Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (14): 2167-2172.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.14.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Human adipose-derived stem cells: in vitro isolation, culture, identification and immunological properties
Eliyar Elham, Wang Yun-hai, Wang Li, Gao Hua, Xu Xin-cai, Zhang Wen-bin
- Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2014-02-24Online:2014-04-02Published:2014-04-02 -
Contact:Zhang Wen-bin, M.D., Associate chief physician, Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Eliyar Elham, Master, Physician, Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Special Project of Tissue Engineering in the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, No. 201022GC02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Eliyar Elham, Wang Yun-hai, Wang Li, Gao Hua, Xu Xin-cai, Zhang Wen-bin. Human adipose-derived stem cells: in vitro isolation, culture, identification and immunological properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(14): 2167-2172.
share this article
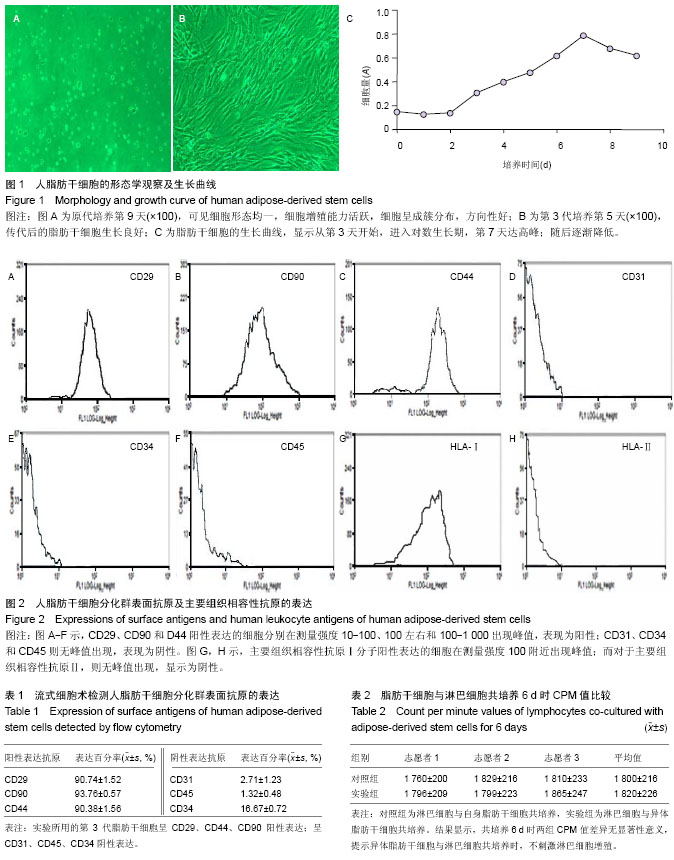
2.1 人脂肪干细胞的形态学观察 将原代培养的脂肪干细胞在倒置显微镜下观察,接种后24 h可见50%细胞基本贴壁,形状为圆形或菱形,原代培养48 h,细胞开始克隆样增生,呈多角形或梭形,此时在培养皿中可见大量红细胞飘浮,用培养基每日清洗换液,到9 d可见细胞形态均一,细胞增殖能力活跃,细胞呈成簇分布,方向性好(图1A)。当细胞融合到85%-90%时,行细胞传代,传代后的脂肪干细胞生长良好,所培养的第3代人脂肪干细胞生长在含10%胎牛血清,含青、链霉素的DMEM-L培养基中,置于含体积分数5% CO2的37 ℃培养箱中培养,细胞生长良好(图1B)。 2.2 人脂肪干细胞的生长曲线 生长曲线呈典型的“S”形,前2 d的A值略有降低,可能与部分细胞死亡有关。从第3天开始,进入对数生长期,第7天达高峰;随后逐渐降低(图1C)。 2.3 人脂肪干细胞分化群表面抗原的表达 应用流式细胞术检测脂肪干细胞分化群表面抗原表达的结果显示,本实验所用的第3代脂肪干细胞呈呈CD29、CD44、CD90阳性表达;同时呈CD31、CD45、CD34阴性表达,间接排除了造血系统和内皮细胞的污染(表1,图2A-F)。 2.4 人脂肪干细胞的组织相容性抗原表达 人脂肪干细胞表面主要组织相容性抗原Ⅰ图2G,H:本实验所分离的脂肪干细胞表面主要组织相容性抗原Ⅰ分子表达呈阳性,而主要组织相容性抗原Ⅱ分子表达呈阴性。和主要组织相容性抗原Ⅱ分子进行检测的结果见 2.5 异体脂肪干细胞与淋巴细胞共培养 培养6 d时,实验组和对照组的CPM值差异无显著性意义(表2)。说明异体脂肪干细胞与淋巴细胞共培养时,不刺激淋巴细胞增殖,再次证实了脂肪干细胞较弱的异体移植排斥反应。 "
| [1] Yagi H,Kitagawa Y. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in cancer development. Front Genet. 2013;4: 261. [2] Sun S,Chen G,Xu M,et al. Differentiation and Migration of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplanted through the Spleen in Rats with Portal Hypertension. PLoS One. 2013; 8(12): e83523. [3] Yang YM,Li H,Zhang L,et al. [A new method for isolating and culturing mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells]. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2013;21(6): 1563-1567. [4] Zuk P A,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2): 211-228. [5] Ong WK,Sugii S. Adipose-derived stem cells: fatty potentials for therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(6): 1083-1086. [6] Zhou Z,Zhang M,Lu MJ.Application of adipose-derived stem cells in lower urinary tract reconstruction. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2013;19(4): 365-369. [7] Ogawa R,Mizuno H,Watanabe A,et al. Osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation by adipose-derived stem cells harvested from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;313(4): 871-877. [8] Yang P,Yin S,Cui L,et al. [Experiment of adipose derived stem cells induced into smooth muscle cells]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2008;22(4): 481-486. [9] Choi YS,Matsuda K,Dusting GJ,et al. Engineering cardiac tissue in vivo from human adipose-derived stem cells. Biomaterials. 2010;31(8): 2236-2242. [10] Fujimura J,Ogawa R,Mizuno H,et al. Neural differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells isolated from GFP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;333(1): 116-121. [11] Liu H,Cheng B,Fu X. [Related issues in clinical translational application of adipose-derived stem cells]. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2012;26(10): 1242-1246. [12] Lakkis FG,Billiar TR. Molecular analysis of transplant rejection: marching onward. J Exp Med. 2013;210(11): 2147-2149. [13] Ali JM,Bolton EM,Bradley JA,et al. Allorecognition pathways in transplant rejection and tolerance. Transplantation. 2013;96(8): 681-688. [14] Ong WK,Tan CS,Chan KL,et al. Identification of specific cell-surface markers of adipose-derived stem cells from subcutaneous and visceral fat depots. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;2(2): 171-179. [15] Nae S,Bordeianu I,Stancioiu AT,et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells: definition, isolation, tissue-engineering applications. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2013;54(4): 919-924. [16] 崔磊,尹烁,杨平,等. 脂肪干细胞HLA分子表达与体外抑制淋巴细胞增殖的实验研究[J]. 中华医学杂志,2005, 85(27): 1890-1894. [17] Leatherman J. Stem cells supporting other stem cells. Front Genet. 2013;4: 257. [18] Kraushaar DC,Zhao K. The Epigenomics of Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. Int J Biol Sci. 2013;9(10): 1134-1144. [19] Biteau B,Hochmuth CE,Jasper H. Maintaining tissue homeostasis: dynamic control of somatic stem cell activity. