Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (21): 3410-3417.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1748
Previous Articles Next Articles
Interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit expression of type II collagen in nucleus pulposus cells
Liang Weidong, Ren Zhouliang, Sheng Jun, Cao Rui, Sheng Weibin
- Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Revised:2019-02-12Online:2019-07-28Published:2019-07-28 -
Contact:Sheng Weibin, MD, Chief physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Liang Weidong, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Ren Zhouliang, Master, physician, Department of Spinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Liang Weidong and Ren Zhouliang contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Institutional Research Fund Project of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, No. 20152RQN05 (to LWD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Weidong, Ren Zhouliang, Sheng Jun, Cao Rui, Sheng Weibin. Interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibit expression of type II collagen in nucleus pulposus cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(21): 3410-3417.
share this article
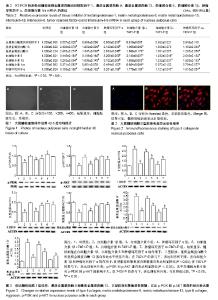
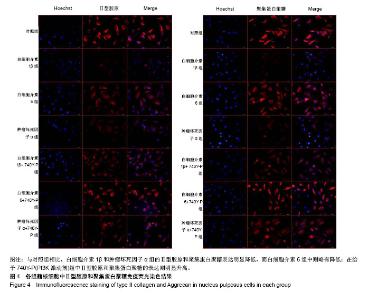
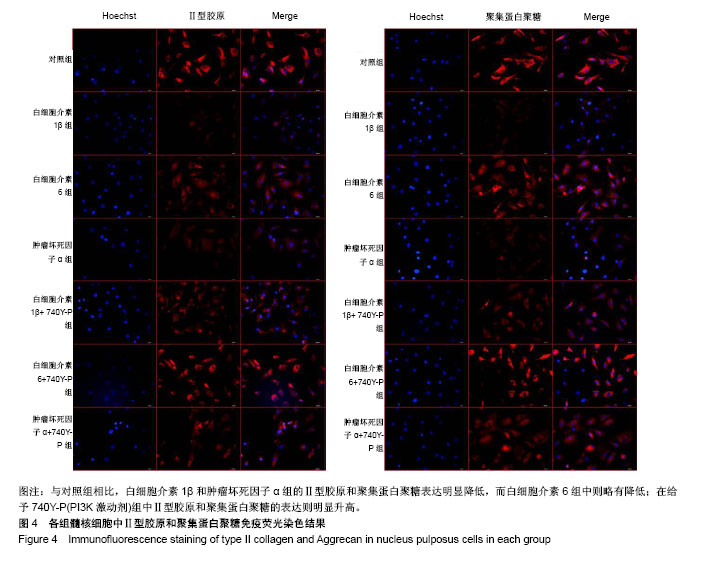
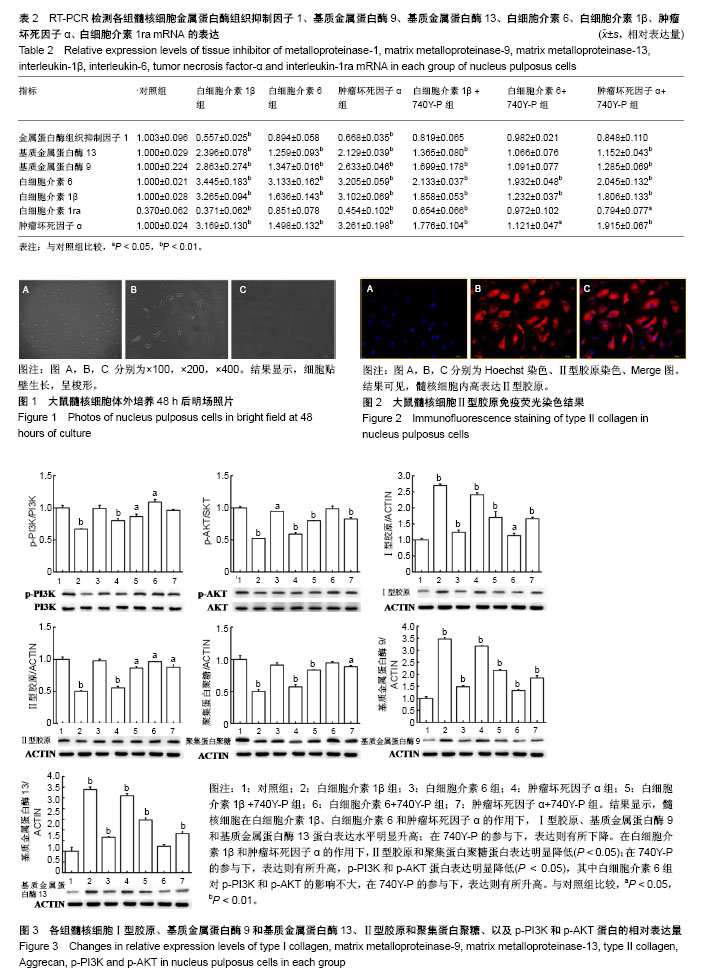
2.1 髓核细胞分离、培养及鉴定结果 椎间盘组织中分离培养存在一定数量髓核细胞,经原代消化,48 h后细胞贴壁生长,呈梭形,见图1。Ⅱ型胶原免疫荧光染色显示:分离得到的髓核细胞高表达Ⅱ型胶原,见图2。 2.2 RT-PCR检测各组髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶、金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子、炎性因子的mRNA表达 结果显示,白细胞介素1β组和肿瘤坏死因子α组中金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1 mRNA表达量明显低于对照组(P < 0.05),白细胞介素1β+740Y-P组和肿瘤坏死因子α+740Y-P组分别高于白细胞介素1β组与肿瘤坏死因子α组。说明在白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,髓核细胞中金属蛋白酶组织抑制因子1 mRNA表达水平明显下降,在740Y-P(PI3K激活剂)的参与下,表达则升高。见表2。 白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α组中基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA表达量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),白细胞介素1β+740Y-P组、白细胞介素6+740Y-P组和肿瘤坏死因子α组+740Y-P组分别低于白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α组。说明髓核细胞在白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,髓核细胞中基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶13 mRNA表达水平明显升高,其中白细胞介素6作用组升高的幅度较小,在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所下降,见表2。 所有实验干预组中白细胞介素6 mRNA表达量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),且白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α组分别高于白细胞介素1β+740Y-P组、白细胞介素6+740Y-P组和肿瘤坏死因子α组+740Y-P组。说明在白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,髓核细胞中白细胞介素6 mRNA表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05),在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所下降。 白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α组中白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达量明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),且分别低于白细胞介素1β+740Y-P组、白细胞介素6+740Y-P组和肿瘤坏死因子α组+740Y-P组,说明在白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,髓核细胞中白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达水平明显升高,其中白细胞介素6作用组升高的幅度较小,在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所下降。 白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α组中白细胞介素1ra表达量明显低于对照组(P < 0.05),分别低于白细胞介素1β+740Y-P组和肿瘤坏死因子α组+740Y-P组,说明在白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,髓核细胞中白细胞介素1ra mRNA的表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所升高,而白细胞介素6作用组无明显变化。 