮肤外敷料的要求[25]。综上所述,聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜材料特性可满足皮肤修复材料以及原位电纺电纺的要求,因此选取聚乳酸/明胶纳米纤维膜进行后续生物学测试。"
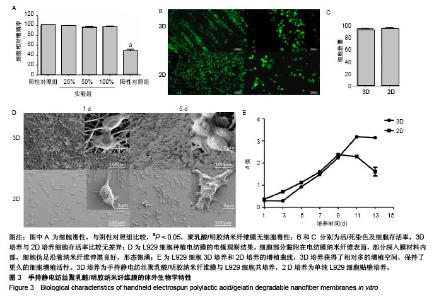
2.2 手持静电纺丝纳米纤维膜的体外生物学特性 2.2.1 细胞毒性 手持静电纺丝膜浸提液的CCK-8细胞毒性实验结果,见图3A,100%,50%,25%浓度浸提液组与阴性对照组的细胞相对增殖率分别为(97.42±1.40)%,(96.73±1.60)%和(99.09±0.94)%,均无细胞明显细胞毒性;阳性对照组细胞相对增殖率为(47.79±4.30)%,有细胞毒性。 2.2.2 细胞存活 L929细胞种植到电纺膜第3天进行活/死染色,见图3B,C,实验组、对照组细胞存活率分别为(96.78±1.41)%,(97.59±1.32)%,两组之间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。 2.2.3 细胞形态 L929细胞种植电纺膜后在电镜下观察,见图3D,可见细胞部分黏附在电纺膜纳米纤维表面,部分深入膜材料内部,细胞伪足沿着纳米纤维伸展良好,形态饱满;对照组可见细胞伸出伪足黏附培养玻片表面,形态良好。 2.2.4 细胞增殖曲线 与对照组对比,实验组细胞增殖启动速度相对慢,但倍增时间并无明显差异,见图3E;实验组增殖到达平台期所用时间长于对照组,对照组在第9天时增殖活性下降,出现明显凋亡,实验组直到13 d仍保持增殖活性,此实验说明实验组细胞保持相当于对照组的细胞活性,而且获得了相对多的增殖空间,保持了更久的细胞增殖活性。"
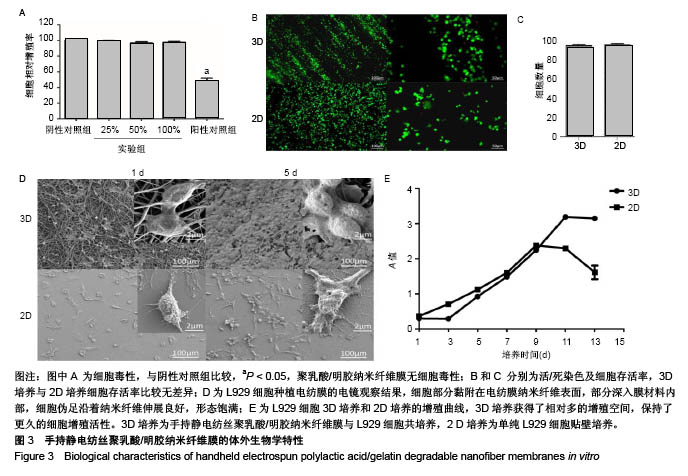
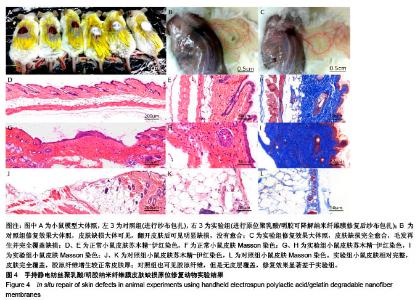
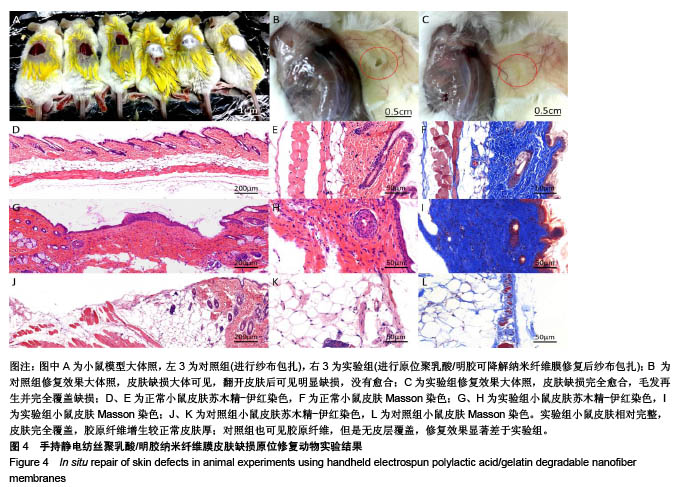
2.3 手持静电纺丝纳米纤维原位修复皮肤缺损 2.3.1 大体观察 修复8周后,实验组小鼠皮肤缺损完全愈合,毛发再生并完全覆盖缺损;对照组小鼠皮肤缺损大体可见,翻开皮肤后可见明显缺损,没有愈合,见图4A-C。 2.3.2 病理染色 病理苏木精-伊红切片显微镜下观察,正常皮肤,如图4D-F所见,皮肤及各附属器官完整;实验组小鼠皮肤修复完整,皮肤全层修复,各层分界良好,部分可见毛囊、毛发再生,见图4G-I;对照组可见皮肤缺损边缘,缺损边界未见皮肤覆盖,以脂肪空泡为主。Masson三色染色结果可见,正常皮肤层级完整,胶原纤维结构完整,见图4F;实验组小鼠皮肤相对完整,皮肤完全覆盖,胶原纤维增生较正常皮肤厚;对照组也可见胶原纤维,但是无皮层覆盖,修复效果显著差于实验组。由此可见手持静电纺丝纳米纤维膜有助于实现小鼠皮肤的全层完整修复。"
| [1] Pérez-Sánchez A, Barrajón-Catalán E, Herranz-López M, et al. Nutraceuticals for Skin Care: A Comprehensive Review of Human Clinical Studies. Nutrients. 2018;10(4). pii: E403. doi: 10. 3390/nu10040403. [2] Sanford JA, Gallo RL. Functions of the skin microbiota in health and disease. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(5):370-377. [3] Swann G. The skin is the body's largest organ. J Vis Commun Med. 2010;33(4):148-149. [4] Na M, Mohammad M, Fei Y, et al. Lack of Receptor for Advanced Glycation End products leads to less severe staphylococcal skin infection but more skin abscesses and prolonged wound healing. J Infect Dis. 2018. doi:10. 1093/infdis/jiy007. [Epub ahead of print][5] Albright V, Xu M, Palanisamy A, et al. Micelle-Coated, Hierarchically Structured Nanofibers with Dual-Release Capability for Accelerated Wound Healing and Infection Control. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018:e1800132. [6] Sadiq A, Shah A, Jeschke MG, et al. The Role of Serotonin during Skin Healing in Post-Thermal Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4). pii: E1034. [7] Shi L, Zhao Y, Xie Q, et al. Moldable Hyaluronan Hydrogel Enabled by Dynamic Metal-Bisphosphonate Coordination Chemistry for Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(5). doi:10. 1002/adhm. 201700973. [8] Shin YC, Shin DM, Lee EJ, et al. Hyaluronic Acid/PLGA Core/Shell Fiber Matrices Loaded with EGCG Beneficial to Diabetic Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(23): 3035-3045. [9] Wang S, Yang H, Tang Z, et al. Wound Dressing Model of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Alginates Complex Promotes Skin Wound Healing by Paracrine Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:3269267. [10] Hsu LC, Peng BY, Chen MS, et al. The potential of the stem cells composite hydrogel wound dressings for promoting wound healing and skin regeneration: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018. doi:10. 