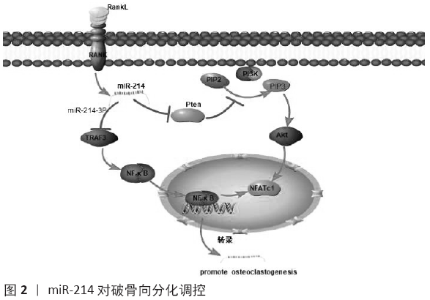
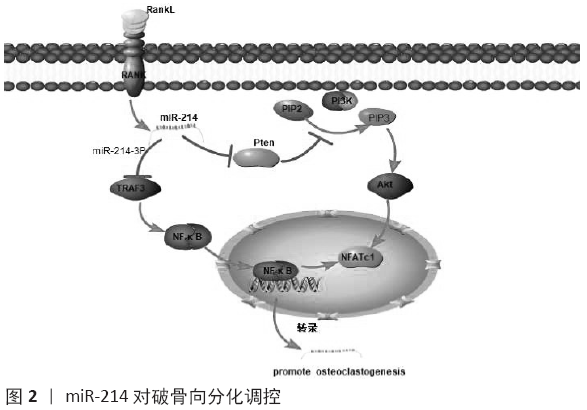
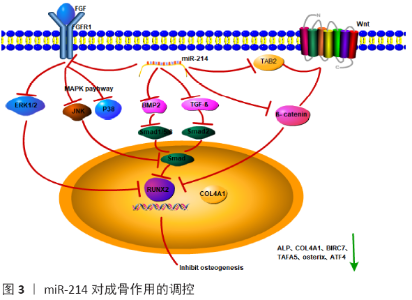
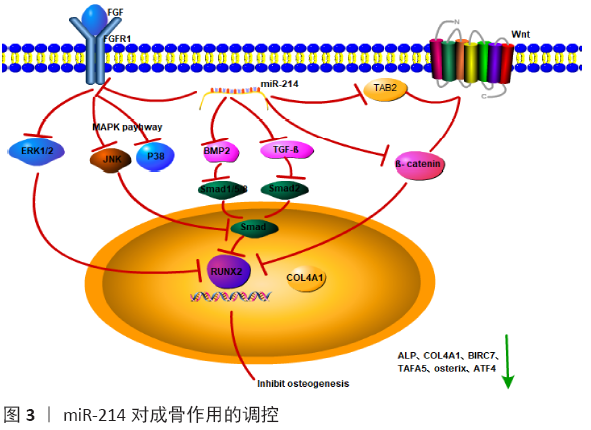
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (11): 1779-1784.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3080
Previous Articles Next Articles
MicroRNA-214 is involved in the regulation of bone metabolism
Li Dongdong1, Liao Hongbing2
- 1Guangxi Key Laboratory of Oral and Maxillofacial Repair and Reconstruction, Guangxi Clinical Research Center for Craniofacial Deformity, Key Laboratory of Maxillofacial Disease Diagnosis and Treatment (Key Laboratory of Guangxi University), School of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Hospital of Stomatology, School of Stomatology, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China