Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (29): 4709-4715.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.29.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Danshen injection with neural stem cells transplantation in rats with craniocerebral injury
Liu Xiao1, Wang Hu2
- 1Department of Brain, Xianshuigu Hospital of Jinnan District, Tianjin 300350, China; 2Fifth Ward, Department of Neurosurgery, Tianjin Huanhu Hospital, Tianjin 300350, China
-
Revised:2017-05-03Online:2017-10-18Published:2017-11-08 -
About author:Liu Xiao, Attending physician, Department of Brain, Xianshuigu Hospital of Jinnan District, Tianjin 300350, China -
Supported by:the Key Project of Health Industry in Tianjin, No. 2013KG134
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Xiao, Wang Hu. Effect of Danshen injection with neural stem cells transplantation in rats with craniocerebral injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(29): 4709-4715.
share this article
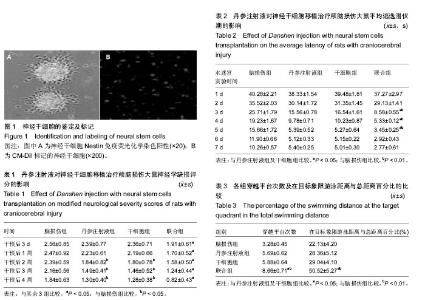
2.1 神经干细胞的形态观察 培养1 d后,神经干细胞增多、较小、形状不规则,小部分细胞团贴壁;培养5 d后,神经干细胞增多,为较大、形状规则的球形,见图1A。免疫荧光染色显示,神经干细胞球呈CM-Dil强阳性表达。神经干细胞的标记,CM-Dil标记的神经干细胞在荧光显微镜下呈红色荧光,见图1B。研究证实,CM-DiI标记后荧光在胞内表达稳定,阳性标记率达97%以上,标记细胞形态良好,能有效观察细胞在体外的诱导分化情况。 2.2 神经学缺损评分检测结果 从整个神经学功能障碍评分实验期看来,随着细胞移植干预后时间的延长,各组大鼠神经功能均在逐渐恢复正常。在干细胞移植3 d之后,联合组神经学缺损评分显著低于其他各组(P < 0.05),丹参注射液组和干细胞组干预后2,3,4周的神经缺损评分显著低于脑损伤组(P < 0.05),见表1。 2.3 Morris水迷宫实验结果 Morris水迷宫实验中,随着实验时间的延长,各组大鼠平均逃逸潜伏期潜伏时间逐渐缩短;实验开始的一二天,各组之间无显著差异(P > 0.05);3-5 d时,联合组平均潜伏时间较丹参注射液组及神经干细胞移植组缩短(P < 0.05),较脑损伤组明显缩短(P < 0.01);六七天时,各组间差异较小,见表2。 联合组穿越平台次数及在目标象限游泳距离与总距离百分比均高于丹参注射液组及干细胞组(P < 0.05),明显高于脑损伤组(P < 0.01),见表3。"
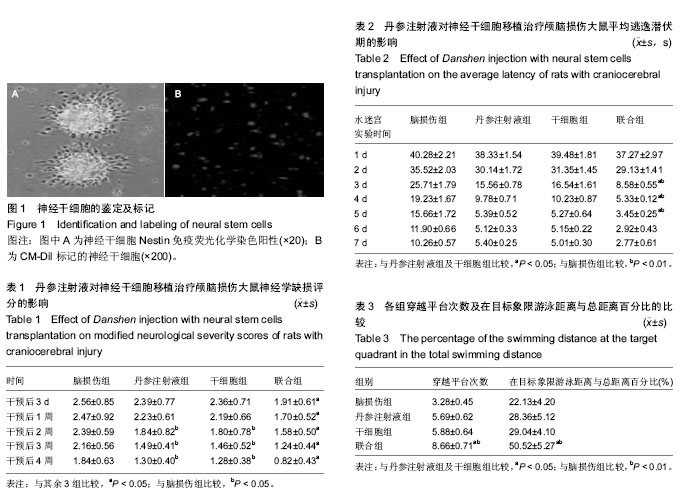
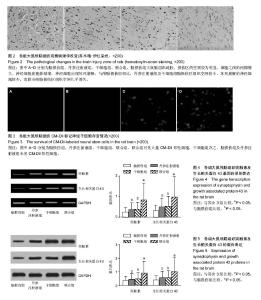
2.4 苏木精-伊红染色观察病理学改变 脑损伤组大鼠脑组织疏松,损伤区的空洞较为明显,细胞之间的间隙增大,神经细胞的胞体皱缩,神经细胞出现坏死崩解;与颅脑损伤组相比,丹参注射液组及干细胞组脑损伤区组织空洞较小,坏死崩解的神经细胞较少,而联合组脑损伤区组织空洞几乎消失,见图2。 2.5 神经干细胞存活及分布情况 神经干细胞移植4周之后在CM-Dil阳性细胞方面,联合组的(26.37±3.41)%显著高于干细胞组(12.67±2.07)%、脑损伤组(0)及丹参注射液组(0),见图3。 2.6 各组突触素及生长相关蛋白43基因转录的表达 联合组突触素及生长相关蛋白43表达显著高于脑损伤组、丹参注射液组和干细胞组(P < 0.05),干细胞组、丹参注射液组突触素及生长相关蛋白43表达高于脑损伤组(P < 0.05),见图4。 2.7 各组突触素及生长相关蛋白43蛋白的表达 联合组突触素及生长相关蛋白43高于其他3组(P < 0.05),干细胞组、丹参注射液组突触素及生长相关蛋白43表达高于脑损伤组(P < 0.05),见图5。"

| [1] Diaz-Arrastia R,Kenney K.Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury.Handb Clin Neurol.2015;127:3-13.[2] Haring RS,Narang K,Canner JK,et al.Traumatic brain injury in the elderly:morbidity and mortality trends and risk factors.J Surg Res.2015;195(1):1-9.[3] Fernandezrodriguez E,Bernabeu I,Castro AI,et al. Hypopituitarism after traumatic brain injury.Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am.2015;44(1):151-159.[4] 黄卫,岑丹辉,黄远德.颅脑损伤治疗进展[J].基层医学论坛,2014, 18(1):107-109.[5] Yoshida Y,Yamanaka S.Recent stem cell advances: induced pluripotent stem cells for disease modeling and stem cell–based regeneration. Circulation. 2010;122(1): 80-87.[6] 刘伟.神经干细胞研究进展及前景[J].科技信息,2011,28(16): 10172-10172.[7] Gage FH,Temple S.Neural stem cells:generating and regenerating the brain.Neuron.2013;80(3):588-601.