Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (2): 310-316.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0651
Previous Articles Next Articles
Self-assembling peptide hydrogel: hemostatic effect and mechanism
Wei Wei, Liu Yanfei, Zhang Ling, Xiong Na
- Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2018-08-09Online:2019-01-18Published:2019-01-18 -
Contact:Liu Yanfei, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Pr -
About author:Wei Wei, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering in Guizhou Province, the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Project of Guizhou Province Science and Technology Department, No. LKZ[2013]01 (to LYF); and the Natural Science Research Project of Education Department of Guizhou Province, No. KY[2015]418
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Wei, Liu Yanfei, Zhang Ling, Xiong Na . Self-assembling peptide hydrogel: hemostatic effect and mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(2): 310-316.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
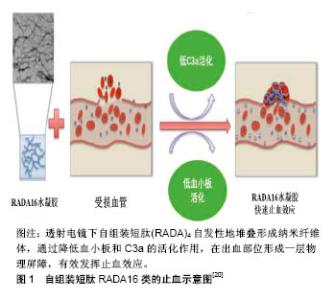
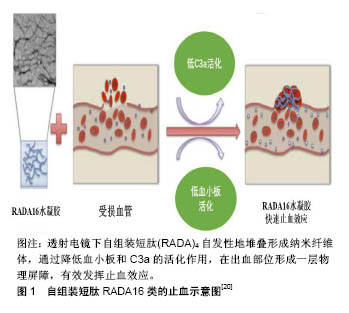
2.1 自组装短肽材料的止血研究 2.1.1 RADA16-1止血材料 自组装短肽分子通过非共价键作用力(包括氢键,离子作用力,疏水作用力,范德华作用力和π-π堆积等)自组装为稳定的水凝胶结 构[17]。单独存在时,每种作用力都较弱,但当它们共同作用时,就可以强化形成各种稳定的结构。 目前,在自组装止血材料中应用与研究最深入的是RADA16-Ⅰ(Ac-RADARADARADARAD-NH2),在水溶液中疏水的丙氨酸形成重叠的疏水作用力,而邻近短肽中带正电的精氨酸(R)和带负电的天冬氨酸(D)残基,通过分子间的非共价键作用力互相堆叠,最终形成宽约 10 nm的纳米纤维体,随后进一步聚合形成水凝胶支架。这些支架具有自我修复的能力:反复使用超声波处理破坏分子间作用力,促使水凝胶瓦解为液体状态,短肽成分会逐渐重组装为与原先结构相同的纳米纤维体。RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶支架能促进细胞生长、分化和迁移,已被广泛用于生物材料领域,包括止血、组织工程、药物缓释、伤口愈合等。鉴于其优秀的生物相容性,RADA16被批准许可作为商业产品PuraMatrix应用于实验室和临床前期。它作为外科止血材料的临床应用已经以商业名PuraStat获得了欧盟认证。 2006年,美国麻省理工大学和香港大学的Ellis-Behnke小组,在研究自组装短肽对仓鼠神经再生的影响时,意外发现了将RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶注入损伤原位,短肽可形成纳米纤维屏障,与周围组织联合形成细胞外基质微环境,发挥止血作用[6]。随后,Ellis-Behnke小组将RADA16-Ⅰ定义为纳米止血剂(NHS),设计了7个实验,第一次研究了自组装材料的止血效应:大鼠和仓鼠矢状窦血管横断止血;脊髓横切止血;股动脉横断止血;左侧肝叶矢状面横切止血;左侧肝叶横向横断包括门静脉主要分支横断止血;肝脏4 mm穿孔止血;裸鼠皮肤多处4 mm穿孔止血。结果显示7组实验中,RADA16-Ⅰ止血剂均可在15 s内快速止血。 实质脏器(如肝脏、脾脏、肾脏等)的出血往往很难控制,易引起较大的出血。Song等[18]评估了不同浓度RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶在大鼠肾切除损伤模型中的止血效应,结果发现2%的RADA16-Ⅰ同明胶海绵一样,可发挥快速止血作用,同时引起更少的组织学反应。李佳楠 等[19]探讨了RADA16-Ⅰ短肽自组装成纤维长度与止血功能的关系,结果显示RADA16-Ⅰ短肽纳米长纤维的数量在自组装期间与时间呈正相关,自组装纳米纤维长度与完全止血时间呈负相关。Saini等[20]在体外评估了RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶的血液相容性,包括:补体激活,血小板的形态和活化,以及血凝块形成的动力学。