2.3 Western Blot检测各组髓核细胞中Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白、聚集蛋白聚糖蛋白及PI3K/AKT信号通路蛋白的表达 结果显示,髓核细胞在白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,Ⅰ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶9和基质金属蛋白酶13蛋白表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05),其中白细胞介素6作用组升高的幅度较小,在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所下降。在白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α的作用下,Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),其中白细胞介素6组无明显影响,在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所升高,p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白表达水平明显降低(P < 0.05),其中白细胞介素6组对p-PI3K和p-AKT的影响不大,在740Y-P的参与下,表达则有所升高。见图3。 2.4 细胞免疫荧光观察各组髓核细胞中Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达 与对照组相比,白细胞介素1β和肿瘤坏死因子α组的Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖表达明显降低,而白细胞介素6组中则略有降低;与白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α组相比,在给予740Y-P(PI3K激动剂)组中Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达则明显升高,见图4。说明激活PI3K/AKT增殖通路可促进髓核细胞Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达。"
| [1] McCarron RF,Wimpee MW,Hudkins PG et al. The inflammatory effect of nucleus pulposus. A possible element in the pathogenesis of low-back pain. Spine.1987;12(8):760-764.[2] Kalichman L,Hunter DJ. The genetics of intervertebral disc degeneration: Familial predisposition and heritability estimation.Joint Bone Spine.2008;75:383-387.[3] Masuda K. Biological repair of the degenerated intervertebral disc by the injection of growth factors. Eur Spine J. 2008; 17(Suppl 4): 441-451. [4] Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, et al. Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(7): 1974-1982. [5] Studer RK,Vo N,Sowa G, et al. Human nucleus pulposus cells react to IL-6: independent actions and amplification of response to IL-1 and TNF-α. Spine. 2011; 36(8):593-599.[6] Scheller J, Garbers C, Rose-John S. Interleukin-6: From basic biology to selective blockade of pro-inflammatory activities. Semin Immunol. 2013;11:002.[7] Shen Jieliang,Xu Shengxi,Zhou Hao et al. IL-1β induces apoptosis and autophagy via mitochondria pathway in human degenerative nucleus pulposus cells. Sci Rep.2017; 7: 41067.[8] Studer RK,Gilbertson LG,Georgescu H, et al. p38 MAPK inhibition modulates rabbit nucleus pulposus cell response to IL-1. Orthop. Res. 2008; 26(7): 991-998.[9] Mwale F,Wang HT,Zukor DJ et al. Effect of a Type II Collagen Fragment on the Expression of Genes of the Extracellular Matrix in Cells of the Intervertebral Disc. Open Orthop J. 2008;2:1-9.[10] Gorth DJ, Mauck RL, Chiaro JA, et al. IL-1ra delivered from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres attenuates IL-1β-mediated degradation of nucleus pulposus in vitro. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(4): R179.[11] Cuéllar JM, Borges PM, Cuéllar VG, et al. Cytokine expression in the epidural space: a model of noncompressive disc herniation-induced inflammation. Spine. 2013; 38(1): 17-23.[12] Studer RK, Aboka AM, et al. p38 MAPK inhibition in nucleus pulposus cells: a potential target for treating intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2007; 32(25): 2827-2833.