[8] 贾璐,闫春华,吴丽娥.神经干细胞研究进展[J].医学综述, 2010,16(8):1149-1151.[9] Kim SU.Neural stem cell-based gene therapy for brain tumors.Stem Cell Rev Rep.2011;7(1):130-140.[10] 方庆,陈新生.神经干细胞相关研究进展[J].中国医药指南, 2011,9(8):44-46.[11] Xie C,Cong D,Wang X,et al.The effect of simvastatin treatment on proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury.Brain Res.2014;1602:1-8.[12] Ahmed A,Shtaya A,Zaben M,et al.Activation of endogenous neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury.Lancet.2014;383(383):S18.[13] Goodus MT,Guzman AM,Calderon F,et al.Neural stem cells in the immature,but not the mature,subventricular zone respond robustly to traumatic brain injury.Dev Neurosci.2015;37(1): 29-42.[14] Liu S,Li Z,Fu J,et al.The effects of harvesting media on biological characteristics and repair potential of neural stem cells after traumatic brain injury.Plos One.2014;9(9): e107865-e107865.[15] Ye YQ,Xu HY,Zhang X,et al.Association between Toll-Like Receptor 4 Expression and Neural Stem Cell Proliferation in the Hippocampus Following Traumatic Brain Injury in Mice.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(7):12651-12664.[16] Jiang S,Chen W,Zhang Y,et al.Acupuncture Induces the Proliferation and Differentiation of Endogenous Neural Stem Cells in Rats with Traumatic Brain Injury.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2016;2016(4):1-8.[17] Thomaidou D.Neural Stem Cell Transplantation in an Animal Model of Traumatic Brain Injury.Methods Mol Biol. 2014; 1210: 9-21.[18] Haus DL,López-Velázquez L,Gold EM,et al.Transplantation of human neural stem cells restores cognition in an immunodeficient rodent model of traumatic brain injury.Exp Neurol.2016;281:1-16.[19] Aligholi H,Rezayat SM,Azari H,et al.Preparing neural stem/progenitor cells in PuraMatrix hydrogel for transplantation after brain injury in rats:A comparative methodological study.Brain Res.2016;1642:197-208.[20] Addington CP,Heffernan JM,Millarhaskell CS,et al.Enhancing neural stem cell response to SDF-1α gradients through hyaluronic acid-laminin hydrogels. Biomaterials.2015; 72: 11-19.[21] 樊欣鑫,李宇龙,万兴,等.神经干细胞移植治疗颅脑损伤后神经功能缺失的研究进展[J].现代医学,2013,41(4):274-278.[22] 刘兴华.神经干细胞移植在颅脑损伤后神经功能缺失中的应用研究进展[J].中国处方药,2015,13(10):20-21.[23] 赵宁,杨万章,李娇,等.丹参注射液对脑梗死患者自体外周血干细胞旁分泌BDNF的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2013 11(1):49-51.[24] 赵宁,陆琳,杨万章,等.丹参注射液对急性脑梗死大鼠脑组织VEGF表达的影响[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2013,11(5): 584-586.[25] 林惠,杨万章.丹参注射液对脑梗死大鼠SVZ干细胞增殖作用的研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2014,12(3):350-352.[26] Wang Y,Jiang YF,Huang QF,et al.Neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acid B against oxygen-glucose deprivation/ reperfusion damage in primary rat cortical neurons.Chin Med J(Engl).2010;123(24):3612-3619.[27] 林惠.丹参注射液干预脑梗死大鼠SVZ干细胞增殖作用的研究[D].湖南中医药大学,2014.[28] 周学萍.重型颅脑损伤诊治进展[J].当代医学,2011,17(28): 20-21.[29] 李坚.重型颅脑损伤的治疗进展[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2011, 32(2):317-319.[30] 刘旭.颅脑损伤治疗的进展研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2011, 14(17):89-91.