Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (16): 2480-2486.doi: 10.12307/2022.244
Previous Articles Next Articles
Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold
Huang Bo1, Chen Mingxue2, Peng Liqing1, Luo Xujiang1, Li Huo1, Wang Hao1, Tian Qinyu1, Lu Xiaobo1, Liu Shuyun3, Guo Quanyi1, 3
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
-
Received:2020-09-19Revised:2020-09-21Accepted:2020-11-09Online:2022-06-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Guo Quanyi, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; Institute of Orthopedics, First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Lab of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China -
About author:Huang Bo, Master candidate, Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Plan Project, No. 2019YFA0110600 (to GQY); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81772319 (to GQY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(16): 2480-2486.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

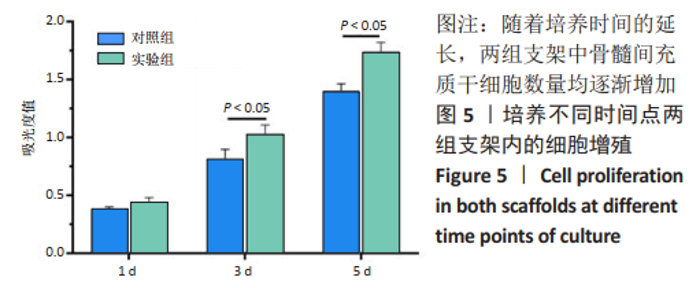
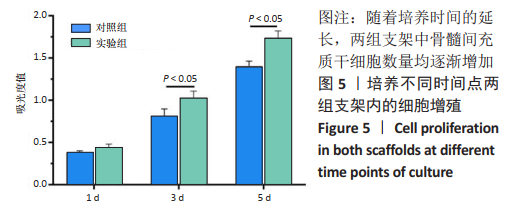
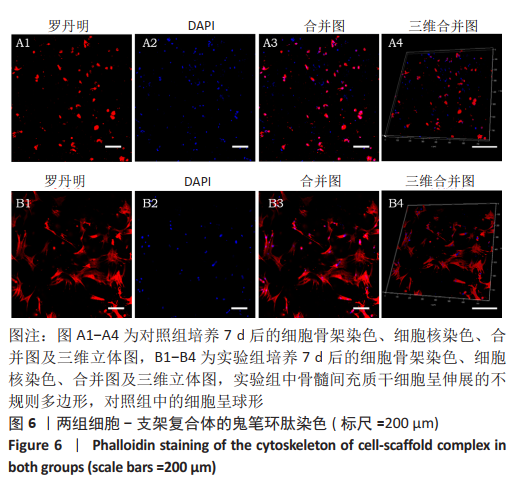
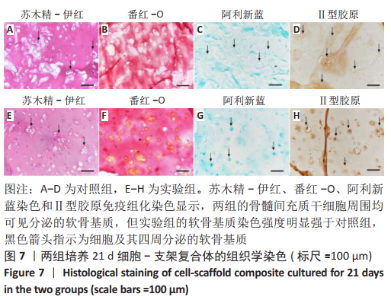
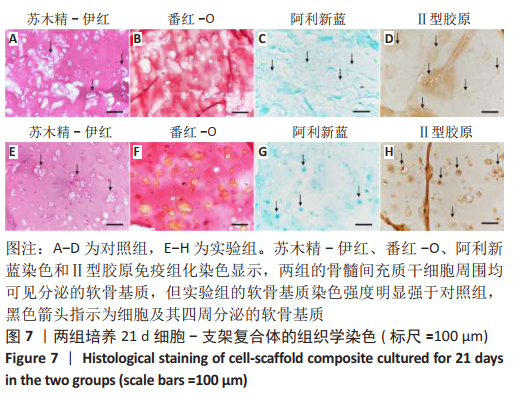
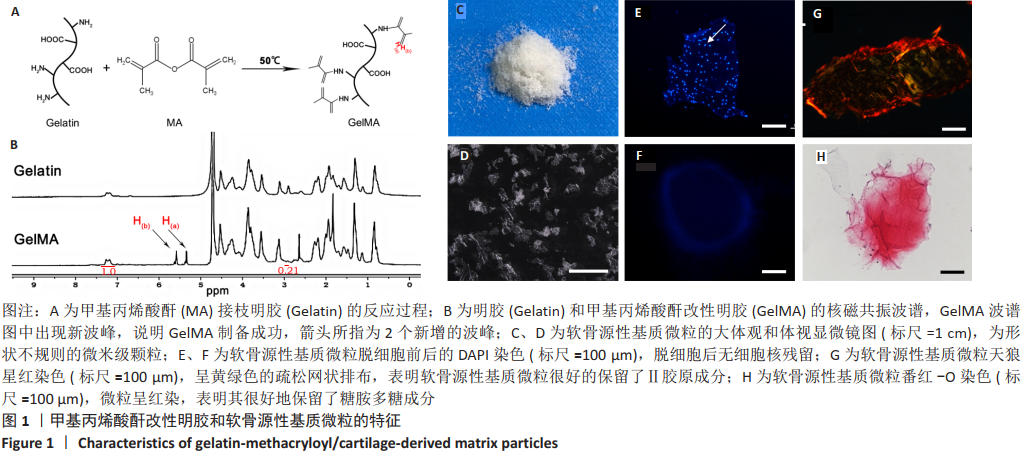
2.1 GelMA的合成及表征 甲基丙烯酸酐改性明胶的制备方案,见图1A。质子核磁共振谱光谱分析显示,与明胶的光谱图相比,GelMA的光谱在5.4,5.6 ppm处出现新信号,见图1B黑色箭头所指,表明甲基丙烯酸基团与明胶接枝成功。根据文献所述计算方法[28],计算得实验制备的GelMA中甲基丙烯酰基的取代度约为79%。 2.2 CDMPs的大体观和成分 大体观图和体视镜图显示,CDMPs为不规则形状的微米级小颗粒(图1C、D)。DAPI染色显示,脱细胞前的软骨微粒含有大量软骨细胞(图1E),经脱细胞处理后软骨微粒内未见残留的软骨细胞(图1F)。CDMPs天狼星红染色偏正光为弱折光性,呈黄绿色的疏松网状排布(图1G),表明Ⅱ型胶原到了很好地保留。CDMPs番红-O染色呈阳性(图1H),表明其同时也很好地保留了糖胺多糖。"
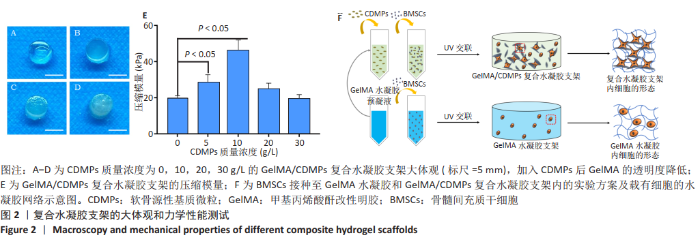
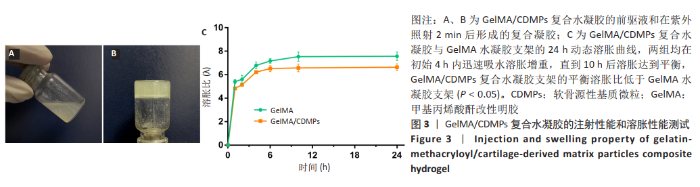
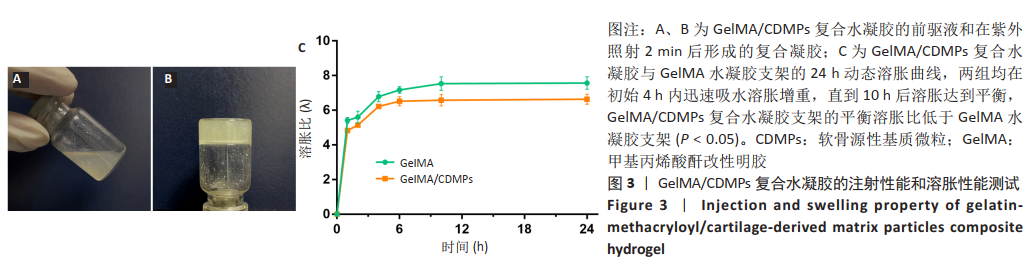
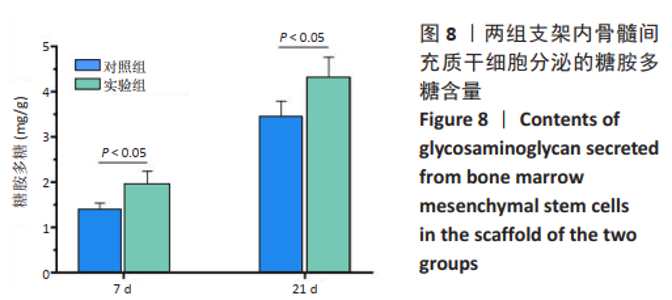
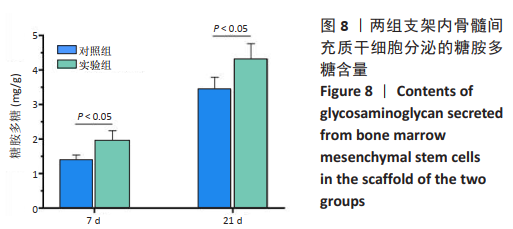
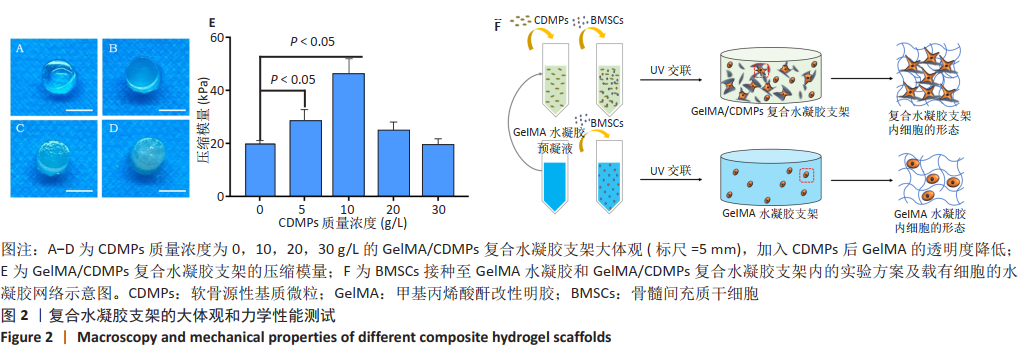
2.3 GelMA/CDMPs复合水凝胶支架的大体观及力学性能 不同CDMPs质量浓度浓度的复合水凝胶支架均呈圆柱形的凝胶状,单纯GelMA水凝胶支架为无色透明状,加入CDMPs后GelMA水凝胶的透明度随CDMPs质量浓度的升高逐渐降低,且CDMPs均匀分布于其中,见图2A-D。支架力学结果显示,复合水凝胶支架的压缩模量随着CDMPs质量浓度的增加而升高,但当CDMPs的质量浓度超过10 g/L后开始下降,其中 10 g/L复合水凝胶支架的压缩模量显著高于其他复合水凝胶支架(P < 0.05);此外,5 g/L复合水凝胶支架的压缩模高于0 g/L复合水凝胶支架(P < 0.05),20,30 g/L复合水凝胶支架与0 g/L复合水凝胶支架的压缩模量比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见图2E。为实现在复合支架力学性能最佳的条件下使CDMPs对支架内细胞发挥最大的生物学作用,因此选择CDMPs质量浓度为10 g/L的GelMA/CDMPs复合水凝胶支架进行后续实验(图2F),作为实验组。"
