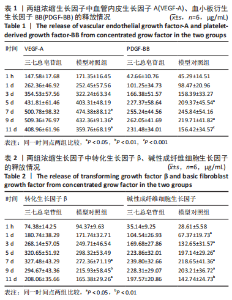
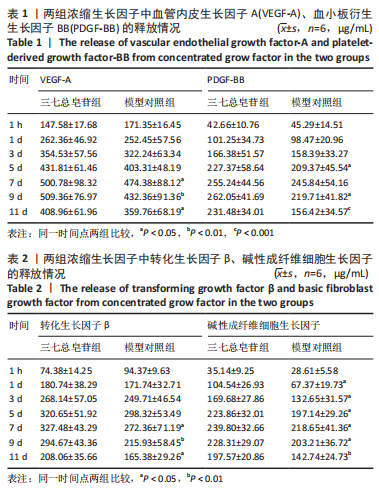
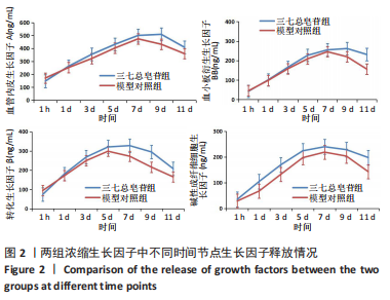
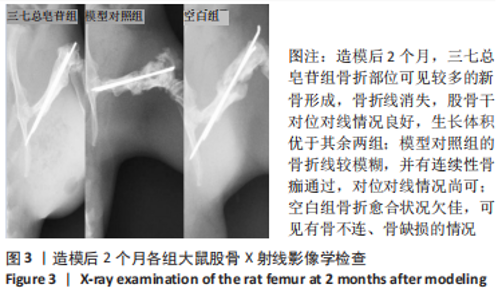
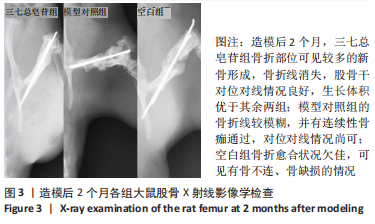
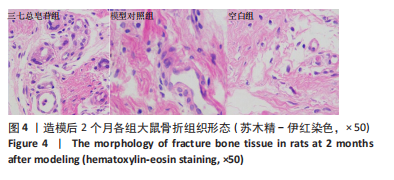
[1] RODELLA LF, FAVERO G, BONINSEGNA R, et al. Growth factors, CD34 positive cells, and fibrin network analysis in concentrated growth factors fraction. Microsc Res Tech. 2011;74(8):772-777.
[2] YU B, WANG Z. Effect of concentrated growth factors on beagle periodontal ligament stem cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep 2014;9(1): 235-242.
[3] 韩尚志,兰玲莉,刘锐,等.CGF、PRF和PRP中各种生长因子定量分析[J].河北医药,2022,44(2):184-187.
[4] BOSWELL SG, COLE BJ, SUNDMAN EA, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: a milieu of bioactive factors. Arthroscopy. 2012;28(3):429-439.
[5] PIETRZAK WS, EPPLEY BL. Platelet rich plasma:biology and new technology. J Craniofacial Surg. 2005;16:1043.
[6] 闫帝,冯佳,孙小娟. 富自体浓缩生长因子纤维蛋白液在口腔骨缺损种植引导骨再生后的骨量变化[J].中外医疗,2019,38(9):55-57.
[7] KIM TH, KIM SH, SÁNDOR GK, et al. Comparison of platelet-rich plasma (PRP), platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and concentrated growth factor (CGF) in rabbit-skull defect healing. Arch Oral Biol. 2014;59(5):550-558.
[8] 陈飞,潘韶霞,冯海兰. 转化生长因子-β1和血管内皮生长因子在浓缩生长因子各层中的分布及含量特点[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(5):860-865.
[9] 陈红艳,陈安,卢芳国,等.三七总皂苷的药理研究进展[J].湖南中医药杂志,2019,35(1):154-157.
[10] 李晋玉,康晟乾,孙旗,等.三七总皂苷在促进骨折愈合的信号通路基础实验研究概况[J].环球中医药,2021,14(3):539-544.
[11] 邓森,何亚青,黄家政,等.三七总皂苷预防髋关节置换术后异位骨化的临床效果分析[J].临床医学工程,2021,28(7):901-902.
[12] 胡广,关智宇,张开伟.三七总皂苷干预去势骨质疏松性骨折模型大鼠的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(2):172-177.
[13] EINHORN TA, GERSTENFELD LC. Fracture healing: mechanisms and interventions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):45-54.
[14] SI L, WINZENBERG TM, JIANG Q, et al. Projection of osteoporosis-related fractures and costs in China: 2010-2050. Osteoporos Int. 2015; 26(7):1929-1937.
[15] 余翔,任辉,沈耿杨. 基于“新三元成骨理论”探讨龟板联合干细胞及浓缩生长因子(CGF)修复绝经后骨质疏松骨缺损[C]//.第十四届中国实验动物科学年会论文集.
