Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (17): 2718-2723.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2557
Previous Articles Next Articles
Expression of cyclic RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 in senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and its regulation mechanism
Xie Mingzhong, Li Sen, Zhu Kai, Jiang Huacai, Qi Lisheng
- Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646600, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2019-07-03Revised:2019-07-04Accepted:2019-08-09Online:2020-06-18Published:2020-03-30 -
Contact:Li Sen, MD, Professor, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646600, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Xie Mingzhong, Master, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Affiliated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646600, Sichuan Province, China -
Supported by:the Second-Batch Science and Technology Plan Project of Sichuan Province in 2018, No. 2018JY0402; Southwest Medical University-Affiliated Chinese Medicine Hospital Joint Innovation Team Project, No. 2018-6-50
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xie Mingzhong, Li Sen, Zhu Kai, Jiang Huacai, Qi Lisheng. Expression of cyclic RNA plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 in senescence of nucleus pulposus cells and its regulation mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(17): 2718-2723.
share this article
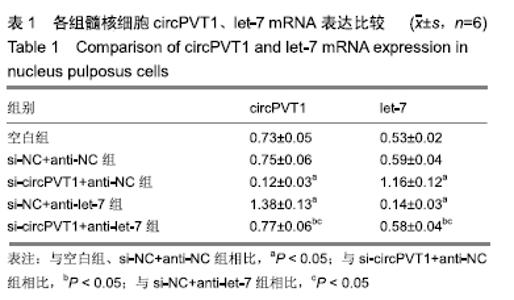
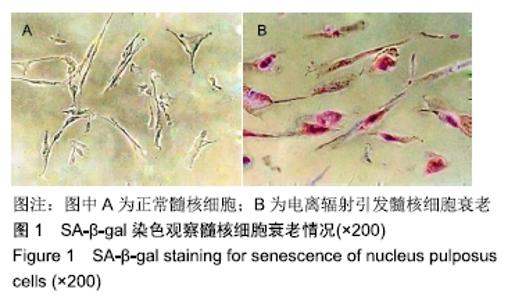
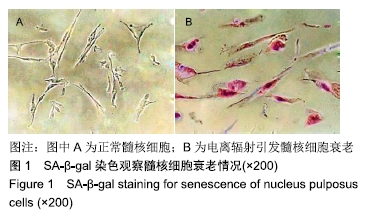
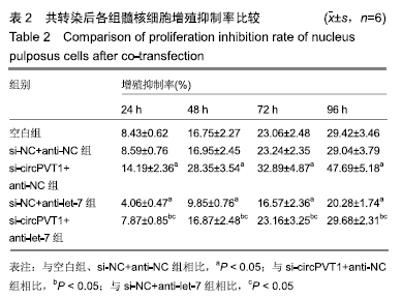
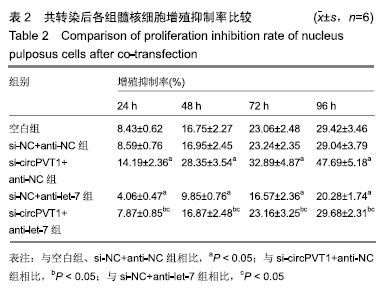
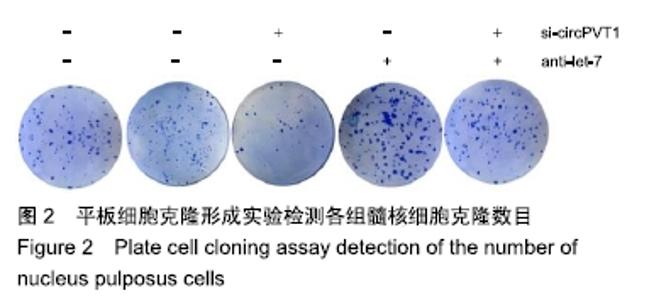
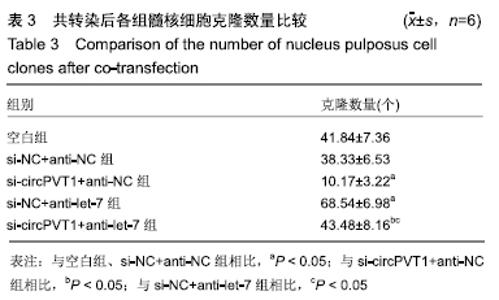
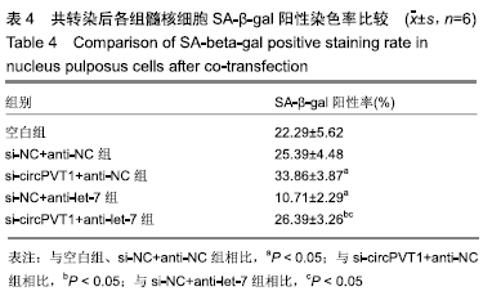
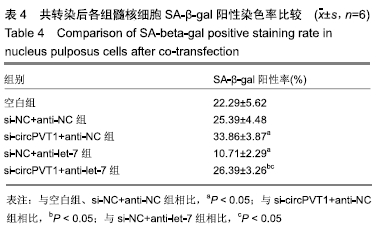
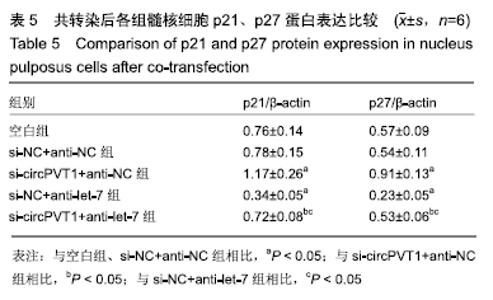
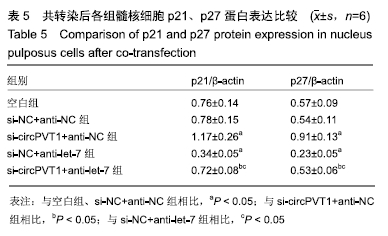
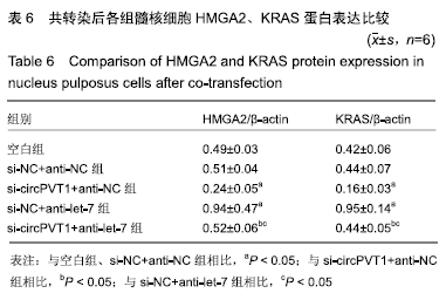
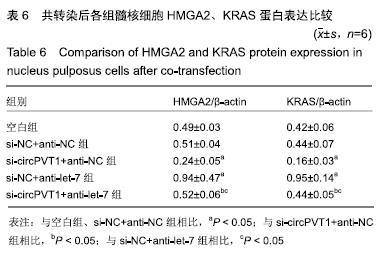
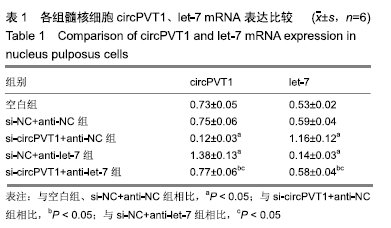
2.2 circPVT1、let-7在衰老髓核细胞中的表达 与正常髓核细胞相比,辐射组细胞中circPVT1 mRNA表达明显降低(1.05±0.04,0.38±0.07),而let-7 mRNA表达明显升高(1.09±0.06,1.59±0.38),差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。 2.3 共转染后各组髓核细胞circPVT1、let-7的表达 与空白组、si-NC+anti-NC组相比,si-circPVT1+anti-NC组circPVT1 mRNA表达降低,let-7 mRNA表达升高,si-NC+anti-let-7组circPVT1 mRNA表达升高,let-7 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05)。si-circPVT1+anti-let-7组circPVT1 mRNA表达高于si-circPVT1+anti-NC组,低于si-NC+anti-let-7组;let-7 mRNA表达低于si-circPVT1+anti-NC组,高于si-NC+anti- let-7组(P < 0.05),见表1。 "