RADA16-Ⅰ纳米纤维可快速引起血凝块形成,但表现出低血小板活化和低补体C3a活化,见图1。研究表明,这些材料在生理条件下具有净中性电荷和高水合度,当使用这些材料时,观察到的快速止血主要来自体液凝固,可能由水凝胶结构内的纳米纤维引起。Taghavi等[21]重点研究分析了不同浓度(0.1%,0.2%,0.3%和0.5%) RADA16-Ⅰ的血液相容性,进行了凝血过程、血小板聚集,补体C3和C4浓度,全血细胞计数,溶血和白细胞形态学测试。结果显示,RADA 16-Ⅰ水凝胶使血细胞数量减少,血块形成时间和血小板聚集现象稍微增加,并且产生可忽略的溶血作用,同时补体C3和C4浓度和白细胞形态仅产生很少的变化。总而言之,血液相容性的体外测试显示,当短肽与血液接触时血液组成没有变化。快速止血效应可能是由于在短肽水凝胶附近形成血凝块所导致的分子局部浓度增加,形成完全止血的屏障。"
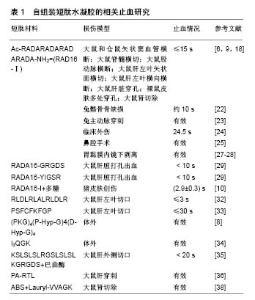
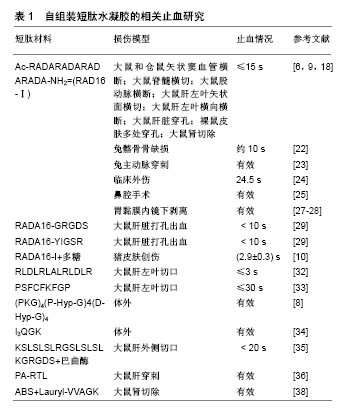
Csukas等[9]研究了自组装短肽RADA16-Ⅰ在大鼠肝脏穿刺模型中使用和未使用肝素抗凝治疗的止血活性,结果显示,RADA16-Ⅰ能够在肝素化和非肝素化处理动物中均等快速地实现止血,解决了外科术中和术后出血使用抗凝药物治疗的一系列问题。Wu等[22]对比了RADA16-Ⅰ和骨蜡在新西兰兔髂骨骨缺损模型中的止血和骨再生性能,可生物降解RADA16-Ⅰ显示出良好的止血和促进骨再生性能。RADA16-Ⅰ在影像学分析和免疫组化分析中都表现出有效的骨再生现象,而骨蜡抑制成骨。而且在体内实验中,RADA16-Ⅰ表现出良好的生物相容性,该水凝胶允许成骨细胞迁移入骨缺陷区域并促进骨再生,而骨蜡在骨损伤界面处表现出严重的炎症反应。因此RADA16-Ⅰ水凝胶在骨性结构止血方面比骨蜡更有优势。 在临床前期实验中,RADA16-Ⅰ短肽水凝胶也表现出良好的止血效果。Masuhara等[23]在动物实验中证实了RADA16-Ⅰ在兔腹主动脉穿刺出血模型中疗效较好,也证实了较低浓度水凝胶静脉注射的安全性。在临床研究中,对25例患者的33个血管吻合口移植位点进行止血研究,疗效和安全率为87.9%(29/33),没有术后出血或其他不良事件的发生。基于这些研究,可认为RADA16-Ⅰ是一个安全有效的止血材料,在心血管手术中表现出优异的局部止血功效。Rahmani等[24]研究了SAPB-T45K(即RADA16)对46例临床外伤患者伤口的止血效果,SAPB-T45K组止血时间约为24.5 s,与生理盐水对照组的44 s相比,止血时间缩短了41%,在抗凝治疗患者中效果更佳。Lee等[25]首次报道PuraStat在鼻腔手术中止血和抗粘连性能,60例患者接受鼻窦术后未观察到术后再出血,而且伤口在没有粘连形成的情况下愈合良好。胃黏膜内镜下剥离可整块切除早期胃肠肿瘤,然而术后会发生较高的延迟出血率(5.5%),引起急性失血,需要再次内镜干预[26]。Uraoka等[27]研究了PuraMatrix短肽水凝胶(RADA16-I)对胃黏膜内镜下剥离后溃疡组织修复作用,他们对45例患者的51个病灶进行了切除,被切除的标本平均大小为(36.5±11.3) mm。肿瘤切除后立即用导管将短肽水凝胶材料应用于损伤原位,通过内镜检查评估溃疡情况,结果发现只有1例患者出现了延迟出血,与之前的报道相比,PuraMatrix可降低内镜术后延迟出血的发生率,同时促进术后黏膜再生和溃疡愈合速度。Pioche等[28]对56例患者的65个黏膜病灶进行内镜手术,其中40例行内镜黏膜下剥离术,16例行内镜下黏膜切除术,平均病灶大小(37.9± 2.2) mm,术中应用PuraStat短肽水凝胶(RADA16-Ⅰ)在损伤原位止血。考虑到有29例高风险出血患者,而术后只有4例发生迟发性出血(6.2%)(3例便血,1例呕血),需要再次内镜止血。PuraStat材料可能有助于减少高风险术后出血,但仍需进一步研究,以充分评估其有效性和安全性。 2.1.2 RADA16衍生止血材料 RADA16具有稳定的成胶性,但由于其较低的pH值(3.0-4.0),易引起组织损伤,且生物活性并不十分理想,因此科研工作者从自然活性肽中挑选出不同的功能序列与RADA16短肽连接,设计出更优秀的RADA16衍生止血材料。Cheng等[29]在RADA16自组装短肽的基础上连接了GRGDS功能序列和YIGSR功能序列,设计出2种新型自组装短肽RADA16-GRGDS和RADA16-YIGSR。GRGDS序列来源于纤连蛋白中的重复片段,是纤连蛋白受体的重要短肽配体。已有研究证明,GRGDS短肽通过结合多种整合素,介导细胞黏附,功能序列YIGSR出现在层粘连蛋白1的β1链中,其表现出较强的细胞黏附、迁移和内皮细胞管形成的能力[30-31]。这些纤连蛋白和层粘连蛋白衍生的肽具有良好的细胞生物学活性,它们已开始被应用于组织工程方向。此外,纤连蛋白和层粘连蛋白也具有促进肝组织伤口愈合的能力。在大鼠肝脏打孔出血模型研究中,RADA16-Ⅰ、RADA16-GRGDS和RADA16- YIGSR三种短肽水凝胶均在10 s内完全止血,表现出优秀的止血功效,同时免疫组化证据显示,在肝打孔损伤原位处的水凝胶,还可显著促进肝脏组织再生。Hsu等[10]在RADA16-Ⅰ的基础上创建出了一种基于凝血策略的新型止血敷料,它使用逐层组装技术将自组装水凝胶转变成干膜配方,通过非变性静电相互作用形成机械稳定的保形薄膜涂层。