[31] 黄海亮.丹参的化学成分分离及其抗氧化活性研究[J].中国现代药物应用,2015,9(21):277-278.[32] 贾巧.丹参制剂及桑白皮的抗氧化药效评价[D].重庆大学,2014.[33] 朱黎霞,王利胜,张英丰.丹参总酚酸、山楂总黄酮组分配伍对高脂血症大鼠血脂、超氧化物歧化酶及丙二醛的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(20):9-12.[34] 周茹,何耀,和丽芬,等.丹参水提物对大鼠心肌缺血-再灌注损伤氧化应激的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2014,30(2):76-78.[35] Lim DA,Alvarez-Buylla A.Adult neural stem cells stake their ground.Trends Neurosci.2014;37(10):563-571.[36] Kosztowski T,Zaidi HA,Quiñoneshinojosa A.Applications of neural and mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of gliomas.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther.2014;9(5):597-612.[37] Bond AM,Ming GL,Song L,et al.Adult Mammalian Neural Stem Cells and Neurogenesis:Five Decades Later.Cell Stem Cell.2015;17(4):385-395.[38] Gnanapavan S,Yousaf N,Heywood W,et al.Growth associated protein (GAP-43):Cloning and the development of a sensitive ELISA for neurological disorders.J Neuroimmunol. 2014; 276(1-2):18-23.[39] 韦理,张俐.丹参注射液对急性脊髓损伤大鼠突触体素和突触素的作用及机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(6):1870-1872.[40] 郭怀兰,张吉才,王建洲,等.碘过量对仔鼠脑突触素表达影响及硒干预作用[J].中国公共卫生,2010,26(1):91-92.[41] Griva M,Lagoudaki R,Touloumi O,et al.Long-term effects of enriched environment following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia on behavior, BDNF and synaptophysin levels in rat hippocampus: Effect of combined treatment with G-CSF.Brain Res. 2017.pii: S0006-8993(17)30184-1. [42] Xia WG,Zheng CJ,Zhang X,et al.Effects of "nourishing liver and kidney" acupuncture therapy on expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor and synaptophysin after cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2017;37(2):271-278. [43] Xiao Z,Peng J,Wu L,et al.The effect of IL-1β on synaptophysin expression and electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in a rat model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurol Res. 2017:1-9. [44] Chen YY,Zhang L,Shi DL,et al.Resveratrol Attenuates Subacute Systemic Inflammation-Induced Spatial Memory Impairment via Inhibition of Astrocyte Activation and Enhancement of Synaptophysin Expression in the Hippocampus.Ann Clin Lab Sci.2017;47(1):17-24.[45] Li X,Wang C,Wang W,et al.Neonatal exposure to BDE 209 impaired learning and memory, decreased expression of hippocampal core SNAREs and synaptophysin in adult rats.Neurotoxicology. 2017;59:40-48. [46] Matsukuma K,Olson KA,Gui D,et al.Synaptophysin-Ki67 double stain: a novel technique that improves interobserver agreement in the grading of well-differentiated gastrointestinal neuroendocrine tumors. Mod Pathol.2017;30(4):620-629. |
| [1] | Wang Jing, Xiong Shan, Cao Jin, Feng Linwei, Wang Xin. Role and mechanism of interleukin-3 in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1260-1265. |
| [2] | Xiao Hao, Liu Jing, Zhou Jun. Research progress of pulsed electromagnetic field in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1266-1271. |
