Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 3961-3967.doi: 10.12307/2022.399
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypoxia-treated dental pulp stem cell exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization
Tan Xu1, Liang Yu2, Liang Yan1, Liao Jian1
- 1Medical School of Stomatology/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang 550002, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2019-12-24Accepted:2020-03-03Online:2022-09-08Published:2022-01-25 -
Contact:Liao Jian, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Medical School of Stomatology/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Tan Xu, MD, Associate chief physician, Medical School of Stomatology/Affiliated Stomatological Hospital, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant No. 82060207 (to LJ); Youth Science and Technology Talents Growth Project of Guizhou Education Department, Grant No. Qian Jiao He KY Zi[2018]195 (to TX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tan Xu, Liang Yu, Liang Yan, Liao Jian. Hypoxia-treated dental pulp stem cell exosomes induce M2 macrophage polarization[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(25): 3961-3967.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
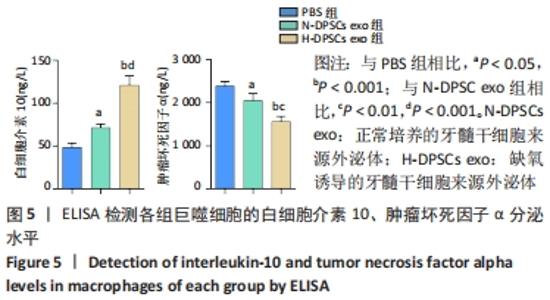
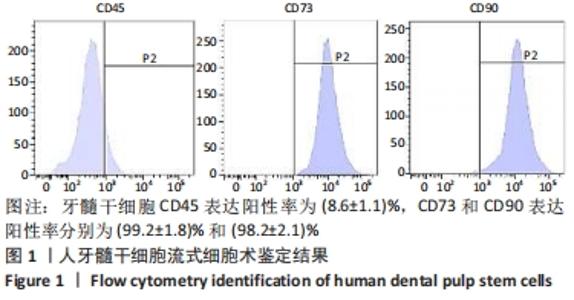
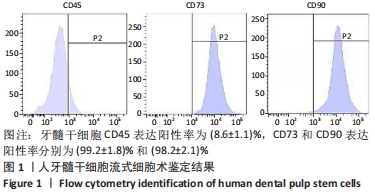
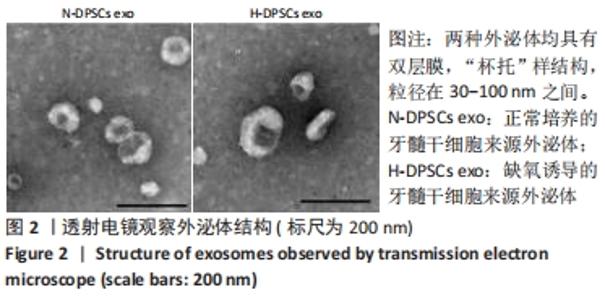
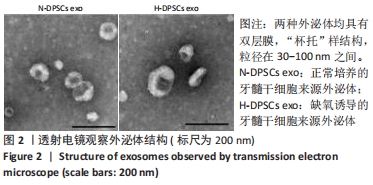
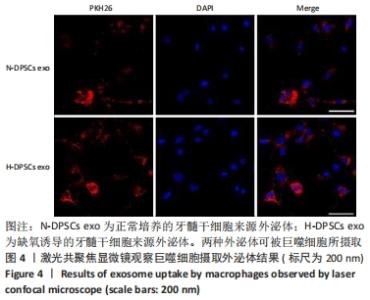
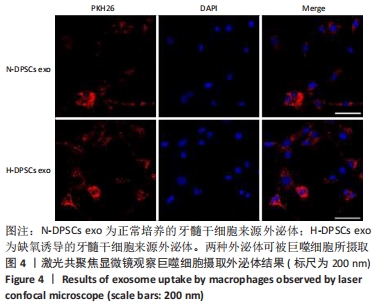
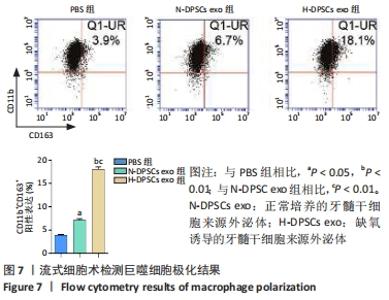
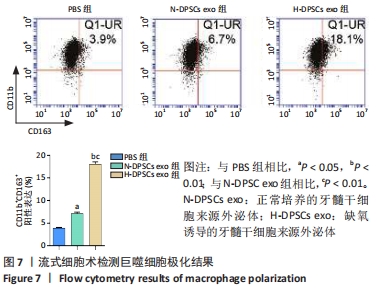
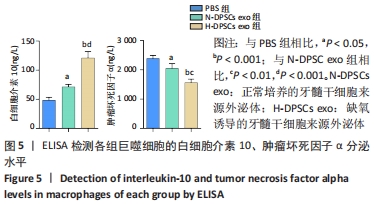
2.4 外泌体对巨噬细胞释放炎症因子的影响 相比于PBS组,N-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞培养上清液中的白细胞介素10水平显著增加(P < 0.05)、肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著降低(P < 0.05),H-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞培养上清液中的白细胞介素10水平亦显著增加(P < 0.001)、肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著降低(P < 0.01);H-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞培养上清液中的白细胞介素10水平显著高于N-DPSC exo组(P < 0.001),肿瘤坏死因子α水平显著低于N-DPSC exo组(P < 0.01);由于白细胞介素10是M2型巨噬细胞主要分泌的炎症因子,说明缺氧诱导的牙髓干细胞外泌体能够促进巨噬细胞向M2型转化,见图5。"
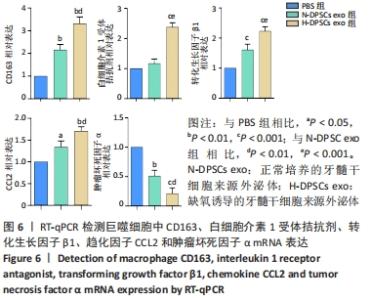
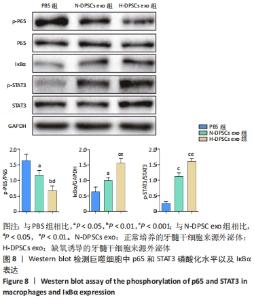
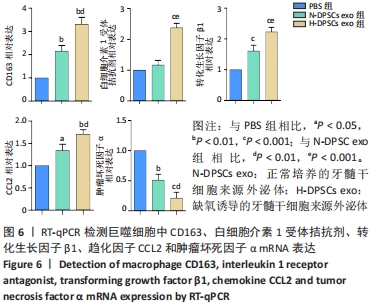
2.5 RT-qPCR检测CD163、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂、转化生长因子β1、趋化因子CCL2和肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达 与PBS组相比,N-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞CD163、转化生长因子β1和趋化因子CCL2 mRNA表达均显著上升(P < 0.05),白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂mRNA表达无显著变化(P > 0.05),肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达显著下降(P < 0.05);而H-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞CD163、转化生长因子β1、趋化因子CCL2和白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂mRNA表达均显著高于PBS组(P < 0.01),肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达显著低于PBS组;相比于N-DPSC exo组,H-DPSC exo组巨噬细胞CD163、转化生长因子β1、趋化因子CCL2和白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂mRNA表达均显著升高(P < 0.01),肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达显著下降(P < 0.01),见图6。由于CD163、白细胞介素1受体拮抗剂、转化生长因子β1、趋化因子CCL2均为M2型巨噬细胞的标志物,肿瘤坏死因子α为M1型巨噬细胞标志物,综上所述,H-DPSC exo能够显著促进巨噬细胞向M2型极化。"
