Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 408-415.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2415
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Song Shilei1, Chen Yueping2, Zhang Xiaoyun2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Traumatic Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2019-04-20Revised:2019-04-29Accepted:2019-06-22Online:2020-01-28Published:2019-12-26 -
Contact:Chen Yueping, MD, Master’s supervisor, Chief physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China Zhang Xiaoyun, Master, Attending physician, Department of Traumatic Orthopedics and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Song Shilei, Master candidate, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796; the Basic Competence Promotion Project for Young Teachers in Universities and Colleges in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2019KY0352; the Basic Competence Promotion Project for Young Teachers in Universities and Colleges in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. KY2016YB204; the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. 2015GXNSFAA139136; the Key Program of Health Department of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, No. S201419-05
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Shilei, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun. Mechanism of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway regulating osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 408-415.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
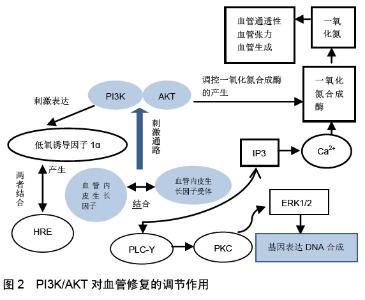
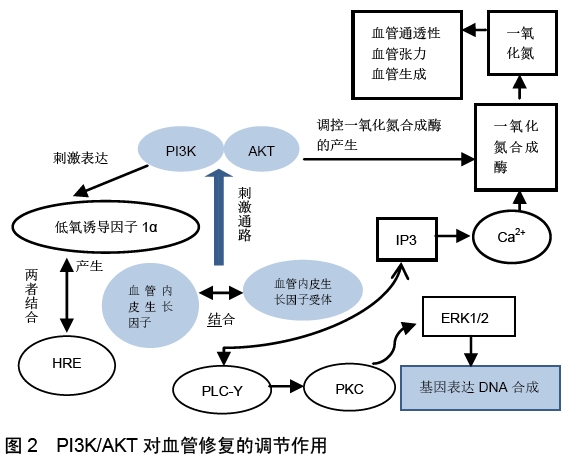
2.1 PI3K/AKT信号通路通过调控血管再生因素影响股骨头坏死 血管损伤或破坏致股骨头周围血运障碍是造成股骨头坏死发生的主要原因,因此通过相关机制调控血管修复与再生对早期截断股骨头坏死病情发展具有可能性。目前研究证实血管内皮生长因子、缺氧诱导因子、一氧化氮、血管生成素等是血管再生及修复中的关键因素,随着研究的深入,发现PI3K/AKT信号通路可对这些因子进行调控[13]。其中血管内皮生长因子是一种多肽蛋白,需与特定的酪氨酸激酶受体结合(血管内皮生长因子受体1、血管内皮生长因子受体2)刺激多种信号通路从而发挥促进内皮细胞增殖迁移,当血管内皮生长因子与其受体结合后,该受体发生酪氨酸磷酸化,致使PLCγ也发生磷酸化从而刺激IP3/Ca2+与DG/PKC信号通路与P38MARK信号通路,刺激钙离子与蛋白增加使得内皮细胞的增殖和刺激MARK蛋白活化激酶等使得内皮细胞中肌动蛋白的重塑实现细胞迁移,释放一氧化氮增加血管通透性等功能,因此血管内皮生长因子及其受体为促进血管修复的重要信号分子[14-15]。目前研究对血管内皮生长因子的调控主要信号因子包括上皮细胞膜蛋白2、miRNA亚型、PDCL3、PI3K/AKT等,其中PI3K/AKT可刺激下游多种蛋白对血管内皮生长因子的分泌产生影响,如:①PI3K/AKT/HIF-1α信号通路,当PI3K/AKT被激活后,可促进低氧诱导因子1α的表达,在股骨头坏死的低氧环境下,低氧诱导因子1α与缺氧反应元件结合后致使血管内皮生长因子的生成及表达增加,刺激血管内皮的新生[16]。ZHANG等[17]的研究证实在低氧条件下软骨细胞中的低氧诱导因子α和血管内皮生长因子的表达均升高,并且体外实验发现当使用低氧诱导因子α激活剂Deferoxamine(DFO)较对照组显示软骨细胞中血管内皮生长因子分泌明显增加。另有大鼠实验发现通过抑制低氧诱导因子α基因表达和蛋白质合成可降低血管内皮生长因子的生成从而阻碍血管的新生,降低癌症发生率[18],这说明PI3K/AKT可通过调控低氧诱导因子α从而介导对血管内皮生长因子的影响,这一结论在ZENG等[19]的人参皂苷Rg3实验中得到证实:当使用Rg3剂量20,40,60,80,100 mg/L分别放置 6,12,24,48 h,与对照组在AKT、ERK1/2与低氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子在培养皿的含量比较发现,当骨髓间充质干细胞中AKT与ERK1/2的表达受到抑制的同时,低氧诱导因子1α/血管内皮生长因子的表达水平亦呈现下降,而这种对比在40 mg/L处理24 h表现较为明显,但是该实验未将骨髓间充质干细胞中ERK1/2去除对比,所以单纯认为是PI3K/AKT的影响并不严谨,而另有研究表明当细胞内无低氧诱导因子活性仅有AKT活性时,血管内皮生长因子转录因子水平依然有明显提升[20],这提示PI3K/AKT也可直接诱导血管内皮生长因子的生成与表达,因此目前缺乏直接证实PI3K/AKT/HIF对血管内皮生长因子影响的实验,这可成为今后的研究方向;②PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路是细胞增殖、存活、血管新生和肿瘤生长的重要途径[21-22],但该通路对血管内皮生长因子的影响机制尚不明确,但YANG等[23]在研究药品DEK与乳腺癌的实验中发现,运用AKT抑制剂LY290042与mTOR抑制剂雷帕霉素后血管内皮生长因子的分泌有所下降,认为DEK在刺激活化PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路后可使得C6的表达增加从而刺激了血管内皮生长因子的分泌与表达,这与YIN 等[24]和TSAI等[25]得出的PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路可促进血管内皮生长因子分泌上调的结论相一致,但仍缺乏更多的实验研究证实。