这些薄膜由RADA16-Ⅰ和可生物降解的多糖组成,涂在纱布和吸收性明胶海绵等包扎材料上,这些纳米纤维在生理条件下发生水合作用,并与血液作用产生纳米纤维血块。将这些止血绷带在暴露于极端的温度条件(-80至60 ℃)下1周,甚至在60 ℃温度下长达5个月后,从止血绷带涂层上洗脱的这些纳米纤维仍保持活性。此外,应用这些由纱布绷带制成的基于纳米纤维薄膜,加速了猪皮肤伤口的止血。材料的热稳定性与自组装短肽的强效止血性能、生物相容性、可生物降解性和低生产成本相结合,使其成为极具前景的止血绷带。 2.1.3 新型自组装短肽止血材料 经典的RADA16-Ⅰ是最具有代表性的自组装短肽止血剂,但随着探索研究的不断深入,科研人员又设计出一系列功能丰富的水凝胶短肽。Komatsu等[32]设计了一种中性的(pH=6.5-7.5)自组装肽水凝胶SPG-178(序列为RLDLRLALRLDLR)。SPG-178短肽可形成反平行β折叠二级结构,自组装形成直径约10 nm的纳米纤维,进一步形成稳定的网状水凝胶结构。该SPG-178水凝胶可对10 mm长、3 mm深的肝左叶切口实现3 s内快速止血,电镜下观察到SPG-178并不总是与肝脏直接接触,大多数情况下在SPG-178和肝脏组织之间可观察到血液。Komatsu的进一步研究发现,止血过程是随着时间进行的,当水凝胶应用于伤口止血后立即移除,伤口会再出血,而将水凝胶应用于伤口止血10 min后再移除,就未发生再出血现象。据此推测,经过了10 min的间隔,伤口可通过生理机制自发性止血(包括血管收缩、血小板形成和凝聚)。Ruan等[33]设计了一种两亲性自组装短肽(序列为PSFCFKFGP),可形成β折叠和β转角等二级结构,进一步自组装为分层排列的超分子聚集体。短肽在浓度较高时主要自组装为球形聚合体,互相连接形成“串珠”样纳米纤维体,这些长纤维体广泛地分支延伸,互相重叠形成含水量大于99%的水凝胶。这种短肽水凝胶可缓慢地释放封装的疏水性药物。对于肝左外叶下部2 cm的伤口止血效果对比实验中,1%短肽水凝胶组可在30 s内有效止血,止血平均时间相当于纱布组的13%及壳聚糖组的19%。 胶原蛋白是细胞外基质中的主要成分,在血液凝固、伤口愈合和组织重塑中发挥着重要作用。胶原蛋白具有促进血栓形成的潜能,因此合成可模拟天然胶原蛋 白纳米结构和特性的生物材料,是止血材料学的一个重要目标。Kumar等[8]设计了一种由36个氨基酸组成的胶原蛋白模拟肽KOD,序列为(PKG)4(P-Hyp-G)4 (D-Hyp-G)4,KOD能自组装成类似于胶原蛋白结构的三股螺旋状纳米纤维,进一步形成纳米纤维水凝胶,这种水凝胶被证明能使全血凝固,最小化出血量和显著地黏附及活化血小板。此外,将THP-1单核细胞植入水凝胶支架后,没有发现促炎细胞因子肿瘤坏死因子α或白细胞介素1β的上调。 Chen等[34]设计了两亲性短肽I3QGK,将短肽的自组装过程与酶催化结合,应用于止血。短肽I3QGK可在水溶液中自组装成长纳米带,加入谷氨酰胺转氨酶(TGase)后,短肽溶液经历独特成胶转变,形成了较硬的水凝胶,显示出较强的剪切应变能力和快速恢复特性。透射电子显微镜和原子力显微镜测量发现,除了原有的纳米条带外,还有相当多的纳米纤维形成。液相色谱和质谱分析显示,短肽单体通过酶促形分子间ε-(γ-谷氨酰)赖氨酸异肽键连接形成短肽二聚体,该二聚体又可迅速自组装成有弹性且互相交缠的纳米纤维,最初的纳米带和新形成的纳米纤维共存,促进了水凝胶的进一步形成。血液中的凝血因子XⅢ,在机体出血期间被凝血酶转化为活性TGase(凝血因子XⅢa),所以该短肽材料通过凝胶化血液和促进血小板黏附,与其他止血方法相比显示出更快和更有效的止血性能。 Kumar等[35]设计了一种自组装短肽纳米纤维水凝胶SLac(序列为KSLSLSLRGSLSLSLKGRGDS),它本身可为出血伤口提供一个物理障碍。巴曲酶是一种蛇毒衍生的丝氨酸蛋白酶,具有明显降低纤维蛋白原和溶栓的作用。SLac装载蛇毒液衍生的巴曲酶(50 mg/L)产生了载药水凝胶SB50。即使是在使用肝素的情况下,SB50载药水凝胶也可加强凝血作用。在大鼠肝外侧切口模型中,装载巴曲酶的水凝胶在正常组和肝素处理组中都可起到一个20 s内迅速止血的作用。与标准护理、明胶海绵和Puramatrix等研究性止血剂相比,只有SB50术后显示出更快速的肝切口止血。这种蛇毒载体短肽水凝胶可通过注射器使用,并适应伤口而发挥止血效应。 组织因子是在所有比毛细血管大的血管外膜细胞中发现的完整膜蛋白,并且仅暴露于血管破裂后血管内空间循环血液成分,使其成为治疗出血的理想靶点。靶向组织因子在启动凝血级联中起重要作用。为了开发针对出血的靶向治疗,Morgan等[36]选择了一种两亲性短肽递送载体,将3个靶向组织因子-结合序列(EGR,RLM和RTL)共价结合到两亲性短肽主链中,透射电子显微镜显示短肽自组装形成纳米纤维。在大鼠肝穿刺活检出血模型中,只有RTL纳米纤维与假手术组相比减少了53%失血量。RTL纳米纤维的生物相容性评估显示,它不仅不诱导红细胞溶血,而且在肝损伤原位没有引起炎症反应,30 min后还有70%的血细胞存在。这些研究表明,两亲性短肽在体外与靶向组织因子成功结合,并且成功地将靶向组织因子-靶向纳米纤维归巢至出血部位,并降低体内伴随的相关失血。 Ankaferd止血剂(ABS)是一种植物来源的止血剂,已被注册用于预防临床出血,它可通过蛋白质凝集效应引起血管内皮中红细胞聚集[37]。Huri等[38]将ABS止血剂与两亲性短肽(序列为Lauryl-VVAGK-Am)1∶1混合得到纳米止血剂,应用于肾部分切除术,可发挥出优秀的止血效应,扫描电镜结果显示,肾组织毛细血管床内存在显著的红细胞聚集,而微毛细管脉管系统周围的肾组织中既无坏死也没有任何组织损伤迹象,证实了这种纳米止血剂在肾脏止血中的安全性。 