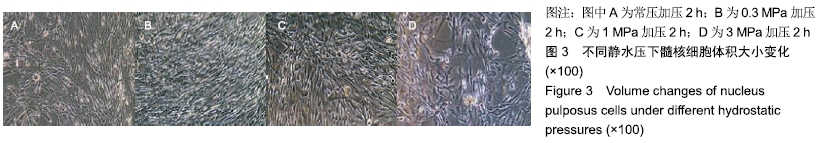
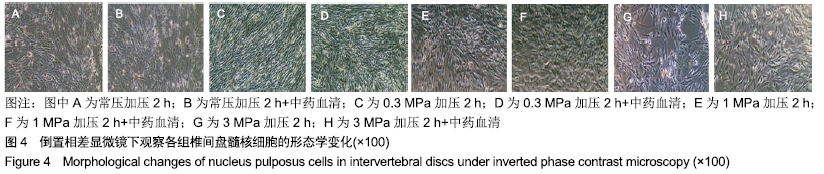
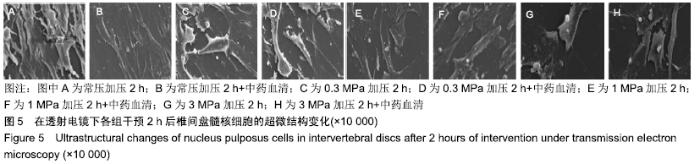
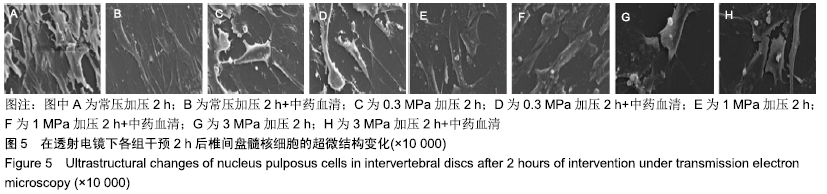
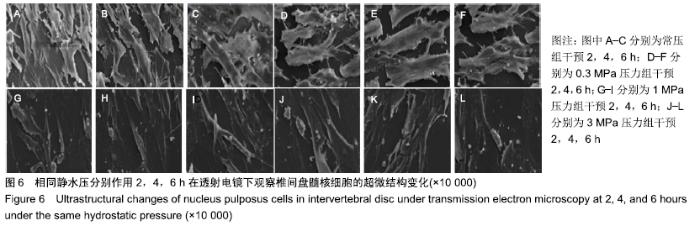
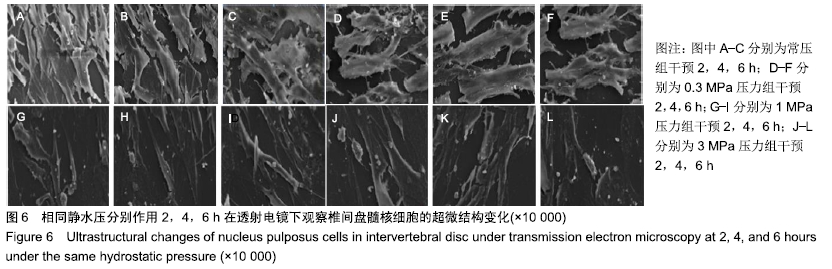
[1] 陈江,贾育松,柳根哲,等.体外静水压环境下细胞因子诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向髓核样细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(2):191-196.
[2] 刘浠,易威威,温亚枫,等.锌指蛋白A20及其相关炎症因子在椎间盘髓核细胞退变前后的表达变化[J].第三军医大学学报, 2016,38(18):2077-2081.
[3] ANNEMANN M, PLAZA-SIRVENT C, SCHUSTER M, et al. Atypical IκB proteins in immune cell differentiation and function. Immunol Lett. 2016;171:26-35.
[4] ZHANG M, WANG H, ZHANG J, et al. Unilateral anterior crossbite induces aberrant mineral deposition in degenerative temporomandibular cartilage in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 24(5):921-931.
[5] LIU Z, MA C, SHEN J, et al. SDF‑1/CXCR4 axis induces apoptosis of human degenerative nucleus pulposus cells via the NF‑κB pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(1):783-789.
[6] 黄云鸿,周红海,周诚恩,等.1991-2010年《中医正骨》刊载中药治疗腰椎间盘突出症文献分析[J].中医正骨,2013,25(8):13-14.
[7] 姜昆,刘晴晴,陶宝琛,等.补益肝肾、活血化瘀类中药复方治疗腰椎间盘突出症的Meta分析[J].中国药房, 2016,27(36):5118-5122.
[8] NACHEMSON AL. Disc pressure measurements.Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 1981;6(1):93-97.
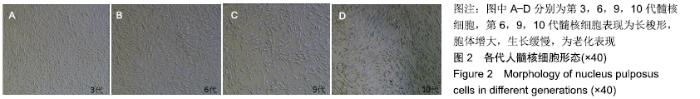
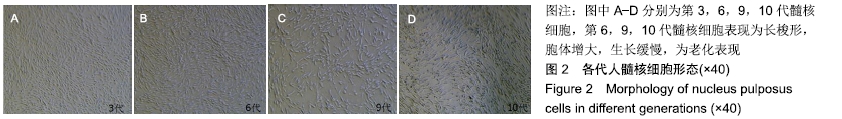
[9] 陈琪,石芳芳,杨曦,等.不同代次髓核细胞生物学特性的比较研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(6):660-667.
[10] GONZÁLEZ MARTÍNEZ E, GARCÍA-COSAMALÓN J, COSAMALÓN-GAN I, et al. Biology and mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2017;28(3):135-140.
[11] 柳根哲,孙旗,陈江,等.高静水压下益气活血汤通过p38MAPK信号通路对兔椎体终板软骨细胞的调控作用[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2018,27(10): 1027-1030,1034.
[12] 李培.离体椎间盘模型中压应力对髓核组织的生物效应及促退变机制的研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2017.
[13] BRIDGEN DT, FEARING BV, JING L, et al. Regulation of human nucleus pulposus cells by peptide-coupled substrates. Acta Biomater. 2017;55:100-108.
[14] HIRATA H, YURUBE T, KAKUTANI K, et al. A rat tail temporary static compression model reproduces different stages of intervertebral disc degeneration with decreased notochordal cell phenotype. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(3):455-463.
[15] GONZÁLEZ MARTÍNEZ E, GARCÍA-COSAMALÓN J, COSAMALÓN-GAN I, et al. Biology and mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc. Neurocirugia (Astur). 2017;28(3):135-140.
[16] 赵泉来,郑权,徐宏光,等. AMP活化蛋白激酶在终板软骨细胞体外传代培养中的表达及意义[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(29):4297-4302.
[17] 王效,徐宏光,肖良,等.大鼠腰椎终板软骨干细胞的分离及分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(13):2093-2097.
[18] 张剑勇,王辉,谢静静,等.痛风泰颗粒对急性痛风大鼠IL-1、IL-6及TNF-α含量的影响[J].新中医,2016(12):201-203.
[19] 崔允强.独活寄生汤加减联合射频热凝术治疗腰椎间盘突出症及对患者血清TNF-α及IL-1β水平的影响研究[J].亚太传统医药,2018,14(6): 158-159.
[20] 刘波,苏小强,王向阳.补肾活血通络方联合针刺治疗神经根型颈椎病的临床研究[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(11):21-24.
[21] 胡晓龙,何剑.活血通络汤联合牵引及按摩手法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效观察[J].四川中医,2018,36(5):151-153.
|