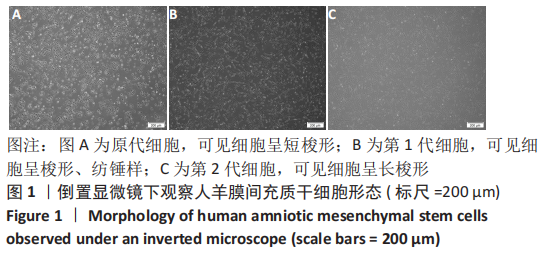
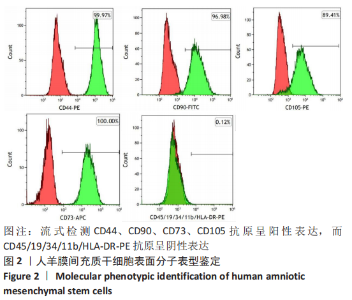
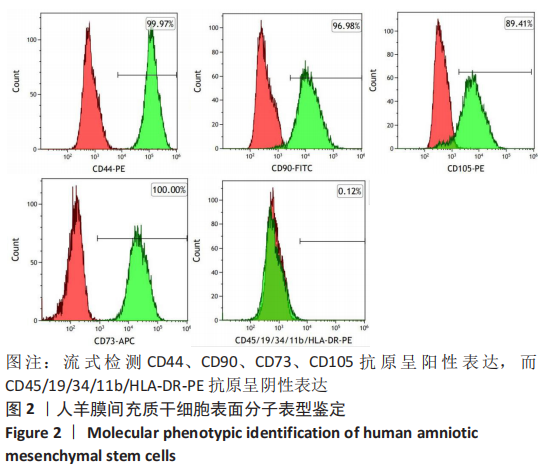
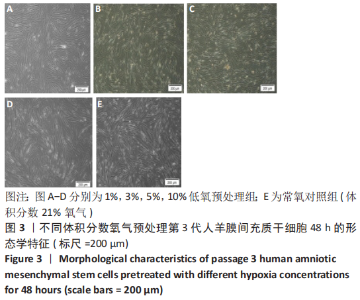
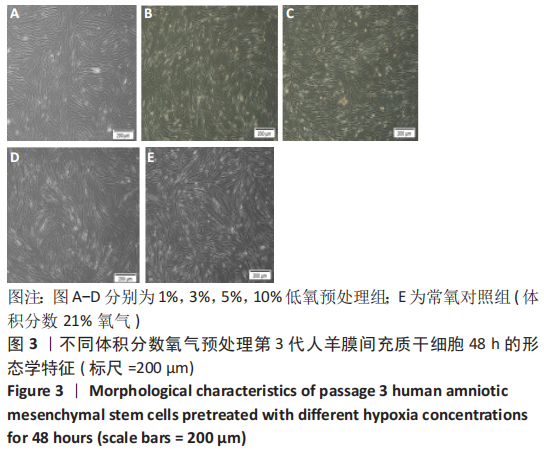
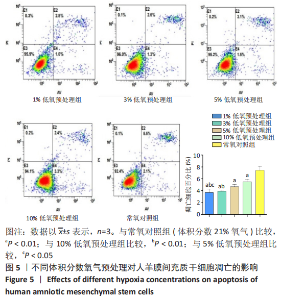
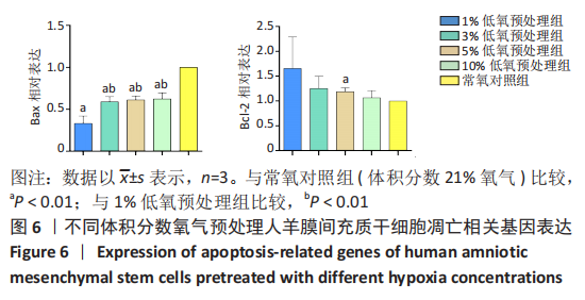
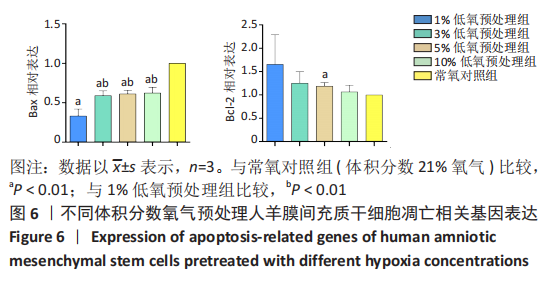
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (15): 2318-2324.doi: 10.12307/2023.392
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biological characteristics of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with different volume fractions of oxygen
Tang Jianhong1, Zhang Nini2, Huang Guilin2, Long Yuanzhu2, Cui Tianning1, Luo Qinliang1, Lang Jiachan1, Dai Min2, Zhang Ligang2
- 1Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2022-05-20Accepted:2022-07-14Online:2023-05-28Published:2022-10-17 -
Contact:Zhang Nini, Master, Associate professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Tang Jianhong, Master, Physician, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860198 (to ZNN); National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960204 (to HGL); Master’s Start-up Fund of Zunyi Medical University, No. KY2019-1 (to DM); a grant from Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwjkj2020-1-165 (to ZLG); “Future Clinical Famous Doctor” Project of Zunyi Medical University, No. 20211017 (to ZNN)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tang Jianhong, Zhang Nini, Huang Guilin, Long Yuanzhu, Cui Tianning, Luo Qinliang, Lang Jiachan, Dai Min, Zhang Ligang. Biological characteristics of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with different volume fractions of oxygen[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(15): 2318-2324.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
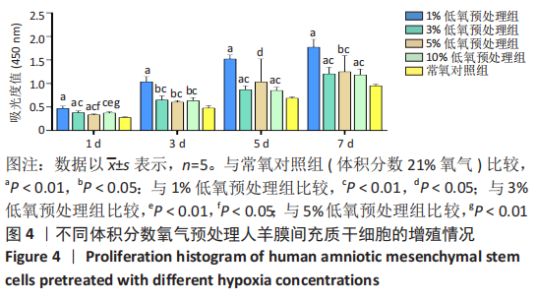
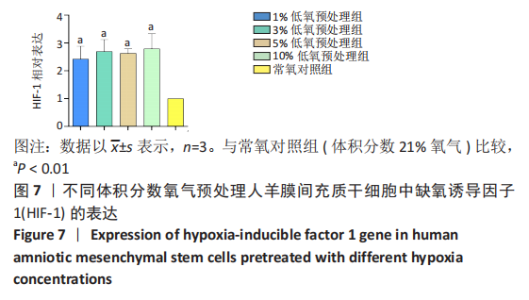
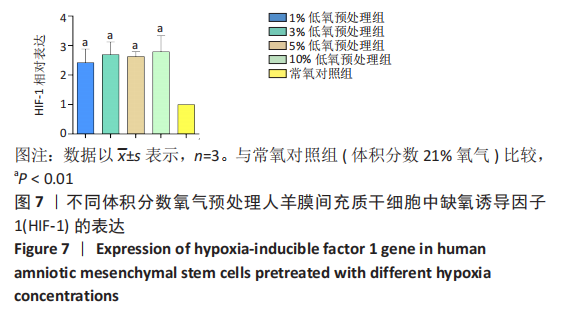
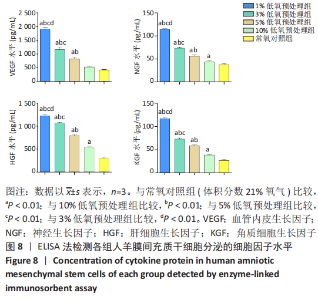
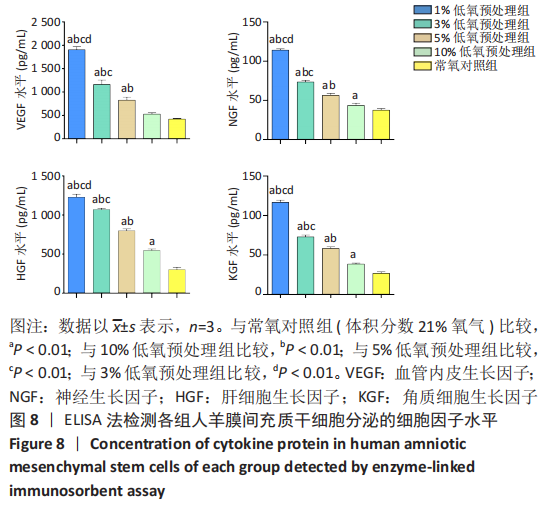
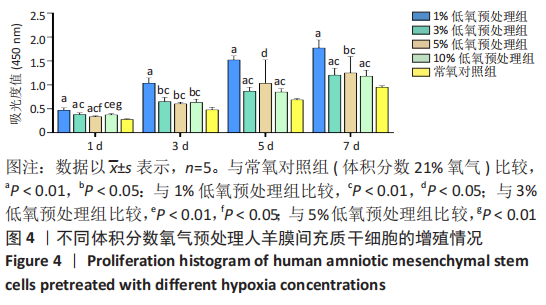
2.2 不同体积分数氧气预处理对人羊膜间充质干细胞增殖的影响 ①第1天:1%,3%,5%低氧预处理组吸光度值均高于常氧对照组(P < 0.01),1%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于3%,5%,10%低氧预处理组(P < 0.01),3%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于5%低氧预处理组(P < 0.05),3%,5%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于10%低氧预处理组(P < 0.01)。②第3天:与常氧对照组相比,1%低氧预处理组吸光度值显著增高(P < 0.01),3%,5%,10%低氧预处理组吸光度值增高(P < 0.05),1%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于3%,5%,10%低氧预处理组(P < 0.01)。③第5天:1%,3%,10%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于常氧对照组(P < 0.01),1%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于3%,10%低氧预处理组(P < 0.01),1%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于5%低氧预处理组(P < 0.05)。④第7天:与常氧对照组相比,1%,3%,10%低氧预处理组吸光度值显著增高(P < 0.01),5%低氧预处理组吸光度值增高(P < 0.05);1%低氧预处理组吸光度值高于3%,5%,10%低氧预处理组(P < 0.01),其余各组比较均无统计学差异,见图4。"
