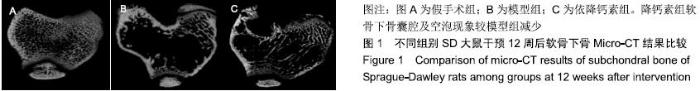
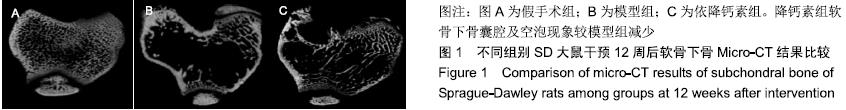
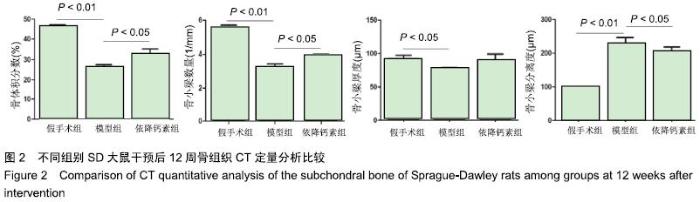
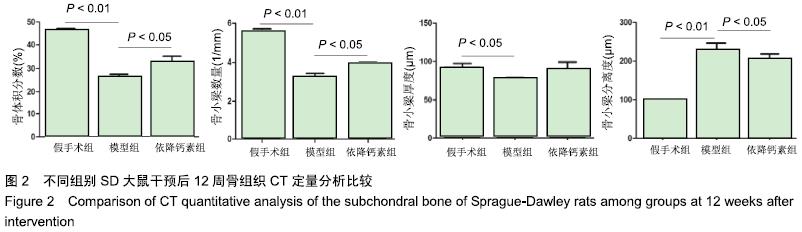
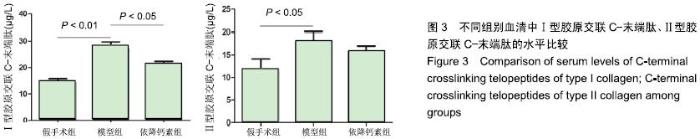
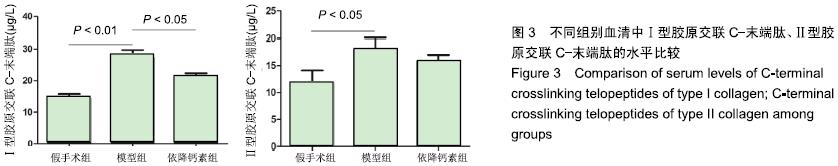
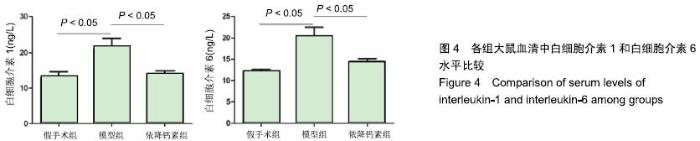
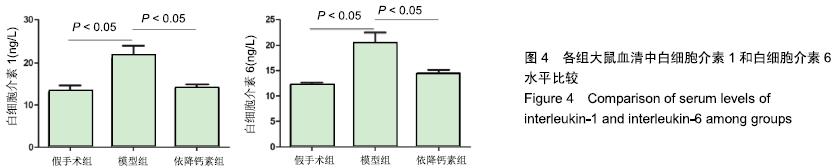
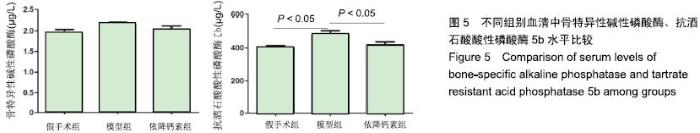
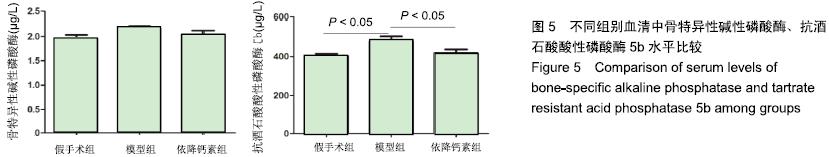
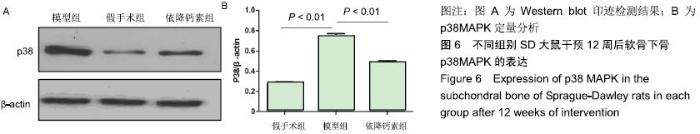
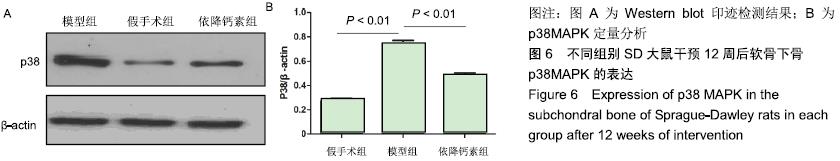
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (5): 709-715.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2433
Previous Articles Next Articles
Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin
Wu Qi1, 2, Liao Ying1, 2, Sun Guanghua1, 2, Zhou Guijuan1, 2, Liao Yuan1, 2, Liu Jing1, 2, Zhong Peirui1, 2, Cheng Guo1, 2, 3, Deng Chengyuan1, 2, 3, Wang Tiantian1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2Rehabilitation Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China; 3University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2019-06-06Revised:2019-06-13Accepted:2019-07-20Online:2020-02-18Published:2020-01-09 -
Contact:Liao Ying, Professor, Master’s supervisor, 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2Rehabilitation Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Wu Qi, Attending physician, 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2Rehabilitation Laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81674045; the Youth Project of Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, No. S2019JJ50536
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Qi, Liao Ying, Sun Guanghua, Zhou Guijuan, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Zhong Peirui, Cheng Guo, Deng Chengyuan, Wang Tiantian. Changes of subchondral bone in rat models of knee osteoarthritis treated by elcatonin[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 709-715.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] PEREIRA D, RAMOS E, BRANCO J.Osteoarthritis.Acta Med Port.2015;28(1):99-106. [2] LI G, YIN J, GAO J, et al.Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: insight into risk factors and microstructural changes.Arthritis Res Ther.2013;15(6):223. [3] MORITA Y, ITO H, ISHIKAWA M, et al.Subchondral bone fragility with meniscal tear accelerates and parathyroid hormone decelerates articular cartilage degeneration in rat osteoarthritis model.J Orthop Res.2018;36(7):1959-1968. [4] SCOTECE M, CONDE J, ABELLA V, et al.Oleocanthal Inhibits Catabolic and Inflammatory Mediators in LPS-Activated Human Primary Osteoarthritis (OA) Chondrocytes Through MAPKs/NF-κB Pathways.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(6):2414-2426. [5] HU N, GAO Y, JAYASURIYA CT, et al. Chondrogenic induction of human osteoarthritic cartilage-derived mesenchymal stem cells activates mineralization and hypertrophic and osteogenic gene expression through a mechanomiR.Arthritis Res Ther.2019;21(1):167. [6] HALL AC.The Role of Chondrocyte Morphology and Volume in Controlling Phenotype-Implications for Osteoarthritis, Cartilage Repair, and Cartilage Engineering.Curr Rheumatol Rep.2019;21(8):38. [7] SEIDL CI, MURPHY CL.Dual and Opposing Regulation of MMP1 and MMP13 by Both Arms of miR-675 in Human Articular Chondrocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(1): 172-185. [8] MURAOKA T, HAGINO H, OKANO T, et al.Role of subchondral bone in osteoarthritis development: a comparative study of two strains of guinea pigs with and without spontaneously occurring osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(10):3366-3374. [9] VAN SPIL WE, KUBASSOVA O, BOESEN M, et al. Osteoarthritis phenotypes and novel therapeutic targets. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:41-48. [10] 钟培瑞,廖瑛,廖源,等.去卵巢对大鼠膝关节软骨及软骨下骨的影响[J].风湿病与关节炎,2017,6(11):5-10,20. [11] AHO OM, FINNILÄ M, THEVENOT J, et al. Subchondral bone histology and grading in osteoarthritis. PLoS One.2017;12(3): e0173726. [12] IZAWA T, HUTAMI IR, TANAKA E.Potential Role of Rebamipide in Osteoclast Differentiation and Mandibular Condylar Cartilage Homeostasis.Curr Rheumatol Rev.2018; 14(1):62-69. [13] JUNG YK, HAN MS, PARK HR, et al.Calcium-phosphate complex increased during subchondral bone remodeling affects earlystage osteoarthritis.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):487. [14] ZHOU Y, MING J, LI Y, et al.Ligustilide attenuates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and cartilage degradation via inhibiting JNK and p38 MAPK pathways.J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3357-3368. [15] LI WM, HAN CL, LIU C, et al.ANGPTL2 deletion inhibits osteoclast generation by modulating NF-κB/MAPKs/Cyclin pathways.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;503(3): 1471-1477. [16] TSUKAMOTO M, MENUKI K, MURAI T, et al. Elcatonin prevents bone loss caused by skeletal unloading by inhibiting preosteoclast fusion through the unloading-induced high expression of calcitonin receptors in bone marrow cells.Bone. 2016;85:70-80. [17] BLANEY DEN, VAN CAAM AP, VAN DER KRAAN PM. Osteoarthritis year in review 2016: biology. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(2):175-180. [18] CHENG T, ZHANG L, FU X, et al.The potential protective effects of calcitonin involved in coordinating chondrocyte response, extracellular matrix, and subchondral trabecular bone in experimental osteoarthritis.Connect Tissue Res. 2013; 54(2):139-146. [19] KETOLA JH, KARHULA SS, FINNILÄ MAJ, et al. Iterative and discrete reconstruction in the evaluation of the rabbit model of osteoarthritis.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):12051. [20] HØEGH-ANDERSEN P, TANKÓ LB, ANDERSEN TL, et al. Ovariectomized rats as a model of postmenopausal osteoarthritis: validation and application.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(2):R169-180. [21] KAMEKURA S, HOSHI K, SHIMOAKA T, et al. Osteoarthritis development in novel experimental mouse models induced by knee joint instability.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2005;13(7): 632-641. [22] KATAE Y, TANAKA S, SAKAI A, et al.Elcatonin injections suppress systemic bone resorption without affecting cortical bone regeneration after drill-hole injuries in mice.J Orthop Res. 2009;27(12):1652-1658. [23] WALLACH S, ROUSSEAU G, MARTIN L, et al.Effects of calcitonin on animal and in vitro models of skeletal metabolism.Bone.1999;25(5):509-516. [24] MIMPEN JY, SNELLING SJB.Chondroprotective Factors in Osteoarthritis: a Joint Affair.