Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (19): 3048-3055.doi: 10.12307/2022.385
Previous Articles Next Articles
Implications of preclinical research on mesenchymal stem cells: relationship between cell function of mesenchymal stem cells and the JAK/STAT signaling pathway
Zou Wanghui1, Qian Nannan1, Zhang Meng1, Pang Qiming2, Yang Yichun3, Zhang Tao1
- 1Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, 2Department of Spine Surgery, 3Department of Dermatology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-06-22Revised:2021-07-23Accepted:2021-08-12Online:2022-07-08Published:2021-12-29 -
Contact:Zhang Tao, PhD, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zou Wanghui, Master candidate, Key Laboratory of Cell Engineering of Guizhou Province, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81960299 (to ZT); Zunyi City Science and Technology Plan Project, No. HZ[2019]90 (to ZT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zou Wanghui, Qian Nannan, Zhang Meng, Pang Qiming, Yang Yichun, Zhang Tao. Implications of preclinical research on mesenchymal stem cells: relationship between cell function of mesenchymal stem cells and the JAK/STAT signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(19): 3048-3055.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
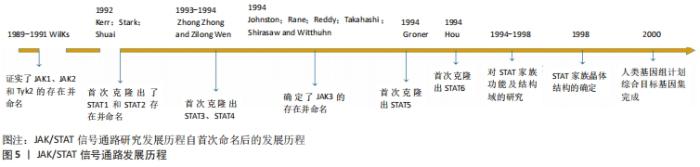
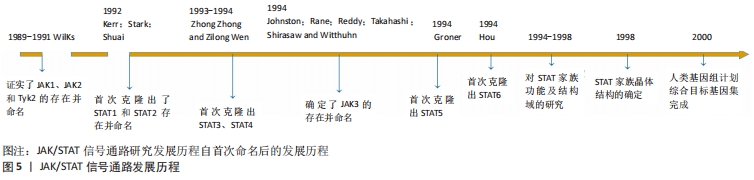
近年来的研究表明,间充质干细胞对体内的免疫细胞具有调节作用,可纠正免疫失衡并促进组织修复作用[2-3]。同时,靶细胞所释放的趋化因子等物质也可帮助间充质干细胞归巢,为间充质干细胞定植存活提供便利[4-5]。然而,在迁移或分化过程中的各类间充质干细胞难免会受到免疫微环境影响,产生未知的细胞生物功能变化,甚至会对机体产生危害[6]。因此,明晰间充质干细胞的生物学特性机制并维持其稳定性,是保证间充质干细胞临床应用安全性的关键所在。 2.2 JAK/STAT信号通路 Janus激酶(Janus Kinase,JAK)属于非受体型酪氨酸蛋白激酶,其家族包含4个成员,分别是Janus激酶1、Janus激酶2、Janus激酶3和酪氨酸激酶2。细胞因子激活受体后,该受体胞内结构域打开,JAK随即与其结合并通过磷酸化成为p-JAK,募集胞内STAT转录因子。随后,募集到的STAT转录因子磷酸化后相互联合成为聚合体,识别并结合到DNA链的目的基因区域,从而调控靶细胞的基因表达。上述信号通路被称为JAK/STAT信号通路,见图5。"
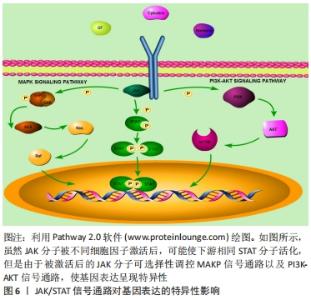
JAK/STAT信号通路是许多细胞因子共用的通路,该通路能接受不同细胞胞外因子产生特异细胞生物学效应[7-11]。在从属于JAK/STAT信号通路内的各种分子中,STAT是最值得关注的重要分子之一[12]。STAT分子之间可互相结合成为同二聚体、异二聚体甚至四聚体结构,进入细胞核内或线粒体内与DNA结合,调控细胞目的蛋白的转录表达[7,13-15]。另外,JAK/STAT信号通路产生作用后能负反馈调节细胞信号通路分子活化,以维持细胞内环境稳态,如细胞因子传导通路抑制因子(suppressors of cytokine signaling,SOCS)是JAK/STAT信号通路被激活后所释放的物质,能抑制JAK分子磷酸化,从而产生负调节作用,是该信号通路调控细胞稳定状态的重要因子之一[16]。 JAK/STAT信号通路对基因表达的影响存在特异性和广泛性的双重表现[7,12]。在特异性方面,不同细胞因子可激活相同的STAT分子,如白细胞介素6、白细胞介素27及白细胞介素10可激活STAT3,但对细胞功能的影响并不完全相同,如白细胞介素10具有抑制疼痛的作用,通过激活STAT3促进神经修复,白细胞介素6则抑制神经修复,通过激活STAT3引起痛觉过敏[17-19]。这是由于信号通路机制各异,JAK受不同细胞因子刺激活化后,导致其他细胞信号通路被激活,影响细胞核内不同基因的转录翻译,从而产生特异性细胞功能变化,见图6。"
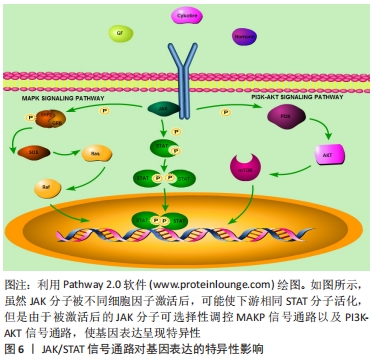
