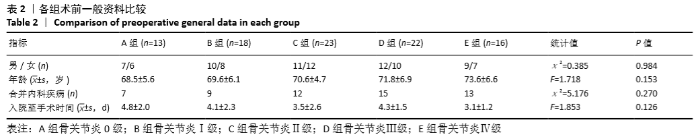
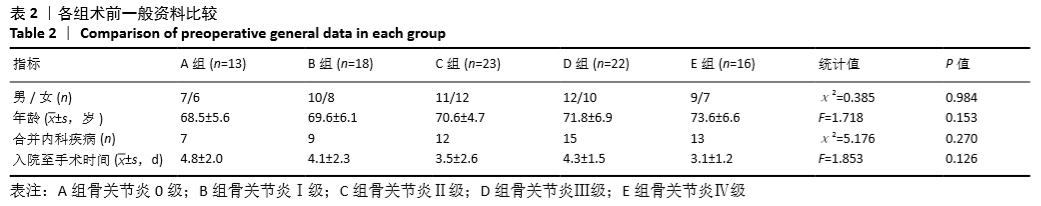
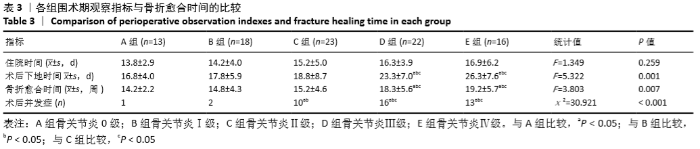
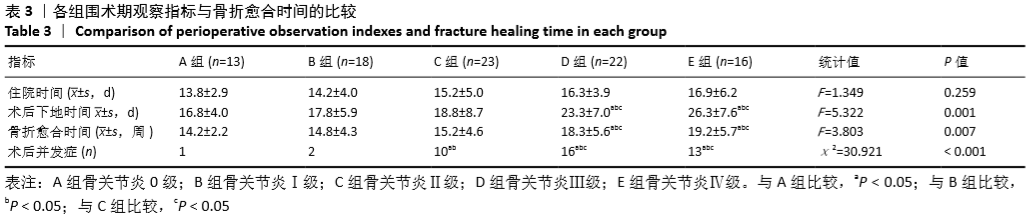
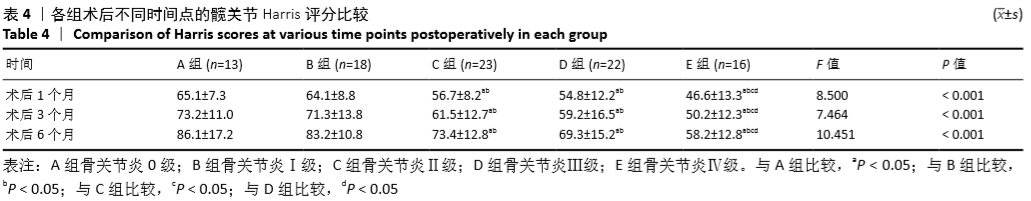
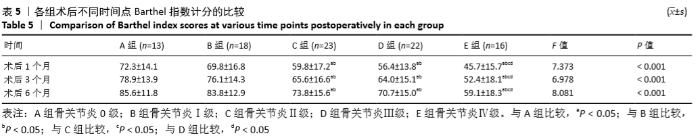
[1] HIRAGAMI K, ISHII J. Embedding the lateral end of the lag screw within the lateral wall in the repair of reverse obliquity intertrochanteric femur fracture.J Int Med Res.2018;46(3):1103-1108.
[2] TUCKER A, DONNELLY KJ, ROWAN C, et al. Is the best plate a nail?A review of 3230 unstable intertrochanteric fractures of the proximal femur.J Orthop Trauma.2018;32(2):53-60.
[3] TIAN F, SUN X, LIU J, et al. Unparallel gender-specific changes in the incidence of hip fractures in Tangshan,China.Arch Osteop.2017; 12(1):18.
[4] YOO JI, HA YC, LIM J Y, et al. Early rehabilitation in elderly after arthroplasty versus internal fixation for unstable intertrochanteric fractures of femur:systematic review and meta-analysis.J Korean Med Sci.2017;32(5):858-867.