| [1] 李审绥,吴沉洲,乔翔鹤,等.辐射损伤唾液腺机制及治疗的研究进展[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2021,39(1):99-104. [2] 高洋,张园,柯学平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在放射性涎腺损伤中的修复作用[J].江苏医药,2016,42(6):625-627. [3] HUANG GL, ZHANG NN, WANG JS, et al. Transdifferentiation of human amniotic epithelial cells into acinar cells using a double-chamber system. Cell Reprogram. 2012;14(4):377-383. [4] ZHANG NN, HUANG GL, HAN QB, et al. Functional regeneration of irradiated salivary glands with human amniotic epithelial cells transplantation. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(10):2039-2047. [5] 王英鑫.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞修复放射性涎腺损伤功能的研究[D].遵义:遵义医学院,2018. [6] 王涛,强艳丽.脂肪干细胞对小鼠放射性唾液腺损伤的治疗作用[J].山东医药,2017,57(33):32-34. [7] VISSINK A, VAN LUIJK P, LANGENDIJK JA, et al. Current ideas to reduce or salvage radiation damage to salivary glands. Oral Dis. 2015;21(1): e1-10. [8] LOMBAERT I, MOVAHEDNIA MM, ADINE C, et al. Concise Review: Salivary Gland Regeneration: Therapeutic Approaches from Stem Cells to Tissue Organoids. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):97-105. [9] GOHI BFCA, LIU XY, ZENG HY, et al. Enhanced efficiency in isolation and expansion of hAMSCs via dual enzyme digestion and micro-carrier. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:2. [10] BIAN Y, DU Y, WANG R, et al. A comparative study of HAMSCs/HBMSCs transwell and mixed coculture systems. IUBMB Life. 2019;71(7):1048-1055. [11] ZHANG C, DU Y, YUAN H, et al. HAMSCs/HBMSCs coculture system ameliorates osteogenesis and angiogenesis against glucolipotoxicity. Biochimie. 2018;152:121-133. [12] CHEN W, XIAO S, WEI Z, et al. Schwann Cell-Like Cells Derived from Human Amniotic Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Peripheral Nerve Regeneration through a MicroRNA-214/c-Jun Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:2490761. [13] LI Y, LIU Z, TANG Y, et al. Schnurri-3 regulates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation and angiogenesis of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells through Runx2 and VEGF. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(1):72. [14] BIAN Y, MA X, WANG R, et al. Human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote osteogenesis of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against glucolipotoxicity. FEBS Open Bio. 2018;9(1):74-81. [15] 肖建辉.人羊膜干细胞:再生医学的理想种子细胞资源[J].遵义医学院学报,2015,38(5):439-449. [16] 姜亦瑶,刘晓程,裴宇,等.不同氧分压时人脂肪干细胞细胞因子的分泌[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(45):7861-7868. [17] 代敏,王帅,张霓霓,等.低氧预处理人羊膜间充质干细胞的生物学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(19):3004-3008. [18] LISINI D, NAVA S, POGLIANI S, et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical application: An efficient isolation approach. Curr Res Transl Med. 2019;67(1):20-27. [19] ANGELOPOULOS I, BRIZUELA C, KHOURY M. Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells Outperform Haploidentical Dental Pulp-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Proliferation Rate, Migration Ability, and Angiogenic Potential. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):967-978. [20] GASIŪNIENĖ M, PETKUS G, MATUZEVIČIUS D, et al. Angiotensin II and TGF-β1 Induce Alterations in Human Amniotic Fluid-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Leading to Cardiomyogenic Differentiation Initiation. Int J Stem Cells. 