| [1] MADEIRA C, SANTHAGUNAM A, SALGUEIRO JB, et al. Advanced cell therapies for articular cartilage regeneration. Trends Biotechnol. 2015;33(1): 35-42. [2] MAKRIS EA, GOMOLL AH, MALIZOS KN, et al. Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34. [3] 刘奕,谢林.组织工程技术修复损伤关节软骨的研究与应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(41):7310-7316. [4] CAI L, DEWI RE, HEILSHORN SC. Injectable Hydrogels with In Situ Double Network Formation Enhance Retention of Transplanted Stem Cells. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25(9):1344-1351. [5] LI J, CHEN G, XU X, et al. Advances of injectable hydrogel-based scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Regen Biomater. 2019;6(3):129-140. [6] VEGA SL, KWON MY, BURDICK JA. Recent advances in hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Eur Cell Mater. 2017;33:59-75. [7] PUPKAITE J, ROSENQUIST J, HILBORN J, et al. Injectable Shape-Holding Collagen Hydrogel for Cell Encapsulation and Delivery Cross-linked Using Thiol-Michael Addition Click Reaction. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(9): 3475-3484. [8] YING G, JIANG N, PARRA-CANTU C, et al. Bioprinted Injectable Hierarchically Porous Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogel Constructs with Shape-Memory Properties. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(46):2003740. [9] SUN M, SUN X, WANG Z, et al. Synthesis and Properties of Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels and Their Recent Applications in Load-Bearing Tissue. Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(11):1290. [10] SPILLER KL, MAHER SA, LOWMAN AM. Hydrogels for the repair of articular cartilage defects. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2011;17(4):281-299. [11] NICHOL JW, KOSHY ST, BAE H, et al. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2010;31(21):5536-5544. [12] WANG Y, MA M, WANG J, et al. Development of a Photo-Crosslinking, Biodegradable GelMA/PEGDA Hydrogel for Guided Bone Regeneration Materials. Materials (Basel, Switzerland). 2018;11(8):1345. [13] SHIN SR, BAE H, CHA JM, et al. Carbon nanotube reinforced hybrid microgels as scaffold materials for cell encapsulation. ACS Nano. 2012;6(1):362-372. [14] SHIN H, OLSEN BD, KHADEMHOSSEINI A. The mechanical properties and cytotoxicity of cell-laden double-network hydrogels based on photocrosslinkable gelatin and gellan gum biomacromolecules. Biomaterials. 2012;33(11):3143-3152. [15] ZHU W, CUI H, BOUALAM B, et al. 3D bioprinting mesenchymal stem cell-laden construct with core-shell nanospheres for cartilage tissue engineering. Nanotechnology. 2018;29(18):185101. [16] SHIN SR, ZIHLMANN C, AKBARI M, et al. Reduced Graphene Oxide-GelMA Hybrid Hydrogels as Scaffolds for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Small. 2016; 12(27):3677-3689. [17] NAVAEI A, SAINI H, CHRISTENSON W, et al. Gold nanorod-incorporated gelatin-based conductive hydrogels for engineering cardiac tissue constructs. Acta Biomater. 2016;41:133-146. [18] 肖统光,张一民,郭维民,等.细胞外基质来源支架在软骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(38):5737-5744. [19] YIN H, WANG Y, SUN X, et al. Functional tissue-engineered microtissue derived from cartilage extracellular matrix for articular cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018;77:127-141. [20] YIN H, WANG Y, SUN Z, et al. Induction of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and functional cartilage microtissue formation for in vivo cartilage regeneration by cartilage extracellular matrix-derived particles. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:96-109. [21] ALMEIDA HV, ESWARAMOORTHY R, CUNNIFFE GM, et al. Fibrin hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix and incorporating freshly isolated stromal cells as an injectable for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:55-62. [22] CHANG CH, CHEN CC, LIAO CH, et al. Human acellular cartilage matrix powders as a biological scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering with synovium-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102(7):2248-2257. [23] SUTHERLAND AJ, DETAMORE MS. Bioactive Microsphere-Based Scaffolds Containing Decellularized Cartilage. Macromol Biosci. 