在广泛性表现方面,STAT在脱氧核糖核酸链可有多个结合位点,通过结合启动子区域或者增强子区域对基因的表达产生广泛影响,如白细胞介素4可激活T细胞的STAT6分子,接着STAT6结合到T细胞胞核的增强子基因区域,促进T细胞改变自身多种表型,向辅助型T细胞2分化[20-22]。 2.3 间充质干细胞与JAK/STAT信号通路的关系 间充质干细胞先后被称为骨髓基质细胞、骨髓基质干细胞和间充质干细胞等,研究发现其可分泌多种细胞因子影响靶细胞或组织,发挥针对损伤组织的再生修复和免疫调节功能[23-26]。间充质干细胞在体外适宜培养环境下可分化出能供移植需要数量级的特定类型细胞,如人骨髓间充质干细胞(human bone marrow derived-mesenchymal stem cells,hBM-MSCs)可在体外分化为骨、软骨、脂肪和肌肉细胞[27-28]。然而,大量的研究表明,移植间充质干细胞的体内定植率低且存活时间短,提示了间充质干细胞可能通过其他机制发挥作用。因此,目前研究的关注点已转向间充质干细胞的外分泌及其免疫调节作用这些可能更为重要的作用上来[2]。 JAK/STAT信号通路对间充质干细胞及其靶细胞的调控方式,主要体现在以下2个方面:①JAK/STAT信号通路可调控靶细胞的生物学特性,例如,大鼠外周血间充质干细胞(rat peripheral blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells,rPB-MSCs)可激活巨噬细胞的JAK/STAT3信号通路,使促炎性巨噬细胞数量减少以及抑炎性巨噬细胞数量增多[29]。②JAK/STAT信号通路可调控间充质干细胞的生物学特性,例如,干扰素γ激活人骨髓间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路,使人骨髓间充质干细胞表面表达FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体(FLT3L),该表面分子FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体可有效抑制树突状细胞成熟,减弱树突状细胞的抗原呈递能力,从而产生免疫调节作用[30]。因此,探讨间充质干细胞生物学特性与JAK/STAT信号通路的关系,可从2个方面进行讨论:一是间充质干细胞对靶细胞JAK/STAT信号通路的影响;二是间充质干细胞自身的JAK/STAT信号通路对间充质干细胞生物学特性的影响。 2.4 间充质干细胞对靶细胞JAK/STAT通路的影响 间充质干细胞可通过外分泌激活靶细胞内信号通路改善病变微环境。研究证实间充质干细胞所分泌的细胞因子可通过JAK/STAT信号通路对靶细胞产生调节作用。 紫杉醇在用于化疗过程中会引起部分患者的周围神经疼痛,导致紫衫醇治疗不得不中断。紫杉醇引起周围神经疼痛的机制,是紫杉醇促进了神经细胞中的白细胞介素6释放,接着白细胞介素6激活神经细胞中JAK2/STAT3信号通路,传导过量递质导致神经痛觉敏感度增加。将大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞经尾静脉注射移植至紫杉醇诱发的周围神经疼痛大鼠模型体内,可使大鼠坐骨神经元磷酸化的JAK 2蛋白表达量及磷酸化的STAT3蛋白表达量下降,有效减轻紫杉醇引起的大鼠模型的疼痛感觉过敏[31]。 缺血再灌损伤表现为缺血组织恢复供血后,白细胞迅速增多并释放大量炎症因子,如促炎因子高迁移率族蛋白1在再灌注损伤机制中充当重要的角色,贯穿缺血再灌注损伤炎症发展的各个时期,介导局部组织或细胞损伤效应[32]。在肾缺血再灌注损伤中,肾小管上皮细胞高迁移率族蛋白1表达量与JAK/STAT信号通路活化状态相关,当JAK/STAT信号通路失活将导致高迁移率族蛋白1表达量下降。而大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞 条件培养基与缺血再灌注损伤的肾小管上皮细胞体外细胞模型共培养后,肾小管上皮细胞内JAK3,STAT1,STAT2,STAT3蛋白表达量均下降,使高迁移率族蛋白1的蛋白表达量下降,提示间充质干细胞可减轻肾缺血再灌注损伤炎症反应所导致的局部组织或细胞损伤[33]。 放射性肠损伤是由于电离辐射损伤肠上皮组织所导致的,常见于需要进行放化疗的肿瘤患者。正常情况下,肠上皮组织中JAK/STAT信号通路分子处于非活化状态,当受到电离辐射损伤后JAK/STAT信号通路分子被激活,导致肠损伤相关基因活化造成肠黏膜上皮细胞凋亡增多。在大鼠放射性肠损伤模型中,经尾静脉注射大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞后明显下调肠上皮细胞内JAK/STAT信号通路分子表达量,促进小肠上皮细胞增殖及绒毛结构恢复,肠黏膜坏死症状明显减轻,各项病理变化明显恢复[34]。 上述研究均说明了间充质干细胞治疗疾病能力与靶细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路变化相关。间充质干细胞通过调节靶细胞JAK/STAT通路纠正失调的微环境,以达到治疗或辅助治疗疾病的效果。 2.5 间充质干细胞自身的JAK/STAT信号通路变化 "
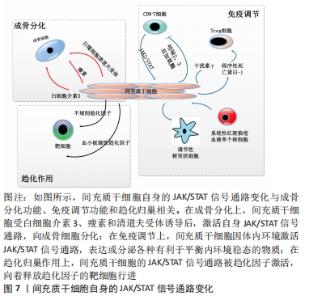
2.5.1 JAK/STAT通路与间充质干细胞组织分化的关系 间充质干细胞组织分化与JAK/STAT信号通路的关系,主要体现在间充质干细胞的成骨分化功能上。全转录组芯片信号通路网分析显示,间充质干细胞的成骨分化潜能与JAK/STAT通路相关[35]。目前间充质干细胞成骨分化与JAK/STAT信号通路的相关研究,多数是与骨形态发生蛋白有关。骨形态发生是一系列有助于骨质生长的物质,可促进间充质干细胞的成骨分化[36]。 从细胞因子对间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路影响举例说明:瘦素是一种能调节骨量和矿物质密度的细胞因子,在体外培养环境中可激活小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路,使骨形态发生蛋白9的表达白量增高促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[37];巨噬细胞清道夫受体1 (macrophage scavenger receptor 1,MSR1)是存在于巨噬细胞表面的一种受体,参与对病原体的识别和清除。