Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (25): 4609-4615.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.25.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
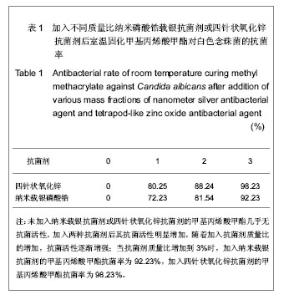
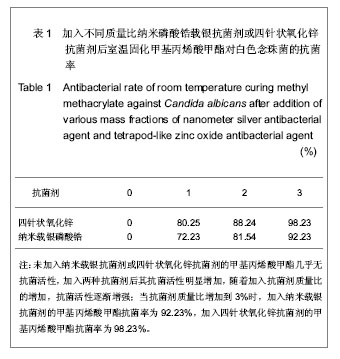
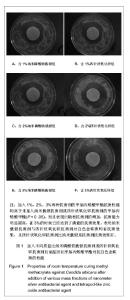
Properties of nanometer silver antibacterial agent and tetrapod-like zinc oxide antibacterial agent against Candida albicans
Xiao Yue, Kang Liang, Lü Qing, Yu Bo-wen, Ma Ying-jun
- Stomatology Hospital, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Received:2013-01-06Revised:2013-01-22Online:2013-06-18Published:2013-06-18 -
Contact:Ma Ying-jun, Associate chief nurse, Stomatology Hospital, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Xiao Yue, Chief physician, Professor, Stomatology Hospital, Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China kangliang008@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xiao Yue, Kang Liang, Lü Qing, Yu Bo-wen, Ma Ying-jun. Properties of nanometer silver antibacterial agent and tetrapod-like zinc oxide antibacterial agent against Candida albicans [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(25): 4609-4615.
share this article
| [1] Li SQ,Cheng XR,Qian FT.Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 1994;29(4):238-241.李四群,程祥荣,钱法汤.氟化物控释装置在可摘局部义齿中应用的初步研究[J].中华口腔医学杂志,1994,29(4): 238-241.[2] Yan SG,Qi XM,Lin LM,et al.Kouqiang Hemian Xiufuxue Zazhi. 2005;6(4):279-282.颜世果,戚向敏,林荔梅,等. 配戴可摘义齿对口腔白色念珠菌的检出及基因分型的影响[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2005,6(4): 279-282.[3] Li Y,Guo W,Li HL,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(42):8337-8340.李苑,郭巍,李惠玲,等.白色念珠菌在义齿软衬材料表面黏附的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(42): 8337-8340.[4] Park SE,Blissett R,Susarla SM,et al.Candida albicans adherence to surface-modified denture resin surfaces.J Prosthodont. 2008;17(5):365-369.[5] Li B,Zhao YM,Yang JC,et al.Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2008;24(2):70-72.李蓓,赵铱民,杨聚才,等.比较纳米载银抗菌剂与纳米二氧化钛抗菌剂抗白色念珠菌性能的实验研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2008, 24(2):70-72.[6] Ji XF,Li YP,Yang LQ,et al.Taiyuan Ligong Daxue Xuebao. 2003; 34(1):11-15.吉向飞,李玉平,杨柳青,等.抗菌剂及抗菌材料的发展和应用[J].太原理工大学学报,2003,34(1):11-15.[7] She WJ,Zhang FQ.Shanghai Kouqiang Yixue. 2003;12(5): 356-358.佘文君,张富强. 6 种纳米级载银无机抗菌剂对口腔病原菌的抗菌活性比较[J].上海口腔医学,2003,12(5):356-358.[8] Liao LL,Liu JP.Xiandai Huagong. 2001;21(7):62-64.廖莉玲,刘吉平.新型无机抗菌剂[J].现代化工,2001,21(7):62-64.[9] You XG,Huang XC.Sichuan Youse Jinshu. 2003;18(3):13-17.游贤贵,黄学超.四脚状氧化锌晶须—特性、应用和制备[J].四川有色金属,2003,18(3):13-17.[10] Saitoh H,Okada Y,Ohshio S, Synthesis of MgO/ZnO Hetero-Epitaxial Whiskers Using Chemical Vapor Deposition Operated Under Atmospheric Pressure. J MaterSci.2002; 37(21):4597-4602.[11] Yoshinaka M,Miyoshi I,Asakara E,et al. Method of Producing Zinc Oxide Whiskers[P]. EP378995,1990-07-25.[12] Zhou ZW,Hu SC. Xincailiao Chanye. 2002;4(6):18-28.周祚万,胡书春.晶须的特点及其产业化前景分析[J].新材料产业,2002,4(6):18-28.[13] Liu L,Yin N,Kang MQ,et al.Cailiao Kexue yu Gongyi. 2000; 18(2):116-119.刘玲,殷宁,亢茂青,等.晶须增韧复合材料机理的研究[J].材料科学与工艺,2000,18(2):116-119.[14] Cheng JQ.Hengshui Shizhuan Xuebao. 2000;2(4):64-67.程敬泉.氧化锌晶须的制备及应用[J].衡水师专学报,2000, 2(4): 64-67.[15] Peng SG.Youse Yelian. 