2019;12(2):251-264. [21] GASIŪNIENĖ M, VALATKAITĖ E, NAVAKAUSKIENĖ R. Long-term cultivation of human amniotic fluid stem cells: The impact on proliferative capacity and differentiation potential. J Cell Biochem. 2020;121(7):3491-3501. [22] TOPOLUK N, HAWKINS R, TOKISH J, et al. Amniotic Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Exhibit Preferential Osteogenic and Chondrogenic Differentiation and Enhanced Matrix Production Compared With Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(11): 2637-2646. [23] YANG L, ZHU S, LI Y, et al. Overexpression of Pygo2 Increases Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Cardiomyocyte-like Cells. Curr Mol Med. 2020;20(4):318-324. [24] DAVIDSON JO, DHILLON SK, BENNET L. Preterm neonatal brain injury: are human amnion epithelial stem cells a pan-treatment for neuroprotection and neurorepair? Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(6): 1261-1262. [25] KIM SW, ZHANG HZ, KIM CE, et al. Amniotic mesenchymal stem cells with robust chemotactic properties are effective in the treatment of a myocardial infarction model. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168(2):1062-1069. [26] KIM SW, ZHANG HZ, GUO L, et al. Amniotic mesenchymal stem cells enhance wound healing in diabetic NOD/SCID mice through high angiogenic and engraftment capabilities. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41105. [27] 陈晶,刘清岩,张海宁,等.脂肪干细胞来源的外泌体对2型糖尿病肾病大鼠的保护作用[J].解剖科学进展,2020,26(4):369-373. [28] SCEPANOVIC G, FLOREA A, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ R. Multiscale In Vivo Imaging of Collective Cell Migration in Drosophila Embryos. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2179:199-224. [29] LIU W, LI L, RONG Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [30] VIZOSO FJ, EIRO N, CID S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: Toward Cell-Free Therapeutic Strategies in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(9):1852. [31] JUN EK, ZHANG Q, YOON BS, et al. Hypoxic conditioned medium from human amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates skin wound healing through TGF-β/SMAD2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(1):605-628. [32] 侯萍,宋志国,李晓丰,等.低氧对间充质干细胞生物学特性影响及相关机制研究进展[J].解剖科学进展,2021,27(5):628-630. [33] 刘林奇.低氧预处理的人脂肪来源干细胞促进血管生成的体外实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013. [34] LIU J, REN J, SU L, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived stem cells inhibit the activity of keloid fibroblasts and fibrosis in a keloid model by paracrine signaling. Burns. 2018;44(2):370-385. [35] HEO DN, HOSPODIUK M, OZBOLAT IT. Synergistic interplay between human MSCs and HUVECs in 3D spheroids laden in collagen/fibrin hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2019;95(11): 348-356. [36] MOEN SH, WESTHRIN M, ZAHOOR M, et al. Caspase-8 regulates the expression of proand anti-inflammatory cytokines in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2017; 4(3):327-337. [37] JAFARINIA M, ALSAHEBFOSOUL F, SALEHI H, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Cell-Free Therapy. Immunol Invest. 2020;49(7):758-780. [38] 侯婧瑛,于萌蕾,郭天柱,等.缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/ VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):985-990. |
