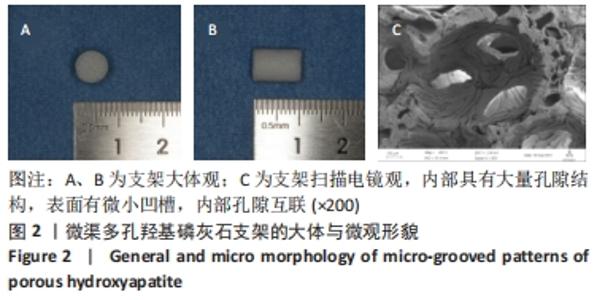
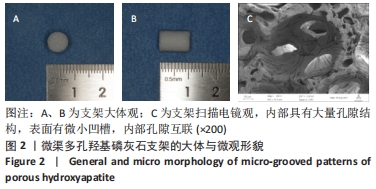
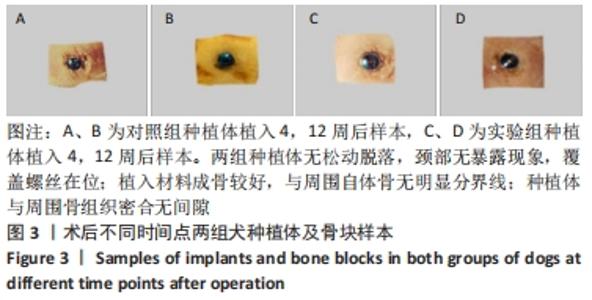
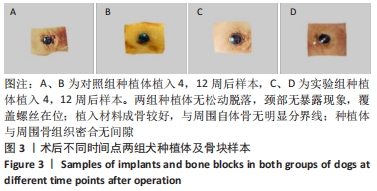
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (12): 1920-1926.doi: 10.12307/2023.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Osseointegration of micro-grooved patterns of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds with implants after repairing large-area canine mandibular defects
Li Jing1, Chen Zhenghui3, Kaidiliya·Yalikun2, Liu Chang2, Jiang Sijing2, Mu Yandong1, 2
- 1Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences · Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China; 3Nanbu County People’s Hospital, Nanchong 637000, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2021-12-03Accepted:2022-01-13Online:2023-04-28Published:2022-07-30 -
Contact:Mu Yandong, Chief physician, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences · Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610072, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Jing, Master candidate, Physician, Affiliated Stomatology Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82071168 (to MYD); Key Research & Development Project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 2021YFS0009 (to MYD); Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Project, No. 2016TD0008 (to MYD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jing, Chen Zhenghui, Kaidiliya·Yalikun, Liu Chang, Jiang Sijing, Mu Yandong. Osseointegration of micro-grooved patterns of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds with implants after repairing large-area canine mandibular defects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(12): 1920-1926.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
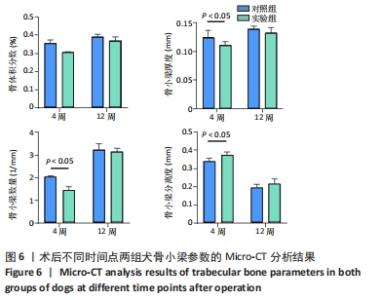
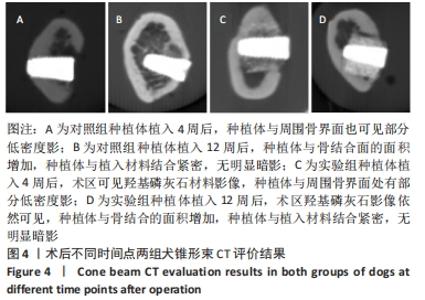
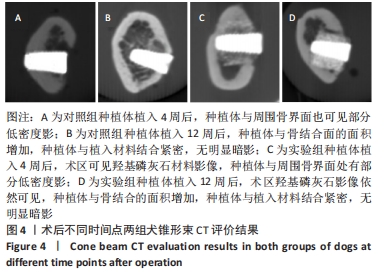
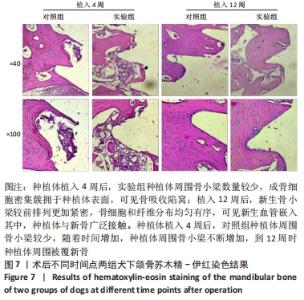
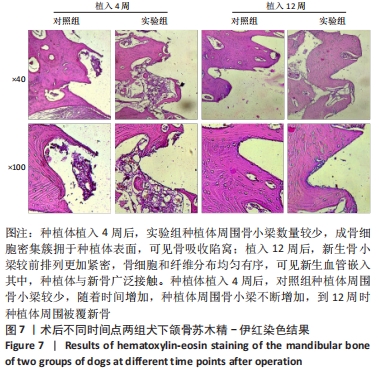
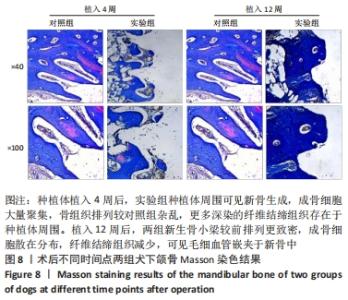
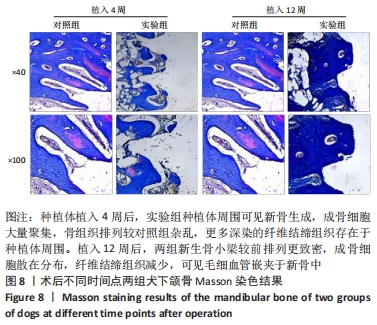
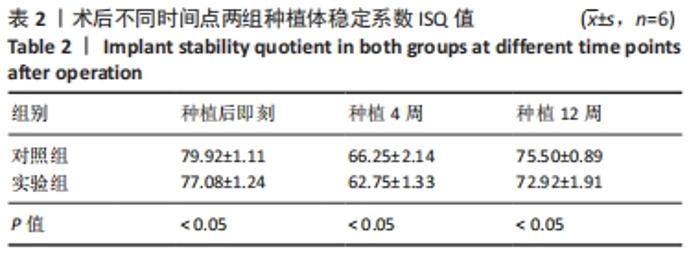
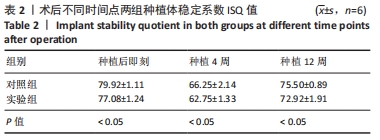
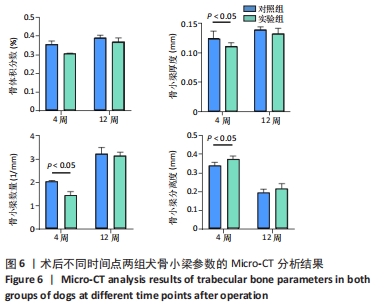
由图5可见,两组种植体表面被覆骨量在种植体植入12周后均较4周时更多。植入4,12周后,两组骨体积分数值比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组植入12周后的骨体积分数值均大于4周(P < 0.05)。植入4周后,实验组骨小梁厚度值明显小于对照组(P < 0.05),12周时两组骨小梁厚度值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组植入12周后的骨小梁厚度值均大于4周(P < 0.05)。植入4周后,实验组骨小梁数值明显小于对照组(P < 0.05),12周时两组骨小梁数值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组植入12周后的骨小梁数值均大于4周(P < 0.05)。植入4周后,实验组骨小梁分离度值明显大于对照组(P < 0.05),12周后两组骨小梁分离度值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);两组植入12周后的骨小梁分离度值均小于4周(P < 0.05),见图6。说明植入4周后,实验组表面被覆骨量小于对照组,随着时间增长,骨不断重塑,种植体周围骨量不断增长,到12周时两组骨量能达到同一水平。 "