通过PI3K/AKT信号调控血管内皮生长因子而促进股骨头血管修复可为营养骨细胞提供必要的场所,而血管通透性是决定营养物质交换效率的关键。一氧化氮具有舒张血管与增加血管通透性的作用,一氧化氮的产生与表达受到血管内皮生长因子与PI3K/AKT的正向双调节。一氧化氮可经血管内皮生长因子与其受体结合后产生,也可通过一氧化氮合成酶催化后产生,而AKT可对一氧化氮合成酶上Ser1177进行磷酸化,在调控一氧化氮产生的同时还促进血管内皮细胞迁移[26]。在尹香琳等[27]的实验中发现当流感病毒感染小鼠4-6 h期间,小鼠肺组织中PI3K下游靶点AKT磷酸化水平与一氧化氮合成酶酶含量变化成正比,这与AHMAD等[28]和王雅婧等[29]的实验结果相似,这证实PI3K/AKT/eNOS信号通路可对一氧化氮进行有效调控。综上,虽然PI3K/AKT信号通路通过加强血管内皮生长因子及一氧化氮的分泌对改善股骨头周围血运状况具有可能性,但由于动物实验及临床试验缺乏更多有价值的研究,目前仍停留于早期探索阶段,但是改善股骨头周围血运是治疗股骨头坏死的关键,值得开展更多的研究去探索,并且作者认为调控血管修复的相关因素存在相互联系,如当PI3K/AKT调控低氧诱导因子刺激血管内皮生长因子时,血管内皮生长因子的增殖又刺激一氧化氮的分泌,而一氧化氮的产生及表达也受到了PI3K/AKT的调控,见图2,这说明PI3K/AKT信号通路对改善血管修复再生与血运恢复的作用特点有2种,即渐进式与推进式,这对恢复血供具有积极意义。 "
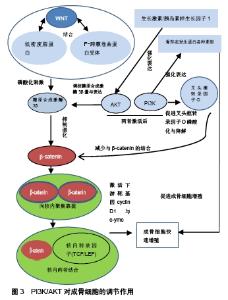
2.2 PI3K/AKT信号通路对多条信号调控进而影响成骨细胞分化 股骨头局部骨质疏松是造成股骨头坏死进一步发展的另一个因素,破骨细胞与成骨细胞之间代谢失衡不仅易造成股骨头塌陷,还对患者术后恢复有不利的影响。引起股骨头局部骨质疏松的因素有很多,其中乙醇的过量使用与激素失衡是造成股骨头坏死的主要原因。成骨细胞是由骨髓基质的间质细胞分化而来,其主要功能是合成和分泌骨基质量,转化为骨细胞从而保持骨的性质,因此促进成骨细胞的增殖与延缓成骨细胞的凋亡是解决骨质疏松的重要途径。目前影响成骨细胞分化与凋亡的信号通路主要有Wnt/β-catenin通路、PI3K/AKT通路、Runx2基因、骨形态发生蛋白等。先前的研究已证实PI3K/AKT信号的增强可以引起成骨细胞增殖、延缓其凋亡时间,这对治疗骨质疏松极为有利[30],但是否有其他因素参与成骨细胞分化是争论的要点,有研究认为PI3K/AKT通路可调控Wnt/β-catenin通路、骨形态发生蛋白与叉头框转录因子O信号通路等影响成骨细胞的分化凋亡,见图3。因此作者通过以下3点论述认为PI3K/AKT在自身调控成骨细胞分化增殖的同时,也可影响其他通路或因子加强这种调控。"
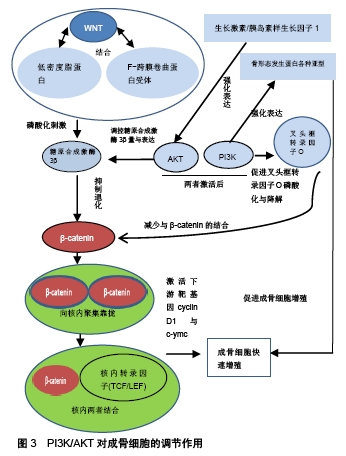
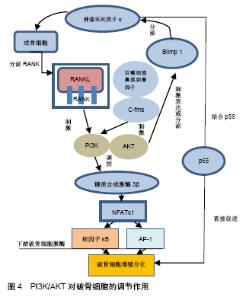
2.2.1 PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β对Wnt/β-catenin调控影响成骨细胞分化及凋亡 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路拥有调控成骨分化能力,在骨形成及吸收过程中都发挥着关键的作用,受到广大研究人员的推崇[31]。经典Wnt信号通路主要在细胞膜上通过与低密度脂蛋白供受体家族成员——细胞膜上供受体(LRP5/6)以及F-跨膜卷曲蛋白受体结合,促进糖原合成激酶3β磷酸化,抑制β-catenin退化,进而激活Wnt/β-catenin通路,使β-catenin蛋白因子大量聚集并移向核内,与核内转录因子(TCF/LEF)结合,激活成骨细胞核内下游靶基因cyclin-D1与c-ymc从而使成骨细胞增值加速,由此可见有糖原合成激酶3β的活化与β-catenin含量对于整个信号通路来说是最为关键的。而糖原合成激酶3β是PI3K/AKT的下游激酶,当PI3K/AKT信号通路被激活后,会使 Thr308和Ser473充分暴露,以供磷酸肌醇的蛋白激酶进行随后的磷酸化,通过磷酸化调节下游表达,当糖原合成激酶3β被大量激活时可增强Wnt/β-catenin通路成骨分化的能力[32-34]。HU等[35]在淫羊藿苷预防糖皮质激素诱导的骨质疏松症的研究中认为PI3K/AKT通路与Wnt/β-catenin通路这2种途径可通过糖原合成激酶3β的磷酸化状态相互连接,当使用淫羊藿苷(剂量为10-9,10-8,10-7,10-6 mol/L)分别刺激PI3K、AKT、糖原合成激酶3β时,三者含量上升趋势接近,其中糖原合成激酶3β涨幅最高,且β-catenin含量也在提高,而在地塞米松时四者下降幅度相似,这不仅表明淫羊藿苷可引导糖原合成激酶3β磷酸化,也证实PI3K、AKT、糖原合成激酶3β三者的正比关系,并且证明PI3K/AKT可通过调控糖原合成激酶3β影响Wnt/β-catenin加强成骨分化具有可能性,但类似研究缺乏,急需更多有价值的数据证实。糖原合成激酶3β磷酸化表达水平并不是越高越有利于成骨分化,有研究证实高水平的糖原合成激酶3β会抑制干细胞在股骨头坏死中的成骨分化,并造成β-catenin的减少[36],并且在大鼠关节炎模型的建立中发现过多糖原合成激酶3β磷酸化表达可加快成骨细胞的凋亡[37]。因此PI3K/AKT在自身促进成骨细胞增殖的同时,也可通过糖原合成激酶3β实现与Wnt/β-catenin的链接从而加强成骨细胞的分化增殖,但需对把控糖原合成激酶3β磷酸化含量引起重视。 2.2.2 PI3K/AKT通路介导骨形态发生蛋白多种亚型对成骨细胞的分化增殖 骨形态发生蛋白作为自分泌和旁分泌骨诱导因子,主要参与骨的形成和修复,其机制主要通过与Ⅰ型(ALK1至ALK-7)和Ⅱ型(骨形态发生蛋白受体Ⅰ、ActRIA、ActRIIA)Ser/Thr激酶受体结合,激活细胞内信号分子从而触发Smad-1/5/8和MAPK等信号级联,引起成骨细胞分化[38-40]。其中骨形态发生蛋白2、骨形态发生蛋白4、骨形态发生蛋白7和骨形态发生蛋白9作为不同骨形态发生蛋白的亚家族成员,在促进成骨细胞分化上机制有所不同,但共同点是都可通过PI3K/AKT信号通路加强对成骨细胞的分化增殖[41-42],如有研究认为骨形态发生蛋白7可由PI3k/AKT/GSK-3β通路调节从而抑制地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞MLO-Y4凋亡[43],而在FURUE等[44]的研究数据表明PI3K/AKT通路参与骨形态发生蛋白9刺激的成骨分化和在成骨培养基中培养的牙周膜成纤维细胞中基质细胞衍生因子1的产生,但目前关于PI3K/AKT调控这2个骨形态发生蛋白对刺激成骨细胞分化的研究数据较少,且停留于体外实验,无更多有价值的数据。而近年PI3K/AKT信号通路通过调控骨形态发生蛋白2影响成骨细胞分化的研究相比于其余骨形态发生蛋白亚型较多,主要原因是PI3K/AKT通过骨形态发生蛋白2对成骨细胞分化具有双向调节功能。有研究发现,当AKT被激活时,可加快骨形态发生蛋白2介导的小鼠基质细胞向成骨细胞分化速度[45],且PI3K/KT信号通路可促进骨形态发生蛋白介导的MAPK(ERK-1/2)和Smad-1/5/8通路的激活[46]。而另有研究认为,AKT抑制活化的Smad-1和Smad-5在细胞核聚集,从而阻断骨形态发生蛋白2调控的成骨分化功能[47],其主要造成2种结果的原因可能在于实验中使用PI3K/AKT抑制剂或激活剂含量不同,引起骨形态发生蛋白2激活水平上调,但尚未研究证实该观点,并且今后关于这方面的实验可能实现对骨形态发生蛋白2体内水平的调控,这具有更高的临床意义。