有研究发现,巨噬细胞清道夫受体在体内体外环境下均可通过直接接触小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,激活JAK/STAT信号通路使小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞释放骨形态发生蛋白2,促进小鼠间充质干细胞的成骨分化[38];白细胞介素3可促进细胞增殖与分化,通过激活JAK/STAT通路增强人骨髓间充质干细胞的骨形态发生蛋白2分泌,促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[39]。 总的来说,间充质干细胞的成骨分化方式与JAK/STAT信号通路的关系,主要体现在细胞因子或细胞表面受体激活间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路,促进间充质干细胞释放骨形态发生蛋白,骨形态发生蛋白继而促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,见图7。"
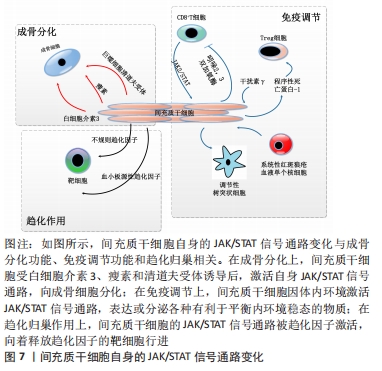
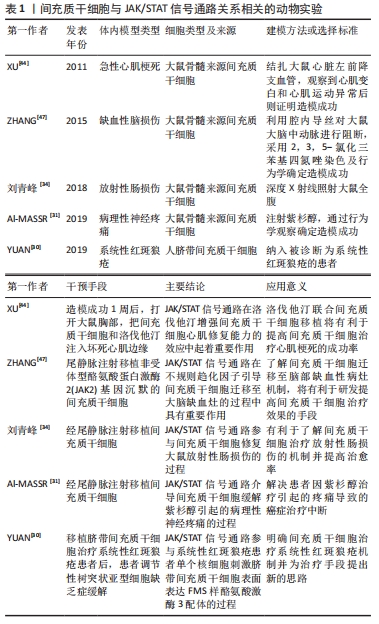
2.5.2 JAK/STAT通路与间充质干细胞免疫调节的关系 间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用是近年来研究的热点,目前大部分研究关注点着落在间充质干细胞调控各种免疫细胞信号通路,然而针对间充质干细胞自身的细胞信号通路机制研究较少。其中间充质干细胞自身JAK/STAT通路与免疫调节的关系,在干扰素γ对间充质干细胞的调节中可见一斑。 在系统性红斑狼疮患者体内,FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体(FLT3L)与外周耐受性树突状细胞血清水平均低于正常人。外周耐受性树突状细胞相对于成熟的树突状细胞而言,抗原呈递能力较弱,具有免疫抑制的作用。细胞表面的FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体和外周耐受性树突状细胞表面受体结合后,能促进外周耐受性树突状细胞增殖。干扰素γ预处理人脐带间充质干细胞后,STAT1、STAT3和STAT5分子水平升高,诱导人脐带间充质干细胞表面的FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体表达增多。FMS样酪氨酸激酶3配体通过直接接触促进外周耐受性树突状细胞增殖,从而有效抑制系统性红斑狼疮带来的严重免疫反应[30]。类似地,细胞表面程序性死亡配体2能促进调节性T细胞增殖。调节性T细胞作为一种具有免疫抑制功能的T细胞,已经被应用多种自身免疫疾病的治疗。在体外培养实验中,干扰素γ激活人胎盘间充质干细胞的STAT1和STAT3分子,促进人胎盘间充质干细胞表达程序性死亡配体2,从而促进调节性T细胞[40]。 系统性红斑狼疮患者体内的细胞毒性T细胞增多,会引发相关的自身免疫性疾病。而吲哚胺2,3-二加氧酶则可抑制狼疮患者的细胞毒性T细胞增殖,减轻细胞毒性T细胞对患者自身组织细胞损伤程度。干扰素γ在体外共培养系统中激活人脐带间充质干细胞的JAK2/STAT信号通路,可提高人脐带间充质干细胞中吲哚胺2,3-二加氧酶表达,选择性抑制细胞毒性T细胞增殖[41]。目前治疗系统性红斑狼疮药物如甲氨蝶呤以及糖皮质激素等对机体免疫环境带来较大的危害,而间充质干细胞治疗可选择性地抑制T细胞,是一种极具应用前景的替代疗法[42]。 综上,JAK/STAT信号通路引导间充质干细胞进行免疫调节,其主要方式是在干扰素γ影响下,间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路被激活,表达相应表面分子或细胞因子,对免疫细胞进行调控,因此产生免疫调节的作用。 2.5.3 JAK/STAT信号通路与间充质干细胞适应微环境能力的关系 不同的干预因素可提高间充质干细胞适应微环境的能力,使间充质干细胞在微环境中稳定存活并发挥作用。在长期不更换新鲜培养基和低氧环境下,仍然存活的人骨髓间充质干细胞将具有更好的增殖活力,经检测细胞中STAT6蛋白表达量升高,表明JAK/STAT信号通路可调控间充质干细胞适应长期缺营养环境的能力[43]。另外,某些药物也可通过JAK/STAT信号通路引导间充质干细胞更好地适应微环境,如洛伐他汀可通过激活大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的JAK2/STAT3信号通路,促使大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞迁移至心脏定植并拥有更高的存活率[44]。由于研究焦点的转移,目前关于JAK/STAT信号通路与间充质干细胞在微环境存活能力研究较少,JAK/STAT通路调控间充质干细胞适应微环境能力的机制仍不太明确,需要更多的实验讨论进行验证。 2.5.4 JAK/STAT通路与间充质干细胞归巢迁移的关系 间充质干细胞的归巢是指移植局部迁移定植至靶组织的过程。JAK/STAT信号通路在间充质干细胞归巢中也具有相应调节作用。血小板源性生长因子是间充质干细胞有效的趋化因子之一,激活人骨髓间充质干细胞表面受体,通过JAK/STAT信号通路引导人骨髓间充质干细胞向血管壁顺趋化因子浓度游动,为人骨髓间充质干细胞穿血管壁到达目的地打下良好的基础[45-46]。不规则趋化因子是一种可诱导单核细胞定向迁移的趋化因子,可激活大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的JAK2/STAT5通路,使大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞发生趋化性迁移[47]。可见间充质干细胞的归巢与JAK/STAT信号通路相关,趋化因子通过间充质干细胞的JAK/STAT信号通路,引导间充质干细胞归巢。 间充质干细胞亦可向肿瘤进行靶向迁移,定植后可促进肿瘤细胞血管生成,从而导致肿瘤加速生长。而托法替尼作为一种JAK/STAT信号通路抑制剂,可抑制JAK/STAT3信号通路,有效降低间充质干细胞向肿瘤迁移的风险[48]。由此可见,通过JAK/STAT信号通路对间充质干细胞归巢影响的机制,可了解间充质干细胞临床应用中致瘤特性的机制,开发降低间充质干细胞致瘤风险临床应用手段。 间充质干细胞及其靶细胞中均拥有JAK/STAT信号通路,该信号通路调控着二者生物学特性的变化,见表1,2。"
