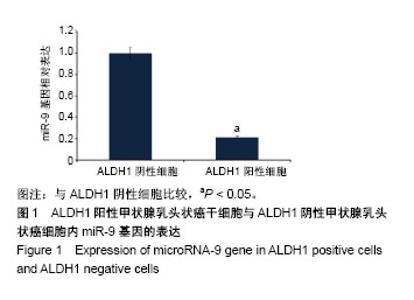
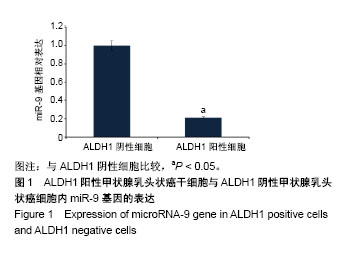
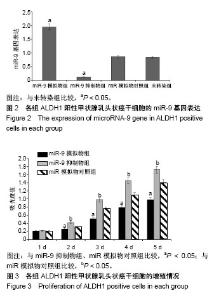
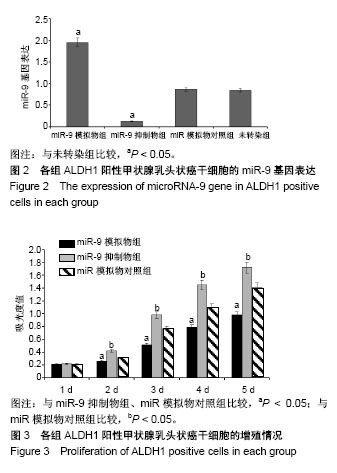
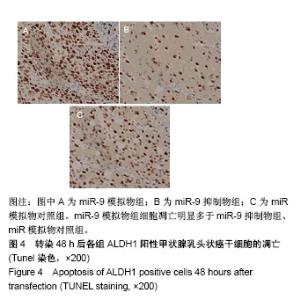
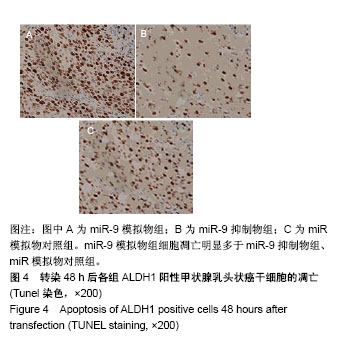
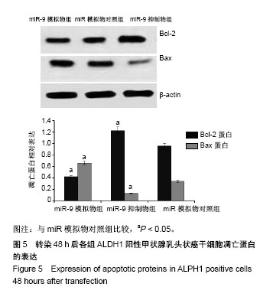
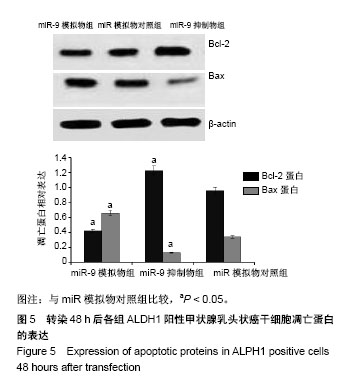
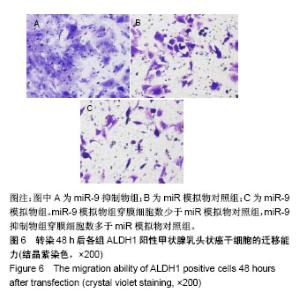
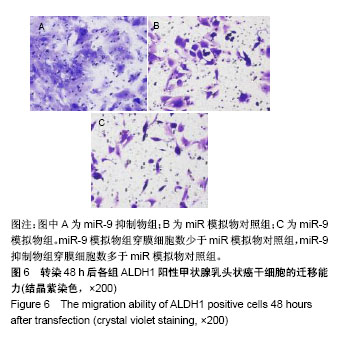
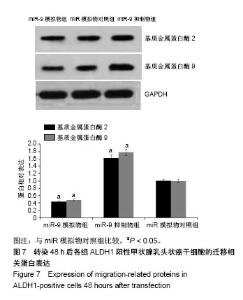
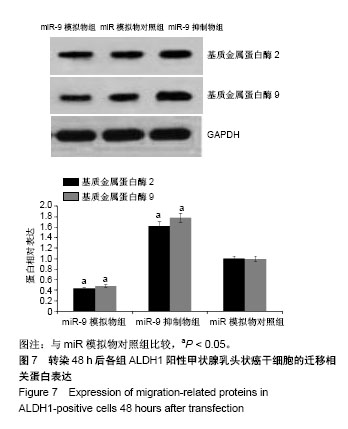
| [1] Xue S, Wang P, Hurst ZA, et al. Active Surveillance for Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: Challenges and Prospects. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018;9:736.[2] Cokmez H, Gulbahar A, Yigit S, et al. Oncocytic and tall columnar type papillary thyroid carcinoma arising on a mature cystic teratoma: A case report and literature review. J Pak Med Assoc. 2019;69(1):116-119.[3] Kuo EJ, Thi WJ, Zheng F, et al. Individualizing Surgery in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma Based on a Detailed Sonographic Assessment of Extrathyroidal Extension. Thyroid. 2017;27(12):1544-1549.[4] Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):203-222.[5] Kim D, Chang HR, Baek D. Rules for functional microRNA targeting. BMB Rep. 2017;50(11):554-559.[6] 刘雯,沙银中,李亚东.循环microRNA在常见肿瘤中的应用研究进展[J].国际检验医学杂志,2018,39(16):1950-1954.[7] Xie H, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, et al. MiR-9 Regulates the Expression of BACE1 in Dementia Induced by Chronic Brain Hypoperfusion in Rats. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(3): 1213-1226.[8] 李晓琳,胡雪玲,孙丽华. 微小 RNA-9在癌症及神经退行性疾病中的研究现状[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2015,31(4): 315-316, 320.[9] 杨珏,宋辉,吕小波,等. MicroRNA-9调控乳腺癌细胞转移机制的研究[J].药物生物技术,2014,21(4):306-310.[10] 木扎帕尔•阿不都克热木,杨乐,孙刚,等.微小RNA-9对乳腺癌细胞MCF-7增殖与转移能力的影响及其机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2016,33(10):2338-2340.[11] 郭伟逢,周波,马丁,等.miR-9通过E-cadherin/snail1信号途径促进卵巢癌细胞侵袭与转移的研究[J].中国妇幼保健, 2015, 30(22):3891-3893.[12] 周波,孙朝阳,夏萌,等.miR-9在卵巢癌细胞上皮间质转化中的初步研究[J].现代生物医学进展, 2016,16(31):6001-6004,6009.[13] Lu MH, Huang CC, Pan MR, et al. Prospero homeobox 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells by inhibiting E-cadherin via miR-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(23):6416-6425.[14] 刘文明,范燕云,田钊旭,等.MiR-9对人胃癌细胞增殖和迁移的影响[J].胃肠病学,2018,23(6):342-346.[15] 宋皓军,周为东,丁小云.miR-9的表达异常对胃癌上皮间质转化的影响[J].