2.2 止血特性 通过对自组装短肽止血材料的不断研究,发现短肽水凝胶具有以下新颖的止血特性:①RADA16类自组装短肽的止血作用并不是通过凝血或血小板聚集。血液凝固通常在损伤后一两分钟后开始,此外,透射电镜观察也未发现自组装短肽材料引起血小板聚集[6]。有研究报道,L型精氨酸(R)具有抗血栓形成效应,可能解释了含精氨酸的自组装短肽水凝胶不引起血小板聚集的现象[39];②自组装短肽首先接触体液中的电解质后,促进了短肽自组装和进一步形成孔径50- 200 nm的网状水凝胶结构。水凝胶覆盖于出血组织表面,快速填充和适应不规则伤口,形成纳米纤维屏障,阻止了细胞和体液的溢出;③短肽的浓度越高自组装的纳米纤维就更多,血液凝集活动变的更快。含红细胞的血液中,离子和电荷可加速短肽自组装成纳米纤维[40];④有研究报道,可用的生物材料应产生少于2%的溶血,较高程度的溶血表明生物材料的血液相容性差[41]。数据表明自组装短肽具有良好的生物相容性,提供了一个可接受的溶血水平[20-21]。RADA 16-Ⅰ似乎仅诱导红细胞的黏附而没有损伤细胞膜,且形成的纳米纤维屏障避免了红细胞暴露于空气中而发生降解;⑤自组装短肽水凝胶的弹性模量过高或过低都不能达到最佳的止血效果,只有当短肽水凝胶紧密贴合伤口时,才能更好地耐受血管搏动,发挥最大止血效应[19];⑥多数的止血材料是不透明的,因此不能观察到伤口内部止血情况。自组装短肽水凝胶为无色透明生物支架,可清晰地观察到伤口内部止血状况;⑦自组装短肽水凝胶降解产物为天然的L型氨基酸,可被周围组织再吸收,用于修复。自组装短肽材料的相关止血研究,见表1。"
| [1] Liu H, Li X, Niu X, et al. Improved hemocompatibility and endothelialization of vascular grafts by covalent immobilization of sulfated silk fibroin on poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds. Biomacromolecules. 2011;12(8):2914-2924. [2] Motlagh D, Yang J, Lui KY, et al. Hemocompatibility evaluation of poly(glycerol-sebacate) in vitro for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2006;27(24):4315-4324. [3] DeAnglis AP, Nur I, Gorman AJ, et al. A method to measure thrombin activity in a mixture of fibrinogen and thrombin powders. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2017;28(2):134-138. [4] Pourshahrestani S, Zeimaran E, Djordjevic I, et al. Inorganic hemostats: The state-of-the-art and recent advances. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;58:1255-1268. [5] Kornecki E, Lenox RH, Hardwick DH, et al. Interactions of the alkyl-ether-phospholipid, platelet activating factor(PAF)with platelets, neural cells, and the psychotropic drugs triazolobenzodiazepines. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;221: 477-488. [6] Ellis-Behnke RG, Liang YX, Tay DK, et al. Nano hemostat solution: immediate hemostasis at the nanoscale. Nanomedicine. 2006;2(4):207-215. [7] Gabay M, Boucher BA. An essential primer for understanding the role of topical hemostats, surgical sealants, and adhesives for maintaining hemostasis. Pharmacotherapy. 2013;33(9):935-955. [8] Kumar VA, Taylor NL, Jalan AA, et al. A nanostructured synthetic collagen mimic for hemostasis. Biomacromolecules. 2014;15(4):1484-1490. [9] Csukas D, Urbanics R, Moritz A, et al. AC5 Surgical Hemostat as an effective hemostatic agent in an anticoagulated rat liver punch biopsy model. Nanomedicine. 