| [1] FRIEDENSTEIN AJ, CHAILAKHJAN RK, LALYKINA KS. The development of fibroblast colonies in monolayer cultures of guinea-pig bone marrow and spleen cells. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1970;3(4):393-403. [2] WANG Y, CHEN XD, CAO W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016. [3] PROCKOP DJ, OH JY. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs): role as guardians of inflammation. Mol Ther. 2012;20(1):14-20. [4] NAJI A, EITOKU M, FAVIER B, et al. Biological functions of mesenchymal stem cells and clinical implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(17):3323-3348. [5] ZACHAR L, BAČENKOVÁ D, ROSOCHA J. Activation, homing, and role of the mesenchymal stem cells in the inflammatory environment. J Inflamm Res. 2016;15(9):231-240. [6] VEZZANI B, PIERANTOZZI E, SORRENTINO V. Mesenchymal stem cells: from the perivascular environment to clinical applications. Histol Histopathol. 2018;33(12):1235-1246. [7] STARK GR, DARNELL JE JR. The JAK-STAT pathway at twenty. Immunity. 2012;36(4):503-514. [8] AHMAD SF, NADEEM A, ANSARI MA, et al. Upregulation of IL-9 and JAK-STAT signaling pathway in children with autism. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2017;79(pt B):472-480. [9] AMANO W, NAKAJIMA S, YAMAMOTO Y, et al. JAK inhibitor JTE-052 regulates contact hypersensitivity by downmodulating T cell activation and differentiation. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84(3):258-265. [10] BROWNING L, PATEL MR, HORVATH EB, et al. IL-6 and ovarian cancer: inflammatory cytokines in promotion of metastasis. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;5(10):6685-6693. [11] CAO C, ZHAO J, DOUGHTY EK, et al. Mac-1 Regulates IL-13 Activity in Macrophages by Directly Interacting with IL-13Rα1. J Biol Chem. 2015; 290(35):21642-21651. [12] VILLARINO AV, KANNO Y, FERDINAND JR, et al. Mechanisms of Jak/STAT signaling in immunity and disease. J Immunol. 2015;194(1):21-27. [13] BEGITT A, DROESCHER M, MEYER T, et al. STAT1-cooperative DNA binding distinguishes type 1 from type 2 interferon signaling. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(2):168-176. [14] WEI L, VAHEDI G, SUN HW, et al. Discrete roles of STAT4 and STAT6 transcription factors in tuning epigenetic modifications and transcription during T helper cell differentiation. Immunity. 