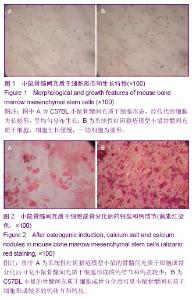
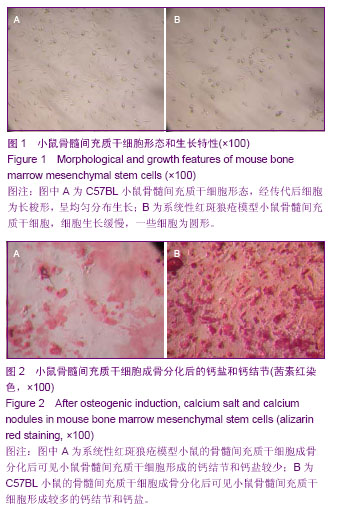
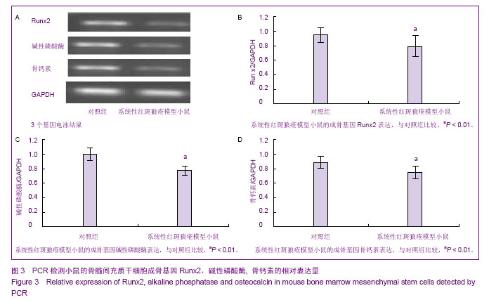
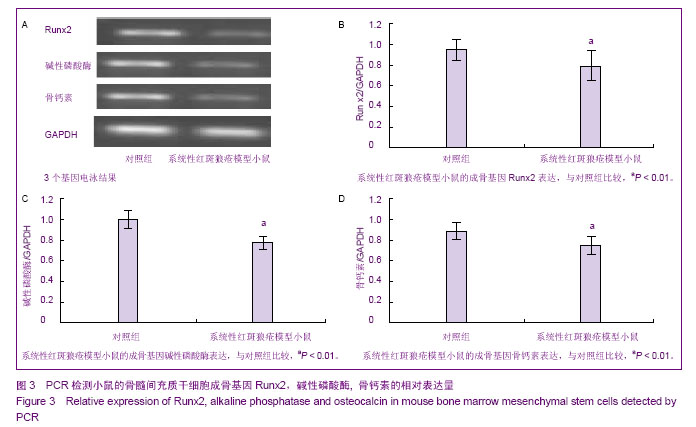
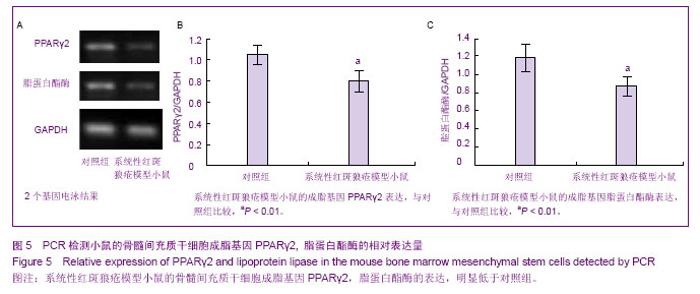
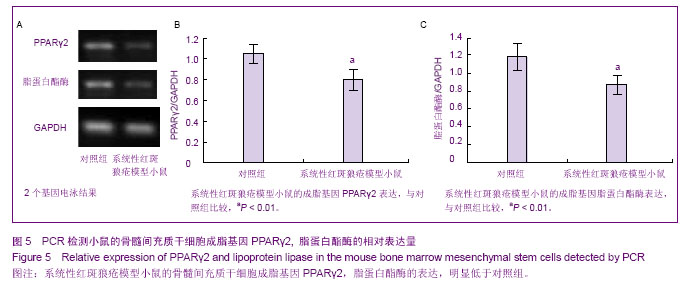
| [1] Rahman A, Isenberg DA.Systemic lupus erythematosus.N Engl J Med.2008;358(9):929-939.[2] Crispín JC, Tsokos GC. Novel molecular targets in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev.2008;7(3):256-261.[3] Kyttaris VC, Juang YT, Tsokos GC. Immune cells and cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus: an update. Curr Opin Rheumatol.2005;17(5): 518-522.[4] Ramanujam M, Davidson A. Targeting of the immune system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Mol Med.2008; 10: e2.[5] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147.[6] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL, et al.Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893): 41-49.[7] da Silva Meirelles L, Chagastelles PC, Nardi NB. Mesenchymal stem cells reside in virtually all post-natal organs and tissues. J Cell Sci.2006;119(Pt 11):2204-2213.[8] 叶艳芬,谭国珍,曾凡钦. SLE患者骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性的研究[J].中国实用医药,2011,6(29):121-123. [9] 张华勇,冯学兵,孙凌云.系统性红斑狼疮患者骨髓间充质干细胞细胞因子分泌及其与病情活动的相关性研究[J].现代临床医学生物工程学杂志,2006,12(6): 460-463.[10] 谌蓉,张缪佳,王嫱,等.系统性红斑狼疮患者骨髓间充质干细胞的体外扩增及鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007, 11(37): 7385-7388.[11] 汤郁,李晶,裘影影,等. SLE患者血清对小鼠BMMSC生长、增殖及凋亡的影响[J]. 江苏医药,2007,33(10):1039-1040. [12] 银广悦,陈素萍,丁俊丽,等.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外分离培养和鉴定方法学探讨[J].中国实验诊断学,2013,17(4): 647-650. [13] 王艳,胡翰青,邢红艳,等.小鼠骨髓干细胞的分离培养鉴定及诱导分化的研究[J].西南国防医药,2013,1(1):8-11. [14] 朱建宇,施伟民.小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的体外培养和鉴定[J].同济大学学报:医学版,2012,33(5):49-52. [15] 靳芳莉,翟亚萍,曹名波,等.C57BL6小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离培养鉴定[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2012,33(7): 1-3,6.[16] 姚瑶,丁从珠,葛卫红.间充质干细胞对类风湿性关节炎骨破坏的治疗作用研究进展[J]. 安徽医药,2013,17(4):544-546. [17] 丘美兰,陈建.