| [3] | Tian Chuan, Zhu Xiangqing, Yang Zailing, Yan Donghai, Li Ye, Wang Yanying, Yang Yukun, He Jie, Lü Guanke, Cai Xuemin, Shu Liping, He Zhixu, Pan Xinghua. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate ovarian aging in macaques [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Guo Tianzhu, Yu Menglei, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning targets and downregulates miR-195 and promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell survival and pro-angiogenic potential by activating MALAT1 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [5] | Zhou Ying, Zhang Huan, Liao Song, Hu Fanqi, Yi Jing, Liu Yubin, Jin Jide. Immunomodulatory effects of deferoxamine and interferon gamma on human dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
| [6] | Liang Xuezhen, Yang Xi, Li Jiacheng, Luo Di, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Bushen Huoxue capsule regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via Hedgehog signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1020-1026. |
| [7] | Wang Jifang, Bao Zhen, Qiao Yahong. miR-206 regulates EVI1 gene expression and cell biological behavior in stem cells of small cell lung cancer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1027-1031. |
| [8] | Liu Feng, Peng Yuhuan, Luo Liangping, Wu Benqing. Plant-derived basic fibroblast growth factor maintains the growth and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1032-1037. |
| [9] | Wen Dandan, Li Qiang, Shen Caiqi, Ji Zhe, Jin Peisheng. Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton for extemal use improves the viability of adipogenic mesenchymal stem cells and promotes diabetes wound repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1038-1044. |
| [10] | Zhu Bingbing, Deng Jianghua, Chen Jingjing, Mu Xiaoling. Interleukin-8 receptor enhances the migration and adhesion of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to injured endothelium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1045-1050. |
| [11] | Luo Xiaoling, Zhang Li, Yang Maohua, Xu Jie, Xu Xiaomei. Effect of naringenin on osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1051-1056. |
| [12] | Wang Xinmin, Liu Fei, Xu Jie, Bai Yuxi, Lü Jian. Core decompression combined with dental pulp stem cells in the treatment of steroid-associated femoral head necrosis in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1074-1079. |
| [13] | Fang Xiaolei, Leng Jun, Zhang Chen, Liu Huimin, Guo Wen. Systematic evaluation of different therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1085-1092. |
| [14] | Guo Jia, Ding Qionghua, Liu Ze, Lü Siyi, Zhou Quancheng, Gao Yuhua, Bai Chunyu. Biological characteristics and immunoregulation of exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1093-1101. |
| [15] | Huang Chenwei, Fei Yankang, Zhu Mengmei, Li Penghao, Yu Bing. Important role of glutathione in stemness and regulation of stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1119-1124. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||