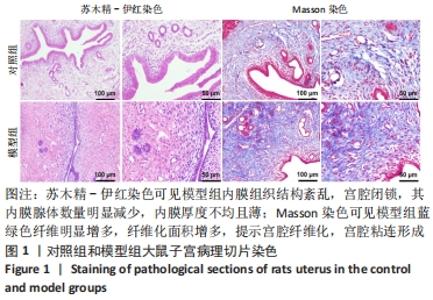
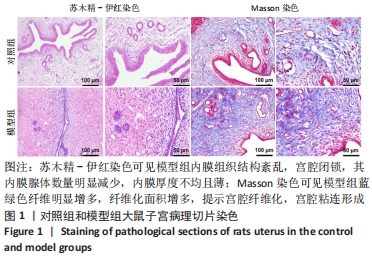
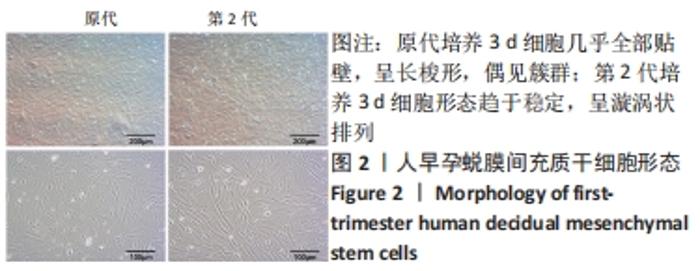
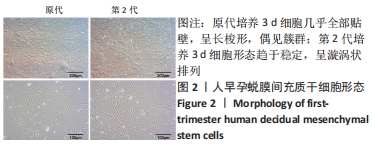
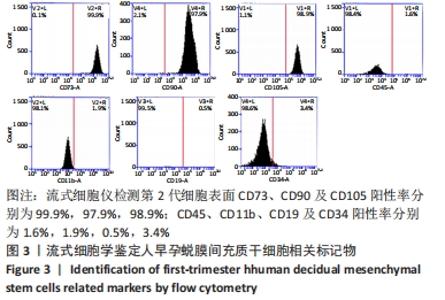
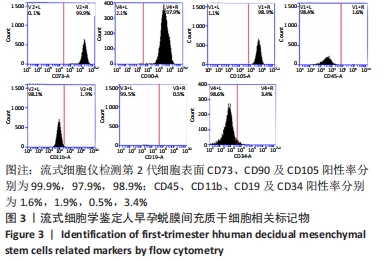
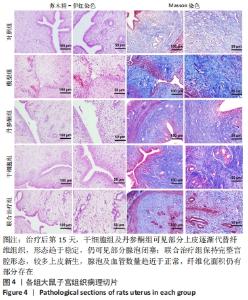
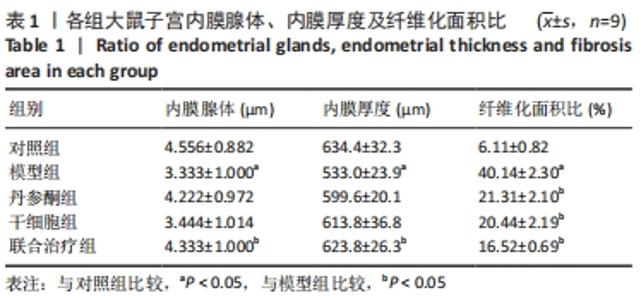
[1] YU D, WONG YM, CHEONG Y, et al. Asherman syndrome--one century later. Fertil Steril. 2008;89(4):759-779.
[2] UGBOAJA JO, OGUEJIOFOR CB, IGWEGBE AO. Clinico-hysteroscopic analysis of severe intrauterine adhesions among Nigerian infertile women. Pan Afr Med J. 2017;28:226.
[3] HU HY, GE TX, PAN YB, et al. Advanced Role of Hippo Signaling in Endometrial Fibrosis: Implications for Intrauterine Adhesion. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017;130(22):2732-2737.
[4] CHEN Y, CHANG Y, YAO S. Role of angiogenesis in endometrial repair of patients with severe intrauterine adhesion. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6(7):1343-1350.
[5] 张慧.综合治疗宫腔粘连的临床效果评价[J].实用妇科内分泌杂志(电子版),2018,5(21):110-112.
[6] SITRUK-WARE R, NATH A. Metabolic effects of contraceptive steroids. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2011;12(2):63-75.
[7] MAROFI F, VAHEDI G, BIGLARI A, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: A New Era in the Cell-Based Targeted Gene Therapy of Cancer. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1770.
[8] 陈波.人早孕蜕膜组织子宫内膜间质干细胞向子宫内膜上皮细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(14):2098-2103.
[9] DIMITROV R, KYURKCHIEV D, TIMEVA T, et al. First-trimester human decidua contains a population of mesenchymal stem cells. Fertil Steril. 2010;93(1):210-219.
[10] 刘静乔,孟亚丽,徐淑稳,等.丹参酮ⅡA对宫腔黏连模型大鼠子宫内膜容受性的改善作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2021,47(1):118-124.