由此可见PI3K/AKT通路对骨形态发生蛋白的各种亚型都有一定的调节作用,但研究数据不足是影响PI3K/AKT/BMPS对成骨细胞分化进一步研究最大的阻碍,但少许体外及动物实验已对此有前瞻性的研究,是今后可以深入发掘的方向。 2.2.3 PI3K/AKT通路对其他影响成骨细胞增殖分化因子的调控 PI3K/AKT可以参与调控 Wnt/β-catenin和骨形态发生蛋白这2个对成骨分化及成骨细胞凋亡有主要影响的信号通路之外,还有很多通路可被其影响从而对成骨分化产生作用,如叉头框转录因子O信号通路与GH/IGF-1轴等。其中AKT可磷酸化叉头框转录因子O的Thr-24,Ser-256和Ser-319位点,促进了叉头框转录因子O1,3a,4的细胞质聚集及降解,并使磷酸化后的叉头框转录因子O与衔接蛋白14-3-3结合,促进叉头框转录因子O向细胞质聚集,从而使叉头框转录因子O丧失活性的同时降低叉头框转录因子O竞争性的结合β-catenin,使β-catenin与TCF结合增多,促进Wnt信号通路与骨形成相关基因的表达[48-49],这结论在PI3K/AKT/FOXO在机械刺激下骨细胞信号转导的研究中得到证实,机械应力可通过PI3K/AKT磷酸化叉头框转录因子O早已被证实的情况下,运用机械应力作用于受ROS/FOXO抑制的Wnt/β- catenin通路发现Wnt/β-catenin水平提升明显,并推测通过PI3K/AKT/FOXO可改善刺激Wnt/β-catenin的成骨细胞分化功能,这一结论与前者相一致[50]。PI3K/AKT是激活生长激素/胰岛素样生长因子1的主要途径之一,促进成骨细胞增殖与发育,生长激素/胰岛素样生长因子1又可反过来激活PI3K/AKT促进成骨分化[51]。因此对于通过研究PI3K/AKT对成骨分化及成骨细胞凋亡的调控机制发现,无论是对于Wnt/β-catenin、骨形态发生蛋白通路还是其他通路,PI3K/AKT是这些通路发挥成骨细胞分化功能的重要中间环节,直接或间接这影响着这些通路子成骨细胞分化的功能,大部分介导的通路对改善骨质疏松具有积极意义,遗憾的是由于缺乏更多有价值的研究数据,部分研究目前只能停留在理论阶段,缺乏临床数据支持,因此做更多相关类研究去证实是今后发展的必经之路。 2.3 PI3K/AKT信号通路对破骨细胞的影响 破骨细胞为多核、形状不规则的由单核细胞融合形成的巨细胞,主要来源于造血组织,其功能为骨吸收。破骨细胞过多的增殖及表达是引起骨质疏松的另一个主要原因,目前对破骨细胞分化增殖可调控的主要信号通路有RANKL通路、肿瘤坏死因子α、microRNA/Pten通路等,而有研究发现PI3K/AKT可对这些通路进行调控,通过抑制破骨细胞增殖维持骨平衡,见图4。"
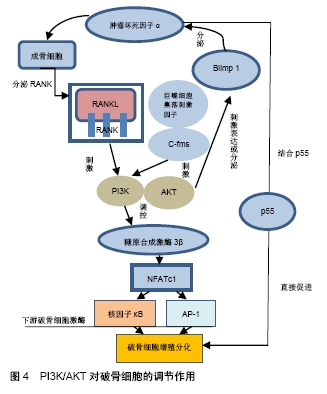

2.3.1 PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β/NFATc-1对RANKL调控影响破骨细胞分化增殖 破骨细胞的分化主要依赖2种关键的细胞因子:核因子受体激活因子B配体(κB配体)(RANKL)和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子。虽然两者是破骨细胞分化的不同影响因子,但两者存在着紧密的联系。巨噬细胞集落刺激因子可诱导骨髓单核细胞向破骨细胞分化增殖,并且可刺激细胞表面受体RANK的表达,使RANKL在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子作用下可在体外促进破骨细胞的发育[52]。当RANKL与受体结合后,下游信号包括核因子κB、JNK、p38 MAPK等会被激活诱导破骨细胞的分化,而c-fos、活化T细胞核因子1等可通过调控下游激酶包括核因子κB、p38 MAPK的表达对破骨细胞的分化造成影响。其中活化T细胞核因子1可通过激活核因子κB和AP-1诱导转录因子使RANKL在破骨细胞前体细胞的分化功能被上调,促进骨髓单核细胞对破骨细胞分化增殖,并且活化T细胞核因子1在前体中的异位表达,即使在RANKL不存在的情况下,也能有效诱导分化破骨细胞[53]。由此可见寻找相关通路抑制活化T细胞核因子1的表达对减弱破骨细胞分化具有重要意义,先前的研究已经证实PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β对活化T细胞核因子转录因子的活性有调节作用[54-56]。该通路机制主要为糖原合成激酶3β直接磷酸化活化T细胞核因子1在其核输出所必需的保守丝氨酸残基,并促进核出口,且糖原合成激酶3β又可通过ser-pro重复序列的磷酸化抑制活化T细胞核因子1与DNA结合的能力,从而抑制了活化T细胞核因子1基因的表达,而糖原合成激酶3β作用于AKT的下游,受其调控[57],由此可见PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β对活化T细胞核因子1的调节是双向的,并且引起双向的调节的主要原因可能在于糖原合成激酶3β的表达剂量,这与PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β在影响Wnt/β-catenin的成骨细胞分化时类似。在MOON等[58]的实验中发现运用不同剂量AKT对活化T细胞核因子1的影响不同,当AKT过多表达的破骨细胞中活化T细胞核因子1的诱导作用比对照载体感染的破骨细胞强,AKT的过多表达显著增加了活化T细胞核因子1和Oscar的表达,而在低的AKT激活剂时活化T细胞核因子1的表达受到抑制,并且在运用PI3K抑制剂LY-29400时,活化T细胞核因子1的表达减少,破骨细胞形成减少。这说明PI3K/AKT/ GSK-3β对活化T细胞核因子1的双向调节可能存在,但实验中未进一步确定多少剂量是引起活化T细胞核因子1的激活或抑制,这需要做更深入的探究。 2.3.2 PI3K/AKT/TNF-α调控B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1对破骨细胞形成的影响 肿瘤坏死因子α是肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族的成员,在细胞增殖、分化、多药耐药等多种细胞反应中起着重要的调节作用。已有研究证实,肿瘤坏死因子α的积累是造成骨质疏松的原因之一,它们可能通过促进破骨细胞增殖引起局部骨质破坏。其主要通过肿瘤坏死因子α诱导成骨细胞分泌RANKL,提高破骨细胞分化水平,并且肿瘤坏死因子α也可与其受体p55的结合直接作用于破骨细胞祖细胞,诱导破骨细胞的增殖[59]。然而,近年发现肿瘤坏死因子α可通过PI3K/Akt途径介导的B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1表达上调,促进破骨细胞形成[60]。B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1是一种转录抑制因子,在多种细胞的分化和功能中起着至关重要的作用。