2003;6(3):16-23.彭曙光.四针状氧化锌晶须的生产和市场[J].有色冶炼, 2003, 6(3): 16-23.[16] Dai Y,Zhang Y,Fang Y,et al.Beijing Keji Daxue Xuebao. 2002; 24(2):200-202.戴英,张跃,方圆,等.高品质四针状氧化锌晶须的结构及生长机理[J].北京科技大学学报,2002,24(2):200-202.[17] Lv YF,Wu HW.Huaxue Tongbao. 1996;11(3):15-18.吕越峰,吴华武. 四脚状氧化锌晶须的制备、性能及应用[J].化学通报,1996,11(3):15-18.[18] Su W.Wujiyan Gongye. 1990;22(4):42.苏威.日本氧化锌晶须扩产[J].无机盐工业,1990,22(4):42.[19] Zhou ZW,Chu LS,Duan XF.Xincailiao Chanye. 2003;5(6): 20-23.周祚万,楚珑晟,段小飞.无机抗菌剂材料的产业化现状[J].新材料产业, 2003,5(6):20-23.[20] Pei XM,Zhang JB.Taoci. 2001;28(4):36-37.裴新美,张聚宝.四针状氧化锌晶须的制备[J].陶瓷,2001,28(4): 36-37.[21] Chen RG,Zhou BL.Suliao Gongye.2003;31(10):40-42.陈尔凡,周本廉.T-ZnO晶须增强环氧树脂复合材料的抗静电性[J].塑料工业,2003,31(10):40-42.[22] Chen EF,Tian YJ,Cheng YJ,et al. Guisuanyan Xuebao. 2001; 29(2):151-156. 陈尔凡,田雅娟,程远杰,等.四脚状氧化锌晶须的生长习性及机理的研究[J].硅酸盐学报,2001,29(2):151-156. [23] Chen EF,Tian YJ,Cheng YJ,et al.Gaodeng Xuexiao Huaxue Xuebao. 2000;21(2):172-176.陈尔凡,田雅娟,程远杰,等.四脚状氧化锌晶须的制备及微观形态研究[J].高等学校化学学报,2000,21(2):172-176.[24] Tian YJ,Chen EF,Cheng YJ,et al.Guisuanyan Xuebao. 2000; 28(2):165-168.田雅娟,陈尔凡,程远杰,等.四脚状氧化锌晶须及应用[J].硅酸盐学报,2000,28(2):165-168.[25] Zhou ZW,Chu LS,Gu LX.Qiche Jishu. 2003;31(7):29-32.周祚万,楚珑晟,顾利霞.ZnOw改善橡胶和轮胎耐磨性能的研究[J].汽车技术,2003,31(7):29-32.[26] Wu HW,Lai YY.Wujiyan Gongye. 1996;28(4):17-20.吴华武,来月英.氧化锌晶须的特点及其应用[J].无机盐工业, 1996,28(4):17-20.[27] Iwanaga H,Kunishige A,Takeuchi S.Anisotropic thermal expansion in wurtzite-type crystals. J Mater Sci.2000;35(10): 2451-2454.[28] Zhu BL,Zeng DW,Wu J,et al.Synthesis and gas sensitivity of In-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Sci Mater Electron.2003; 14(8):521-526.[29] Tian YJ,Y DM,Chen EF. Suliao Gongye. 2002;30(5):32-34.田雅娟,杨东梅,陈尔凡.四脚状氧化锌晶须增强尼龙6复合材料的研究[J].塑料工业,2002,30(5):32-34.[30] Chen EF,Tian YJ,Zhou BL.Suliao Gongye. 2003;31(4):19-21.陈尔凡,田雅娟,周本廉.偶联剂对T-ZnO晶须/环氧树脂复合材料的影响[J].塑料工业,2003,31(4):19-21.[31] Zhou ZW,Chu LS,Lei Q.Huagong Cinxing Cailiao. 2001;29(9): 45-47.周祚万,楚珑晟,雷强.氧化锌晶须在树脂基复合材料中的应用[J].化工新型材料,2001,29(9):45-47.[32] Zhou ZW,Chu LS,Zhang ZC.Xiangjiao Gongye. 2002;49(7): 403-405.周祚万,楚珑晟,张再昌.纳米氧化锌晶须在橡胶复合材料中的初步应用[J].橡胶工业,2002,49(7):403-405.[33] Skidan BS. The Effect of Additives on Properties of Ceramics Based on Zinc Oxide. Glass Ceram.2003;60(9):339-341.[34] Hng HH,Tse KY. Grain Growth of ZnO in Binary ZnO-V2O5Ceramics. Journal Mater Sci.2003;38(11): 2367-2372.[35] Stroyuk AL,Shvalagin VV,Kuchmii S Ya. Photochemical Synthesis, Spectral-optical and Electrophysical Properties of Composite Nanoparticles of ZnO/Ag. Theore Exp Chem.2004;40(2):98-104.[36] Thurgood CP,Amphlett JC,Mann RF,et al.Deactivation of Cu/ZnO/Al2O3Catalyst: Evolution of Site Concentrations with Time. Top Catal.2003;22(3-4):253-259.[37] Cao HT,Sun C,Pei ZL,et al.Properties of Transparent Conductiong ZnO: Al Oxide Thin Films and Their Application for Molecular Organic Light-Emitting Diodes.J Mater Sci Mater Electron.2004;15(3):169-174.[38] Shaldin Yu V,Varchulska J. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Magnetic Properties of Hydrothermally Grown ZnO Crystals. Inorganic Mat.2003;39(10):1052-1057.[39] French SA,Sokol AA,Bromley ST,et al. Identification and characterization of active sites and their catalytic processes— the Cu/ZnO methanol catalyst. Top Catal.2003;24(1):161-172.