1002/jbm. b. 34118. [Epub ahead of print][11] Zarei F, Soleimaninejad M. Role of growth factors and biomaterials in wound healing. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;15:1-6. [12] Sheikholeslam M, Wright MEE, Jeschke MG, et al. Biomaterials for Skin Substitutes. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(5). doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700897.[13] Zhang W, Chen L, Chen J, et al. Silk Fibroin Biomaterial Shows Safe and Effective Wound Healing in Animal Models and a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017;6(10). doi:10.1002/adhm. 201700121. [14] Paschoalin RT, Traldi B, Aydin G, et al. Solution blow spinning fibres: New immunologically inert substrates for the analysis of cell adhesion and motility. Acta Biomater. 2017;51:161-174. [15] Su K, Wang C. Recent advances in the use of gelatin in biomedical research. Biotechnol Lett. 2015;37(11):2139-2145. [16] Deng K, Yang Y, Ke Y, et al. A novel biomimetic composite substitute of PLLA/gelatin nanofiber membrane for dura repairing. Neurol Res. 2017;39(9):819-829. [17] Liu Y, Cui H, Zhuang X, et al. Electrospinning of aniline pentamer-graft-gelatin/PLLA nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(12):5074-5080. [18] 陈亮,许运.静电纺丝微米/纳米纤维材料在硬膜组织损伤修复中的应用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(7):1880-1883.[19] Xu SC, Qin CC, Yu M, et al. A battery-operated portable handheld electrospinning apparatus. Nanoscale. 2015;7(29): 12351-12355. [20] Dong RH, Jia YX, Qin CC, et al. In situ deposition of a personalized nanofibrous dressing via a handy electrospinning device for skin wound care. Nanoscale. 2016;8(6):3482-3488. [21] Dong RH, Qin CC, Qiu X, et al. In situ precision electrospinning as an effective delivery technique for cyanoacrylate medical glue with high efficiency and low toxicity. Nanoscale. 2015;7(46):19468-19475. [22] Lv FY, Dong RH, Li ZJ, et al. In situ precise electrospinning of medical glue fibers as nonsuture dural repair with high sealing capability and flexibility. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11: 4213-4220. [23] Deng K, Ye X, Yang Y, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and biocompatibility of a new absorbable synthetic substitute as a dural onlay graft in a large animal model. Neurol Res. 2016; 38(9):799-808. [24] van Wachem PB, Hogt AH, Beugeling T, et al. Adhesion of cultured human endothelial cells onto methacrylate polymers with varying surface wettability and charge. Biomaterials. 1987;8(5):323-328. [25] Kailani MH, Jafar H, Awidi A. Synthetic Biomaterials for Skin Tissue Engineering[M]// Skin Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 2016:163-183. [26] 郑崇亮,陆树良.创伤后表皮更新和修复的研究进展[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(2):185-188.