| [1] 姜倍,胡舟扬,李新华,等.代谢性疾病与椎间盘退变关系的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,18(6):567-571. [2] 邵高海.腰椎退行性病组织特异性干细胞功能活性及表观遗传调控[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(53):8639-8639. [3] 马凯歌,熊蠡茗,邵增务.椎间盘内源性修复失效机制的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(12):763-768. [4] TAM WK, CHEUNG KM, LEUNG VY. Intervertebral Disc Engineering through Exploiting Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Progress and Perspective. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(6):505-512. [5] SI C, WANG J, MA W, et al. Circular RNA expression profile in human fibroblast premature senescence after repeated ultraviolet B irradiations revealed by microarray. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10): 18156-18168. [6] 赵明,谢浩,胡志迪,等.环状RNA:新型生物标记物与治疗靶点[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2016,43(7):635-643. [7] PANDA AC, GRAMMATIKAKIS I, KIM KM, et al. Identification of senescence-associated circular RNAs (SAC-RNAs) reveals senescence suppressor CircPVT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(7): 4021-4035. [8] ASHWAL-FLUSS R, MEYER M, PAMUDURTI NR, et al. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell. 2014; 56(1):55-66. [9] DORI M, BICCIATO S. Integration of Bioinformatic Predictions and Experimental Data to Identify circRNA-miRNA Associations. Genes (Basel). 2019;10(9): E642. [10] RONG D, SUN H, LI Z, et al. An emerging function of circRNA- miRNAs-mRNA axis in human diseases. Oncotarget. 2017;8(42): 73271-73281. [11] LU C, SUN X, LI N, et al. CircRNAs in the tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri) brain during postnatal development and aging. Aging (Albany NY). 2018;10(4):833-852. [12] KNUPP D, MIURA P. CircRNA accumulation: A new hallmark of aging? Mech Ageing Dev. 2018;173:71-79. [13] XU Y, YAO Y, LIU Y, et al. Elevation of circular RNA circ_0005230 facilitates cell growth and metastasis via sponging miR-1238 and miR-1299 in cholangiocarcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(7): 1907-1917. [14] ZHANG S, ZHU D, LI H, et al. Characterization of circRNA-Associated- ceRNA Networks in a Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Prone 8 Brain. Mol Ther. 2017;25(9):2053-2061. [15] CHEN X, SHI W, CHEN C. Differential circular RNAs expression in ovary during oviposition in honey bees. Genomics. 2019;111(4):598-606. [16] CHENG J, HUANG J, YUAN S, et al. Circular RNA expression profiling of human granulosa cells during maternal aging reveals novel transcripts associated with assisted reproductive technology outcomes. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0177888. [17] CHEN J, LI Y, ZHENG Q, et al. Circular RNA profile identifies circPVT1 as a proliferative factor and prognostic marker in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:208-219. [18] ASHRAF HM, MOSER J, SPENCER SL. Senescence Evasion in Chemotherapy: A Sweet Spot for p21. Cell. 2019;178(2):267-269. [19] CHI C, LI DJ, JIANG YJ, et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell senescence and age-related diseases: State of the art. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865(7):1810-1821. [20] MARKOWSKI DN, WINTER N, MEYER F, et al. p14Arf acts as an antagonist of HMGA2 in senescence of mesenchymal stem cells-implications for benign tumorigenesis. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2011;50(7):489-498. [21] CAPPELLETTI C, GALBARDI B, BRUTTINI M, et al. Aging-associated genes and let-7 microRNAs: a contribution to myogenic program dysregulation in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. FASEB J. 2019;33(6):7155-7167. [22] PENG CH, LIU JH, WOUNG LC, et al. MicroRNAs and cataracts: correlation among let-7 expression, age and the severity of lens opacity. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96(5):747-751. [23] WANG D, HOU L, NAKAMURA S, et al. LIN-28 balances longevity and germline stem cell number in Caenorhabditis elegans through let-7/AKT/DAF-16 axis. Aging Cell. 2017;16(1):113-124. [24] XU F, PANG L, CAI X, et al. let-7-repressesed Shc translation delays replicative senescence. Aging Cell. 2014;13(1):185-192. [25] SHI X, TIAN B, MA C, et al. GSK3β activity is essential for senescence-associated heterochromatin foci (SAHF) formation induced by HMGA2 in WI38 cells. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(1):167-174. [26] VENKATACHALAM G, SURANA U, CLÉMENT MV. Replication stress-induced endogenous DNA damage drives cellular senescence induced by a sub-lethal oxidative stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45(18):10564-10582. [27] TAN M, LI H, SUN Y. Inactivation of Sag/Rbx2/Roc2 e3 ubiquitin ligase triggers senescence and inhibits kras-induced immortalization. Neoplasia. 2015;17(1):114-123. [28] KEANE M, DE MAGALHÃES JP. MYCN/LIN28B/Let-7/HMGA2 pathway implicated by meta-analysis of GWAS in suppression of post-natal proliferation thereby potentially contributing to aging. Mech Ageing Dev. 2013;134(7-8):346-348. [29] APPARI M, BABU KR, KACZOROWSKI A, et al. Sulforaphane, quercetin and catechins complement each other in elimination of advanced pancreatic cancer by miR-let-7 induction and K-ras inhibition. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(4):1391-1400. [30] LI XX, DI X, CONG S, et al. The role of let-7 and HMGA2 in the occurrence and development of lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(23):8353-8366. |
| [1] | Min Youjiang, Yao Haihua, Sun Jie, Zhou Xuan, Yu Hang, Sun Qianpu, Hong Ensi. Effect of “three-tong acupuncture” on brain function of patients with spinal cord injury based on magnetic resonance technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-8. |
| [2] | Liu Zhichao, Zhang Fan, Sun Qi, Kang Xiaole, Yuan Qiaomei, Liu Genzhe, Chen Jiang. Morphology and activity of human nucleus pulposus cells under different hydrostatic pressures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1172-1176. |