[40] Dang Z,Fan L,Shen Y,et al. Study of thermal and dielectric behavior of low-density polyethylene composites reinforced with zinc oxide whisker. J Therm Anal Calorim.2003;71(2): 635-641.[41] Zhang WZ,Wang GW.Huagong Xinxing Cailiao. 2003; 31(2): 42-44.张文钲,王广文.纳米银抗菌材料研发现状[J].化工新型材料, 2003, 31(2):42-44.[42] Zhang WZ,Wei WJ.Xiyou Jinshu Cailiao yu Gongcheng. 1996;25(1):46-51.张文钲,韦卫军. 一种新型含银离子杀菌剂[J].稀有金属材料与工程,1996,25(1):46-51.[43] Qiang Q,Ni HW,Xing W,et al.Wuhan Keji Daxue Xuebao:Ziran Kexueban. 2007;30(2): 121-124.墙蔷,倪红卫,幸伟,等.银的抗菌作用机理[J].武汉科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2007,30(2): 121-124.[44] Wang WQ,Feng QM,Dong FQ.Yingyong Huagong. 2004; 33(4): 123.王维清,冯启明,董发勤.银系抗菌材料及其研发应用现状[J].应用化工,2004,33(4): 123.[45] Inoue Y,Hoshino M,Takahashi H,et al.Bactericidal activity of Ag-zeolitemediated by reactive oxygen speciesunder aerated conditions. J ofInorg Biochem.2002;92(1): 37-42.[46] She WJ,Hu B,Zhang FQ.Shanghai jiaotong Daxue Xuebao. 2006;26(10):1096-1098.佘文君,胡滨,张富强.纳米载银无机抗菌剂对义齿基托树脂抗菌性能的影响[J].上海交通大学学报,2006,26(10):1096-1098.[47] Xiao Y,Du Y,Wang JP,et al.Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2011; 29(4)434-436.肖月,杜滢,王健平,等.添加四针状氧化锌晶须抗菌剂对义齿软衬材料抗菌性能的初步研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2011,29(4): 434-436.[48] Zhang FQ,She WJ,Fu YF.Zhonghua Kouqiang Yixue Zahzi. 2005;40(6):504-507.张富强,佘文君,傅远飞. 6 种纳米载银无机抗菌剂的体外细胞毒性比较[J].中华口腔医学杂志,2005,40(6):504-507.[49] Qu ML,Jiang WC.Yinran Zhuji. 2004;21(6):44-45.曲敏丽,姜万超.纳米氧化锌抗菌机理探讨[J].印染助剂,2004, 21(6): 44-45.[50] Bosset M,Masse A,Tobin E,et al.Silver coated materials for ex-ternal fixationdevices: in vitro biocompatibility and genotoxicity. Biomaterial.2002; 23(3):887-892.[51] Yu RY,Zhou YS,Feng HL,et al.Beijing Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2006;38(5):522-524.余日月,周永胜,冯海兰,等.纳米载银基托树脂的生物相容性评价[J].北京大学学报:医学版,2006,38(5):522-524.[52] Ma QQ,Zhao YM,Wu GF,et al.Linchuang Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2007;23(2):98-99.马千淇,赵铱民,吴国锋,等.添加抗菌剂的硅橡胶赝复材料体外抗白色念珠菌性能研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2007,23(2):98-99.[53] Liu Y,Chen JH,Fang M,et al.Zhongguo Meirong Yixue. 2006; 15(5):584-586.刘奕,陈吉华,方明,等.添加载银抗菌剂的藻酸盐印模材料抗菌性能及物理性能研究[J].中国美容医学,2006,15(5):584-586.[54] Zhang LQ,Gao B,Yang JC,et al.Yati Yasui Yazhoubingxue Zazhi. 2006;16(5): 191-193.张林祺,高勃,杨聚才,等.三种纳米级载银无机抗菌剂对口腔致病菌的抗菌活性比较[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2006,16(5): 191-193.[55] Yu RY,Zhou YS,Feng HL.Shiyong Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi. 2005; 21(5): 670-672.余日月,周永胜,冯海兰.纳米载银树脂基托的体外抗菌效果[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2005,21(5): 670-672.[56] Hu T,Wang ML,Wu JJ,et al.Jibing Kongzhi Zazhi. 2005;9(3): 273-274.胡涛,王明丽,吴建军,等.四针状氧化锌复合抗菌材料滤片抑菌和毒性作用的实验研究[J].疾病控制杂志,2005,9(3):273-274.[57] Jia CL,Wang XR,Zhang CT,et al.Jilin Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2012;38(5):87-91.贾春丽,王晓容,张赐童,等.添加纳米载银无机抗菌剂的室温固化PMMA材料体外抗菌效果评价[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2012, 38(5):87-91. |
| [1] | Li Li, Ma Li. Immobilization of lactase on magnetic chitosan microspheres and its effect on enzymatic properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 576-581. |
