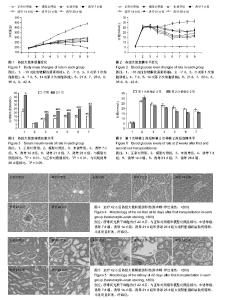
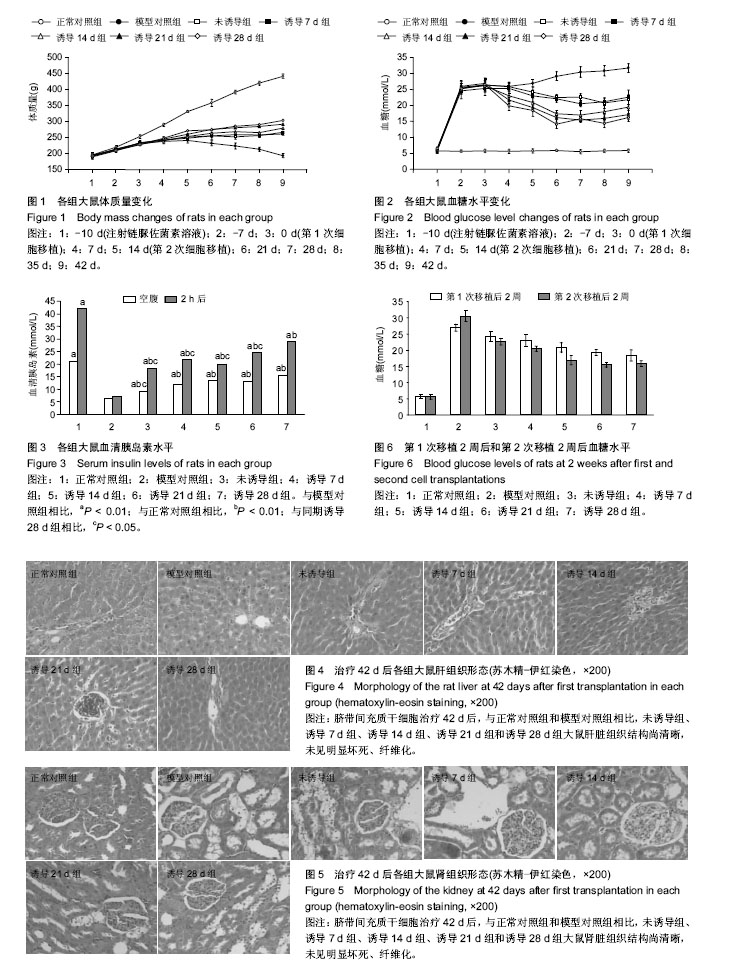
| [1] Kharroubi AT, Darwish HM. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes. 2015;6(6):850-867.[2] van Dieren S, Beulens JW, van der Schouw YT, et al. The global burden of diabetes and its complications: an emerging pandemic. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010;17 Suppl 1: S3-8.[3] Vanikar AV, Trivedi HL, Thakkar UG. Stem cell therapy emerging as the key player in treating type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(9):1077-1086.[4] Friedenstein AJ, Piatetzky-Shapiro II, Petrakova KV. Osteogenesis in transplants of bone marrow cells. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1966;16(3):381-390.[5] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Shyr YM, et al. Transplantation of insulin-producing cells from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19:47.[6] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Lin CH, et al. Intraportal injection of insulin-producing cells generated from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells decreases blood glucose level in diabetic rats. Endocr Res. 2014;39(1):26-33.[7] Wang HS, Hung SC, Peng ST, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in the Wharton's jelly of the human umbilical cord. Stem Cells. 2004;22(7):1330-1337.[8] Wang HS, Shyu JF, Shen WS, et al. Transplantation of insulin-producing cells derived from umbilical cord stromal mesenchymal stem cells to treat NOD mice. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(3):455-466.[9] Li T, Xia M, Gao Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(9):1293-1306.[10] Tsai PJ, Wang HS, Lin GJ, et al. Undifferentiated Wharton's Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation Induces Insulin-Producing Cell Differentiation and Suppression of T-Cell-Mediated Autoimmunity in Nonobese Diabetic Mice. Cell Transplant. 2015;24(8):1555-1570.[11] 林丽敏,邱学荣,邱晓燕,等.人脐带间充质干细胞、人脐带间充质干细胞源男性生殖细胞样细胞的免疫学特性[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2011,26(17):1343-1346.[12] 李伟中,邱晓燕,邱学荣,等.人脐带间充质干细胞向胰岛素分泌细胞分化过程免疫特性的研究[J].中国小儿血液与肿瘤杂志,2011, 16(4):173-177.[13] El-Hossary N, Hassanein H, El-Ghareeb AW, et al. Intravenous vs intraperitoneal transplantation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells from Wharton's jelly in the treatment of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016;121:102-111.[14] Xin Y, Jiang X, Wang Y, et al. Insulin-Producing Cells Differentiated from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro Ameliorate Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Hyperglycemia. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0145838.[15] 臧丽,谢宗燕,刘杰杰,等.骨髓和脂肪来源的间充质干细胞治疗2型糖尿病的疗效比较[J].解放军医学杂志,2016,41(7):534-538.[16] Vivatbutsiri P, Nowwarote N, Sawangmake C, et al. Characterization of femur, mandible and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells from streptozotocin-injected mice. Thai Veterinary Medicine. 2014; 44(4):477-486.[17] Banerjee M, Kumar A, Bhonde RR. Reversal of experimental diabetes by multiple bone marrow transplantation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(1):318-325.[18] 方厚华.医学实验模型动物[M].北京:军事医学出版社,2002: 28-50.[19] Borisov MA, Petrakova OS, Gvazava IG,et al. Stem Cells in the Treatment of Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Acta Naturae. 2016;8(3):31-43.[20] Banerjee M, Kumar A, Bhonde RR. Reversal of experimental diabetes by multiple bone marrow transplantation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328(1):318-325.[21] Parekh VS, Joglekar MV, Hardikar AA. Differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mononuclear cells to endocrine pancreatic lineage. Differentiation. 2009;78(4): 232-240.[22] Shah R, Jindal RM. Reversal of diabetes in the rat by injection of hematopoietic stem cells infected with recombinant adeno-associated virus containing the preproinsulin II gene. Pancreatology. 2003;3(5):422-428.[23] Li T, Zhu J, Ma K, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes liver regeneration after portal vein embolization in cirrhotic rats. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2):1161-1173.[24] Nam JS, Kang HM, Kim J, et al. Transplantation of insulin-secreting cells differentiated from human adipose tissue-derived stem cells into type 2 diabetes mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;443(2):775-781.[25] Zhang Z, Fu J, Xu X, et al. Safety and immunological responses to human mesenchymal stem cell therapy in difficult-to-treat HIV-1-infected patients. AIDS. 2013;27(8): 1283-1293.[26] Xie B, Gu P, Wang W, et al. Therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Am J Transl Res. 2016; 8(7): 3241-3250.[27] Shao CH, Chen SL, Dong TF, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after regional hepatic irradiation ameliorates thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in rats. J Surg Res. 2014;186(1):408-416.[28] Yu F, Ji S, Su L, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro and ameliorate rat liver fibrosis in vivo. J Formos Med Assoc. 2015;114(2):130-138. |