| [3] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [4] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| [5] | Liu Zhao, Xu Xilin, Shen Yiwei, Zhang Xiaofeng, Lü Hang, Zhao Jun, Wang Zhengchun, Liu Xuzhuo, Wang Haitao. Guiding role and prospect of staging and classification combined collapse prediction method for osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 929-934. |
| [6] | Yi Meizhi, Luo Guanghua, Xiao Yawen, Hu Rong, Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng. MRI findings of anatomical variations of the talus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3888-3893. |
| [7] | Xie Jingshu, Zhang Xianglin, Liu Jinlei, Wen Jing. Application of High Resolution reconstruction algorithm in precision CT scans of the middle and inner ears [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3614-3618. |
| [8] | Yu Yinghao, Zhao Jijun, Liu Dongcheng, Chen Yuhao, Feng Dehong. Clinical significance of preoperative planning assisted unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with digital imaging system for fixed-bearing prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3324-3331. |
| [9] | Dong Liping, Luo Huaiqing, Yuan Heng, Long Juan, Xu Shaohui. Effect of aging on collateral vessel growth in rats with ischemic hind limbs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3156-3161. |
| [10] | Liu Xing, Wei Xiaohan, Deng Jie, Li Zhongming . Preparing a blunt contusion model of rabbit skeletal muscle under different blow strengths [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 196-200. |
| [11] | Fu Yuanfei, He Shenghua, Lai Juyi, Sun Zhitao, Feng Hualong, Lan Zhiming . Pheretima extract ameliorates nucleus pulposus cell degeneration in the intervertebral disc by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 264-268. |
| [12] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [13] | Du Xueting, Yang Yang, Huang Wenhua, Chen Wubiao. Clinical application and breakthrough of three-dimensional printing based on medical imaging technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2887-2894. |
| [14] | Chen Xiaolong, Zhao Heng, Hu Rong, Luo Guanghua, Liu Jincai . Correlation of infrapatellar fat pad edema with trochlear and patellofemoral joint morphology: MRI evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2410-2415. |
| [15] | He Shenghua, Fu Yuanfei, Lan Zhiming, Sun Zhitao, Lai Juyi, Feng Hualong, Guo Zibin, Li Gai . Yaotu Granule deals with the proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via regulating the expression of microRNA-221 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2177-2182. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||