| [1] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(205):299-308. [2] HAUGEN HJ, LYNGSTADAAS SP, ROSSI F, et al. Bone grafts: which is the ideal biomaterial? J Clin Periodontol. 2019;46 Suppl 21:92-102. [3] FERNANDEZ DE GRADO G, KELLER L, IDOUX-GILLET Y, et al. Bone substitutes: a review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J Tissue Eng. 2018; 9:2041731418776819. [4] SZCZEŚ A, HOŁYSZ L, CHIBOWSKI E. Synthesis of hydroxyapatite for biomedical applications. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2017;249:321-330. [5] 高飞,闫明,朱珊珊,等.羟基磷灰石在生物材料中的应用[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2019,33(5):310-313. [6] KUNISADA T, HASEI J, FUJIWARA T, et al. Radiographic and clinical assessment of unidirectional porous hydroxyapatite to treat benign bone tumors. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21578. [7] LINH NTB, ABUEVA CDG, JANG DW, et al. Collagen and bone morphogenetic protein-2 functionalized hydroxyapatite scaffolds induce osteogenic differentiation in human adipose-derived stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1363-1371. [8] YANG L, ULLAH I, YU K, et al. Bioactive Sr2+/Fe3+co-substituted hydroxyapatite in cryogenically 3D printed porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biofabrication. 2021;13(3) doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/abcf8d. [9] LI J, XU T, WANG Q, et al. Integrating surface topography of stripe pattern on pore surface of 3-dimensional hydroxyapatiye scaffolds. Mater Lett. 2016;169:148-152. [10] LI J, ZH W, XU T, et al. Ectopic osteogenesis and angiogenesis regulated by porous architecture of hydroxyapatite scaffolds with similar interconnecting structure in vivo. Regen Biomater. 2016;3(5):285-297. [11] REN X, TUO Q, TIAN K, et al. Enhancement of osteogenesis using a novel porous hydroxyapatite scaffold in vivo and vitro. Ceram Int. 2018; 44(17):21656-21665. [12] LI C, YANG L, REN X, et al. Grooved hydroxyapatite scaffold modulates mitochondria homeostasis and thus promotes osteogenesis in bone mesenchymal stromal cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(4):2801-2809. [13] LI C, YANG L, REN X, et al. Groove structure of porous hydroxyapatite scaffolds (HAS) modulates immune environment via regulating macrophages and subsequently enhances osteogenesis. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2019;24(5):733-745. [14] ATTIA MS, MOHAMMED HM, ATTIA MG, et al. Histological and histomorphometric evaluation of hydroxyapatite-based biomaterials in surgically created defects around implants in dogs. J Periodontol. 2019;90(3):281-287. [15] MYEROFF C, ARCHDEACON M. Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(23):2227-2236. [16] TASDEMIR U, IYILIKÇI B, AKTÜRK MC, et al. The Effect of Autogenous Bone Graft Mixed With Recombinant Human Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor on Bone Regeneration. J Craniofac Surg. 2021;32(6):2233-2237. [17] IIJIMA K, OTSUKA H. Cell Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Bioengineering (Basel). 2020;7(4):119. [18] KUBOKI Y, JIN Q, TAKITA H. Geometry of carriers controlling phenotypic expression in BMP-induced osteogenesis and chondrogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001;83-A Suppl 1(Pt 2):S105-S115. [19] HAN X, SUN M, CHEN B, et al. Lotus seedpod-inspired internal vascularized 3D printed scaffold for bone tissue repair. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(6):1639-1652. [20] JIN QM, TAKITA H, KOHGO T, et al. Effects of geometry of hydroxyapatite as a cell substratum in BMP-induced ectopic bone formation. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;51(3):491-499. [21] MAREW T, BIRHANU G. Three dimensional printed nanostructure biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Regen Ther. 2021;18:102-111. [22] MURPHY CM, HAUGH MG. The effect of mean pore size on cell attachment, proliferation and migration in collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2010;31(3):461-466. [23] 魏莉,马保金,邵金龙,等.羟基磷灰石复合材料在骨组织工程中应用的研究进展[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2021,52(3):357-363. [24] 李杜晨晖,田艾,唐正龙.骨生物支架材料诱导的血管生成[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3602-3608. [25] HE J, CHEN G, LIU M, et al. Scaffold strategies for modulating immune microenvironment during bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;108:110411. [26] 吕欣荣,温永梅,伍佳,等.微渠表面多孔羟基磷灰石支架体内异位成骨性的研究[J].实用医院临床杂志,2017,14(3):28-31. [27] 陈胡贵,覃建国,李理,等.大动物节段性骨缺损模型的研究进展[J].北京生物医学工程,2021,40(2):203-208. [28] DRAENERT M, DRAENERT A, DRAENERT K. Osseointegration of hydroxyapatite and remodeling-resorption of tricalciumphosphate ceramics. Microsc Res Tech. 2013;76(4):370-380. [29] TSAI MT, HE RT, HUANG HL, et al. Effect of Scanning Resolution on the Prediction of Trabecular Bone Microarchitectures Using Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(6):368. [30] HUANG Y, LI Z, VAN DESSEL J, et al. Effect of platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant trabecular bone volume and architecture: A preclinical micro-CT study in beagle dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2019;30(12):1190-1199. [31] 朱福余,袁暾,张杰,等.含植入物不脱钙骨组织病理切片技术在骨组织形态学研究中的应用[J].医疗装备,2020,33(19):30-34. [32] INSUA A, MONJE A, WANG HL, et al. Basis of bone metabolism around dental implants during osseointegration and peri-implant bone loss. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(7):2075-2089. [33] CHÁVARRI-PRADO D, BRIZUELA-VELASCO A, DIÉGUEZ-PEREIRA M, et al. Influence of cortical bone and implant design in the primary stability of dental implants measured by two different devices of resonance frequency analysis: An in vitro study. J Clin Exp Dent. 2020; 12(3):e242-e248. [34] HÉRIVEAUX Y, VAYRON R, FRAULOB M, et al. Assessment of dental implant stability using resonance frequency analysis and quantitative ultrasound methods. J Prosthodont Res. 2021;65(3):421-427. [35] SIM CP, LANG NP. Factors influencing resonance frequency analysis assessed by Osstell mentor during implant tissue integration: I. Instrument positioning, bone structure, implant length. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(6):598-604. [36] DAVIES JE. Mechanisms of endosseous integration. Int J Prosthodont. 1998;11(5):391-401. |
| [1] | Wen Xinghua, Ding Huanwen, Cheng Kai, Yan Xiaonan, Peng Yuanhao, Wang Yuning, Liu Kang, Zhang Huiwu. Three-dimensional finite element model analysis of intramedullary nailing fixation design for large femoral defects in Beagle dogs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(9): 1371-1376. |