现代实用医学,2016,28(7):851-853,封3.[16] 南寿山,王珏磊.MicroRNA-9通过NRP1抑制胃癌SGC-7901细胞上皮-间充质转化功能[J].中国病理生理杂志,2017,33(7): 1191-1195.[17] 罗花南,马思敬,易春曦,等.miR-9过表达对鼻咽癌细胞迁移和侵袭的影响[J].陕西医学杂志,2017,46(10):1332-1334.[18] 郑朝攀,韩灵,侯伟坚,等.负向调控miR-9抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭[J].中国病理生理杂志,2014,30(4): 640-644.[19] 李锋.经典型霍奇金淋巴瘤细胞CD99、miR-9与NF-κB信号通路调控机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2011.[20] Kiani S, Akhavan-Niaki H, Fattahi S, et al. Purified sulforaphane from broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica) leads to alterations of CDX1 and CDX2 expression and changes in miR-9 and miR-326 levels in human gastric cancer cells. Gene. 2018;678:115-123.[21] Lu J, Liu QH, Wang F, et al. Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):147.[22] Khosravi A, Alizadeh S, Jalili A, et al. The impact of Mir-9 regulation in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Oncol Rev. 2018;12(1):348.[23] Nowek K, Wiemer EAC, Jongen-Lavrencic M. The versatile nature of miR-9/9* in human cancer. Oncotarget. 2018; 9(29):20838-20854.[24] 靖林林,姚学清,符秀琼,等.肿瘤干细胞及其niche的中医属性及发生病机[J].南京中医药大学学报, 2018,34(2):214-216.[25] 秦越,丁宁,陈艺,等.肿瘤微环境与肿瘤演进作用的研究进展及展望[J].临床普外科电子杂志,2018,6(1):37-40.[26] 岳常丽,赵晓丽,田澄,等.甲状腺乳头状癌 ALDH1A1表达与淋巴结转移的相关性[J].中华病理学杂志, 2015,44(7): 490-494.[27] 郝博,高小玲,贺红. MicroRNA-9对口腔鳞状细胞癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2017,16(18):1779-1783.[28] 艾晓兰,姚芳,王晓睛,等.同种异体移植物炎症因子-1在结直肠癌细胞增殖、迁移及凋亡中的作用[J].南方医科大学学报,2018, 38(5):511-519.[29] 向利军,贺翊峰,鲁才杰,等.siRNA干扰Notchl诱导肝癌细胞凋亡的机制研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2018,38(3):284-288.[30] Xu J, Koizumi K, Liu M, et al. Shikonin induces an anti?tumor effect on murine mammary cancer via p38?dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):2020-2026.[31] 王公平,周博,金灿辉,等.微小RNA-9对胃癌细胞SGC-7901增殖及凋亡的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2015,32(8):1899-1901.[32] 蔡坤,喻超,田舍,等. TRIM31沉默抑制胰腺癌侵袭和迁移[J].贵州医科大学学报,2018,43(8):869-873.[33] 张达容,王维莲,吴立翔,等. Twist促进人三阴性乳腺癌细胞迁移和侵袭[J].基础医学与临床,2018,38(6):771-775.[34] Srinivasan M, Bharali DJ, Sudha T, et al. Downregulation of Bmi1 in breast cancer stem cells suppresses tumor growth and proliferation. Oncotarget. 2017;8(24):38731-38742.[35] Huang L, Xu C, Xu P, et al. Intelligent Photosensitive Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cell-Derived Microvesicles for Photothermal Therapy of Prostate Cancer. Nanotheranostics. 2018;3(1):41-53. |