2015;11(8): 2025-2031. [10] Hsu BB, Conway W, Tschabrunn CM, et al. Clotting Mimicry from Robust Hemostatic Bandages Based on Self-Assembling Peptides. ACS Nano. 2015;9(9):9394-9406. [11] Momeni A, Filiaggi MJ. Degradation and hemostatic properties of polyphosphate coacervates. Acta Biomater. 2016;41:328-341. [12] Dowling MB, Chaturvedi A, MacIntire IC, et al. Determination of efficacy of a novel alginate dressing in a lethal arterial injury model in swine. Injury. 2016;47(10):2105-2109. [13] Ghobril C, Grinstaff MW. The chemistry and engineering of polymeric hydrogel adhesives for wound closure: a tutorial. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(7):1820-1835. [14] Kondo Y, Nagasaka T, Kobayashi S, et al. Management of peritoneal effusion by sealing with a self-assembling nanofiber polypeptide following pelvic surgery. Hepatogastroenterology. 2014;61(130):349-353. [15] Gao XR, Xu HJ, Wang LF, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation carried in SVVYGLR modified self-assembling peptide promoted cardiac repair and angiogenesis after myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017; 491(1):112-118. [16] Rad-Malekshahi M, Lempsink L, Amidi M, et al. Biomedical Applications of Self-Assembling Peptides. Bioconjug Chem. 2016;27(1):3-18. [17] Whitesides GM, Mathias JP, Seto CT. Molecular self-assembly and nanochemistry: a chemical strategy for the synthesis of nanostructures. Science. 1991;254(5036): 1312-1319. [18] Song H, Zhang L, Zhao X. Hemostatic efficacy of biological self-assembling peptide nanofibers in a rat kidney model. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(1):33-39. [19] 李佳楠,钟小忠,王婷.短肽RADA16-1自组装纤维长度与止血关系研究[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版),2013,41(5):76-80.[20] Saini A, Serrano K, Koss K, et al. Evaluation of the hemocompatibility and rapid hemostasis of (RADA)4 peptide-based hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:71-79. [21] Taghavi L, Aramvash A, Seyedkarimi MS, et al. Evaluation of the hemocompatibility of RADA 16-I peptide. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(8):1024-1031. [22] Wu M, Ye Z, Zhu H, et al. Self-Assembling Peptide Nanofibrous Hydrogel on Immediate Hemostasis and Accelerative Osteosis. Biomacromolecules. 