[27] 杨道朋,夏旭.3D打印生物材料研究及其临床应用优势[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,22(18):2927-2933.[28] Dash BC, Xu Z, Lin L, et al. Stem Cells and Engineered Scaffolds for Regenerative Wound Healing. Bioengineering (Basel). 2018;5(1). pii: E23. doi: 10. 3390/bioengineering 5010023. Review. [29] Sun L, Gao W, Fu X, et al. Enhanced wound healing in diabetic rats by nanofibrous scaffolds mimicking the basketweave pattern of collagen fibrils in native skin. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(2):340-349. [30] Lien SM, Ko LY, Huang TJ. Effect of pore size on ECM secretion and cell growth in gelatin scaffold for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009;5(2): 670-679. [31] Hoveizi E, Ebrahimi-Barough S, Tavakol S, et al. In Vitro Differentiation of Human iPS Cells into Neural like Cells on a Biomimetic Polyurea. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(1):601-607. [32] Kim HW, Yu HS, Lee HH. Nanofibrous matrices of poly(lactic acid) and gelatin polymeric blends for the improvement of cellular responses. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;87(1):25-32. [33] Wang S, Zhang Y, Wang H, et al. Fabrication and properties of the electrospun polylactide/silk fibroin-gelatin composite tubular scaffold. Biomacromolecules. 2009;10(8):2240-2244. [34] Chiou BS, Jafri H, Avena-Bustillos R, et al. Properties of electrospun pollock gelatin/poly(vinyl alcohol) and pollock gelatin/poly(lactic acid) fibers. Int J Biol Macromol. 2013; 55:214-220. [35] Shi Z, Xu T, Yuan Y, et al. A New Absorbable Synthetic Substitute With Biomimetic Design for Dural Tissue Repair. Artif Organs. 2016;40(4):403-413. [36] Haik J, Kornhaber R, Blal B, et al. The Feasibility of a Handheld Electrospinning Device for the Application of Nanofibrous Wound Dressings. Adv Wound Care(New Rochelle). 2017;6(5):166-174. [37] Sofokleous P, Stride E, Bonfield W, et al. Design, construction and performance of a portable handheld electrohydrodynamic multi-needle spray gun for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(1):213-223. [38] 林青,郝宏,王坤,等.逆向设计在制造工程中的应用[J].新技术新工艺,2017,37(12):65-67.[39] Wong JY, Pfahnl AC. 3D Printed Surgical Instruments Evaluated by a Simulated Crew of a Mars Mission. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2016;87(9):806-810. [40] Azimifar F, Hassani K, Saveh AH, et al. A medium invasiveness multi-level patient's specific template for pedicle screw placement in the scoliosis surgery. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(1):130. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [12] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [13] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [14] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| [15] | Liu Liyong, Zhou Lei. Research and development status and development trend of hydrogel in tissue engineering based on patent information [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3527-3533. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||