在大鼠实验结果表明当肿瘤坏死因子α通过加强激活PI3K/AKT信号通路而增加B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1的表达,而阻断PI3K/AKT通路可减轻肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1表达和破骨细胞形成,但是该研究忽略肿瘤坏死因子α本身的积累会造成破骨细胞的分化加强,并没有将肿瘤坏死因子α排除在实验基础外,并且目前暂无肿瘤坏死因子α对B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1诱导因子明确的作用机制,因此单纯的比较激活或抑制PI3K/AKT对B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1的影响,未排除肿瘤坏死因子α的作用,并不足以说明是肿瘤坏死因子α介导PI3K/Akt对B淋巴细胞诱导成熟蛋白1的调控对破骨细胞的分化增殖产生作用,这需要更多的证据支持。 2.3.3 PI3K/AKT通路通过microRNA/Pten通路对破骨细胞的分化与增殖双向调节 microRNA是是由22个核苷酸组成的小型非编码RNA,在破骨细胞分化过程中具有重要的转录后调控作用[61]。有研究发现microRNA的含量在巨噬细胞集落刺激因子和核因子RANKL诱导骨髓单核细胞形成破骨细胞过程中的被上调,且进一步发现miR-214的作用通过受Pten调控的PI3K/Akt途径实现。实验中破骨细胞特异性miR-214转基因小鼠pten水平较低,但破骨细胞活性增加从而降低了骨密度。Pten作为一种靶基因在RANKL诱导的破骨细胞分化中起着关键作用,但当microRNA上调时明显抑制了Pten的表达而抗microRNA抑制剂使用后Pten的水平明显上升,这说明microRNA可造成这Pten后诱导的AKT与活化T细胞核因子1的表达水平下降进而影响破骨分化,但后续的研究中发现PI3K抑制剂LY294002强烈下调miR-214诱导的Akt激活,抗miR-214和pi3k抑制剂又可阻断因RANKL与microRNA作用下上升的活化T细胞核因子1、Acp5、Clcn7、Mmp9等破骨细胞分化和活性标志物的基因水平[62]。这说明通过PI3K/Akt通路调节microRNA/Pten对破骨细胞的分化与增殖有利也有弊,所以一味的追求提高或抑制PI3K/Akt的水平解决破骨细胞的分化与过分表达是不可取的,但是通过上述对PI3K/AKT对影响破骨细胞相关机制的研究又为阻断股骨头坏死进展中骨质疏松的发生提供了新思路,但是解决方案仍需要通过多种研究实验提供。 "

| [1] AO W, MING R, JINCHENG W. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109. [2] 马剑雄,何伟伟,赵杰,等.股骨头坏死发病机制研究的最新进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(27):4397-4402. [3] Microsurgery Department of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Doctor Association; Group from the Osteonecrosis and Bone Defect Branch of the Chinese Association of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery; Microsurgery and Reconstructive Surgery Group of the Orthopedics Branch of the Chinese Medical Association. Chinese Guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults. Orthop Surg. 2017; 9(1):3-12. [4] WANG XS, ZHUANG QY, WENG XS, et al. Etiological and clinical analysis of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Chinese patients. Chin Med J. 2013;126(2):290-295. [5] ARBAB D, KÖNIG DP. Atraumatic femoral head necrosis in adults. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2016;113(3):31-38. [6] IKEUCHI K , HASEGAWA Y , SEKI T , et al. Epidemiology of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2015;25(2):278-281. [7] XIE M, SHI R, PAN Y, et al. Proteasome inhibition-induced downregulation of akt/gsk-3β pathway contributes to abnormality of tau in hippocampal slice. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;50(3):888-895. [8] ZHAO X, XIONG W, XIAO S, et al. Membrane targeting of TIRAP is negatively regulated by phosphorylation in its phosphoinositide- binding motif. Sci Rep.2017;7(3):43043. [9] ANDJELKOVIC M , ALESSI DR , MEIER R , et al. Role of Translocation in the Activation and Function of Protein Kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(50):31515-31524. [10] KILIC U, CAGLAYAN AB, BEKER MC, et al. Particular phosphorylation of PI3K/Akt on Thr308 via PDK-1 and PTEN mediates melatonin's neuroprotective activity after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Redox Biol. 2017;12(C):657. [11] RISSO G, BLAUSTEIN M, POZZI B, et al. Akt/PKB: one kinase, many modifications. Biochem J. 2015;468(2):203-214. [12] TOLEDO-LEYVA A, VILLEGAS-PINEDA JC, ENCARNACIÓN- GUEVARA S, et al. Effect of ovarian cancer ascites on SKOV-3 cells proteome: new proteins associated with aggressive phenotype in epithelial ovarian cancer. Proteome Sci. 2018;16:3. [13] 耿军辉,张丽军,王亚丽,等.PI3K/Akt信号通路与肿瘤血管新生的研究进展[J].