Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (49): 8001-8006.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.49.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Inhibitory effect of colchicine on transforming growth factor β1/Smads pathway in rat models of chronic pancreatitis
Lu Hong-wei, Zhang Ya-fei, Ji Hong, Wang Jin-long, Li Yi-ming
- Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2014-09-19Online:2014-11-30Published:2014-11-30 -
Contact:Li Yi-ming, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Lu Hong-wei, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710004, Shaanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Research Project of Social Development in Shaanxi Province of China, No. 2007k14-02(17)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Hong-wei, Zhang Ya-fei, Ji Hong, Wang Jin-long, Li Yi-ming. Inhibitory effect of colchicine on transforming growth factor β1/Smads pathway in rat models of chronic pancreatitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(49): 8001-8006.
share this article
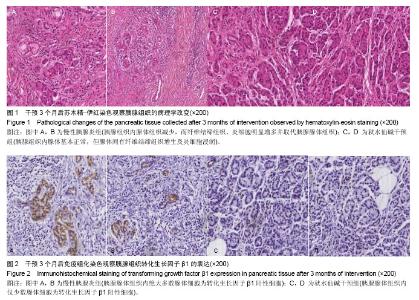
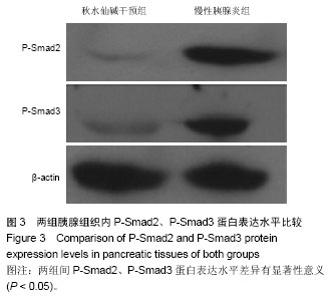
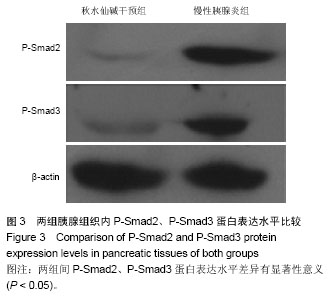
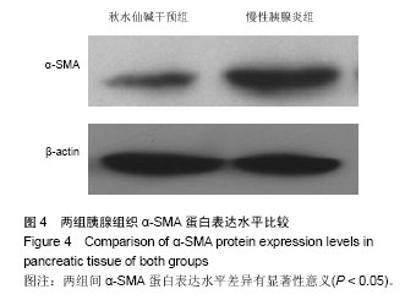
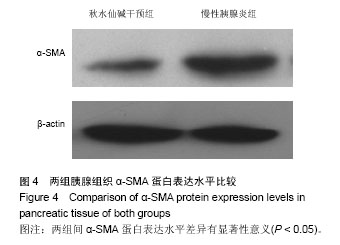
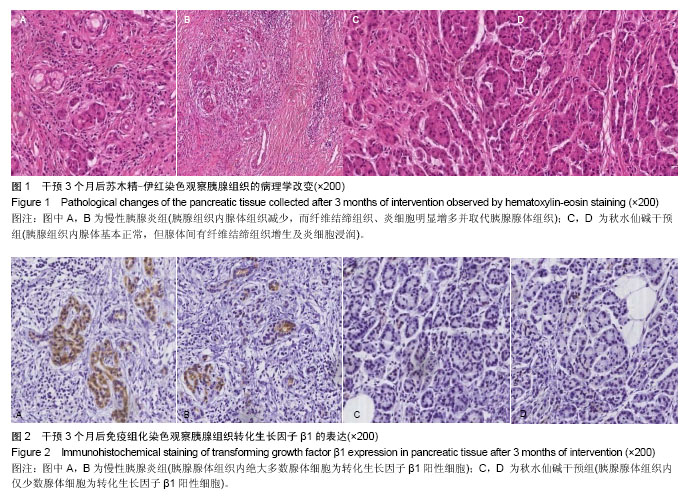
2.1 实验动物数量分析 选取20只SD大鼠,分为慢性胰腺炎组及秋水仙碱干预组,每组10只,造模成功,实验过程无动物脱失,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 慢性胰腺炎大鼠模型的建立及秋水仙碱对慢性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺组织内纤维化的抑制作用 实验后3个月取大鼠胰腺组织制成冰冻切片,进行病理学观察。慢性胰腺炎组胰腺组织内腺体组织减少,而纤维结缔组织、炎细胞明显增多并取代胰腺腺体组织;而秋水仙碱干预组胰腺组织内腺体基本正常,但腺体间有纤维结缔组织增生及炎细胞浸润显著少于慢性胰腺炎组(图1)。 2.3 秋水仙碱能够抑制慢性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺组织内TGF-β1的表达 秋水仙碱干预组TGF-β1阳性表达级别为+,慢性胰腺炎组为+++;秋水仙碱干预组TGF-β1表达阳性细胞指数为11.92±6.57,慢性胰腺炎组为60.53±5.57。秋水仙碱干预组TGF-β1阳性表达级别和阳性细胞指数显著低于慢性胰腺炎组,两组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图2。 2.4 秋水仙碱能够抑制慢性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺组织内P-Smad2、P-Smad3的表达 两组均在实验后3个月时取材,Western blot法测定胰腺组织中的P-Smad2、P-Smad3及β-actin,将所拍照片结果应用Image Pro图像分析软件处理后,分别得出其积分吸光度值,然后分别计算出两组P-Smad2、P-Smad3与β-actin积分吸光度之比值,数据经统计学处理并进行比较。