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019;21(8): 41. [25] LI X, HE P, HOU Y, et al.Berberine inhibits the interleukin-1 beta-induced inflammatory response via MAPK downregulation in rat articular chondrocytes.Drug Dev Res. Drug Dev Res. 2019 Apr 29. [26] WANG CJ, CHENG JH, CHOU WY, et al.Changes of articular cartilage and subchondral bone after extracorporeal shockwave therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee.Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(3):213-223. [27] CHEN K, LV ZT, ZHOU CH, et al.Peimine suppresses interleukin‑1β‑induced inflammation via MAPK downregulation in chondrocytes.Int J Mol Med.2019;43(5): 2241-2251. [28] PARK C, JEONG JW, LEE DS, et al.Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB,p38 MAPK,and PI3K/Akt.Int J Mol Sci.Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(8). pii: E2308. [29] ZHANG R, WANG CM, JIANG HJ, et al.Protective Effects of Sweroside on IL-1β-Induced Inflammation in Rat Articular Chondrocytes Through Suppression of NF-κB and mTORC1 Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2019;42(2):496-505. [30] ELLIOTT SF, COON CI, HAYS E, et al.Bcl-3 is an interleukin-1-responsive gene in chondrocytes and synovial fibroblasts that activates transcription of the matrix metalloproteinase 1 gene. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(12): 3230-3239. [31] VINCENT TL.IL-1 in osteoarthritis: time for a critical review of the literature.F1000Res. F1000Res. 2019;8. pii: F1000 Faculty Rev-934. [32] HAN PF, WEI L, DUAN ZQ, et al.Contribution of IL-1β, 6 and TNF-α to the form of post-traumatic osteoarthritis induced by "idealized" anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in a porcine model.Int Immunopharmacol.2018;65:212-220. [33] CHE ATNA, LAU SF, MOHAMED S.Ficus deltoidea Prevented Bone Loss in Preclinical Osteoporosis/ Osteoarthritis Model by Suppressing Inflammation.Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;103(4):388-399. [34] CHEN X, CHEN X, ZHOU Z, et al.Nirogacestat suppresses RANKL-Induced osteoclast formation in vitro and attenuates LPS-Induced bone resorption in vivo.Exp Cell Res. 2019;15: 111470. [35] OK SM, LEE SM, PARK HR, et al.Concentrations of CTX I, CTX II, DPD, and PYD in the urine as a biomarker for the diagnosis of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A preliminary study. Cranio. 2018;36(6):366-372. [36] SHEN J, ABU-AMER Y, O'KEEFE RJ, et al.Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):49-63. [37] ISHIDA M, KITAURA H, KIMURA K, et al.Muramyl dipeptide enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorption through increased RANKL expression in stromal cells.J Immunol Res.2015;2015:132765. [38] ZHENG X, NIE Y, SUN C, et al.Long-term electroacupuncture stimulation prevents osteoporosis in ovariectomised osteopaenic rats through multiple signalling pathways. Acupunct Med. 2018;36(3):176-182. [39] KARSDAL MA, HENRIKSEN K, ARNOLD M, et al. Calcitonin: a drug of the past or for the future? Physiologic inhibition of bone resorption while sustaining osteoclast numbers improves bone quality. BioDrugs.2008;22(3):137-144. [40] SHIBAKAWA A, YUDOH K, MASUKO-HONGO K, et al.The role of subchondral bone resorption pits in osteoarthritis: MMP production by cells derived from bone marrow. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(8):679-687. [41] ZHANG LB, MAN ZT, LI W, et al.Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-κB pathways. Mol Immunol.2017;87:249-257. [42] VLOT MC, DEN HEIJER M, DE JONGH RT, et al.Clinical utility of bone markers in various diseases. Bone.2018;114: 215-225. [43] GLENDENNING P, CHUBB SAP, VASIKARAN S.Clinical utility of bone turnover markers in the management of common metabolic bone diseases in adults.Clin Chim Acta. 2018;481:161-170. |