[16] 陈修,徐叔云,卞如濂.药理实验方法学[M]. 2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:1203.
[17] SOHN DS, HEO JU, KWAK DH, et al. Bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated growth factors alone. Implant Dent. 2011;20(5):389-395.
[18] ISOBE K, WATANEBE T, KAWABATA H, et al. Mechanical and degradation properties of advanced platelet-rich fibrin (A-PRF), concentrated growth factors (CGF), and platelet-poor plasma-derived fibrin (PPTF). Int J Implant Dent. 2017;3(1):17.
[19] 胡流超,罗毅文,程英雄,等.补肾活血汤通过Runx2/Osterix促进骨质疏松模型大鼠的骨折愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(11):1717-1722.
[20] MARX RE. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): what is PRP and what is not PRP? Implant Dent. 2001;10(4):225-228.
[21] PLACHOKOVA AS, NIKOLIDAKIS D, MULDER J, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on bone regeneration in dentistry: a systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19(6):539-545.
[22] FANG D, LONG Z, HOU J. Clinical Application of Concentrated Growth Factor Fibrin Combined With Bone Repair Materials in Jaw Defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;78(6):882-892.
[23] ROBSON MC, PHILLIPS LG, LAWRENCE WT, et al. The safety and effect of topically applied recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor on the healing of chronic pressure sores. Ann Surg. 1992;216(4):401-406; discussion 406-408.
[24] SOUZA TF, ANDRADE AL, FERREIRA GT, et al. Healing and expression of growth factors (TGF-β and PDGF) in canine radial ostectomy gap containing platelet-rich plasma. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2012; 25(6):445-452.
[25] SHING Y, FOLKMAN J, HAUDENSCHILD C, et al. Angiogenesis is stimulated by a tumor-derived endothelial cell growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1985;29(4):275-287.
[26] 李钢. 淫羊藿苷及富自体浓缩生长因子促进兔颅骨缺损修复的分子机制探讨[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2015.
[27] 汤凯,招文华,尚奇. 浓缩生长因子干预大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖、成骨分化及迁移[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(31):4935-4939.
[28] 吴训,孟娟红,张建运,等.浓缩生长因子修复兔髁突全层软骨损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(8):1166-1171.
[29] 黄依丹,成嘉欣,石颖,等.近五年三七化学成分、色谱分析、三七提取物和药理活性的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2022,47(10): 2584-2596.
[30] ZHAO S, YAN L, LI X, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 suppresses wear particle-induced osteolysis and RANKL mediated osteoclastogenesis in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:118-125.
[31] LI X, LIN H, ZHANG X, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates oxidative stress-induced osteoblast dysfunction through JNK signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(24):11278-11289.
[32] HUANG L, LI Q. Notoginsenoside R1 promotes differentiation of human alveolar osteoblasts in inflammatory microenvironment through inhibiting NFκB pathway and activating Wnt/βcatenin pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):4754-4762.
[33] YANG N, LIU D, XIAO Z, et al. Effects of ginsenosides on bone remodelling for novel drug applications: a review. Chin Med. 2020; 15:42.
[34] LIU Q, ZHOU J, ZHOU Y, et al. The Ginsenoside Exhibits Antiosteoporosis Effects in Ketogenic-Diet-Induced Osteoporosis via Rebalancing Bone Turnover. Front Pharmacol. 2021;11:593820.
[35] SIDDIQI MH, SIDDIQI MZ, AHN S, et al. Ginsenoside Rh1 induces mouse osteoblast growth and differentiation through the bone morphogenetic protein 2/runt-related gene 2 signalling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014;66(12):1763-1773.
[36] GU Y, ZHOU J, WANG Q, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of rBMSCs and healing of rat tibial fractures through regulation of GR-dependent BMP-2/SMAD signaling. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 25282.
[37] KIM HM, KIM DH, HAN HJ, et al. Ginsenoside Re Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation in Mouse Osteoblast Precursor MC3T3-E1 Cells and a Zebrafish Model. Molecules. 2016;22(1):42.
[38] YANG B, ZHAO S, YAN L. Withdrawal Notice: The Role of Ginsenoside Rb1 in Bone Homeostasis. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020. doi: 10.2174/1574888X15666200628141743.
[39] QIAO J, AN N, OUYANG X. Quantification of growth factors in different platelet concentrates. Platelets. 2017;28(8):774-778.
[40] WEIBRICH G, KLEIS WK, HAFNER G, et al. Growth factor levels in platelet-rich plasma and correlations with donor age, sex, and platelet count. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2002;30(2):97-102.
[41] KREUZ PC, KRÜGER JP, METZLAFF S, et al. Platelet-rich plasma preparation types show impact on chondrogenic differentiation, migration, and proliferation of human subchondral mesenchymal progenitor Cells. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(10):1951-1961.
[42] NGUYEN TH, PALANKAR R, BUI VC, et al. Rupture forces among human blood platelets at different degrees of activation. Sci Rep. 2016;5(6):25402.
|