结果所示,术后3个月时慢性胰腺炎组胰腺组织内P-Smad2/β-actin、P-Smad3/β-actin达到了1.02±0.38和0.87±0.26,而秋水仙碱干预组则分别为0.21±0.11和0.34±0.14,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图3。 2.5 秋水仙碱能够抑制慢性胰腺炎大鼠胰腺组织内α-SMA的表达 Western blot法测定胰腺组织中的α-SMA及β-actin,将所拍照片结果应用Image Pro图像分析软件处理后,分别得出其积分吸光度值,然后分别计算出两组α-SMA与β-actin积分吸光度之比值,数据经统计学处理并进行比较。结果所示,术后3个月时慢性胰腺炎组胰腺组织内α-SMA/β-actin达到了1.86±0.73,而秋水仙碱干预组则为0.42±0.15,两组间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),见图4。"
| [1] Zhang SK, Cui NQ, Zhuo YZ,et al. Modified Xiaochaihu Decoction prevents the progression of chronic pancreatitis in rats possibly by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β1/Sma- and mad-related proteins signaling pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2013;19(12):935-939.
[2] Chen JM, Férec C. Genetics and pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis: the 2012 update.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2012;36(4):334-340.
[3] Chen JM, Férec C.Chronic pancreatitis: genetics and pathogenesis.Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10: 63-87.
[4] Inui K, Yoshino J, Miyoshi H,et al.New developments in diagnosis and non-surgical treatment of chronic pancreatitis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28 Suppl 4:108-112.
[5] Rebibo L,Yzet T, Cosse C,et al. Frey procedure for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis associated with common bile duct stricture.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2013;12(6): 637-644.
[6] 王洛伟,李兆申.慢性胰腺炎研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2007,15(34):3598-3603.
[7] 闫晶晶,崔乃强.慢性胰腺炎胰腺纤维化发病机制及其治疗的研究进展[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2007,13(6):422-424.
[8] 王兴鹏,张汝玲.慢性胰腺炎的病因和发病机制[J].中国实用外科杂志,2011,31(9):778-780.
[9] 狄扬,傅德良.慢性胰腺炎胰腺纤维化发病机制的研究进展[J].中国实用外科杂志,2011,31(9):826-829.
[10] 郑振江,向光明,刘续宝.胰腺星状细胞在胰腺纤维化中的作用[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2010,17(8):876-879.
