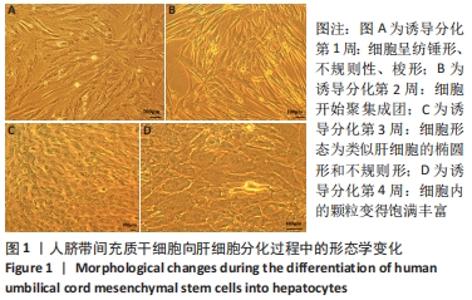
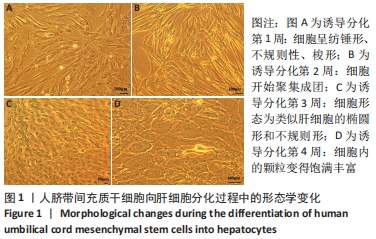
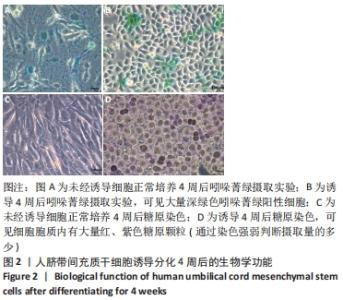
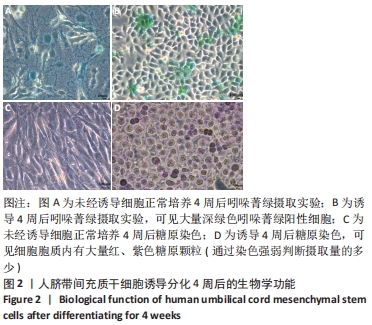
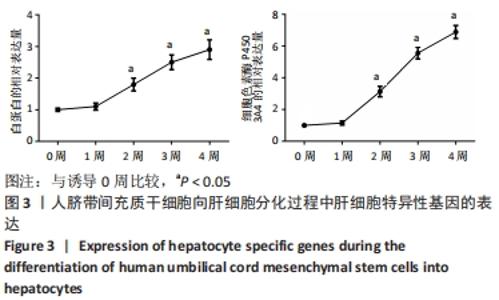
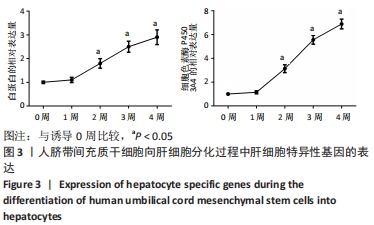
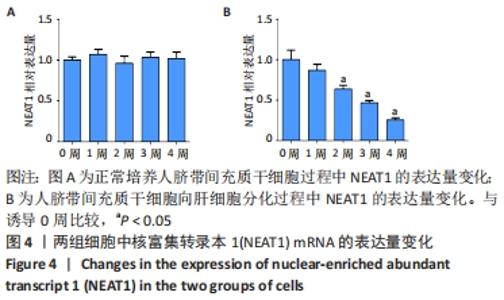
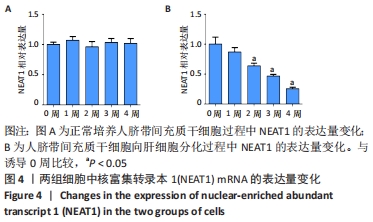
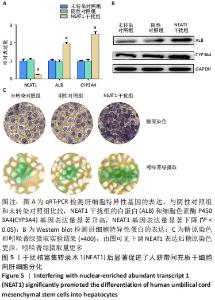
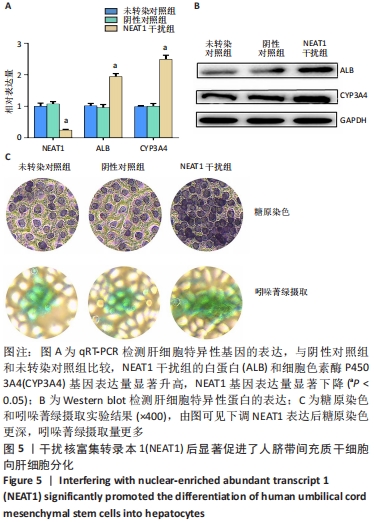
[1] TUSHER VG, TIBSHIRANI R, CHU G. Significance analysis of microarrays applied to the ionizing radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(9):5116-5121.
[2] DHAWAN A, PUPPI J, HUGHES RD, et al. Human hepatocyte transplantation: current experience and future challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7(5):288-298.
[3] ZHOU WL, MEDINE CN, ZHU L, et al. Stem cell differentiation and human liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(17):2018-2025.