[11] 牛凯迪,王春雪,于月新.反复植入失败与子宫内膜容受性标志物研究进展[J].生殖医学杂志,2019,28(8):961-964.
[12] SCHMITZ CR, OEHNINGER S, GENRO VK, et al. Alterations in expression of endometrial milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 (MFG-E8) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) in patients with infertility and endometriosis. JBRA Assist Reprod. 2017;21(4):313-320.
[13] 秦琰,高金芳,王蔼明,等.宫腔粘连术后放置三角子宫球囊的临床疗效观察[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(8):717-720.
[14] KILIC S, YUKSEL B, PINARLI F, et al. Effect of stem cell application on Asherman syndrome, an experimental rat model. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31(8):975-982.
[15] 贺斯黎,肖松舒,邓新粮,等.重度宫腔粘连危险因素分析[J].中华妇产科杂志,2015,50(1):54-56.
[16] 朱霞,程春霞,徐大宝,等.两种中度宫腔粘连治疗方案的临床对照研究[J].中国内镜杂志,2014,20(1):26-30.
[17] ZHOU Q, WU X, DAI X, et al. The different dosages of estrogen affect endometrial fibrosis and receptivity, but not SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2018; 34(1):49-55.
[18] 王剑,曹敏.定坤丹对宫腔粘连患者宫腔镜术后再粘连的预防及相关细胞因子的影响[J].湖南中医药大学学报, 2018,38(8):913-916.
[19] 尤爱娟,徐妃.补肾活血法联合透明质酸钠预防人工流产术后宫腔粘连的研究[J].中国实用医药,2016,11(30):197-198.
[20] 吴丹,罗健,陈伟志,等.补肾活血法对宫腔粘连术后患者子宫内膜及血流参数影响的临床研究[J].成都中医药大学学报,2017,40(1): 26-28.
[21] 李莉莉,周艳.益母逐瘀汤联合西药治疗宫腔粘连分解术后中重度宫腔粘连临床研究[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(5):27-31.
[22] 邓谋,朱兰.子宫内膜的再生及宫腔粘连干细胞修复的研究进展[J].中国计划生育和妇产科,2016,8(3):6-8,23.
[23] Bueno C, Martínez S. Neurogenesis similarities in different human adult stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(1):123-124.
[24] 韩笑,黄晓武.干细胞在子宫内膜损伤后修复的研究进展[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2019,46(4):365-369.
[25] 段华,夏恩兰.宫腔粘连临床诊疗中国专家共识[J].中华妇产科杂志,2015,50(12):881-887.
[26] CHEN X, ZHANG L, SONG Q, et al. MicroRNA-216b regulates cell proliferation, invasion and cycle progression via interaction with cyclin T2 in gastric cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 2020;31(6):623-631.
[27] 张永裕,谭国胜,罗灿桥,等.多重损伤法建立大鼠宫腔粘连模型及其对子宫内膜LIF及整合素ανβ3的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2016,37(1):15-22.
[28] 邹会莲.宫腔粘连子宫内膜中整合素αVβ3、LIF的表达及麒麟丸改善宫腔粘连子宫内膜容受性的动物研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2016.
[29] 林鑫子,黄晨玲子,罗新,等.人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠宫腔粘连[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(6):1099-1105.
[30] 陈芳,段华,张颖,等.不同水平雌激素在宫腔粘连形成中的作用及相关机制[J].中华妇产科杂志,2010,45(12):917-920.
[31] 刘智敏,周春慧,龙文香,等.miR-29及VEGF在宫腔粘连患者子宫内膜的表达[J].临床医学,2018,38(2):4-7,128.
[32] 许梦婷,刘乃国,董洪亮,等.活性维生素D3在大鼠肺纤维化发生发展中的作用及对miR-29a表达的影响[J].解剖学报,2017,48(1): 78-86.
[33] 孙梦雪,莫海亚,何晓璞,等.miR-29a通过调控PTEN/AKT信号通路对CCl4诱导的肝纤维化大鼠的影响[J].国际消化病杂志,2020, 40(1):26-30.
[34] 周曼萍,何援利,刘芳.miR-29a、TGF-β1、Smad2及Smad3在宫腔粘连中的表达及意义[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(8):1231-1234.
[35] 高红艳,刘芳,谢军,等.TGF-β1及MMP-9在宫腔粘连内膜组织中的表达与意义[J].中国妇幼保健,2014,29(24):3971-3974.
[36] 尚雪,孙广范,林霞,等.宫腔粘连患者人工周期治疗前后子宫内膜雌激素受体及基质金属蛋白酶的表达研究[J].河北医药,2018, 40(12):1884-1886.
[37] IYER AK, RAMESH V, CASTRO CA, et al. Nitric oxide mediates bleomycin-induced angiogenesis and pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of VEGF. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(11):2484-2493.
[38] 安钟健,金燕,延光海,等.Pyrin重组蛋白对肺纤维化大鼠VEGF/VEGFR2/MMP-9信号通路的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2016,32(2): 234-238.
|