[11] 范昕,王莹,侯雯跻,等.小鼠胰腺星状细胞的分离培养与鉴定[J].江苏大学学报:医学版,2012,22(6):468-471.
[12] 陈启龙,李国威,陈晓,等.转化生长因子β1在胰腺组织中的表达:慢性胰腺炎发病机制探讨[J].中国普通外科杂志,2002,11(10): 612-615.
[13] 王东盛,刘倩.己酮可可碱对大鼠胰腺纤维化及TGF-β1、α-SMA、MMP-1、TIMP-1表达的影响[J].中国现代普通外科进展,2006, 9(4):222-224.
[14] 何少武,胡先贵,金钢,等. TGF-β1和α-SMA在慢性胰腺炎组织中的表达及意义[J].第二军医大学学报,2003,24(11):1215-1218.
[15] Gu H, Mickler EA, Cummings OW,et al. Crosstalk between TGF-β1 and complement activation augments epithelial injury in pulmonary fibrosis.FASEB J. 2014. [Epub ahead of print].
[16] Kinashi H, Ito Y, Mizuno M,et al.TGF-β1 promotes lymphangiogenesis during peritoneal fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24(10):1627-1642.
[17] Pang L, Wei C, Duan J,et al.TGF-β1/Smad signaling, MMP-14, and MSC markers in arterial injury: discovery of the molecular basis of restenosis.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7(6):2915-2924.
[18] Yu C, Liu Y, Huang D,et al.TGF-β1 mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition via the TGF-β/Smad pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.Oncol Rep. 2011;25(6):1581-1587.
[19] Fang L, Chang HM, Cheng JC,et al.TGF-β1 induces COX-2 expression and PGE2 production in human granulosa cells through Smad signaling pathways.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(7):E1217-1226.
[20] Zhou F, Li GY, Gao ZZ,et al.The TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF pathway and corpus cavernosum fibrous-muscular alterations in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.J Androl. 2012; 33(4):651-659.
[21] Pan MM, Zhang MH, Ni HF,et al. Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signal pathway is involved in the effect of Cordyceps sinensis against renal fibrosis in 5/6 nephrectomy rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;58:487-494.
[22] Gao Y, Lui WY.Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) regulates cell junction restructuring via Smad-mediated repression and clathrin-mediated endocytosis of nectin-like molecule 2 (Necl-2).PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64316.
[23] Lo GH, Perng DS, Chang CY,et al.Controlled trial of ligation plus vasoconstrictor versus proton pump inhibitor in the control of acute esophageal variceal bleeding.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(4):684-689.
[24] Tasci I, Deveci S, Isik AT,et al. Allopurinol in rat chronic pancreatitis: effects on pancreatic stellate cell activation. Pancreas. 2007;35(4):366-371.
[25] Ozdemir O, Calisaneller T, Sonmez E,et al.Topical use of colchicine to prevent spinal epidural fibrosis in rats.Neurol Res. 2010;32(10):1117-1120.
[26] Ozdemir BH, Ozdemir FN, Sezer S,et al. Does colchicine have an antifibrotic effect on development of interstitial fibrosis in renal allografts of recipients with familial Mediterranean fever.Transplant Proc. 2006;38(2):473-476.
[27] Nikolaidis N, Kountouras J, Giouleme O,et al. Colchicine treatment of liver fibrosis.Hepatogastroenterology. 2006; 53(68):281-285.
[28] D'Haese JG, Ceyhan GO, Demir IE,et al.Treatment options in painful chronic pancreatitis: a systematic review.HPB (Oxford). 2014;16(6):512-521.
[29] Apte MV, Pirola RC, Wilson JS. Battle-scarred pancreas: role of alcohol and pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic fibrosis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21 Suppl 3:S97-S101.
[30] Cocco G, Chu DC, Pandolfi S.Colchicine in clinical medicine. A guide for internists.Eur J Intern Med. 2010;21(6):503-508.