2010;32(6):840-851. [15] MEIER JA, LARNER AC. Toward a new STATe: the role of STATs in mitochondrial function. Semin Immunol. 2014;26(1):20-28. [16] TAMIYA T, KASHIWAGI I, TAKAHASHI R, et al. Suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and JAK/STAT pathways: regulation of T-cell inflammation by SOCS1 and SOCS3. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31(5):980-985. [17] ZHU Y, LIU Z, PENG YP, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits neuroinflammation-mediated apoptosis of ventral mesencephalic neurons via JAK-STAT3 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;50:353-360. [18] MEKA RR, VENKATESHA SH, DUDICS S, et al. IL-27-induced modulation of autoimmunity and its therapeutic potential. Autoimmun Rev. 2015; 14(12):1131-1141. [19] UCIECHOWSKI P, DEMPKE WCM. Interleukin-6: a masterplayer in the cytokine network. Oncology. 2020;98(3):131-137. [20] XU X, SUN YL, HOEY T. Cooperative DNA binding and sequence-selective recognition conferred by the STAT amino-terminal domain. Science. 1996;273(5276):794-797. [21] KANNO Y, VAHEDI G, HIRAHARA K, et al. Transcriptional and epigenetic control of T helper cell specification: molecular mechanisms underlying commitment and plasticity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:707-731. [22] Vahedi G, Takahashi H, Nakayamada S, et al. STATs shape the active enhancer landscape of T cell populations. Cell. 2012;151(5):981-993. [23] KNOSPE WH, HINRICHS B, FRIED W, et al. Normal colony stimulating factor (CSF) production by bone marrow stromal cells and abnormal granulopoiesis with decreased CFUc in S1/S1d mice. Exp Hematol. 1976;4(3):125-130. [24] OWEN M. Marrow stromal stem cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1988;10: 63-76. [25] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641-650. [26] CAPLAN AI. What’s in a name? Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(8):2415-2417. [27] SARUGASER R, HANOUN L, KEATING A, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells self-renew and differentiate according to a deterministic hierarchy. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6498. [28] ZHANG B, LUO Q, HALIM A, et al. Directed Differentiation and Paracrine Mechanisms of Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Potential Implications for Tendon Repair and Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(6): 447-454. [29] 杨睿.