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;9(5): 402-411. [20] Mayani H. A glance into somatic stem cell biology: basic principles, new concepts, and clinical relevance. Arch Med Res. 2003;34(1): 3-15. [21] Zanetti AS,Sabliov C,Gimble JM,et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells and three-dimensional scaffold constructs: a review of the biomaterials and models currently used for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013;101(1): 187-199. [22] Kaewsuwan S,Song SY,Kim JH,et al. Mimicking the functional niche of adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(12): 1575-1588. [23] Mizuno H,Tobita M,Uysal AC. Concise review: Adipose-derived stem cells as a novel tool for future regenerative medicine. Stem Cells. 2012;30(5): 804-810. [24] Markarian CF,Frey GZ,Silveira MD,et al. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: a comparison among different methods. Biotechnol Lett. 2013. [Epub ahead of print] [25] Arana M,Mazo M,Aranda P,et al. Adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells: isolation, expansion, and characterization. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1036: 47-61. [26] Dubey A,Malik HN,Singhal DK,et al. 198 isolation, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of goat adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into pancreatic islets-like cells. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2013;26(1): 213. [27] Mischen BT,Follmar KE,Moyer KE,et al. Metabolic and functional characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells in tissue engineering. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008; 122(3): 725-738. [28] Roemeling-Van RM,Mensah FK,Korevaar SS,et al. Effects of Hypoxia on the Immunomodulatory Properties of Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem cells. Front Immunol. 2013;4: 203. [29] Lee RH,Kim B,Choi I,et al. Characterization and expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow and adipose tissue. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004; 14(4-6): 311-324. [30] Dubey A,Malik HN,Singhal DK,et al. 198 isolation, characterization, and in vitro differentiation of goat adipose-tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells into pancreatic islets-like cells. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2013;26(1): 213. [31] Malik HN,Dubey A,Singhal DK,et al. 204 isolation, characterization, and differentiation of adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells: an autologous transplantation to patients. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2013;26(1): 216. [32] Vieira NM,Brandalise V,Zucconi E,et al. Isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential of canine adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(3): 279-289. [33] Caviggioli F,Vinci V,Salval A,et al. Human adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery. ANZ J Surg. 2009;79(11): 856. [34] Huang SJ,Fu RH,Shyu WC,et al. Adipose-derived stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation potential. Cell Transplant. 2013;22(4): 701-709. [35] Lee MW,Choi J,Yang MS,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells from cryopreserved human umbilical cord blood. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;320(1): 273-278. [36] Liundup AV,Medvedev I,Balasanova KV,et al. [Methods of tissue engineering of bone tissue in maxillofacial surgery]. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2013;(5): 10-15. [37] Zhang Q,Cheng B. Tendon-derived stem cells as a new cell source for tendon tissue engineering. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013;18: 756-764. [38] Beeson W,Woods E,Agha R. Tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and rejuvenation in 2010: the role of adipose-derived stem cells. Facial Plast Surg. 2011;27(4): 378-387. [39] Sterodimas A,de Faria J,Nicaretta B,et al. Tissue engineering with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs): current and future applications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010; 63(11): 1886-1892. [40] Campbell P. Clinical relevance of human leukocyte antigen antibodies in liver, heart, lung and intestine transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2013;18(4): 463-469. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Guan Qian, Luan Zuo, Ye Dou, Yang Yinxiang, Wang Zhaoyan, Wang Qian, Yao Ruiqin. Morphological changes in human oligodendrocyte progenitor cells during passage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1045-1049. |
| [14] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [15] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||