| [2] | Zhou Anqi, Tang Yufei, Wu Bingfeng, Xiang Lin. Designing of periosteum tissue engineering: combination of generality and individuality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3551-3557. |
| [3] | Lang Limin, He Sheng, Jiang Zengyu, Hu Yiyi, Zhang Zhixing, Liang Minqian. Application progress of conductive composite materials in the field of tissue engineering treatment of myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3584-3590. |
| [4] | Xie Jian, Su Jiansheng. Advantages and characteristics of electrospun aligned nanofibers as scaffolds for tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2575-2581. |
| [5] | Ji Qi, Yu Zhengwen, Zhang Jian. Problems and trends of technique and clinical application of metallic biomaterials prepared by three-dimensional printing technology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2597-2604. |
| [6] | Qian Nannan, Zhang Qian, Yang Rui, Ao Jun, Zhang Tao. Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury: cell therapy and combination of new drugs and biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(13): 2114-2120. |
| [7] | Jia Wei, Zhang Mandong, Chen Weiyi, Wang Chenyan, Guo Yuan. Effects of femoral prosthetic materials on artificial knee arthroplasty performance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1477-1481. |
| [8] | Wang Qian, Li Lu, Shu Jingyuan, Dong Zhiheng, Jin Youshi, Wang Qingshan. Micro-morphology and phase of zirconia-based nano-hydroxyapatite functional gradient biomaterials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1517-1521. |
| [9] | Li Li, Ma Li, Li He. Preparation and characterization of magnetic chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 577-582. |
| [10] | Tang Mengmeng, Chen Hechun, Xie Hongchen, Zhang Yu, Tan Xiaoshuang, Sun Yixuan, Huang Yina. Histocompatibility of poly(L-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone)/cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone ureteral stent grafted into the rat bladder [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 583-588. |
| [11] | Xin Pengfei, Sun Youqiang, Li Jie, Chen Jianfa, Deng Baogui, Xiang Xiaobing . Research progress of biomaterials for repair of rotator cuff tear [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4459-4464. |
| [12] | Liu Yanhua, Zhu Zhou, Wan Qianbing. A drug-loading system for electrospinning wound repair: component selection and construction strategy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4465-4473. |
| [13] | Guo Enhui, Xu Zitong, Liang Yize, Zhou Liang, Lu Zhaoxiang, You Liang, Xia Yujun. Properties of a novel photocrosslinked fish collagen peptide-hyaluronic acid hydrogel [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4518-4525. |
| [14] | Jiang Li, Fang Xiaojuan, Pan Banglun, Lin Hanchao, Li Wei. Polyisobutylene and its thermoplastic elastomers: how to transform from industry to medical treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3559-3565. |
| [15] | Xia Tianwei, Liu Jinzhu, Shi Le, Gao Runzi, Wei Wei, Zhang Chao, Shen Jirong. New idea of tissue engineering technology in the treatment of osteonecrosis of femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2919-2925. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||