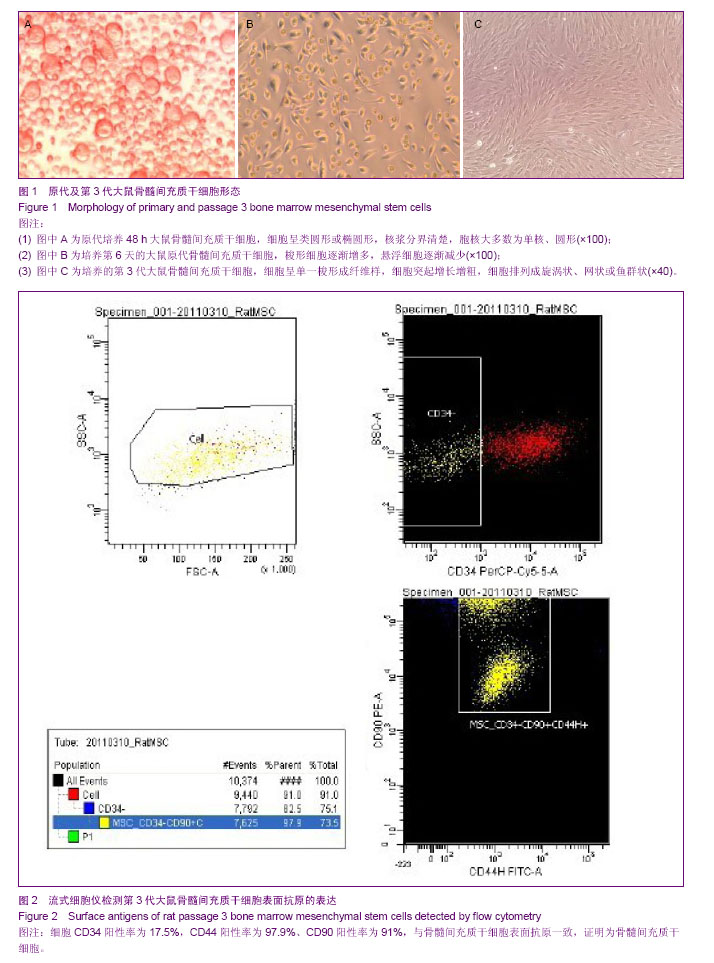
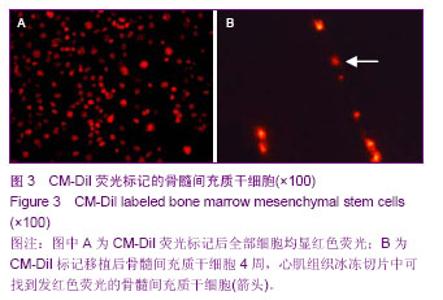
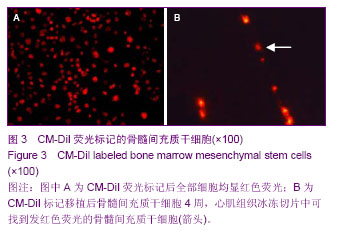
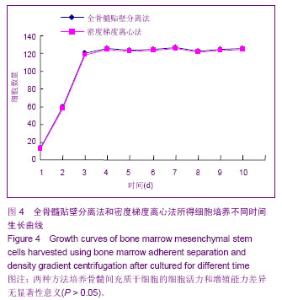
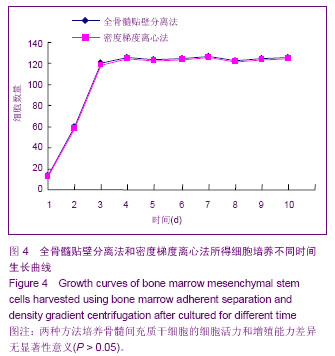
| [1] Chiellini C, Cochet O, Negroni L,et al.Characterization of human mesenchymal stem cell secretome at early steps of adipocyte and osteoblast differentiation. BMC Mol Biol.2008; 9:26.[2] Soleimani M, Nadri S.A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone marrow.Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):102-106.[3] Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Mosca JD, et al. Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and stromal cells. J Cell Physiol.1998;176(1):57-66.[4] Friedenstein AJ, Petrakova KV, Kurolesova AI, et al. Hetero topic of bone marrow. Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues. Transplantation. 1968; 6(2):230-247.[5] Lennon DP,Edmison JM,Caplan A. Cultivation of rat marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in reduced oxygen tension:effects on in Vitro and in Vivo osteochondrogenesis.J Cell Physiol.2001;187(3):345-355.[6] Zohar R, Sodek J, McCulloch CA. Characterization of stromal progenitor cells enriched by flow cytometry. Blood.1997;90 (9) :3471-3481.[7] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[8] De Ugarte DA, Alfonso Z, Zuk PA, et al. Differential expression of stem cell mobilization- associated molecules on multi-lineage cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow. Immunol Lett.2003;89(2-3): 267-270.[9] Lin D, Najbauer J, Salvaterra PM,et al. Novel method for visualizing and modeling the spatial distribution of neural stem cells within intracranial glioma. Neuroimage. 2007;37 Suppl 1: S18-26.[10] 杨丽,张荣华,谢厚杰,等.建立大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞稳定分离培养体系与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(6): 1064-1068.[11] Polisetti N,Chaitanya VG,Babu PP,et al. Isolation, characterization and differentiation potential of rat bone marrow stromal cells. Neurol India. 2010;58(2):201-208.[12] Patel SA, Sherman L, MunozJ,et al.Immunological properties of mesenchymal stromal cells.and clinical implications.Arch lmmunol Ther Exp.2008;56(1):1-8.[13] Nauta AJ,Fibbe WE.Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stromal cells.Blood.2007;110(10):3499-3506.[14] Donadoni C, Corti S, Locatelli F, et al.Improvement of combined FISH and immun- ofluorescence to trace the fate of somatic stem cells after transplantation.J Histochem Cytochem, 2004;52(10):1333-1339.[15] Lim SY, Kim YS, Ahn Y, et al.The effects of mesenchymal stem cells transduced with Akt in a porcine myocar-dial infarction model. Cardiovasc Res.2006;70(3):530-542.[16] Zhang M, Methot D, Poppa V, et al. Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair : graft cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2001;33:907-921.[17] 毛雨红,莫碧文,李劳冬,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养及CM-DiI标记的实验研究[J].安徽医科大学学报,2013,48(6): 607-611. [18] 盛闽,陈志耀,黄鹤光,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗重症急性胰腺炎相关肺损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(36): 6702-6709. [19] 高峰,张近宝,周凯,等.血管内皮生长因子基因修饰骨髓间充质干细胞移植心肌梗死大鼠:高压氧干预促进治疗性血管生成[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(27):5011-5016. [20] 解芳,靳小雷,徐家杰,等.体内构建组织工程骨的示踪观察: CM-DiI长效示踪骨髓间充质干细胞的可行性研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(4):195-197. [21] 王立梅,崔晓兰,丁明超,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞经动脉介入移植治疗犬糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(19): 3545-3550. [22] 王晓燕,郑岩,孟宝玺,等.静脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞参与皮肤扩张的可行性研究[J].中国美容医学,2012, 21(4):596-599. [23] 赖丽莎,陈俊伟,王劲,等. 骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性肝衰竭[J].中国医学影像技术,2011,27(2):232-236. [24] 张兆华,王一彪,栾云,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗实验性大鼠肺动脉高压损伤的作用[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2011,49(8): 31-33.[25] 熊全,冯吉,王军,等. 3种不同途径移植骨髓间充质干细胞治疗肝硬化模型大鼠的效果比较[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(8): 804-808. [26] 曾力,张爽,魏玲玲,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对大鼠到小鼠胰岛移植的保护作用[J].华西医学,2011,26(5): 641-645. [27] 娄远蕾,涂伟,汪泱,等.经阿魏酸钠定向诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞在脑缺血大鼠体内移植研究[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2010, 15(12):558-561. [28] 窦兴葵,郭涛,思永玉,等.超顺磁性氧化铁纳米粒子和CM-DiI荧光双标记骨髓间充质干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(14):2513-2517. [29] 王美华,胡锴勋,邱泽武.改良小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞培养方法及长效荧光标记的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(45): 8929-8934. [30] 何庚戌,要彤,张浩,等.体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞经大鼠冠状动脉内移植的可行性研究[J].华北国防医药,2009,21(5): 3-5. [31] 赖文玉,岑丹阳,曾巧慧,等.骨髓间充质干细胞两种示踪方法的优缺点比较[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2009,30(2): 232-236. [32] 何庚戌,要彤,张浩,等.骨髓间充质干细胞经大鼠冠状动脉内移植的可行性[J].基础医学与临床,2009,29(1): 69-73. [33] 倪玉霞,刘小青,李连达.CM-DiI标记大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外体内的示踪观察[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2008,7(12):1-3.[34] 倪玉霞,刘小青,李贻奎,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植联合冠心Ⅱ号对大鼠急性心肌梗死心功能和血管新生的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9201-9209.[35] 要彤,何庚戌,张浩,等.经冠状动脉内注射体外培养骨髓间充质干细胞的安全性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(25): 4819-4823. [36] 何庚戌,要彤,张浩,等.经冠状动脉内移植骨髓间充质干细胞在体示踪及体内再分布的实验研究[J].中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2008,15(3):195-199. [37] 高峰,蔡振杰,李利,等.血管内皮生长因子基因转染骨髓间充质干细胞移植促进缺血心肌血管生成的研究[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2006,26(20):1600-1602. |