[13] Freemont AJ.The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2009;48(1):5-10. [14] Vergroesen PP,Kingma I,Emanuel KS,et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration:a vicious circle. Osteoarthri- tis Cartilage.2015;23(7):1057-1070. [15] Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 Collaborators. Global,region al,and national incidence,prevalence,and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries,1990-2013:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(9995):743-800. [16] Willems N, Tellegen AR, Bergknut N, et al. Inflammatory profiles in canine intervertebral disc degeneration. BMC Vet. Res.2016;12:10.[17] Gu SX, Li X, Hamilton JL, et al. MicroRNA-146a reduces IL-1 dependent inflammatory responses in the intervertebral disc. Gene. 2015; 555(2): 80-87.[18] Zhou T, Lin H, Cheng Z, et al. Mechanism of microRNA-146a- mediated IL-6/STAT3 signaling in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(2): 1131-1135.[19] Yang H, Gao F, Li X, et al. TGF-β1 antagonizes TNF-α induced up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 3 in nucleus pulposus cells: role of the ERK1/2 pathway. Connect. Tissue Res. 2015;56(6): 461-468. [20] Freemont AJ. Keep up the heat on IL-l. Blood. 2012; 120(13): 2538-2539.[21] Croker BA, Kiu H,Roberts AW.IL-6 promotes acute and chronic inflammatory disease in the absence of SOCS3.Immunol Cell Biol. 2012;90 (1):124-129.[22] Hiyama A, Yokoyama K, Nukaga T,et al. A complex interaction between Wnt signaling and TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(6): R189.[23] Holm S,Mackiewicz Z,Holm AK et al. Pro-inflammatory, pleiotropic, and anti-inflammatory TNF-alpha, IL-6, and IL-10 in experimental porcine intervertebral disk degeneration.Vet. Pathol. 2009; 46(6): 1292-300.[24] Kim HJ, Yeom JS, Koh YG, et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of platelet-rich plasma on nucleus pulposus cells with response of TNF-α and IL-1. Orthop. Res.2014; 32(4): 551-556.[25] Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007; 9(4): R77.[26] Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ. Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNF alpha expression profile. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R77. [27] Jiang L,Zhang X,Zheng X,et al. Apoptosis,senescence,and autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus cells:implications for diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013; 31(5): 692-702. [28] Chen ZH,Jin SH,Wang MY,et al. Enhanced NLRP3,caspase 1, and IL 1β levels in degenerate human intervertebral disc and their association with the grades of discdegeneration. Anat Rec(Hoboken).2015;298(4):720-726.[29] Yang W,Yu XH,Wang C, et al. Interleukin-1β in intervertebral disk degeneration.Clin Chim Acta. 2015; 450: 262-272.[30] Phillips KL,Jordan Mahy N,Nicklin MJ,et al. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist deficient mice provide insights into pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis.2013;72(11):1860-1907. [31] Gruber HE,Hoelscher GL,Ingram JA,et al. Increased IL 17 expression in degenerated human discs and increased production in cultured annulus cells exposed to IL 1β and TNF α. Biotech Histochem.2013;88(6):302-310. [32] Cai F,Zhu L,Wang F, et al. The Paracrine Effect of Degenerated Disc Cells on Healthy Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells Is Mediated by MAPK and NF-κB Pathways and Can Be Reduced by TGF-β1.DNA Cell Biol. 2017; 36: 143-158.