[31] Poloz Y, O'Day DH.Colchicine affects cell motility, pattern formation and stalk cell differentiation in Dictyostelium by altering calcium signaling.Differentiation. 2012;83(4):185-199.
[32] Tseng CY, Mane JY, Winter P,et al.Quantitative analysis of the effect of tubulin isotype expression on sensitivity of cancer cell lines to a set of novel colchicine derivatives.Mol Cancer. 2010;9:131.
[33] 孙嘉临,王先化.秋水仙碱对实验性大鼠肝纤维化的影响[J].中国现代医生,2012, 50(14): 1-2.
[34] Massagué J, Wotton D.Transcriptional control by the TGF-beta/ Smad signaling system.EMBO J. 2000;19(8): 1745-1754.
[35] Lin Y, Zhang B, Liang H,et al. JNK inhibitor SP600125 enhances TGF-β-induced apoptosis of RBE human cholangiocarcinoma cells in a Smad-dependent manner.Mol Med Rep. 2013;8(6):1623-1629.
[36] Karathanasi V, Tosios KI, Nikitakis NG,et al.TGF-β1, Smad-2/-3, Smad-1/-5/-8, and Smad-4 signaling factors are expressed in ameloblastomas, adenomatoid odontogenic tumors, and calcifying cystic odontogenic tumors: an immunohistochemical study.J Oral Pathol Med. 2013;42(5): 415-423.
[37] Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P.TGF-beta signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins.Nature. 1997;390(6659):465-471.
[38] 陆宏伟,袁甫军,单涛,等.秋水仙碱通过阻滞TGF-β1/Smads通路抑制胰腺星状细胞生物学行为的研究[J].中国现代普通外科进展, 2014,17(4):258-262. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | Yang Junhui, Luo Jinli, Yuan Xiaoping. Effects of human growth hormone on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | Sun Jianwei, Yang Xinming, Zhang Ying. Effect of montelukast combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on spinal cord injury in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | Hao Xiaona, Zhang Yingjie, Li Yuyun, Xu Tao. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing prolyl oligopeptidase on the repair of liver fibrosis in rat models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | Liu Jianyou, Jia Zhongwei, Niu Jiawei, Cao Xinjie, Zhang Dong, Wei Jie. A new method for measuring the anteversion angle of the femoral neck by constructing the three-dimensional digital model of the femur [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | Meng Lingjie, Qian Hui, Sheng Xiaolei, Lu Jianfeng, Huang Jianping, Qi Liangang, Liu Zongbao. Application of three-dimensional printing technology combined with bone cement in minimally invasive treatment of the collapsed Sanders III type of calcaneal fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | Hu Jing, Xiang Yang, Ye Chuan, Han Ziji. Three-dimensional printing assisted screw placement and freehand pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracolumbar fractures: 1-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | Shu Qihang, Liao Yijia, Xue Jingbo, Yan Yiguo, Wang Cheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new three-dimensional printed porous fusion cage for cervical vertebra [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | Wang Yihan, Li Yang, Zhang Ling, Zhang Rui, Xu Ruida, Han Xiaofeng, Cheng Guangqi, Wang Weil. Application of three-dimensional visualization technology for digital orthopedics in the reduction and fixation of intertrochanteric fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | Sun Maji, Wang Qiuan, Zhang Xingchen, Guo Chong, Yuan Feng, Guo Kaijin. Development and biomechanical analysis of a new anterior cervical pedicle screw fixation system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | Lin Wang, Wang Yingying, Guo Weizhong, Yuan Cuihua, Xu Shenggui, Zhang Shenshen, Lin Chengshou. Adopting expanded lateral approach to enhance the mechanical stability and knee function for treating posterolateral column fracture of tibial plateau [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | Zhu Yun, Chen Yu, Qiu Hao, Liu Dun, Jin Guorong, Chen Shimou, Weng Zheng. Finite element analysis for treatment of osteoporotic femoral fracture with far cortical locking screw [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||