| [2] | Zhu Lin, Gu Weiping, Wang Can, Chen Gang. Biomechanical analysis of All-on-Four and pterygomaxillary implants under different maxillary bone conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 985-991. |
| [3] | Sun Jiangwei, Wang Junxiang, Baibujiafu·Yellisi, Dai Huijuan, Nijati·Turson. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of stress distribution in different smooth collar implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1004-1011. |
| [4] | Zhang Tingting, Liu Juan, Zhang Xu. Bioactivity of phase-transition lysozyme for surface modification of zirconia all-ceramic implant material mediating hydroxyapatite coating [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1043-1049. |
| [5] | Xu Xingxing, Wen Chaoju, Meng Maohua, Wang Qinying, Chen Jingqiao, Dong Qiang. Carbon nanomaterials in oral implant [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1062-1070. |
| [6] | Yang Yitian, Wang Lu, Yao Wei, Zhao Bin. Application of the interaction between biological scaffolds and macrophages in bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [7] | Li Cheng, Zheng Guoshuang, Kuai Xiandong, Yu Weiting. Alginate scaffold in articular cartilage repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [8] | Lu Di, Zhang Cheng, Duan Rongquan, Liu Zongxiang. Osteoinductive properties of calcium phosphate ceramic bone repair materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1103-1109. |
| [9] | Tang Haotian, Liao Rongdong, Tian Jing. Application and design of piezoelectric materials for bone defect repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1117-1125. |
| [10] | Xu Yan, Li Ping, Lai Chunhua, Zhu Peijun, Yang Shuo, Xu Shulan. Piezoelectric materials for vascularized bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(7): 1126-1132. |
| [11] | Zhang Min, Zhang Xiaoming, Liu Tongbin. Application potential of naringin in bone tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(5): 787-792. |
| [12] | Xu Xiangjun, Wang Chao, Song Qunshan, Li Bingyan, Zhang Jichao, Wang Guodong, Dong Yuefu. Optimal angle for prosthesis implantation in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 612-618. |
| [13] | Wang Junxiang, Sun Jiangwei, Bai Bujiafu·Yellisi, Wang Zhaoxin, Nijati·Turson. Effect of three abutment materials on bone stress around maxillary angle implant under dynamic loading [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 398-405. |
| [14] | Chen Jingqiao, Li Ying, Meng Maohua, Xu Xingxing, Wang Qinying, Wang Huan, Lu Jing, Shu Jiayu, Dong Qiang. Research progress in platelet-rich fibrin in stomatology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 441-446. |
| [15] | Wang Kaiyu, Hu Peng, Wei Zairong, Huang Guangtao, Zhou Jian, He Guijia, Nie Kaiyu. Use of expanders and implants in breast reconstruction complicated with infection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(3): 461-469. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||