| [1] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [2] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [3] | Liu Xiangxiang, Huang Yunmei, Chen Wenlie, Lin Ruhui, Lu Xiaodong, Li Zuanfang, Xu Yaye, Huang Meiya, Li Xihai. Ultrastructural changes of the white zone cells of the meniscus in a rat model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [4] | Zheng Xiaolong, He Xiaoming, Gong Shuidi, Pang Fengxiang, Yang Fan, He Wei, Liu Shaojun, Wei Qiushi. Bone turnover characteristics in patients with alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 657-661. |
| [5] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [6] | Ma Zetao, Zeng Hui, Wang Deli, Weng Jian, Feng Song. MicroRNA-138-5p regulates chondrocyte proliferation and autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [7] | Cao Xuhan, Bai Zixing, Sun Chengyi, Yang Yanjun, Sun Weidong. Mechanism of “Ruxiang-Moyao” herbal pair in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 746-753. |
| [8] | Li Yonghua, Feng Qiang, Tan Renting, Huang Shifu, Qiu Jinlong, Yin Heng. Molecular mechanism of Eucommia ulmoides active ingredients treating synovitis of knee osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 765-771. |
| [9] | Song Shan, Hu Fangyuan, Qiao Jun, Wang Jia, Zhang Shengxiao, Li Xiaofeng. An insight into biomarkers of osteoarthritis synovium based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 785-790. |
| [10] | Deng Zhenhan, Huang Yong, Xiao Lulu, Chen Yulin, Zhu Weimin, Lu Wei, Wang Daping. Role and application of bone morphogenetic proteins in articular cartilage regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [11] | Zheng Li, Li Dadi, Hu Weifan, Tang Jinlong, Zhao Fengchao. Risk assessment of contralateral knee arthroplasty after unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 374-379. |
| [12] | Lü Jiaxing, Bai Leipeng, Yang Zhaoxin, Miao Yuesong, Jin Yu, Li Zhehong, Sun Guangpu, Xu Ying, Zhang Qingzhu. Evaluation of internal fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation in elderly knee osteoarthritis patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [13] | Liu Jinfu, Zeng Ping, Nong Jiao, Fan Siqi, Feng Chengqin, Huang Jiaxing. Integrative analysis of biomarkers and therapeutic targets in synovium of patients with osteoarthritis by multiple microarrays [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3690-3696. |
| [14] | Chen Feng, Zhang Xiaoyun, Chen Yueping, Liao Jianzhao, Li Jiajun, Song Shilei, Lai Yu. Molecular mechanism of anhydroicaritin in the treatment of osteoarthritis: an analysis based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3704-3710. |
| [15] | Yang Wei, Chen Zehua, Yi Zhiyong, Huang Xudong, Han Qingmin, Zhang Ronghua. Effectiveness of intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid versus placebo in the treatment of early and mid-stage knee osteoarthritis: a Meta-analysis based on randomized, double-blind, controlled, clinical trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3760-3766. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||