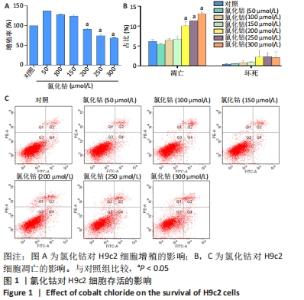
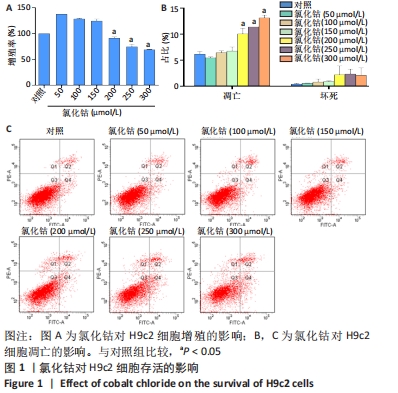
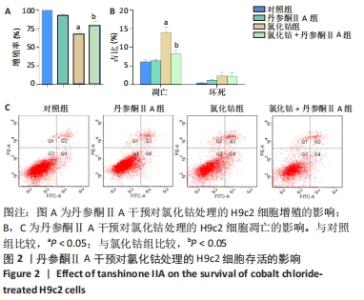
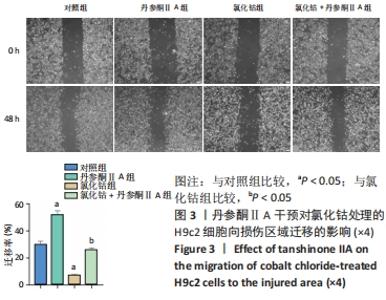
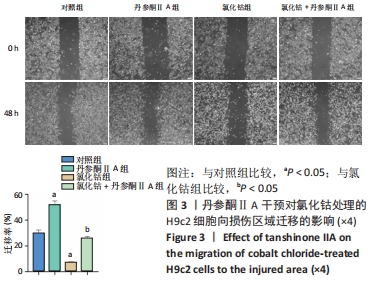
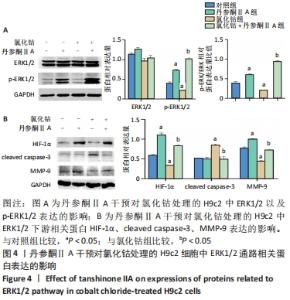
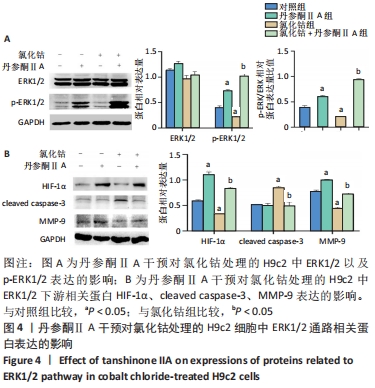
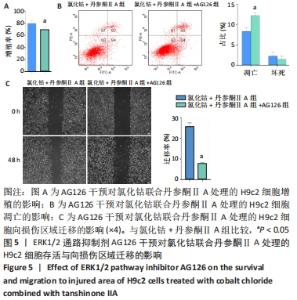
[1] YU H, LU K, ZHU J, et al. Stem cell therapy for ischemic heart diseases. Br Med Bull. 2017;121(1):135-154.
[2] KADOTA S, SHIBA Y. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocyte Transplantation for Heart Disease Treatment. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019;21(8):73.
[3] WU KH, MO XM, HAN ZC, et al. Stem cell engraftment and survival in the ischemic heart. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;92(5):1917-1925.
[4] NAGY RD, TSAI BM, WANG M, et al. Stem cell transplantation as a therapeutic approach to organ failure. J Surg Res. 2005;129(1):152-160.
[5] GULBINS H, MEISER BM, REICHENSPURNER H, et al. Cell transplantation--a potential therapy for cardiac repair in the future? Heart Surg Forum. 2002;5(4):E28-34.
[6] HASHIMOTO H, OLSON EN, BASSEL-DUBY R. Therapeutic approaches for cardiac regeneration and repair. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2018;15(10):585-600.