[33] Wang C,Yu XH,Yan Y, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α: a key contributor to intervertebral disc degeneration.Acta Biochim. Biophys Sin. 2017;49:1-13.[34] Cornejo MC,Cho SK,Giannarelli C,et al. Soluble factors from the notochordal rich intervertebral disc inhibit endothelial cell inva- sion and vessel formation in the presenceand absence of pro inflammatory cytokines. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23 (3):487 - 496. [35] Yang H, Liu H, Li X, et al. TNF-α and TGF-β1 regulate Syndecan-4 expression in nucleus pulposus cells: role of the mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB pathways.Connect Tissue Res.2015; 56: 281-287.[36] Wang WJ, Yu XH, Wang C, et al.MMPs and ADAMTSs in intervertebral disc degeneration.Clin Chim Acta. 2015; 448: 238-246.[37] Walter BA,Likhitpanichkul M,Illien Junger S,et al.TNF-α transport induced by dynamic loading alters biomechanics of intact intervertebral discs. PLoS One.2015;10(3):e0118358. |
| [1] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [2] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [3] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [4] | Fu Yuanfei, He Shenghua, Lai Juyi, Sun Zhitao, Feng Hualong, Lan Zhiming . Pheretima extract ameliorates nucleus pulposus cell degeneration in the intervertebral disc by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 264-268. |
| [5] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [6] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [7] | He Shenghua, Fu Yuanfei, Lan Zhiming, Sun Zhitao, Lai Juyi, Feng Hualong, Guo Zibin, Li Gai . Yaotu Granule deals with the proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via regulating the expression of microRNA-221 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2177-2182. |
| [8] | Liu Zhigang, Guo Qinggong, Chen Jingtao. Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1699-1704. |
| [9] | Cheng Bingkun, Liang Jianfei, Qin Dongze, Cheng Zixu, Zhao Yunzhuan. Isolation, culture and biological characteristics of high-purity orofacial-bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells of the rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 67-72. |
| [10] | Chen Jiang, Xiao Huideng, Sun Qi, Zhang Fan, Zhu Yonggang, Liu Zhichao, Guo Feiyu, Liu Genzhe. Proliferative activity of nucleus pulposus cells in human intervertebral disc and intervention with Yishen Huoxue Tongluo Recipe [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1200-1206. |
| [11] | Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715. |
| [12] | Xiao Lei, Hou Ligang. Effect of glucosamine capsule on cartilage metabolism-related genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5007-5012. |
| [13] | Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |
| [14] | Yin Xunlu, Zhu Liguo, Feng Minshan, Yu Jie, Zhan Jiawen, Liang Long, Han Tao. Effect of continuous loading pressure on apoptosis and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in nucleus pulposus cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4125-4128. |
| [15] | Yang Fan, Liu Baoyi, Cao Meng, Zhu Xiaoshu, Zhang Yu, Qin Kairong, Zhao Dewei. Basic fibroblast growth factors protect chondrocytes by antagonizing extracellular inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3621-3626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||