外周血间充质干细胞通过STAT3介导的IL-10信号调控巨噬细胞极化的机制研究[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2020. [30] YUAN X, QIN X, WANG D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy induces FLT3L and CD1c(+) dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):2498. [31] AL-MASSRI KF, AHMED LA, EL-ABHAR HS. Mesenchymal stem cells therapy enhances the efficacy of pregabalin and prevents its motor impairment in paclitaxel-induced neuropathy in rats: Role of Notch1 receptor and JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Behav Brain Res. 2019;360: 303-311. [32] 杨利娇,王虹,王文丰,等.高迁移率族蛋白B1与缺血再灌注损伤的研究新进展[J].老年心脑血管病杂志,2017,19(7):772-774. [33] ZHANG L, WANG Y, MA J, et al. Exogenous MSCs ameliorate hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in renal tubular epithelial cells through JAK/STAT signaling pathway-mediated regulation of HMGB1. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2412-2420. [34] 刘青峰,王葳,王亿龙.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对放射性肠损伤大鼠的修复作用及对JAK/STAT通路的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2018, 18(2):163-166. [35] ZHANG W, DONG R, DIAO S, et al. Differential long noncoding RNA/mRNA expression profiling and functional network analysis during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):30. [36] CHENG YH, DONG JC, BIAN Q. Small molecules for mesenchymal stem cell fate determination. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11(12):1084-1103. [37] ZHANG B, YANG L, ZENG Z, et al. Leptin potentiates BMP9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through the activation of JAK/STAT signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(8):498-510. [38] 殷旻皓,刘浩,张永杰.巨噬细胞清道夫受体1通过JAK/STAT3信号通路调节骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2020,40(8):1105-1110. [39] BARHANPURKAR AP, GUPTA N, SRIVASTAVA RK, et al. IL-3 promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;418(4):669-675. [40] LI H, WANG W, WANG G, et al. Interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α promote the ability of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stromal cells to express programmed death ligand-2 and induce the differentiation of CD4(+) interleukin-10(+) and CD8(+) interleukin-10(+)Treg subsets. Cytotherapy. 2015;17(11):1560-1571. [41] WANG D, FENG X, LU L, et al. A CD8 T cell/indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase axis is required for mesenchymal stem cell suppression of human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(8):2234-2245. [42] CRISPÍN JC, KYTTARIS VC, TERHORST C, et al. T cells as therapeutic targets in SLE. Nature reviews. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010;6(6):317-325. [43] FERRO F, SPELAT R, SHAW G, et al. Survival/adaptation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after long-term starvation through selective processes. Stem cells. 