2015;15(7):979-989. [24] ABRAMS GD, MALL NA, FORTIER LA, et al. BioCartilage: Background and Operative Technique. Oper Tech Sports Med. 2013;21(2):116-124. [25] LOESSNER D, MEINERT C, KAEMMERER E, et al. Functionalization, preparation and use of cell-laden gelatin methacryloyl-based hydrogels as modular tissue culture platforms. Nat Protoc. 2016;11(4):727-746. [26] 杨俊丽,韩霞,孙明启,等.兔骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特征及原代培养[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(50):8043-8047. [27] ROTHRAUFF BB, SHIMOMURA K, GOTTARDI R, et al. Anatomical region-dependent enhancement of 3-dimensional chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by soluble meniscus extracellular matrix. Acta Biomater. 2017;49:140-151. [28] KILIC BEKTAS C, HASIRCI V. Mimicking corneal stroma using keratocyte-loaded photopolymerizable methacrylated gelatin hydrogels. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(4):e1899-e1910. [29] PEPELANOVA I, KRUPPA K, SCHEPER T, et al. Gelatin-Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels with Defined Degree of Functionalization as a Versatile Toolkit for 3D Cell Culture and Extrusion Bioprinting. Bioengineering (Basel, Switzerland). 2018;5(3):55. [30] YUE K, TRUJILLO-DE SANTIAGO G, ALVAREZ MM, et al. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2015;73:254-271. [31] VISSER J, GAWLITTA D, BENDERS KE, et al. Endochondral bone formation in gelatin methacrylamide hydrogel with embedded cartilage-derived matrix particles. Biomaterials. 2015;37:174-182. [32] GU L, LI T, SONG X, et al. Preparation and characterization of methacrylated gelatin/bacterial cellulose composite hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Regen Biomater. 2020;7(2):195-202. [33] FRANTZ C, STEWART KM, WEAVER VM. The extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 24):4195-4200. [34] FERNANDES H, MORONI L, VAN BLITTERSWIJK C, et al. Extracellular matrix and tissue engineering applications. J Mater Chem. 2009;19(31):5474-5484. [35] LIU Y, CHAN-PARK MB. A biomimetic hydrogel based on methacrylated dextran-graft-lysine and gelatin for 3D smooth muscle cell culture. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6):1158-1170. |