| [1] MEAD B, LOGAN A, BERRY M, et al. Concise Review: Dental Pulp Stem Cells: A Novel Cell Therapy for Retinal and Central Nervous System Repair. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):61-67. [2] JI L, BAO L, GU Z, et al. Comparison of immunomodulatory properties of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and dental pulp stem cells. Immunol Res. 2019;67(4-5):432-442. [3] 曾宪海,萧苑,邓祖辉,等.人牙髓间充质干细胞外泌体对小鼠树突状细胞成熟和功能的抑制作用[J].中华微生物学和免疫学杂志, 2019,39(7):506-513. [4] LANCASTER GI, FEBBRAIO MA. Exosome-dependent trafficking of HSP70: a novel secretory pathway for cellular stress proteins. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(24):23349-23355. [5] LI J, JU Y, LIU S, et al. Exosomes derived from lipopolysaccharide-preconditioned human dental pulp stem cells regulate Schwann cell migration and differentiation. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(3):277-286. [6] PIVORAITĖ U, JARMALAVIČIŪTĖ A, TUNAITIS V, et al. Exosomes from Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Suppress Carrageenan-Induced Acute Inflammation in Mice. Inflammation. 2015;38(5):1933-1941. [7] JARMALAVIČIŪTĖ A, TUNAITIS V, PIVORAITĖ U, et al. Exosomes from dental pulp stem cells rescue human dopaminergic neurons from 6-hydroxy-dopamine-induced apoptosis. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(7):932-939. [8] BONAVENTURA G, INCONTRO S, IEMMOLO R, et al. Dental mesenchymal stem cells and neuro-regeneration: a focus on spinal cord injury. Cell Tissue Res. 2020;379(3):421-428. [9] MOHAN SP, RAMALINGAM M. Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Neuroregeneration. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020;12(Suppl 1):S60-S66. [10] ALTANER C, ALTANEROVA V, CIHOVA M, et al. Complete regression of glioblastoma by mesenchymal stem cells mediated prodrug gene therapy simulating clinical therapeutic scenario. Int J Cancer. 2014; 134(6):1458-1465. [11] 刘佳宁,王鑫雅,孙玥.巨噬细胞极化对炎症性疾病影响的研究进展[J].生物化工,2020,6(1):112-115. [12] BURAVKOVA LB, ANDREEVA ER, GOGVADZE V, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and hypoxia: where are we? Mitochondrion. 2014;19 Pt A:105-112. [13] 赵敏,冯柳祥,陈垚,等.低氧环境下外泌体可作为疾病的标志物[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):1104-1108. [14] 黄芳.缺氧预处理牙髓干细胞治疗根尖周炎骨缺损的研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2016. [15] WU Y, HUANG F, ZHOU X, et al. Hypoxic Preconditioning Enhances Dental Pulp Stem Cell Therapy for Infection-Caused Bone Destruction. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(19-20):1191-1203. [16] TSUTSUI TW. Dental Pulp Stem Cells: Advances to Applications. Stem Cells Cloning. 2020;13:33-42. [17] SUI B, WU D, XIANG L, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cells: From Discovery to Clinical Application. J Endod. 