[7] JOHNSON TA, SINGLA DK. Therapeutic Application of Adult Stem Cells in the Heart. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1553:249-264.
[8] KATARZYNA R. Adult Stem Cell Therapy for Cardiac Repair in Patients After Acute Myocardial Infarction Leading to Ischemic Heart Failure: An Overview of Evidence from the Recent Clinical Trials. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2017;13(3):223-231.
[9] 向群,陆士娟.干细胞移植在心血管疾病应用中急待解决的问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(36):6800-6804.
[10] 鲍晓明,程晓曙.干细胞移植治疗急性心肌梗死的临床研究新进展[J].心血管病学进展,2009,30(6):1053-1055.
[11] LI ZM, XU SW, LIU PQ. Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(5):802-824.
[12] FANG J, LITTLE PJ, XU S. Atheroprotective Effects and Molecular Targets of Tanshinones Derived From Herbal Medicine Danshen. Med Res Rev. 2018;38(1):201-228.
[13] 樊晨星,王秀艳,赵千,等.丹参酮ⅡA诱导人胎盘间充质干细胞向心肌细胞分化、提高预分化细胞归巢能力的研究[J].中国医科大学学报,2020,49(4):294-300.
[14] LI K, LI SZ, ZHANG YL, et al. The effects of dan-shen root on cardiomyogenic differentiation of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;415(1):147-151.
[15] LI K, SONG J, ZHAO Q, et al. Effective component of Salvia miltiorrhiza in promoting cardiomyogenic differentiation of human placenta‑derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):962-968.
[16] LI K, WANG X, FAN C, et al. Tanshinone IIA promotes cardiac differentiation and improves cell motility by modulating the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(3):1839-1846.
[17] 黄爱梅.丹参酮ⅡA的药理作用机制及不良反应研究进展[J].临床合理用药杂志,2021,14(25):179-181.
[18] WU DM, WANG YJ, HAN XR, et al. Tanshinone IIA prevents left ventricular remodelling via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signalling pathway in rats with myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(6):3058-3072.
[19] SHANG Q, XU H, HUANG L. Tanshinone IIA: A Promising Natural Cardioprotective Agent. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:716459.
[20] LU N, MALEMUD CJ. Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase: A Regulator of Cell Growth, Inflammation, Chondrocyte and Bone Cell Receptor-Mediated Gene Expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3792.
[21] LIU QH, SHI ML, SUN C, et al. Role of the ERK1/2 pathway in tumor chemoresistance and tumor therapy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015;25(2):192-197.
[22] CHENG P, ALBERTS I, LI X. The role of ERK1/2 in the regulation of proliferation and differentiation of astrocytes in developing brain. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013;31(8):783-789.
[23] WEI L, ZHOU Q, TIAN H, et al. Integrin β3 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis via regulating the PTEN/Akt/mTOR and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Biol Sci. 2020;16(4):644-654.
[24] 秦霞,蒋莉,张咏梅,等.甘氨酸改善缺氧性MDCK细胞损伤的作用依赖于ERK1/2、Akt及p38MAPK信号通路[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2012, 32(10):1337-1342.
[25] YONG J, VON BREMEN J, GROEGER S, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha acts as a bridge factor for crosstalk between ERK1/2 and caspases in hypoxia-induced apoptosis of cementoblasts. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(20):9710-9723.
[26] 赵雅宁,高俊玲.ERK1/2信号通路与脑创伤后神经细胞凋亡的研究新进展[J].河北医科大学学报,2008,29(6):953-955.
[27] 李亚洲,周燕园,白红妍,等.青天葵甲醇提取物通过ERK信号通路诱导鼻咽癌CNE-2细胞凋亡[J].中国现代应用药学,2021,38(16):1928-1933.
[28] HE Y, GUO Y, XIA Y, et al. Resistin promotes cardiac homing of mesenchymal stem cells and functional recovery after myocardial ischemia-reperfusion via the ERK1/2-MMP-9 pathway. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019;316(1):H233-H244.
|