间充质干细胞的免疫学特性与系统性红斑狼疮的治疗[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012,6(22): 7347-7349. [18] 韩艳芳,曾凡钦,谭国珍,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对狼疮鼠B淋巴细胞AKT/GSK3β信号通路影响的检测[J].皮肤性病诊疗学杂志,2012,19(6):331-334.[19] 董毅,刘蕾,夏瑞祥,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮患者T细胞活化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(27): 4960-4963.[20] 夏云飞,顾志峰,李立人.间充质干细胞与调节性T细胞的研究进展[J].南通大学学报:医学版,2010,33(3):216-219.[21] 裘影影,李晶.间充质干细胞的免疫调节作用与系统性红斑狼疮[J].国外医学:内科学分册,2006,33(9):372.[22] 夏宇欧,王宏.脐带源间充质干细胞移植治疗难治性系统性红斑狼疮[J].中国现代药物应用,2013,7(5): 44-45. [23] 肖玉翠,王吉波,董静,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植对系统性红斑狼疮免疫系统的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(19): 3489-3493. [24] 戴林,姜津霞,曹晓蕾,等.间充质干细胞的衰老与系统性红斑狼疮的研究进展[J].医学综述,2011,17(3):321-324. [25] 刘博,赵铖.间充质干细胞在系统性红斑狼疮治疗中的研究进展[J].内科,2010,5(2):180-181. [26] 张晓,张光峰.间充质干细胞和造血干细胞联合移植治疗系统性红斑狼疮的前景[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2006,10(5):300-302.[27] 徐婷,顾志峰,吴敏,等.脐带间质干细胞移植治疗对MRL/lpr狼疮鼠单核细胞趋化蛋白-1的影响[J].交通医学,2011,25(4): 325-328. [28] 向晓丽,王莲,李江津.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗自身免疫性疾病10例的护理[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(28):7030-7031. [29] 樊剑锋,沈颖. 系统性红斑狼疮治疗新方法疗效及评价[J].中国实用儿科杂志,2012,27(9): 663-666. [30] 林传明,顾健. 间充质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮血栓易发状态的免疫调节和修复机制研究新进展[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2011, 19(4):1092-1096. [31] 郭君其,陈建,罗芳,等.自体骨髓间充质干细胞治疗狼疮性肾炎一例[J].中华细胞与干细胞移植:电子版,2009,(2):54. [32] 李慧,张育,顾健.系统性红斑狼疮患者骨髓间质干细胞对T细胞增殖作用的研究[J].实用临床医药杂志,2009,13(9):73-74. [33] 周培媚,路永红.系统性红斑狼疮的治疗进展[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2009,23(6):379-381. [34] 孙凌云. 干细胞移植治疗自身免疫性病[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(27):5001. [35] 孙凌云. 间质干细胞治疗系统性红斑狼疮的机制和应用[J].内科理论与实践,2008,3(3):158-161. [36] 潘延斌,李建民. 系统性红斑狼疮治疗新进展[J].医学综述,2008, 14(5):781-783. [37] 孙凌云,张华勇,冯学兵,等.异基因骨髓间质干细胞移植治疗难治性红斑狼疮[J].实用临床医药杂志,2007,11(7): 2-4,9. [38] 谌蓉,刘晓华,张缪佳,等.间质干细胞对系统性红斑狼疮患者外周血T细胞亚群的影响[J].江苏医药,2006,32(8):716-718. [39] 孙凌云,顾宁琰,侯亚义,等.系统性红斑狼疮骨髓间质干细胞的初步研究[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2005,9(10):86-589.[40] 李晓林,薛燕,杨扬,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗系统性红斑狼疮的临床研究[J].临床血液学杂志,2004,17(6):329-330. |