| [1] | Tan Xinfang, Guo Yanxing, Qin Xiaofei, Zhang Binqing, Zhao Dongliang, Pan Kunkun, Li Yuzhuo, Chen Haoyu. Effect of uniaxial fatigue exercise on patellofemoral cartilage injury in a rabbit [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-6. |
| [2] | Yao Xiaoling, Peng Jiancheng, Xu Yuerong, Yang Zhidong, Zhang Shuncong. Variable-angle zero-notch anterior interbody fusion system in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy: 30-month follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(9): 1377-1382. |
| [3] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [4] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [5] | Wu Cong, Jia Quanzhong, Liu Lun. Relationship between transforming growth factor beta1 expression and chondrocyte migration in adult articular cartilage after fragmentation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1167-1172. |
| [6] | An Weizheng, He Xiao, Ren Shuai, Liu Jianyu. Potential of muscle-derived stem cells in peripheral nerve regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [7] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [8] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [9] | Zhang Jinglin, Leng Min, Zhu Boheng, Wang Hong. Mechanism and application of stem cell-derived exosomes in promoting diabetic wound healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1113-1118. |
| [10] | Hu Wei, Xie Xingqi, Tu Guanjun. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improve the integrity of the blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [11] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [12] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [13] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [14] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [15] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||