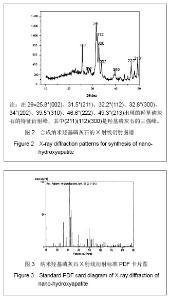
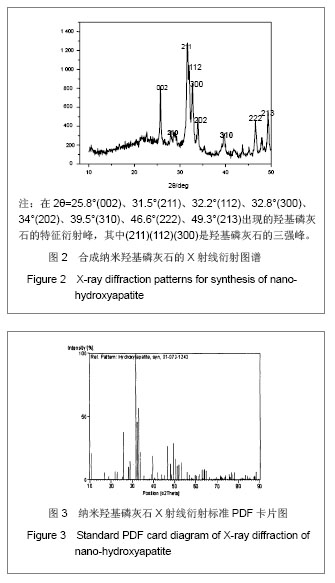
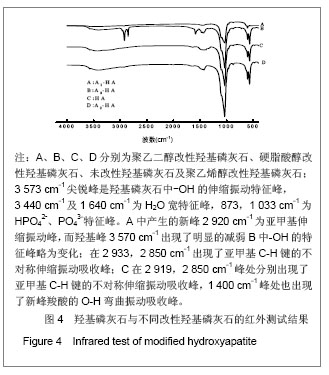
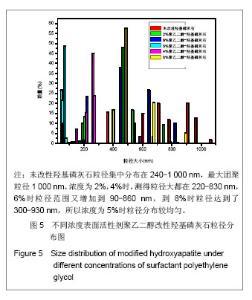
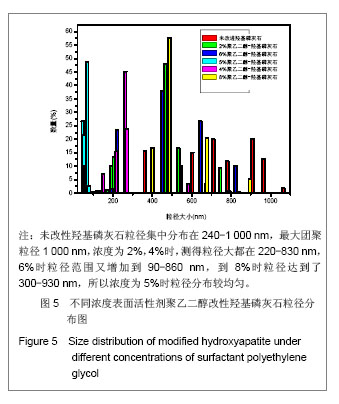
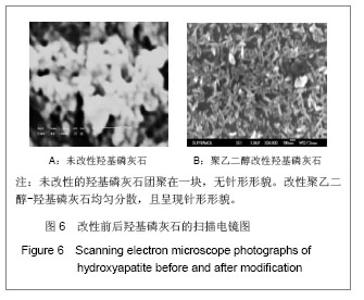
| [1]Zhang HQ,Wang YF,Yan YH,et al.Precipitation of biocompatible hydroxyl apatite whiskers from moderately acid solution.Ceram Int.2003;29(4):413-418.[2]Yang L,Ning X,Chen k,et al. Preparation and properties of hydroxyapatite filters for microbial filtration. Ceramics International.2007;33(3):483-489.[3]Zhang CW,Li JY.Cailiao Daobao. 2006;20(S2):390-396.张超武,李娟莹.共沉淀法制备羟基磷灰石影响因素的研究[J].材料导报,2006,20(S2):390-396.[4]Liu DM, Yang Q, Troczynski T, et al. Structural evolution of sol-gel derived hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials.2002;23(7): 679-1687.[5]Mostafa NY.Characterization, thermal stability and sintering of hydroxyapatite powders prepared by different routes. Macromol Chem Phys.2005; 94(2-3): 333-341.[6]Cengiz B,Gokce Y,YildizN,et al.Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.Colloid Surface A.2008;322(1-3):29-33.[7]Liu CS,Huang Y,Shen W,et al. Kinetics of hydroxyapatite precipitation at pH 10 to 11.Biomaterials.2001;22(4):301-306.[8]Afshar A,Ghorbani M,Ehsani N,et al.Some important factors in the wet precipitation process of hydroxyapatite.Mater Design. 2003;24(3): 197-202.[9]Yang C,Cheng K,Weng W,et al.OTS-modified HA and its toughening effect on PLLA/ HA porous composite. J Mater Sci Mater Med.2009;20(3): 667-672. |