| [1] | He Yinhao, Li Xiaosheng, Chen Hongwen, Chen Tiezhu. 3D printed porous tantalum metal in the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: current status and application prospect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1455-1461. |
| [2] | Li Qicheng, Deng Jin, Fu Xiaoyang, Han Na. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes on hypoxia-treated myoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(6): 853-859. |
| [3] | Liu Yuan. Effect of hypoxic training on the oxygen sensing pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 793-798. |
| [4] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [5] | Sun Ruihua, Du Yu, Bao Qiaoling, Liu Tao. Effect of heat shock protein on neurological function and heme oxygenase-1 protein expression in a rat model of cerebral ischemia and hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(14): 2146-2151. |
| [6] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [7] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [8] | Xu Yixin, Wang Yixin, Li Yongming. Autophagy level of the mandible in nasal obstruction rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(35): 5633-5638. |
| [9] | Li Hongyuan, Yang Liu, Jin Xianhui. Relationship between hypoxia-inducible factors and bone homeostasis disorders [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(33): 5393-5399. |
| [10] | Mo Yunfang, Wang Zejian, Qi Nianmin, Chen Yantian. Biological characteristics of umbilical cord and menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells under physiological hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4819-4825. |
| [11] | Zhao Lin, Fan Chenxing, Li Kun. Mechanism underlying tanshinone IIA effect on survival and homing ability of myocardial precursor cells under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(30): 4852-4856. |
| [12] | Lu Qigui, Xie Pingjin, Luo Zhen, Li Feilong, Chen Qunqun, Chai Shengting. MicroRNA-20b-5p effects on cartilage and subchondral bone angiogenesis in early-stage osteoarthritis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(29): 4658-4665. |
| [13] | Tan Xu, Liang Yu, Liang Yan, Liao Jian. Hypoxia-treated dental pulp stem cell exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3961-3967. |
| [14] | Wang Yuying, Yu Limei. Key problems of preparation and quality control of human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells pharmaceutics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 4016-4021. |
| [15] | Yu Xiaofan, Jiang Huijiao, Tan Xiaowu, Wu Xiangwei. Expression of vasohibin-1 and other factors after the co-culture of two kinds of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex and endothelial progenitor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(24): 3892-3896. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||