现代肿瘤医学,2018,26(9):1462-1466. [14] VETRI F, CHAVEZ R, XU HL, et al. Complex modulation of the expression of PKC isoforms in the rat brain during chronic type 1 diabetes mellitus. Brain Res. 2013;1490:202-209. [15] DEL BARCO BARRANTES I, STEPHAN-OTTO ATTOLINI C, SLOBODNYUK K, et al. Regulation of Mammary Luminal Cell Fate and Tumorigenesis by p38α. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10(1):257-271. [16] KAR S, SAMII A, BERTALANFFY H. PTEN/PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling and the cross talk to KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10 proteins in cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Rev. 2015;38(2):229-237. [17] ZHANG C , LI Y , CORNELIA R , et al. Regulation of VEGF expression by HIF-1α in the femoral head cartilage following ischemia osteonecrosis. Sci Reports.2012;2:650. [18] ZHANG K, HAN ES, DELLINGER TH, et al. Cinnamon extract reduces VEGF expression via suppressing HIF-1α gene expression and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Mol Carcinog.2017;56(2):436-446. [19] ZENG D, WANG J, KONG P, et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 inhibits HIF-1α and VEGF expression in patient with acute leukemia via inhibiting the activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(5):2172-2178. [20] WANG P, TIAN XF, RONG JB, et al. Protein Kinase B (Akt) Promotes Pathological Angiogenesis in Murine Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy. Acta Hstochemica Et Cytochemica. 2011;44(2): 103-111. [21] SHARMA VR, GUPTA GK, SHARMA AK, et al. PI3K/Akt/mTOR intracellular pathway and breast cancer: factors, mechanism and regulation. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(11):1633-1638. [22] JIAO D, WANG J, LU W, et al. Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/ mTOR signaling pathways in lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016; 3:16018. [23] YANG Y, GAO M, LIN Z, et al. DEK promoted EMT and angiogenesis through regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98708-98722. [24] YIN T, WANG G, HE S, et al. Malignant pleural effusion and ascites induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem-like cell properties via the vascular endothelial growth factor (vegf)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (pi3k)/akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mtor) pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;291(52):26750. [25] TSAI JL, LEE YM, PAN CY, et al. The Novel VEGF121-VEGF165 Fusion Attenuates Angiogenesis and Drug Resistance via Targeting VEGFR2-HIF-1α-VEGF165 /Lon Signaling Through PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(3):275-286. [26] WANG Y, YAN W, LU X, et al. Overexpression of osteopontin induces angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells via the avβ3/PI3K/AKT/ eNOS/NO signaling pathway in glioma cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011; 90(8):642-648. [27] 尹香琳,张婧瑶,刘卫东,等.1-磷酸鞘氨醇受体2介导PI3K/AKT/eNOS通路抑制甲型流感病毒诱导的病毒性肺炎[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(11): 2062-2067. [28] AHMAD KA, ZE H, CHEN JC,et al. The protective effects of a novel synthetic β-elemene derivative on human umbilical vein endothelial cells against oxidative stress-induced injury: Involvement of antioxidation and PI3k/Akt/eNOS/NO signaling pathways. Biomed Pharmacother.2018;106:1734-1741. [29] 王雅婧,张学志,刁力,等.PI3K/AKt/eNOS信号通路在硫化氢抑制ET-1诱导的心肌肥大中的作用[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2014,6(5): 551-554+557. [30] AGATA M, MAGDALENA W, PIOTR S. Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: current knowledge and, clinical significance. Molecules. 2014;19(9): 14304-14315. [31] YANG H, ZHANG X, DU K, et al. Inhibition of β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes induces delayed fracture healing in mice. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(4):304-310. [32] GUNTUR AR, ROSEN CJ, NASKI MC. N-cadherin adherens junctions mediate osteogenesis through PI3K signaling. Bone. 2012; 50(1):54-62. [33] RISSO G, BLAUSTEIN M, POZZI B, et al. Akt/PKB: one kinase, many modifications. Biochem J. 2015; 468(2):203-214. [34] MENG YB, LI X, LI ZY, et al. microRNA-21 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by the PI3K/β-catenin pathway. J Orthop Res. 2015; 33(7):957-964. [35] HU J, MAO Z, HE S, et al. Icariin protects against glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis, increases the expression of the bone enhancer DEC1 and modulates the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin integrated signaling pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 2017:S0006295217301995. [36] HUANG L, WANG Y, JIANG Y, et al. High levels of GSK-3β signalling reduce osteogenic differentiation of stem cells in osteonecrosis of femoral head. J Biochem. 2018;163(3):243-251. [37] DENG S, NIE Z, PENG P, et al. Decrease of GSK3β Ser-9 phosphorylation induced osteoblast apoptosis in rat osteoarthritis model. Curr Med Sci. 2019;39(1):75-80. [38] LAUZON MA , DAVIAU A , DREVELLE O , et al. Identification of a growth factor mimicking the synergistic effect of fetal bovine serum on BMP-9 cell response. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(17-18):2524-2535. [39] FONG D, BISSON M, LABERGE G, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-9 activates Smad and ERK pathways and supports human osteoclast function and survival in vitro. Cell Signal. 2013; 25(4): 717-728. [40] WU X, CHIM SM, KUEK V, et al. HtrA1 is upregulated during RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis, and negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation and BMP2-induced Smad1/5/8, ERK and p38 phosphorylation. FEBS Lett.2014;588(1):143-150. [41] LAUZON MA, DREVELLE O, DAVIAU A, et al. Effects of BMP-9 and BMP-2 on the PI3K/Akt pathway in MC3T3-E1 preosteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(17-18):1075-1085. [42] MIN YL, LIM HW, SANG HL, et al. Smad, PI3K/Akt, and Wnt-dependent signaling pathways are involved in BMP-4-induced ESC self-renewal. Stem Cells, 2010;27(8):1858-1868. [43] WANG Z, GUO J. Mechanical induction of BMP-7 in osteocyte blocks glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis through PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2013;67(2):567-574. [44] FURUE K, SENA K, SAKODA K, et al. Involvement of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway in bone morphogenetic protein 9-stimulated osteogenic differentiation and stromal cell-derived factor 1 production in human periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Eur J Oral Sci. 2017;125(2):119-126. [45] MUKHERJEE A, ROTWEIN P. Akt promotes BMP2-mediated osteoblast differentiation and bone development. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122(5):716. [46] REN W, LIU Y, WAN S, et al. BMP9 inhibits proliferation and metastasis of HER2-positive SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells through ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT pathways. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96816. [47] AGAS D, SABBIETI MG, MARCHETTI L, et al. FGF-2 enhances Runx-2/Smads nuclear localization in BMP-2 canonical signaling in osteoblasts.J Cell Physiol. 2013;228(11):2149-2158. [48] LU J, BHARGAV D, WEI AQ, et al. Posterolateral intertransverse spinal fusion possible in osteoporotic rats with BMP-7 in a higher dose delivered on a composite carrier. Spine. 2008;33(3):242. [49] BAHIA PK , PUGH V , HOYLAND K , et al. Neuroprotective effects of phenolic antioxidant tBHQ associate with inhibition of FoxO3a nuclear translocation and activity. J Neurochem. 2012;123(1):182-191. [50] MA Y, WANG H. PI3K/Akt/FoxO: a novel participant in signal transduction in bone cells under mechanical stimulation. Cell Biol Int. 2012;36(10):923-926. [51] HAMANN I, PETROLL K, GRIMM L, et al. Insulin-like modulation of Akt/FoxO signaling by copper ions is independent of insulin receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014; 558:42-50. [52] 陈小香,邓伟民,魏秋实,等.从GH/IGF-1轴与PI3K/Akt通路探讨老年骨质疏松症的发病机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(11):1412-1415. [53] YUAN FL, XU RS, JIANG DL, et al. Leonurine hydrochloride inhibits osteoclastogenesis and prevents osteoporosis associated with estrogen deficiency by inhibiting the NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Bone.2015;75:128-137. [54] DUAN L, REN Y. Role of notch signaling in osteoimmunology-from the standpoint of osteoclast differentiation. Eur J Orthod. 2013;35(2): 175-182. [55] MEDINA MA, ANDRADE VM, CARACCI MO, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling stimulates the expression and synaptic clustering of the autism-associated Neuroligin 3 gene. Transl Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):45. [56] MOORE SF, VAN DEN BOSCH MT, HUNTER RW, et al. Dual regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)α/β by protein kinase C (PKC)α and Akt promotes thrombin-mediated integrin αIIbβ3 activation and granule secretion in platelets. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288(6):3918-3928. [57] TAYLOR A, ROTHSTEIN D, RUDD CE. Small-Molecule Inhibition of PD-1 Transcription Is an Effective Alternative to Antibody Blockade in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Res. 2018;78(3):706-717. [58] MOON JB , KIM JH , KIM K , et al. Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):163-169. [59] ZHA L, HE L, LIANG Y, et al. TNF-α contributes to postmenopausal osteoporosis by synergistically promoting RANKL-induced osteoclast formation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;102:369-374. [60] WU LC, GUO QF, YANG J, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes osteoclast formation via PI3K/Akt Pathway‐Mediated Blimp1 expression upregulation. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(6): 1308-1315. [61] VAN WIJNEN AJ, VAN DE PEPPEL J, VAN LEEUWEN JP, et al. MicroRNA Functions in Osteogenesis and Dysfunctions in Osteoporosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2013;11(2):72-82. [62] ZHAO C, SUN W, ZHANG P, et al. miR-214 promotes osteoclastogenesis by targeting Pten/PI3k/Akt pathway. RNA Biol. 2015;12(3):343-353.