2020;46(9S):S46-S55. [18] CHEN W, ZHUO Y, DUAN D, et al. Effects of Hypoxia on Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(4):332-339. [19] LIU J, HAO H, XIA L, et al. Hypoxia pretreatment of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells facilitates angiogenesis by improving the function of endothelial cells in diabetic rats with lower ischemia. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0126715. [20] VANACKER J, VISWANATH A, DE BERDT P, et al. Hypoxia modulates the differentiation potential of stem cells of the apical papilla. J Endod. 2014;40(9):1410-1418. [21] CHUNG IM, RAJAKUMAR G, VENKIDASAMY B, et al. Exosomes: Current use and future applications. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;500:226-232. [22] CHEN BY, SUNG CW, CHEN C, et al. Advances in exosomes technology. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;493:14-19. [23] CONSOLE L, SCALISE M, INDIVERI C. Exosomes in inflammation and role as biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta. 2019;488:165-171. [24] PULLAN JE, CONFELD MI, OSBORN JK, et al. Exosomes as Drug Carriers for Cancer Therapy. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(5):1789-1798. [25] 何泓志,麻丹丹.牙髓干细胞外泌体的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治, 2019,27(10):652-657. [26] HUANG CC, NARAYANAN R, ALAPATI S, et al. Exosomes as biomimetic tools for stem cell differentiation: Applications in dental pulp tissue regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;111:103-115. [27] 苏晓磊,张庆林,靳继德,等.牙髓干细胞来源的外泌体对急性肺损伤的作用及机制研究[J].军事医学,2018,42(2):130-137. [28] ALTANEROVA U, BENEJOVA K, ALTANEROVA V, et al. Dental pulp mesenchymal stem/stromal cells labeled with iron sucrose release exosomes and cells applied intra-nasally migrate to intracerebral glioblastoma. Neoplasma. 2016;63(6):925-933. [29] ATRI C, GUERFALI FZ, LAOUINI D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(6):1801. [30] LIU J, CHEN B, BAO J, et al. Macrophage polarization in periodontal ligament stem cells enhanced periodontal regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):320. [31] WANG LX, ZHANG SX, WU HJ, et al. M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(2):345-358. [32] PARISI L, GINI E, BACI D, et al. Macrophage Polarization in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Killers or Builders? J Immunol Res. 2018; 2018:8917804. [33] MURRAY PJ. Macrophage Polarization. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:541-566. [34] DINASARAPU AR, GUPTA S, RAM MAURYA M, et al. A combined omics study on activated macrophages--enhanced role of STATs in apoptosis, immunity and lipid metabolism. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(21):2735-2743. [35] POLAK KL, CHERNOSKY NM, SMIGIEL JM, et al. Balancing STAT Activity as a Therapeutic Strategy. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(11):1716. [36] QUERO L, TIADEN AN, HANSER E, et al. miR-221-3p Drives the Shift of M2-Macrophages to a Pro-Inflammatory Function by Suppressing JAK3/STAT3 Activation. Front Immunol. 2020;10:3087. [37] HUANG FM, CHANG YC, LEE SS, et al. Expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators induced by Bisphenol A via ERK-NFκB and JAK1/2-STAT3 pathways in macrophages. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(4): 486-494. [38] 柳笑彦,刘力.代谢及炎症反应相关的巨噬细胞极化调控的研究进展[J].转化医学电子杂志,2018,5(10):92-96. [39] QIN C, FAN WH, LIU Q, et al. Fingolimod Protects Against Ischemic White Matter Damage by Modulating Microglia Toward M2 Polarization via STAT3 Pathway. Stroke. 2017;48(12):3336-3346. [40] WANG N, GAO J, JIA M, et al. Exendin-4 Induces Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Migration Through Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages Polarization via PKA-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1696-1714. [41] YUAN F, FU X, SHI H, et al. Induction of murine macrophage M2 polarization by cigarette smoke extract via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e107063. [42] SUI A, CHEN X, DEMETRIADES AM, et al. Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Activation Reduces Retinal Neovascularization by Promoting a Polarization Shift in Macrophages. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020; 61(6):4. [43] DORRINGTON MG, FRASER IDC. NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages: Dynamics, Crosstalk, and Signal Integration. Front Immunol. 2019;10: 705. [44] ZHANG Y, LIU F, YUAN Y, et al. Inflammasome-Derived Exosomes Activate NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages. J Proteome Res. 2017;16(1): 170-178. |
| [1] | Wang Baojuan, Zheng Shuguang, Zhang Qi, Li Tianyang. Miao medicine fumigation can delay extracellular matrix destruction in a rabbit model of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1180-1186. |
| [2] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [3] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [5] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [6] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [7] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [8] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [9] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [10] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [11] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [12] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| [13] | Hui Xiaoshan, Bai Jing, Zhou Siyuan, Wang Jie, Zhang Jinsheng, He Qingyong, Meng Peipei. Theoretical mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine theory on stem cell induced differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1125-1129. |
| [14] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [15] | Fan Yiming, Liu Fangyu, Zhang Hongyu, Li Shuai, Wang Yansong. Serial questions about endogenous neural stem cell response in the ependymal zone after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||