2015;16(10): 3112-3118. [23] Masuhara H, Fujii T, Watanabe Y, et al. Novel Infectious Agent-Free Hemostatic Material (TDM-621) in Cardiovascular Surgery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2012;18(5):444-451. [24] Rahmani G, Prats J, Norchi T, et al. First Safety and Performance Evaluation of T45K, a Self-Assembling Peptide Barrier Hemostatic Device, After Skin Lesion Excision. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44(7):939-948.[25] Lee MF, Ma Z, Ananda A. A novel haemostatic agent based on self-assembling peptides in the setting of nasal endoscopic surgery, a case series. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2017; 41:461-464. [26] Goto O, Fujishiro M, Oda I, et al. A multicenter survey of the management after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection related to postoperative bleeding. Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57(2): 435-439. [27] Uraoka T, Ochiai Y, Fujimoto A, et al. A novel fully synthetic and self-assembled peptide solution for endoscopic submucosal dissection-induced ulcer in the stomach. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83(6):1259-1264. [28] Pioche M, Camus M, Rivory J, et al. A self-assembling matrix-forming gel can be easily and safely applied to prevent delayed bleeding after endoscopic resections. Endosc Int Open. 2016;4(4):E415-419. [29] Cheng TY, Wu HC, Huang MY, et al. Self-assembling functionalized nanopeptides for immediate hemostasis and accelerative liver tissue regeneration. Nanoscale. 2013; 5(7): 2734-2744. [30] Chada D, Mather T, Nollert MU. The synergy site of fibronectin is required for strong interaction with the platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Ann Biomed Eng. 2006;34(10): 1542-1552. [31] Nomizu M, Kim WH, Yamamura K, et al. Identification of cell binding sites in the laminin alpha 1 chain carboxyl-terminal globular domain by systematic screening of synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1995;270(35):20583-20590. [32] Komatsu S, Nagai Y, Naruse K, et al. The neutral self-assembling peptide hydrogel SPG-178 as a topical hemostatic agent. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102778. [33] Ruan L, Zhang H, Luo H, et al. Designed amphiphilic peptide forms stable nanoweb, slowly releases encapsulated hydrophobic drug, and accelerates animal hemostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(13):5105-5110. [34] Chen C, Zhang Y, Fei R, et al. Hydrogelation of the Short Self-Assembling Peptide I3QGK Regulated by Transglutaminase and Use for Rapid Hemostasis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(28):17833-17841. [35] Kumar VA, Wickremasinghe NC, Shi S, et al. Nanofibrous Snake Venom Hemostat. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2015;1(12): 1300-1305. [36] Morgan CE, Dombrowski AW, Rubert Perez CM, et al. Tissue-Factor Targeted Peptide Amphiphile Nanofibers as an Injectable Therapy To Control Hemorrhage. ACS Nano. 2016; 10(1):899-909. [37] Haznedaroglu BZ, Beyazit Y, Walker SL, et al. Pleiotropic cellular, hemostatic, and biological actions of Ankaferd hemostat. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2012;83(1):21-34. [38] Huri E, Dogantekin E, Hayran M, et al. Ultrastructural analyses of the novel chimeric hemostatic agent generated via nanotechnology, ABS nanohemostat, at the renal tissue level. Springerplus. 2016;5(1):1931. [39] Cylwik D, Mogielnicki A, Kramkowski K, et al. Antithrombotic effect of L-arginine in hypertensive rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2004;55(3):563-574. [40] Luo Z, Wang S, Zhang S. Fabrication of self-assembling D-form peptide nanofiber scaffold d-EAK16 for rapid hemostasis. Biomaterials. 2011;32(8):2013-2020. [41] Immunology LM. The new view of complement. Science. 2012;337(6098):1034-1037. [42] Liu Y, Zhang L, Wei W. Effect of noncovalent interaction on the self-assembly of a designed peptide and its potential use as a carrier for controlled bFGF release. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:659-670. [43] Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang C, et al. Stimuli-responsive self-assembling peptides made from antibacterial peptides. Nanoscale. 2013;5(14):6413-6421. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Liu Fang, Shan Zhengming, Tang Yulei, Wu Xiaomin, Tian Weiqun. Effects of hemostasis and promoting wound healing of ozone sustained-release hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3445-3449. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Li Xinping, Cui Qiuju, Zeng Shuguang, Ran Gaoying, Zhang Zhaoqiang, Liu Xianwen, Fang Wei, Xu Shuaimei. Effect of modification of β-tricalcium phosphate/chitosan hydrogel on growth and mineralization of dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3493-3499. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||