[5] KLESTIL T, RODER C, STOTTER C, et al. Impact of timing of surgery in elderly hip fracture patients:a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep.2018;8(1):13933.
[6] BEAUPRE LA, KHONG H, SMITH C, et al. The impact of time to surgery after hip fracture on mortality at 30-and 90-days:Does a single benchmark apply to all?.Injury.2019;50(4):950-955.
[7] HAO Z, WANG X, ZHANG X. Comparing surgical interventions for intertrochanteric hip fracture by blood loss and operation time:a network meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2018;13(1):157.
[8] 赵文杰,张斌,高松,等.低能量性髋部骨折与膝关节退变的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(37):5938-5942.
[9] SMITH TO, HIGSON E, PEARSON M, et al. Is there an increased risk of falls and fractures in people with early diagnosed hip and knee osteoarthritis?Data from the osteoarthritis initiative.Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(6):1193-1201.
[10] KOHN MD, SASSOON AA, FERNANDO ND. Classifications in brief: kellgren-lawrence classification of osteoarthritis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(8):1886-1893.
[11] REN H, HUANG Q, HE J, et al. Does isolated greater trochanter implication affect hip abducent strength and functions in intertrochanteric fracture?.BMC Musculoskelet Disord.2019;20(1):79.
[12] HULSBÆK S, LARSEN RF, ROSTHØJ S, et al.The barthel index and the cumulated ambulation score are superior to the de morton mobility index for the early assessment of outcome in patients with a hip fracture admitted to an acute geriatric ward.Disabil Rehabil. 2019;41(11):1351-1359.
[13] 唐佩福.股骨转子间骨折的治疗进展与策略[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2017,19(2):93-94.
[14] 郭金超,曹源,黄俊灵,等.股骨转子间骨折618例患者的流行病学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(12):1840-1845.
[15] 中国老年医学学会骨与关节分会创伤骨科学术工作委员会.老年髋部骨折诊疗专家共识(2017)[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11): 921-927.
[16] LU J. Comparison of PFNA and DHS for the treatment of elderly unstable intertrochanteric fractures of femur.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(9):824-829.
[17] 张轩轩,李宝丰,章莹,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉与髋关节置换术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折Meta分析[J].实用医学杂志,2019, 35(6):903-907.
[18] EMMERT D, RASCHE T, STIEBER C, et al. Knee pain-symptoms,diagnosis and therapy of osteoarthritis.MMW Fortschr Med.2018;160(15):58-64.
[19] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[20] HALL M, BENNELL KL, WRIGLEY TV, et al. The knee adduction moment and knee osteoarthritis symptoms:relationships according to radiographic disease severity.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2017;25(1):34-41.
[21] 王强,苟海昕,曹月龙,等.膝骨关节炎X线分级与疼痛程度的相关性分析[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(6):18-21.
[22] OTTESEN TD, MCLYNN RP, GALIVANCHE AR, et al. Increased complications in geriatric patients with a fracture of the hip whose postoperative weight-bearing is restricted:an analysis of 4918 patients.Bone Joint J.2018;100-B(10):1377-1384.
[23] KATES SL, SATPATHY J, PETRISOR BA, et al. Outside the bone:What is happening systemically to influence fracture healing?J Orthop Trauma.2018;32 Suppl 1:S33-S36.
[24] 王阳.骨折愈合相关因素的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012, 20(8):724-726.
[25] WARREN J, SUNDARAM K, ANIS H, et al. The association between weight-bearing status and early complications in hip fractures.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2019;29(7):1419-1427.
[26] BINDAWAS SM, VENNU V, ALFHADEL S, et al. Knee pain and health-related quality of life among older patients with different knee osteoarthritis severity in Saudi Arabia.PLoS One.2018;13(5):e196150.
[27] PORTEGIJS E, RANTANEN T, KALLINEN M, et al. Lower-limb pain,disease,and injury burden as determinants of muscle strength deficit after hip fracture.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2009;91(7):1720-1728.
[28] FUKAYA T, MUTSUZAKI H, NAKANO W, et al. Characteristics of frontal plane lower limb movement during walking in patients with knee osteoarthritis of varying severity.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(2):615508373. |