|
| [1] | Yang Caihui, Liu Qicheng, Dong Ming, Wang Lina, Zuo Meina, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Serine/threonine protein kinases can promote bone destruction in mouse models of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3654-3659. |
| [2] | Fan Junchao, Chen Yong, Song Junjie. Sevoflurance combined with xenon pretreatment protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in a rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3660-3665. |
| [3] | Huo Hua, Cheng Yuting, Zhou Qian, Qi Yuhan, Wu Chao, Shi Qianhui, Yang Tongjing, Liao Jian, Hong Wei. Effects of drug coating on implant surface on the osseointegration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3558-3564. |
| [4] | Jiang Shengyuan, Li Dan, Jiang Jianhao, Shang-you Yang, Yang Shuye. Biological response of Co2+ to preosteoblasts during aseptic loosening of the prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3292-3299. |
| [5] | Chen Xinling, Wang Shenglan. Cell autophagy, pathway, regulation and its multiple correlations with pulmonary hypertension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 311-316. |
| [6] | Wei Qin, Zhang Xue, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Jia Qiyu, Ma Chuang. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB induces the differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2953-2957. |
| [7] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [8] | Wu Yukun, Han Jie, Wen Shuaibo. Mechanism of Runx2 gene in fracture healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2274-2279. |
| [9] | Chen Qiang, Zhuo Hongwu, Xia Tian, Ye Zhewei . Toxic effects of different-concentration isoniazid on newborn rat osteoblasts in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1162-1167. |
| [10] | Xu Nuo, Cao Zhen, Li Xiaojie, Shi Chun. MicroRNA-21 regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoclasts in periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1225-1230. |
| [11] | Li Jinyu, Yu Xing, Jiang Junjie, Xu Lin, Zhao Xueqian, Sun Qi, Zheng Chenying, Bai Chunxiao, Liu Chuyin, Jia Yusong. Promoting effect of osteopractic total flavone combined with nano-bone materials on proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1030-1036. |
| [12] | Qiao Jiutao, Guan Dehong, Wang Dongyan, Liu Aiyun. Zuogui Pill has protective effect against oxidative stress injury in osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(7): 1052-1056. |
| [13] | Ge Juncheng, Ma Jinhui, Wang Bailiang, Yue Debo, Sun Wei, Wang Weiguo, Guo Wanshou, Li Zirong. Application of bisphosphonates in avascular necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 753-759. |
| [14] | Zhang Yanan, Yan Xia, Meng Zengdong. Zn and Mg increase the bioactivity and osteogenic induction of hydroxyapatite biomaterial in bone repair: clinical application and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 606-611. |
| [15] | Zhang Chao, Li Xingyong, Ma Guifu, Pu Xingyu, Luo Wenyuan. Hoxa9 silencing promotes tibial fracture healing by regulating osteogenic differentiation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5600-5606. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||