[4] HONG HS, KIM YH, SON Y. Perspectives on mesenchymal stem cells: tissue repair, immune modulation, and tumor homing. Arch Pharm Res. 2012;35(2):201-211.
[5] ZHONG YS, LIN N, DENG MH, et al. Deficient proliferation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infections and cirrhosis of the liver. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55(2):438-445.
[6] MU N, LIU HB, MENG QH, et al. The differentiation of human multipotent adult progenitor cells into hepatocyte-like cells induced by coculture with human hepatocyte line L02. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 88(1):1-7.
[7] ZHANG G, LAN Y, XIE A, et al. Comprehensive analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-chromatin interactions reveals lncRNA functions dependent on binding diverse regulatory elements. J Biol Chem. 2019; 294(43):15613-15622.
[8] 张瑞欣, 董语迪, 肖建辉.lncRNA调控间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化的研究进展[J].天津医药,2021,49(6):662-667.
[9] 李梦,周云,禹亚彬,等.长链非编码RNA肝癌高表达转录本促进人骨髓间充质干细胞向肝样细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(29):4656-4661.
[10] 张晓宇,张赫.LncRNA在多能干细胞早期谱系分化中的作用与机制研究进展[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2021,42(2):147-151.
[11] LOEWEN G, JAYAWICKRAMARAJAH J, ZHUO Y, et al. Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:90.
[12] YU X, LI Z, ZHENG H, et al. NEAT1: A novel cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Cell Prolif. 2017;50(2):e12329.
[13] COURCHAINE E, NEUGEBAUER KM. Paraspeckles: paragons of functional aggregation. J Cell Biol. 2015;210(4):527-528.
[14] BARRA J, GAIDOSH GS, Blumenthal E, et al. Integrator restrains paraspeckles assembly by promoting isoform switching of the lncRNA NEAT1. Sci Adv. 2020;6(27):eaaz9072.
[15] 张喜,段效军,李林瑞,等.lncRNA NEAT1通过靶向抑制miR-29a促进低氧低糖诱导的肺纤维化进程的机制研究[J].实用药物与临床, 2021,24(3):210-218.
[16] HUANG S, XU Y, GE X, et al. Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 accelerates the proliferation and fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy through activating Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(7):11200-11207.
[17] CHI Y, WANG D, WANG J, et al. Long Non-Coding RNA in the Pathogenesis of Cancers. Cells. 2019;8(9):1015.
[18] DERRIEN T, JOHNSON R, BUSSOTTI G, et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012;22(9):1775-1789.
[19] CABILI MN, DUNAGIN MC, MCCLANAHAN PD, et al. Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 2015;16(1):20.
[20] XU C, ZHANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 controls human embryonic stem cell self-renewal by maintaining NODAL signalling. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13287.
[21] GUTTMAN M, RINN JL. Modular regulatory principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature. 2012;482(7385):339-346.
[22] WANG J, LIU S, SHI J, et al. The Role of lncRNAs in Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;15(3):243-249.
[23] LU T, SUN H, LV J, et al. EZH2 suppresses hepatocellular differentiation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Genet Mol Res. 2014; 13(1):2231-2239.
[24] 刘莹,谢锦霞,李恒.长链非编码RNA NEAT1通过miR-34a靶向GAS1激活PI3K-AKT信号通路对宫颈癌的增殖、侵袭和上皮细胞-间充质转化的影响研究[J].中国性科学,2021,30(5):59-63.
[25] 陶正贵,杜静虎,田葵,等.干扰长链非编码RNA NEAT1上调miR-126抑制胃癌细胞的生长、间质转换及裸鼠肿瘤形成[J].实验动物科学,2021,38(2):8-16.
[26] 李宝辉,马辉,侯明明,等.长链非编码RNA NEAT1对非小细胞肺
癌增殖和凋亡的影响及其机制[J].中国免疫学杂志,2019,35(23): 2869-2872.
[27] 任晓阳.长链非编码RNA PVT1和NEAT1在食管鳞状细胞癌中的表达及意义[D].青岛:青岛大学,2017.
[28] 帅勇锋,王小军,张一中,等.长链非编码RNA NEAT1对胃癌细胞
增殖和凋亡的影响及其机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2018,35(7): 1259-1261.
[29] CHEN H, XIA W, HOU M. Correction to: LncRNA-NEAT1 from the competing endogenous RNA network promotes cardioprotective efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes induced by macrophage migration inhibitory factor via the miR-142-3p/FOXO1 signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):376.
[30] 喻大军,郭晨旭,李靖,等.lncRNA NEAT1/miR-103a/STAMBPL1轴对胃癌细胞增殖和侵袭的调控作用[J].山西医科大学学报,2020, 51(9):883-887.
|