2019;37(6):813-827. [44] XU H, YANG YJ, QIAN HY, et al. Rosuvastatin treatment activates JAK-STAT pathway and increases efficacy of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in infarcted hearts. Circ J. 2011;75(6):1476-1485. [45] PONTE AL, MARAIS E, GALLAY N, et al. The in vitro migration capacity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: comparison of chemokine and growth factor chemotactic activities. Stem Cells. 2007; 25(7):1737-1745. [46] POPIELARCZYK TL, HUCKLE WR, BARRETT JG. Human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells home via the PI3K-Akt, MAPK, and Jak/Stat signaling pathways in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(17):1191-1202. [47] ZHANG Y, ZHENG J, ZHOU Z, et al. Fractalkine promotes chemotaxis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells towards ischemic brain lesions through Jak2 signaling and cytoskeletal reorganization. FEBS J. 2015;282(5):891-903. [48] ZGHEIB A, PELLETIER-BONNIER M, LEVROS L-C, et al. Selective JAK/STAT3 signalling regulates transcription of colony stimulating factor-2 and -3 in Concanavalin-A-activated mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytokine. 2013;63(2):187-193. |
| [1] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhou Qian, Zhang Qiang, Chen Qiu. Human salivary components and osteoporosis/osteopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1439-1444. |
| [2] | Jin Tao, Liu Lin, Zhu Xiaoyan, Shi Yucong, Niu Jianxiong, Zhang Tongtong, Wu Shujin, Yang Qingshan. Osteoarthritis and mitochondrial abnormalities [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1452-1458. |
| [3] | Zhang Lichuang, Xu Hao, Ma Yinghui, Xiong Mengting, Han Haihui, Bao Jiamin, Zhai Weitao, Liang Qianqian. Mechanism and prospects of regulating lymphatic reflux function in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1459-1466. |
| [4] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [5] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [6] | Zhu Chan, Han Xuke, Yao Chengjiao, Zhang Qiang, Liu Jing, Shao Ming. Acupuncture for Parkinson’s disease: an insight into the action mechanism in animal experiments [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [8] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [9] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [10] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [11] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [12] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [14] | Wu Weiyue, Guo Xiaodong, Bao Chongyun. Application of engineered exosomes in bone repair and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1102-1106. |
| [15] | Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||